Abstract
We measured pressure excursions at the airway opening and at the alveoli (PA) as well as measured the regional distribution of PA during forced oscillations of six excised dog lungs while frequency (f[2-32 Hz]), tidal volume (VT [5-80 ml]), and mean transpulmonary pressure (PL [25, 10, and 6 cm H2O]) were varied. PA's were measured in four alveolar capsules glued to the pleura of different lobes. The apex-to-base ratio of PA's was used as an index of the distribution of dynamic lung distension. At low f, there was slight preferential distension of the lung base which was independent of VT, but at higher f, preferential distension of the lung apex was found when VT's were small, whereas preferential distension of the lung base was found when VT's approached or exceeded dead space. These VT-related changes in distribution at high frequencies seem to depend upon the branching geometry of the central airways and the relative importance of convective momentum flux vs. unsteady inertia of gas residing therein, which, in this study, we showed to be proportional to the ratio VT/VD*, where VD* is an index of dead space. Furthermore, they imply substantial alteration in the distribution of ventilation during high frequency ventilation as f, VT, and PL vary. The data also indicate that alveolar and airway opening pressure costs per unit flow delivered at the airway opening exhibit weakly nonlinear behavior and that resonant amplification of PA's, which has been described previously for the case of very small VT's, persists but is damped as VT's approach dead space values.
Full text
PDF

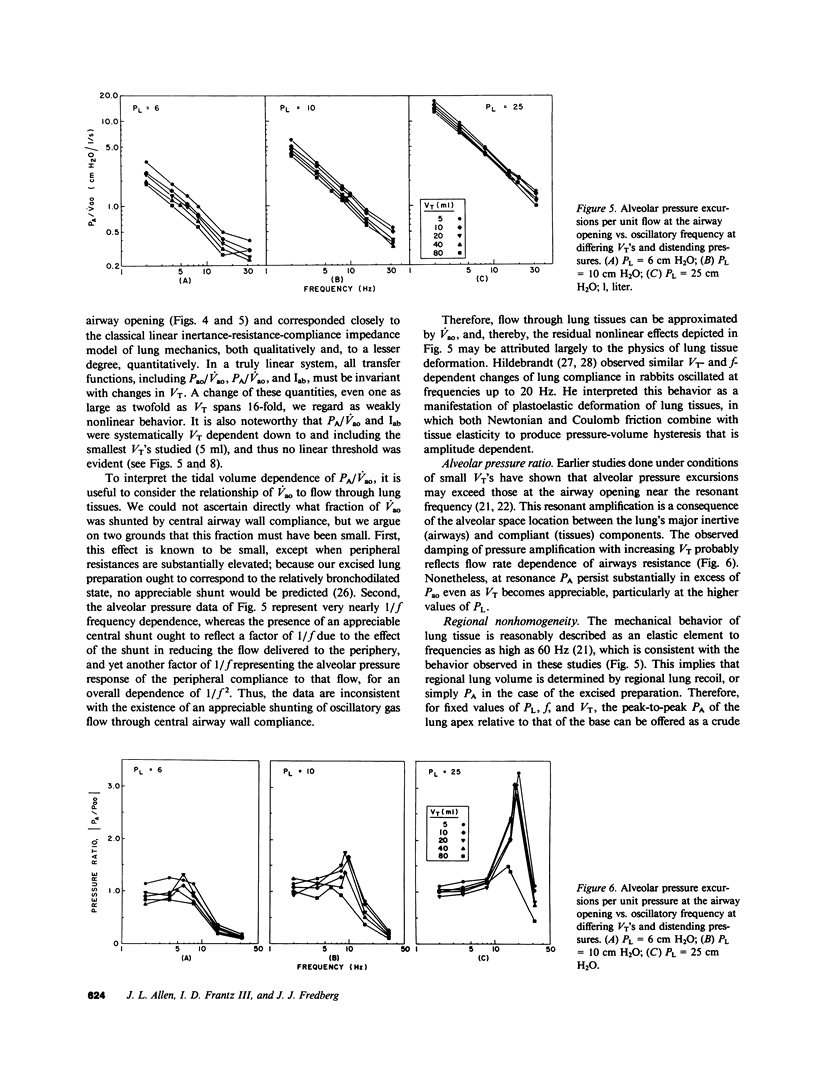



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
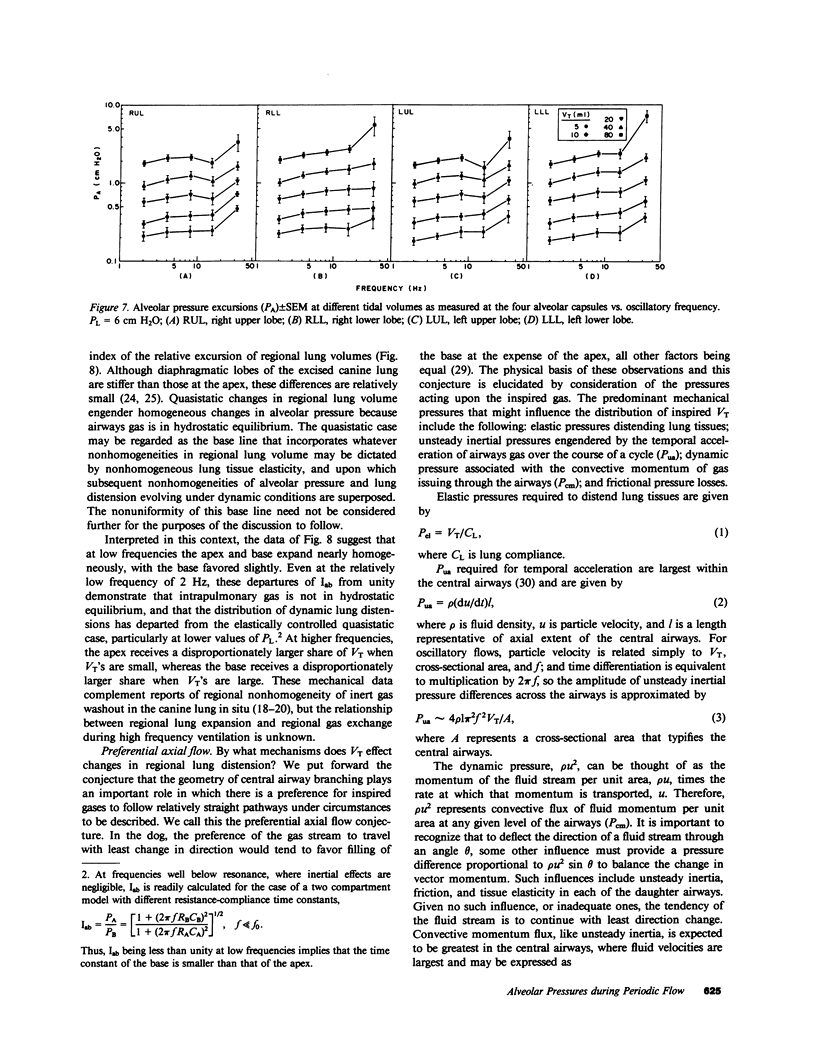
- Bake B., Wood L., Murphy B., Macklem P. T., Milic-Emili J. Effect of inspiratory flow rate on regional distribution of inspired gas. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Jul;37(1):8–17. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusasco V., Knopp T. J., Rehder K. Gas transport during high-frequency ventilation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Aug;55(2):472–478. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K., El Masry O. A. A model study of flow dynamics in human central airways. Part I: axial velocity profiles. Respir Physiol. 1982 Jul;49(1):75–95. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(82)90104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K. Mechanisms of gas transport during ventilation by high-frequency oscillation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Mar;56(3):553–563. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.3.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK N. R. A comparison of static volume-pressure relations of excised pulmonary lobes of dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1963 Mar;18:274–278. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1963.18.2.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faridy E. E., Kidd R., Milic-Emili J. Topographical distribution of inspired gas in excised lobes of dogs. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Apr;22(4):760–766. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.4.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fixley M. S., Roussos C. S., Murphy B., Martin R. R., Engel L. A. Flow dependence of gas distribution and the pattern of inspiratory muscle contraction. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Nov;45(5):733–741. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.5.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forkert L., Anthonisen N. R., Wood L. D. Frequency dependence of regional lung washout. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Aug;45(2):161–170. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredberg J. J. Augmented diffusion in the airways can support pulmonary gas exchange. