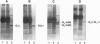Abstract
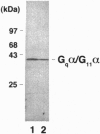
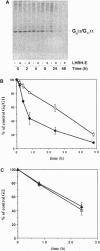
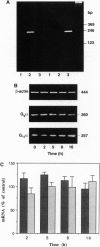
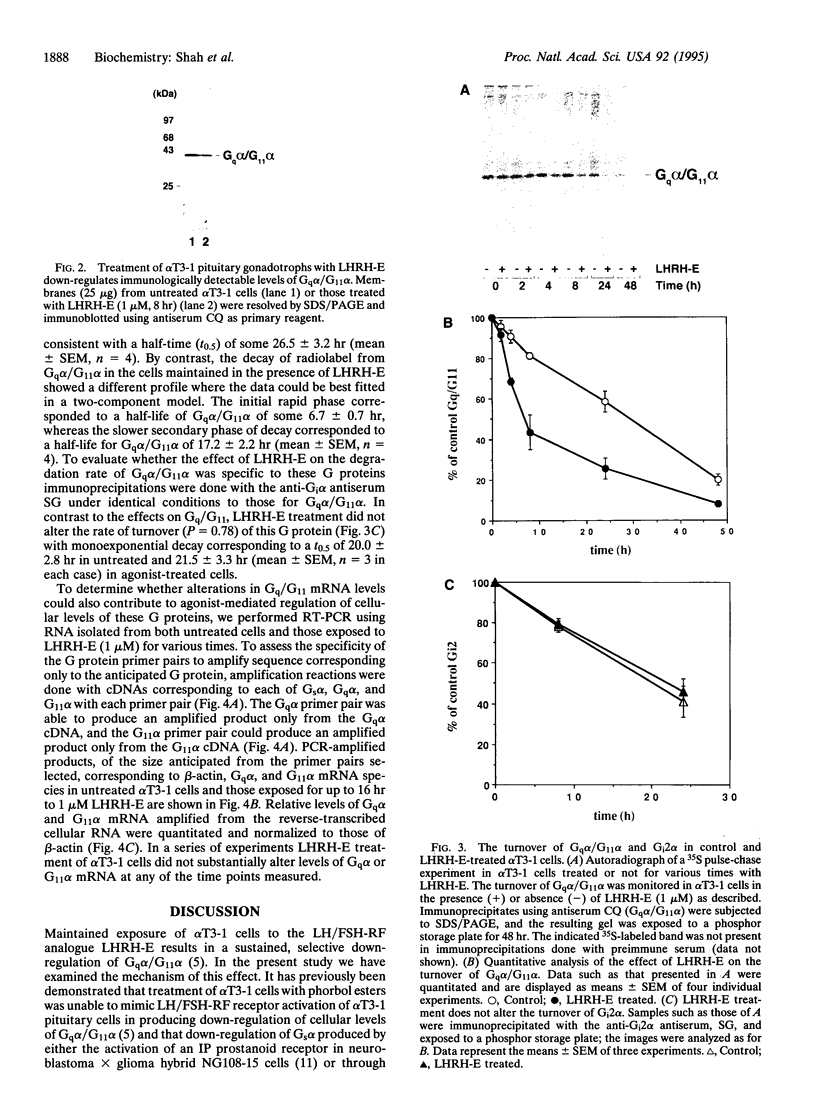
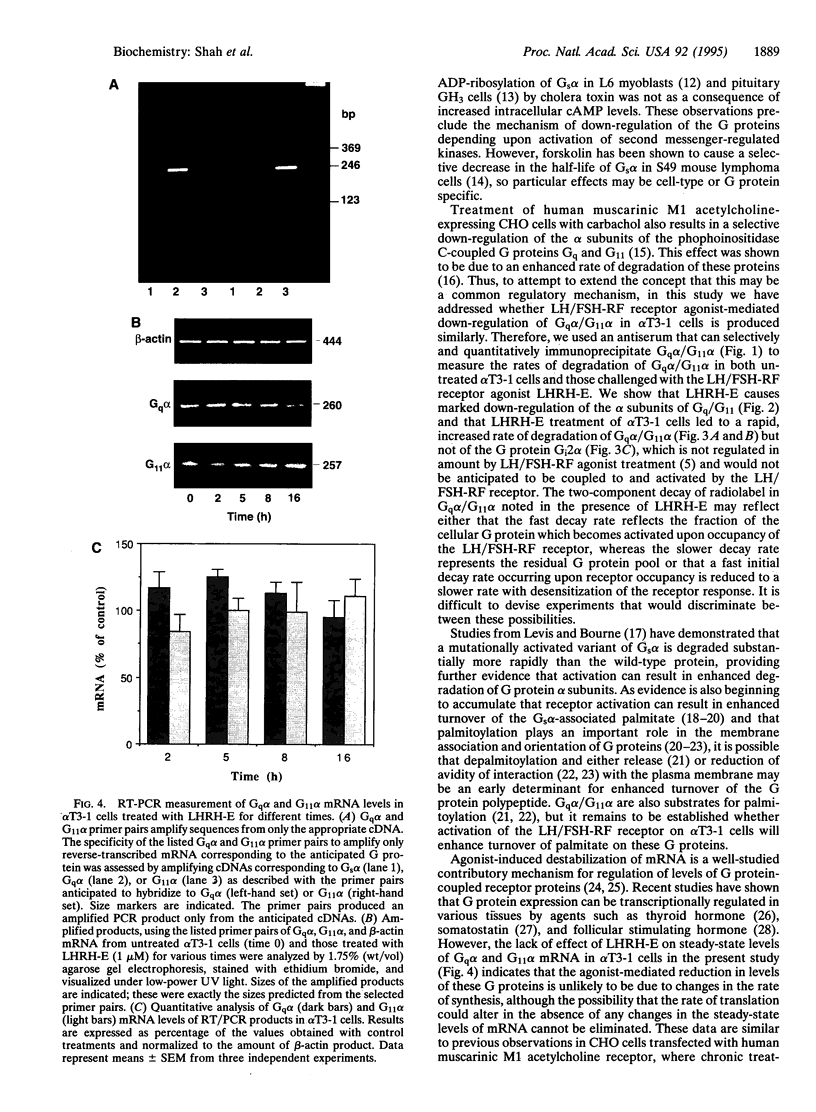
Prolonged exposure of alpha T3-1 pituitary gonadotrophs to a gonadotrophin-releasing hormone receptor agonist results in marked down-regulation of the pertussis toxin-insensitive G proteins Gq alpha and G11 alpha. The turnover of Gq alpha/G11 alpha was substantially accelerated in the presence of agonist. By contrast, the rate of degradation of the G protein Gi2 alpha was unaffected by agonist treatment. Analysis of Gq alpha/G11 alpha mRNA levels by reverse transcription-PCR demonstrated no detectable differences between control and agonist-treated cells. These studies indicate that gonadotrophin-releasing hormone receptor agonist-mediated down-regulation of Gq alpha/G11 alpha is a reflection of enhanced proteolysis of the activated G proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang F. H., Bourne H. R. Cholera toxin induces cAMP-independent degradation of Gs. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5352–5357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degtyarev M. Y., Spiegel A. M., Jones T. L. Increased palmitoylation of the Gs protein alpha subunit after activation by the beta-adrenergic receptor or cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23769–23772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassie M. A., McCallum J. F., Guzzi F., Magee A. I., Milligan G., Parenti M. The palmitoylation status of the G-protein G(o)1 alpha regulates its activity of interaction with the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1994 Sep 15;302(Pt 3):913–920. doi: 10.1042/bj3020913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Johnson J. L., Milligan G. Down-regulation of Gi sub-types by prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5206–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Port J. D., Malbon C. C. Cross-regulation between G-protein-mediated pathways. Activation of the inhibitory pathway of adenylylcylclase increases the expression of beta 2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11915–11922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Ros M., Watkins D. C., Malbon C. C. Cross-regulation between G-protein-mediated pathways. Stimulation of adenylyl cyclase increases expression of the inhibitory G-protein, Gi alpha 2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14784–14790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh K. P., Martin T. F. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors activate phospholipase C by coupling to the guanosine triphosphate-binding proteins Gq and G11. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;6(10):1673–1681. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.10.1333052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Park D., Wu D., Rhee S. G., Simon M. I. Members of the Gq alpha subunit gene family activate phospholipase C beta isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16044–16047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis M. J., Bourne H. R. Activation of the alpha subunit of Gs in intact cells alters its abundance, rate of degradation, and membrane avidity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(5):1297–1307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loganzo F., Jr, Fletcher P. W. Follicle-stimulating hormone increases the turnover of G-protein alpha i-1- and alpha i-2-subunit messenger RNA in Sertoli cells by a mechanism that is independent of protein synthesis. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Mar;7(3):434–440. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.3.8483480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Delta-opioid-receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase is transduced specifically by the guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gi2. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2670391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Prostaglandin E1-mediated, cyclic AMP-independent, down-regulation of Gs alpha in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17084–17093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Unson C. G., Wakelam M. J. Cholera toxin treatment produces down-regulation of the alpha-subunit of the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gs). Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):643–649. doi: 10.1042/bj2620643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Buckley N. J., Milligan G. Enhanced degradation of the phosphoinositidase C-linked guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Gq alpha/G11 alpha following activation of the human M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in CHO cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):495–499. doi: 10.1042/bj2930495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Mullaney I., Godfrey P. P., Arkinstall S. J., Wakelam M. J., Milligan G. Widespread distribution of Gq alpha/G11 alpha detected immunologically by an antipeptide antiserum directed against the predicted C-terminal decapeptide. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney I., Dodd M. W., Buckley N., Milligan G. Agonist activation of transfected human M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in CHO cells results in down-regulation of both the receptor and the alpha subunit of the G-protein Gq. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):125–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2890125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kleuss C., Gilman A. G. Receptor regulation of G-protein palmitoylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenti M., Viganó M. A., Newman C. M., Milligan G., Magee A. I. A novel N-terminal motif for palmitoylation of G-protein alpha subunits. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):349–353. doi: 10.1042/bj2910349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulssen E. J., Paulssen R. H., Haugen T. B., Gautvik K. M., Gordeladze J. O. Regulation of G protein mRNA levels by thyroliberin, vasoactive intestinal peptide and somatostatin in prolactin-producing rat pituitary adenoma cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1991 Oct;143(2):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1991.tb09221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Port J. D., Huang L. Y., Malbon C. C. Beta-adrenergic agonists that down-regulate receptor mRNA up-regulate a M(r) 35,000 protein(s) that selectively binds to beta-adrenergic receptor mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):24103–24108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapiejko P. J., Watkins D. C., Ros M., Malbon C. C. Thyroid hormones regulate G-protein beta-subunit mRNA expression in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16183–16189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah B. H., Milligan G. The gonadotrophin-releasing hormone receptor of alpha T3-1 pituitary cells regulates cellular levels of both of the phosphoinositidase C-linked G proteins, Gq alpha and G11 alpha, equally. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;46(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel M. C., Buckley N. J. Differential regulation of muscarinic receptor mRNA levels in neuroblastoma cells by chronic agonist exposure: a comparative polymerase chain reaction study. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 May;43(5):694–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner P. B., Bourne H. R. Activation and depalmitoylation of Gs alpha. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner P. B., Chu D. H., Wilson P. T., Levis M. J., Bourne H. R. Palmitoylation is required for signaling functions and membrane attachment of Gq alpha and Gs alpha. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25001–25008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windle J. J., Weiner R. I., Mellon P. L. Cell lines of the pituitary gonadotrope lineage derived by targeted oncogenesis in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):597–603. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]