Abstract
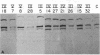
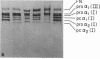
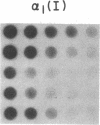
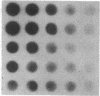
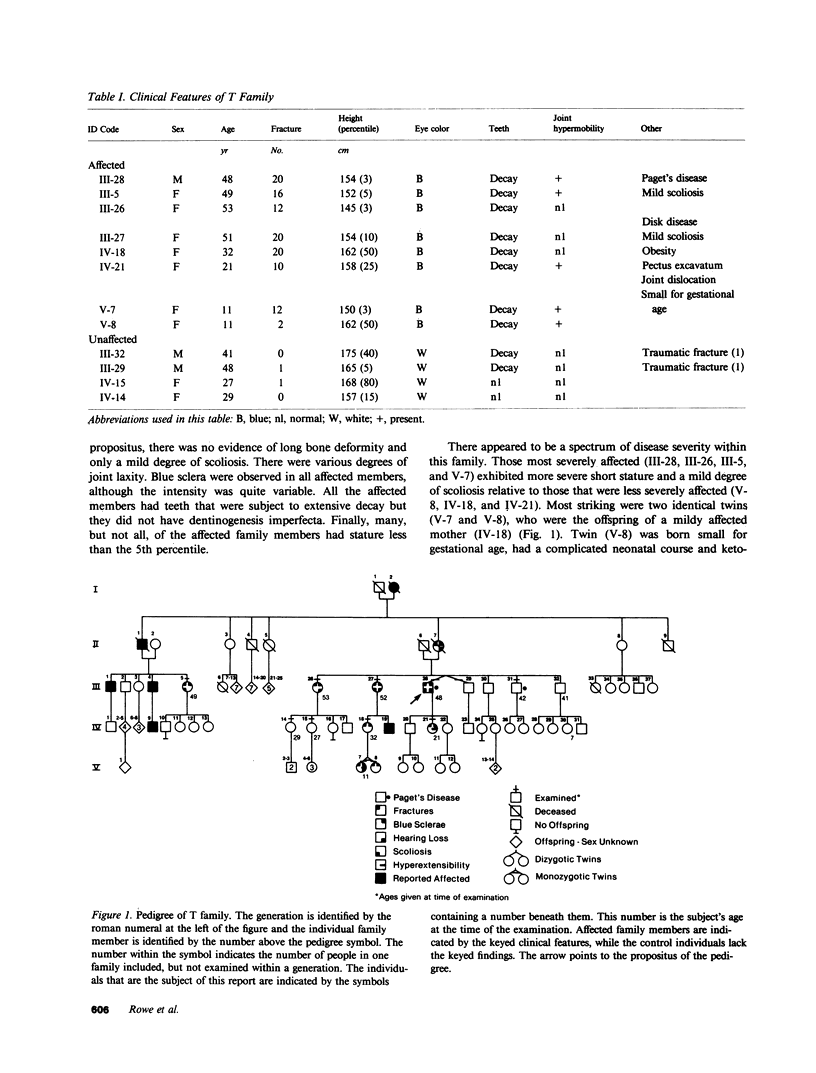
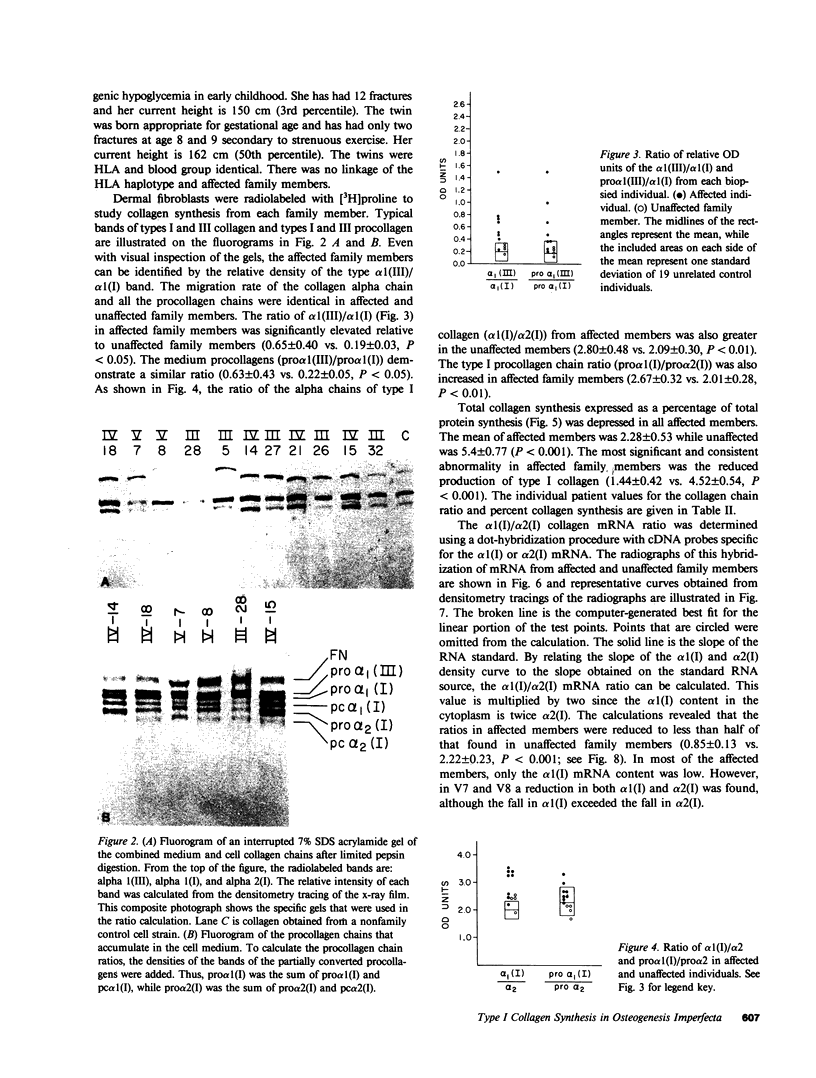
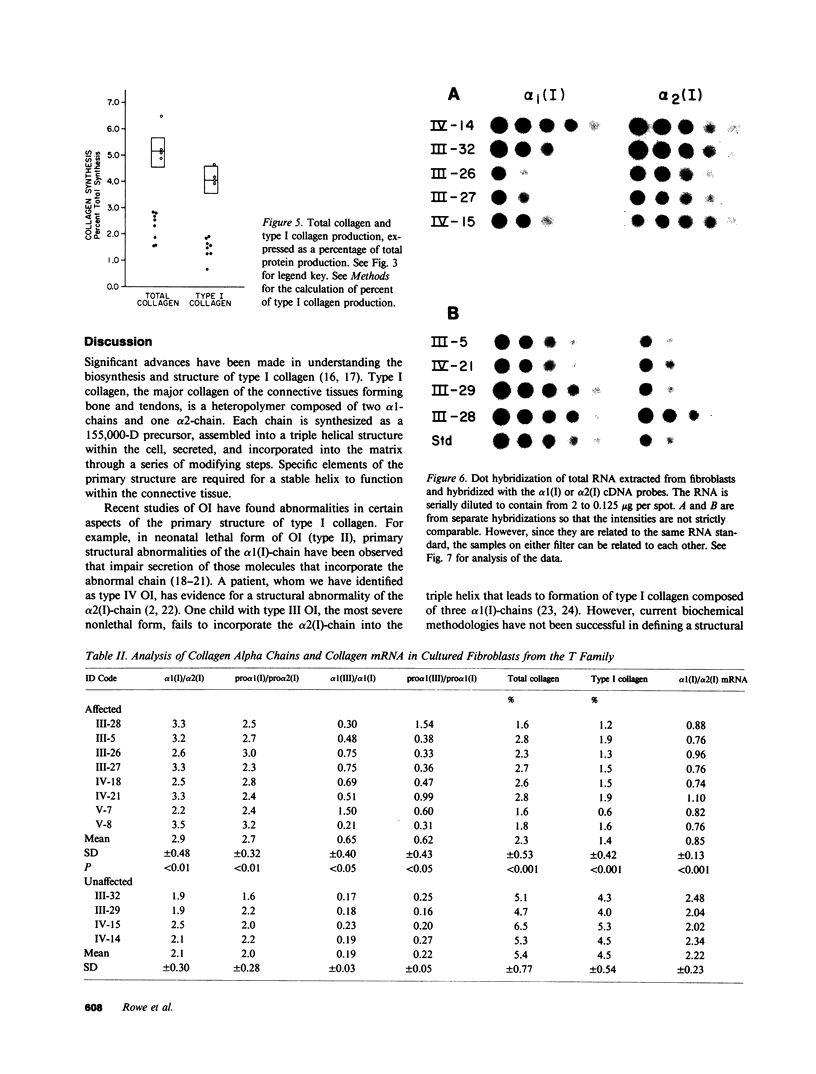
Type I osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is characterized clinically by a moderate fracture frequency with minimal bone deformity and dominant inheritance. Previous studies of the collagenous proteins synthesized by dermal fibroblasts obtained from unrelated patients with this form of OI suggested that the biochemical basis of the disease was reduced production of type I collagen. This study was designed to determine if this biochemical finding segregated with the disease within an individual family. Dermal fibroblast strains were established from three generations of a family having the typical features of type I OI. Analysis of the collagenous proteins made in culture revealed an elevated alpha 1(III) to alpha 1(I) collagen type ratio and an elevated alpha 1(I) to alpha 2(I) collagen chain ratio. The procollagen that accumulated in the medium reflected these ratios to the same degree. Total collagen synthesis was significantly reduced in affected family members. Therefore, the most striking abnormality in affected members was a 50-75% reduction of type I collagen production. Furthermore, the ratio of the alpha 1(I)/alpha 2(I) collagen messenger RNA (mRNA), measured by dot hybridization, was one-half of the value of uninvolved family members and unrelated controls. Since the reduction in the production of type I collagen and the altered alpha 1(I)/alpha 2(I) mRNA ratio clearly segregated with affected individuals within this family, these biochemical measurements may be a useful genetic marker for type I OI.
Full text
PDF




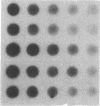
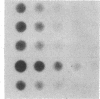
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsh G. S., Byers P. H. Reduced secretion of structurally abnormal type I procollagen in a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., David K. E., Byers P. H. Type I osteogenesis imperfecta: a nonfunctional allele for pro alpha 1 (I) chains of type I procollagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3838–3842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. J., Jr, Scarpa A. L., Tonkonow B. L., Pearson H. A., Ritchey A. K. Posttranscriptional defects in beta-globin messenger RNA metabolism in beta-thalassemia: abnormal accumulation of beta-messenger RNA precursor sequences. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1529–1538. doi: 10.1172/JCI110407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard M. P., Myers J. C., Chu M. L., Ramirez F., Eikenberry E. F., Prockop D. J. Structure of a cDNA for the pro alpha 2 chain of human type I procollagen. Comparison with chick cDNA for pro alpha 2(I) identifies structurally conserved features of the protein and the gene. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1139–1145. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:957–1003. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Moschonas N., Flavell R. A. Beta + thalassemia: aberrant splicing results from a single point mutation in an intron. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Shapiro J. R., Rowe D. W., David K. E., Holbrook K. A. Abnormal alpha 2-chain in type I collagen from a patient with a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):689–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI110815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey J. C., Laub J. M., Hall B. D. Penetrance and variability in neurofibromatosis: a genetic study of 60 families. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1979;15(5B):271–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Bernard M. P., Ding J. F., Ramirez F. Cloning and characterization of five overlapping cDNAs specific for the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5925–5934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Williams C. J., Pepe G., Hirsch J. L., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Internal deletion in a collagen gene in a perinatal lethal form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):78–80. doi: 10.1038/304078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., de Wet W., Bernard M., Ding J. F., Morabito M., Myers J., Williams C., Ramirez F. Human pro alpha 1(I) collagen gene structure reveals evolutionary conservation of a pattern of introns and exons. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):337–340. doi: 10.1038/310337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung E., Miller E. J. Collagen polymorphism: characterization of molecules with the chain composition (alpha 1 (3)03 in human tissues. Science. 1974 Mar;183(130):1200–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4130.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner D. B. Recovery of DNA fragments from gels by transfer to DEAE-paper in an electrophoresis chamber. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;125(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deak S. B., Nicholls A., Pope F. M., Prockop D. J. The molecular defect in a nonlethal variant of osteogenesis imperfecta. Synthesis of pro-alpha 2(I) chains which are not incorporated into trimers of type I procollagen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15192–15197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumaki Y., Ghosh P. K., Benz E. J., Jr, Reddy V. B., Lebowitz P., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Abnormally spliced messenger RNA in erythroid cells from patients with beta+ thalassemia and monkey cells expressing a cloned beta+-thalassemic gene. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A. C., Pope F. M., Schloon H. Biochemical heterogeneity of osteogenesis imperfecta: New variant. Lancet. 1979 Jun 2;1(8127):1193–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91872-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Goff S. C. Nonsense and frameshift mutations in beta 0-thalassemia detected in cloned beta-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9782–9784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson C. R., McAllion S., Stellman J. L. Osteogenesis imperfecta after the menopause. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 28;310(26):1694–1696. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406283102602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pergolizzi R., Spritz R. A., Spence S., Goossens M., Kan Y. W., Bank A. Two cloned beta thalassemia genes are associated with amber mutations at codon 39. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):7065–7072. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.7065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Ballantine M., Solowiejczyk D., Barak I., Schwartz E., Surrey S. beta-Thalassemia in a Kurdish Jew. Single base changes in the T-A-T-A box. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):5994–5996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Kream B. E. Regulation of collagen synthesis in fetal rat calvaria by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8009–8015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. R., Triche T., Rowe D. W., Munabi A., Cattell H. S., Schlesinger S. Osteogenesis imperfecta and Paget's disease of bone. Biochemical and morphologic studies. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Dec;143(12):2250–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillence D. Osteogenesis imperfecta: an expanding panorama of variants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981 Sep;(159):11–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Hiorns L., Sheer D., Rowe D. Confirmation that the type I collagen gene on chromosome 17 is COL1A1 (alpha 1(I), using a human genomic probe. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;48(Pt 1):39–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B., Puddle B., Francis M., Smith R. The estimation of two collagens from human dermis by interrupted gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1472–1480. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzer M. L., Church R. L., Yaeger J. A., Wampler D. E., Park E. Procollagen: intermediate forms containing several types of peptide chains and non-collagen peptide extensions at NH2 and COOH ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkocz C., Kühn K. The formation of triple-helical collagen molecules from alpha-1 or alpha-2 polypeptide chains. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):454–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Proudfoot N. J., Shander M., Maniatis T. A single-base change at a splice site in a beta 0-thalassemic gene causes abnormal RNA splicing. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):903–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90452-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Børresen A. L., Dickson L. A., Berg K., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Molecular heterogeneity in the mild autosomal dominant forms of osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1172–1179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Myers J. C., Ramirez F., Prockop D. J. Restriction fragment length polymorphism associated with the pro alpha 2(I) gene of human type I procollagen. Application to a family with an autosomal dominant form of osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1262–1267. doi: 10.1172/JCI111082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Thalassemia revisited. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. J., Prockop D. J. Synthesis and processing of a type I procollagen containing shortened pro-alpha 1(I) chains by fibroblasts from a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne-Davies R., Gormley J. Clinical and genetic patterns in osteogenesis imperfecta. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1981 Sep;(159):26–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W. J., Chu M. L., Prockop D. J. The mRNAs for the pro-alpha 1(I) and pro-alpha 2(I) chains of type I procollagen are translated at the same rate in normal human fibroblasts and in fibroblasts from two variants of osteogenesis imperfecta with altered steady state ratios of the two mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14385–14389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W. J., Pihlajaniemi T., Myers J., Kelly T. E., Prockop D. J. Synthesis of a shortened pro-alpha 2(I) chain and decreased synthesis of pro-alpha 2(I) chains in a proband with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7721–7728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]