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Aug;49(2):232–238. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredberg J. J., Keefe D. H., Glass G. M., Castile R. G., Frantz I. D., 3rd Alveolar pressure nonhomogeneity during small-amplitude high-frequency oscillation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Sep;57(3):788–800. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.3.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredberg J. J., Mead J. Impedance of intrathoracic airway models during low-frequency periodic flow. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Aug;47(2):347–351. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.2.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselton F. R., Scherer P. W. Bronchial bifurcations and respiratory mass transport. Science. 1980 Apr 4;208(4439):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.7361109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. Comparison of mathematical models for cat lung and viscoelastic balloon derived by Laplace transform methods from pressure-volume data. Bull Math Biophys. 1969 Dec;31(4):651–667. doi: 10.1007/BF02477779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. Pressure-volume data of cat lung interpreted by a plastoelastic, linear viscoelastic model. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Mar;28(3):365–372. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isabey D. Steady and pulsatile flow distribution in a multiple branching network with physiological applications. J Biomech. 1982;15(5):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(82)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg R. S., Wangensteen O. D., Ponto R. A. Frequency dependence of regional lung clearance of 133Xe in normal men. Respir Physiol. 1976 Sep;27(3):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(76)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEAD J. Measurement of inertia of the lungs at increased ambient pressure. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Sep;9(2):208–212. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.9.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J. Contribution of compliance of airways to frequency-dependent behavior of lungs. J Appl Physiol. 1969 May;26(5):670–673. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.5.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson E. D., Grassman E. D., Peters W. R. Pulmonary mechanics by spectral analysis of forced random noise. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1210–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI108198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milic-Emili J., Henderson J. A., Dolovich M. B., Trop D., Kaneko K. Regional distribution of inspired gas in the lung. J Appl Physiol. 1966 May;21(3):749–759. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.3.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngeow Y. K., Mitzner W. A new system for ventilating with high-frequency oscillation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Dec;53(6):1638–1642. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.6.1638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTIS A. B., MCKERROW C. B., BARTLETT R. A., MEAD J., MCILROY M. B., SELVER-STONE N. J., RADFORD E. P., Jr Mechanical factors in distribution of pulmonary ventilation. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Jan;8(4):427–443. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.8.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley T. J., Sudlow M. F., Milic-Emili J. A non-linear theory of the distribution of pulmonary ventilation. Respir Physiol. 1972 May;15(1):1–38. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehder K., Didier E. P. Gas transport and pulmonary perfusion during high-frequency ventilation in humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Oct;57(4):1231–1237. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.4.1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson P. C., Anthonisen N. R., Ross D. Effect of inspiratory flow rate on regional distribution of inspired gas. J Appl Physiol. 1969 Apr;26(4):438–443. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.4.438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid E. R., Knopp T. J., Rehder K. Intrapulmonary gas transport and perfusion during high-frequency oscillation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Dec;51(6):1507–1514. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.6.1507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shykoff B. E., Van Grondelle A., Chang H. K. Effects of unequal pressure swings and different waveforms on distribution of ventilation: a non-linear model simulation. Respir Physiol. 1982 Apr;48(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(82)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. A., Weinmann G. G., Mitzner W. Mean airway pressure and alveolar pressure during high-frequency ventilation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Oct;57(4):1069–1078. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.4.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky A. S., Berdine G. G., Drazen J. M. Oscillatory flow and quasi-steady behavior in a model of human central airways. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jun;50(6):1293–1299. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky A. S., Berdine G. G., Drazen J. M. Steady flow in a model of human central airways. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Sep;49(3):417–423. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky A. S., Drazen F. M., Ingram R. H., Jr, Kamm R. D., Shapiro A. H., Fredberg J. J., Loring S. H., Lehr J. Effective pulmonary ventilation with small-volume oscillations at high frequency. Science. 1980 Aug 1;209(4456):609–671. doi: 10.1126/science.6771872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky A. S., Kamm R. D., Rossing T. H., Loring S. H., Lehr J., Shapiro A. H., Ingram R. H., Jr, Drazen J. M. Effects of frequency, tidal volume, and lung volume on CO2 elimination in dogs by high frequency (2-30 Hz), low tidal volume ventilation. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1475–1484. doi: 10.1172/JCI110400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder B., Dantzker D. R., Jaeger M. J. Flow partitioning in symmetric cascades of branches. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Sep;51(3):598–606. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.3.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder B., Jaeger M. J. Lobar flow patterns in a hollow cast of canine central airways. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Mar;54(3):749–756. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.3.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann G. G., Mitzner W., Permutt S. Physiological dead space during high-frequency ventilation in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Sep;57(3):881–887. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.3.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woldehiwot Z., Horsfield K. Diameter, length and branching angles of the upper airways in the dog lung. Respir Physiol. 1978 May;33(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(78)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zidulka A., Gross D., Minami H., Vartian V., Chang H. K. Ventilation by high-frequency chest wall compression in dogs with normal lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jun;127(6):709–713. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.6.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


