Abstract
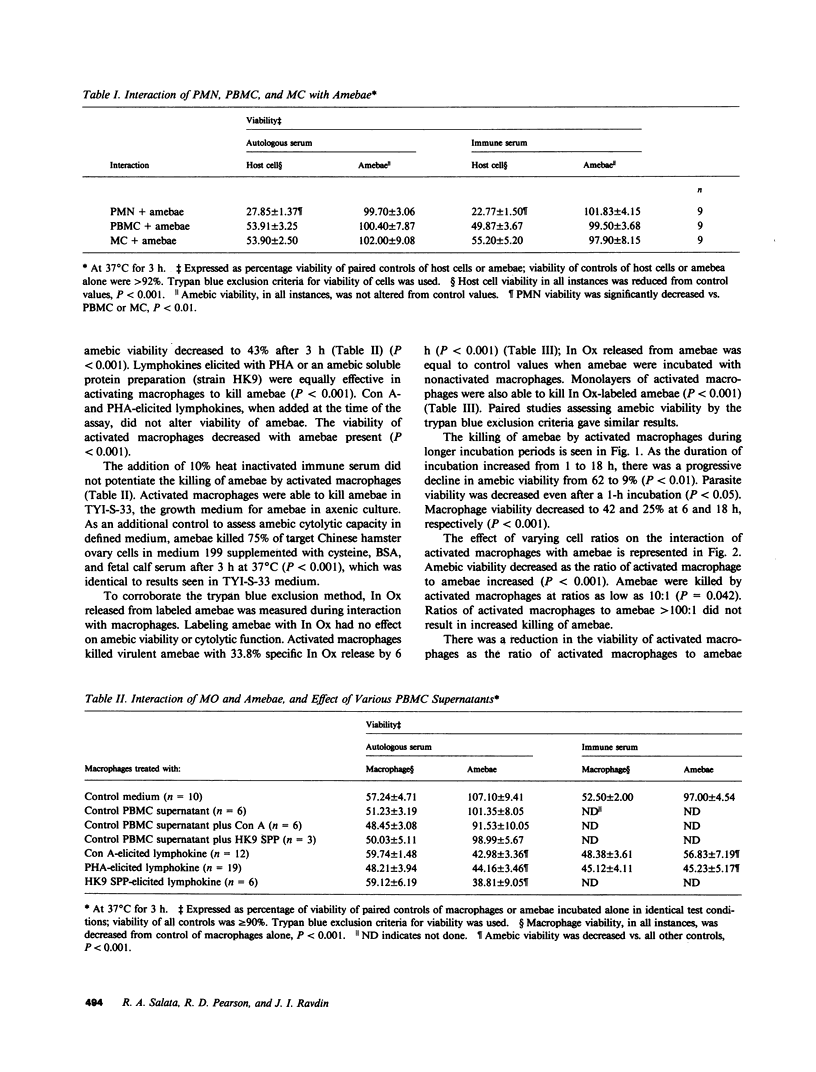
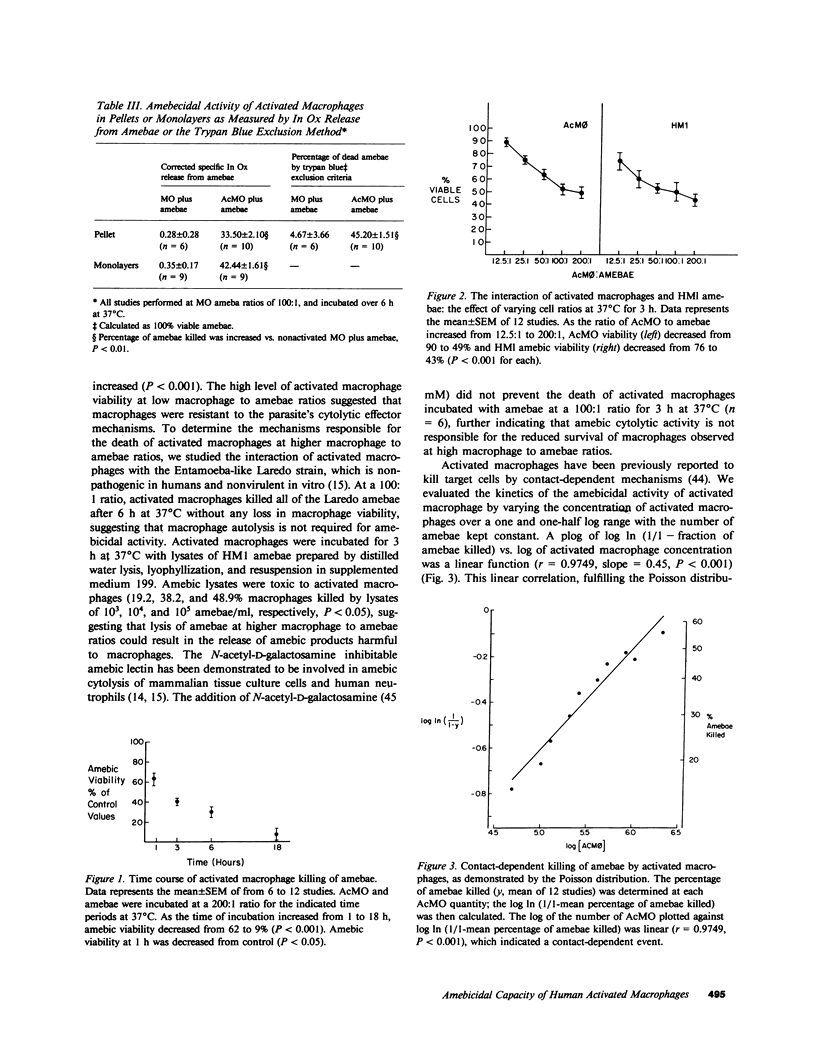
Capable effector mechanisms in the human immune response against the cytolytic, protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica have not been described. To identify a competent human effector cell, we studied the in vitro interactions of normal human polymorphonuclear neutrophils, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), monocytes (MC), and MC-derived macrophages with virulent axenic amebae (strain HMI-IMSS). Amebae killed neutrophils, PBMC, MC, and MC-derived macrophages (P less than 0.001), without loss of parasite viability. The addition of heat-inactivated immune serum did not enable leukocytes to kill amebae, nor did it protect these host cells from amebae. MC-derived macrophages, activated with lymphokine elicited by the mitogens conconavalin A, phytohemagglutinin, or an amebic soluble protein preparation (strain HK9), killed 55% of amebae by 3 h in a trypan blue exclusion assay (P less than 0.001); during this time, 40% of the activated macrophages died. Lysis of amebae was confirmed using 111Indium oxine radiolabeled parasites and was antibody independent. Macrophage death appeared to be due to the deleterious effect of lysed amebae rather than the contact-dependent effector mechanisms of E. histolytica. Adherence between activated macrophages and amebae was greater than that between other leukocytes and amebae (P less than 0.001). Microscopic observations, kinetic analysis of the killing of amebae by activated macrophages, and suspension of amebae with adherent activated macrophages in a 10% dextran solution indicated that contact by activated macrophages was necessary to initiate the killing of amebae. Catalase but not superoxide dismutase inhibited the amebicidal capacity of activated macrophages (P less than 0.001). However, activated macrophages from an individual with chronic granulomatous disease were able to kill amebae, but not as effectively as normal cells (P less than 0.01). In summary, activated MC-derived macrophages killed virulent E. histolytica trophozoites through a contact-dependent, antibody-independent mechanism involving oxidative-dependent and -independent processes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya D. P., Sen P. C. E-rosetting cells in amoebic liver abscess. Indian J Med Res. 1981 Sep;74:348–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Ferluga J., Janossy G. Non-specific cytotoxicity by T cells activated with plant mitogens in vitro and the requirement for plant agents during the killing reaction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Dec;15(4):573–589. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aust-Kettis A., Thorstensson R., Sundqvist K. G. Dynamics of the interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and components of the immune response. III. Fate of antibodies after binding to the cell surface. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(5):473–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges J. S., Johnson W. D., Jr Inhibition of multiplication of Toxoplasma gondii by human monocytes exposed to T-lymphocyte products. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):483–496. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderón J., de Lourdes Muñoz M., Acosta H. M. Surface redistribution and release of antibody-induced caps in entamoebae. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):184–193. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. J., Churchill W. H. Cytotoxicity of human macrophages for tumor cells. Enhancement by human lymphocyte mediators. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):977–984. doi: 10.1172/JCI109398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., May M. Preliminary demonstration of human tuberculoimmunity in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):453–464. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.453-464.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Densen P., Mandell G. L. Gonococcal interactions with polymorphonuclear neutrophils: importance of the phagosome for bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1161–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamantstein T., Klos M., Gold D., Hahn H. Interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and the immune system. I. Mitogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica extracts for human peripheral T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2084–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Huber E., Haudenschild C. C. Mechanisms of destruction of Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae mediated by human monocytes. J Infect Dis. 1983 Mar;147(3):474–483. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.3.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donowitz G. R., Mandell G. L. Monocyte function in patients with chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. Blood. 1982 Nov;60(5):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost P., Smith J., Frost H. The radiolabeling of lymphocytes and tumor cells with 111indium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Jan;157(1):61–65. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-39991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly N. K., Mahajan R. C., Gill N. J., Koshy A. Kinetics of lymphocyte subpopulations and their functions in cases of amoebic liver abscess. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1981;75(6):807–810. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(81)90417-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Effect of immunosuppression on the size and metastasis of amoebic liver abscesses in hamsters. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Winter;3(4):329–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Effect of splenectomy on the size of amoebic liver abscesses and metastatic foci in hamsters. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):571–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.571-573.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E., Hartmann D. P. Protection against amebic liver abscess in hamsters by means of immunization with amebic antigen and some of its fractions. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Sep;29(5):779–784. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. In vitro amoebicidal activity of immune cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):243–246. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.243-246.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E., Kongshavn P. A. Role of macrophages in host defense against hepatic amoebiasis in hamsters. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1017–1019. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1017-1019.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadirian E., Meerovitch E. Macrophage requirement for host defence against experimental hepatic amoebiasis in the hamster. Parasite Immunol. 1982 Jul;4(4):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brush J., Ravdin J. I., Sullivan J. A., Mandell G. L. Interaction between Entamoeba histolytica and human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jan;143(1):83–93. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. G., Bray R. S. Cellular sensitivity in amoebiasis--preliminary results of lymphocytic transformation in response to specific antigen and to mitogen in carrier and disease states. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1976;70(4):340–343. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(76)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy G. R., Kagan I. G., Gleason N. N. Use of the indirect hemagglutination test in some studies of seroepidemiology of amebiasis in the western hemisphere. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Jul;7(3):109–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huldt G., Davies P., Allison A. C., Schorlemmer H. U. Interactions between Entamoeba histolytica and complement. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):214–216. doi: 10.1038/277214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARUMILINTA R., KRADOLFER F. THE TOXIC EFFECT OF ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA ON LEUCOCYTES. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1964 Sep;58:375–381. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1964.11686259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M. Antibody response in intestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Jan;19(1):57–62. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M., Powell S. J. Comparative study of the antibody response in amebiasis. Persistence after successful treatment. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 May;20(3):421–424. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E. Mechanism of specific tumor-cell lysis by alloimmune T lymphocytes: resolution and characterization of discrete steps in the cellular interaction. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:301–361. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch H., Brombach J. Analysis of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay for antibodies to cytoplasmic antigen fractions of Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch E., Ghadirian E. Effect of Trichinella spiralis infection on the experimental amebic liver abscess in hamsters. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1980;11(1 Suppl):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Aley S. B., Scott W. A. Susceptibility of Entamoeba histolytica to oxygen intermediates. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Oct;3(6):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cartelli D. M. Killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani by human mononuclear phagocytes. Evidence for oxygen-dependent and -independent leishmanicidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):32–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI110972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. Cell-mediated immune response in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. II. Oxygen-dependent killing of intracellular Leishmania donovani amastigotes. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. I. Susceptibility of Toxoplasma gondii to oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):938–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. III. Enhanced oxidative metabolism as an expression of macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1596–1609. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Masur H., Keithly J. S. Cell-mediated immune response in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. I. Correlation between resistance to Leishmania donovani and lymphokine-generating capacity. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawara A., DeSantis N. M., Nogueira N., Nathan C. F. Lymphokines enhance the capacity of human monocytes to secret reactive oxygen intermediates. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1042–1048. doi: 10.1172/JCI110691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. The macrophage as an effector cell. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Silverstein S. C., Brukner L. H., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. II. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):100–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Cohn Z. Role of oxygen-dependent mechanisms in antibody-induced lysis of tumor cells by activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):198–208. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Nogueira N., Juangbhanich C., Ellis J., Cohn Z. Activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between hydrogen peroxide release and killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Chaplan S., Reesink M., Tydings J., Cohn Z. A. Trypanosoma cruzi: induction of microbicidal activity in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2142–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Capin R., Capin N. R., Sepúlveda B., Zamacona G. Activation of the alternative pathway of complement by Entamoeba histolytica. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Oct;34(1):10–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Sepúlveda B., Chévez A. Nuevos estudios acerca de la acción de sueros humanos normales e immunes sobre el trofozoíto de E. histolytica. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 1974;5(Suppl 2):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Zamacona G., Sepúlveda B., Capín N. R. Cell-mediated immunity in patients with amebic abscess of the liver. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Romito R., Symes P. H., Harcus J. L. Interaction of Leishmania donovani promastigotes with human monocyte-derived macrophages: parasite entry, intracellular survival, and multiplication. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1249-1253.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Croft B. Y., Guerrant R. L. Cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):377–390. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Murphy C. F., Salata R. A., Guerrant R. L., Hewlett E. L. N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine-inhibitable adherence lectin of Entamoeba histolytica. I. Partial purification and relation to amoebic virulence in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):804–815. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. L., Sargeaunt P. G., Braude A. I. Resistance to lysis by human serum of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(2):248–253. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss M., Roos D. Differences in oxygen metabolism of phagocytosing monocytes and neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):480–488. doi: 10.1172/JCI108959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasada M., Johnston R. B., Jr Macrophage microbicidal activity. Correlation between phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolism and the killing of Candida by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):85–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. D., Piessens W. F. Tumor cell killing by macrophages activated in vitro with lymphocyte mediators. III. Inhibition by cytochalasins, colchicine, and vinblastine. Cell Immunol. 1978 Jul;38(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. J., Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Murine amebiasis: the role of the macrophage in host defense. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 May;33(3):372–380. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trissl D. Immunology of Entamoeba histolytica in human and animal hosts. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):1154–1184. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.6.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi V., Mena-Lopez R., Anaya-Velazquez F., Martinez-Palomo A. Cellular bases of experimental amebic liver abscess formation. Am J Pathol. 1984 Oct;117(1):81–91. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinayak V. K., Chitkara N. L., Chhuttani P. N. Effect of corticosteroid and irradiation on caecal amoebic infection in rats. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(3):266–268. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiltrout R. H., Frost P., Cummings G. D. Isotope-release cytotoxicity assay with the use of indium-111: advantage over chromium-51 in long-term assays. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Jul;61(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/jnci/61.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



