Abstract
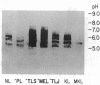
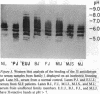
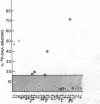
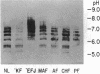
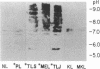
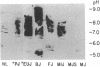
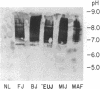
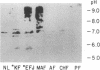
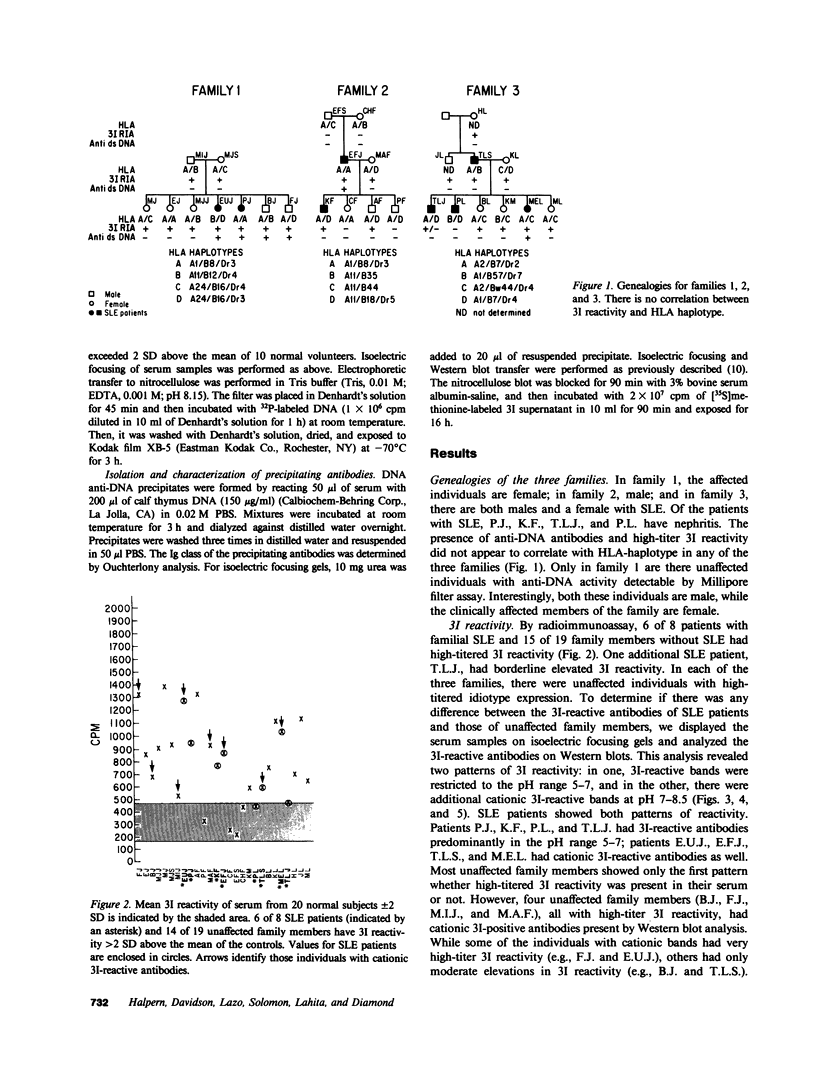
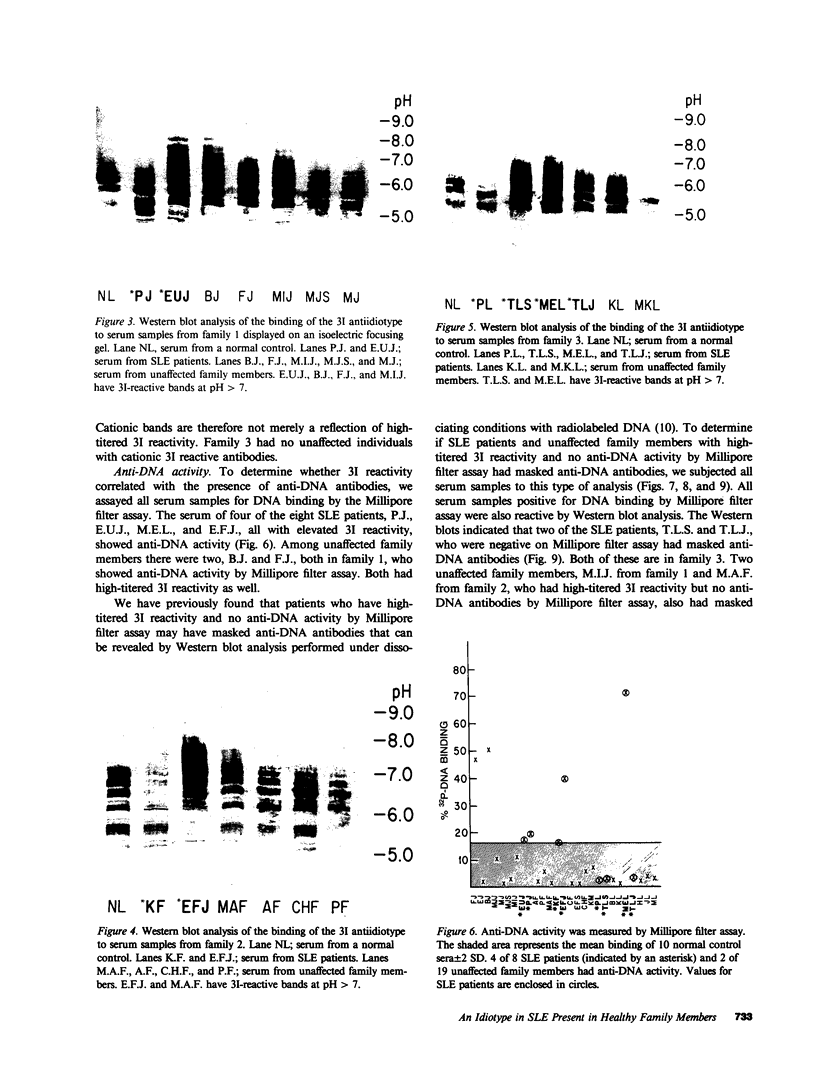
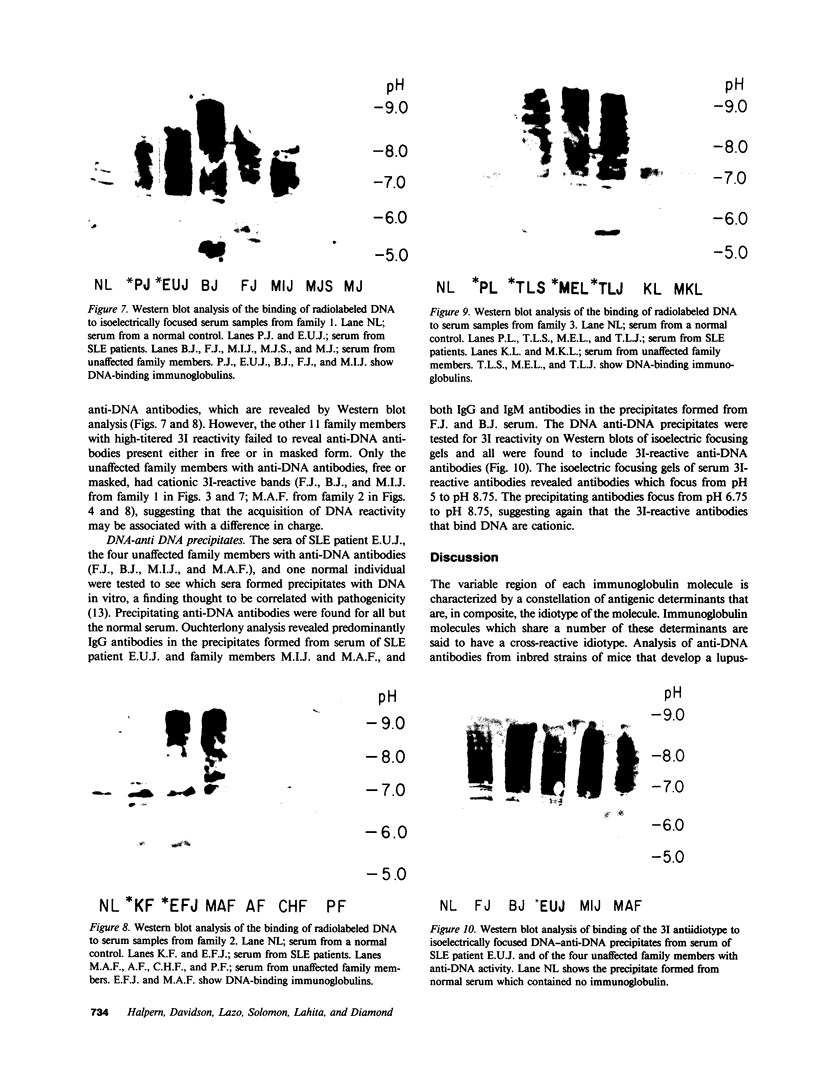
Sera of 27 members of 3 human kindreds with familial systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) were examined for expression of a cross-reactive idiotype present on anti-DNA antibodies of SLE patients. By radioimmunoassay, serum samples from 6 of 8 SLE patients and 15 of 19 family members had high-titered reactivity with the antiidiotype, 3I. Isoelectric focusing and Western blot analysis of 3I-reactive bands revealed two patterns of reactivity: either a pattern of bands present at pH 5-7, or bands present at pH 5-7 with additional bands present at pH 7-8.5. Cationic bands were found to correlate with the presence of anti-DNA antibodies, indicating that immunoglobulin charge may be a factor in determining specificity for DNA. Millipore filter analysis revealed anti-DNA antibodies in sera of 4 of 8 SLE patients and 2 of 19 family members without SLE. In 2 additional SLE patients and 2 additional family members, anti-DNA antibodies were revealed when sera were analyzed under conditions that dissociate immune complexes. This study indicates that expression of an idiotype associated with anti-DNA antibodies is significantly increased in relatives of SLE patients and usually occurs in the absence of anti-DNA activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Provost T. T., Dorsch C. A., Stevens M. B., Bias W. B., Arnett F. C. Interrelationships of HLA-DR, MB, and MT phenotypes, autoantibody expression, and clinical features in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1031–1040. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Reveille J. D., Wilson R. W., Provost T. T., Bias W. B. Systemic lupus erythematosus: current state of the genetic hypothesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;14(1):24–35. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(84)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. R., Winfield J. B., Lockshin M. D., D'Angelo W. A., Christian C. L. Studies of twins with systemic lupus erythematosus. A review of the literature and presentation of 12 additional sets. Am J Med. 1975 Oct;59(4):533–552. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonagura V. R., Kunkel H. G., Pernis B. Cellular localization of rheumatoid factor idiotypes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1356–1365. doi: 10.1172/JCI110575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation of the T15 heavy chain gives rise to an antibody with autoantibody specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5841–5844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer D. S., Bradley R. J., Urquhart C. K., Kearney J. F. Naturally occurring anti-idiotypic antibodies in myasthenia gravis patients. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):611–614. doi: 10.1038/301611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebling F., Hahn B. H. Restricted subpopulations of DNA antibodies in kidneys of mice with systemic lupus. Comparison of antibodies in serum and renal eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):392–403. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folomeeva O., Nassonova V. A., Alekberova A. S., Talal N., Williams R. C., Jr Comparative studies of antilymphocyte, antipolynucleotide, and antiviral antibodies among families of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jan-Feb;21(1):23–27. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Qualitative characteristics of anti-DNA antibodies in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Nov-Dec;17(6):947–954. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg B., Keiser H. A Millipore filter assay for antibodies to native DNA in sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Mar-Apr;16(2):199–207. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Ebling F. M. A public idiotypic determinant is present on spontaneous cationic IgG antibodies to DNA from mice of unrelated lupus-prone strains. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3015–3019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern R., Schiffenbauer J., Solomon G., Diamond B. Detection of masked anti-DNA antibodies in lupus sera by a monoclonal anti-idiotype. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahita R. G., Chiorazzi N., Gibofsky A., Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. Familial systemic lupus erythematosus in males. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):39–44. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion T. N., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Kearney J. F., Briles D. E. Anti-DNA autoantibodies in (NZB X NZW)F1 mice are clonally heterogeneous, but the majority share a common idiotype. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquali J. L., Fong S., Tsoukas C., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Inheritance of immunoglobulin M rheumatoid-factor idiotypes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):863–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI109927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch J., Murphy E., Roths J. B., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. A high frequency idiotypic marker of anti-DNA autoantibodies in MRL-Ipr/Ipr mice. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):236–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenfeld Y., Isenberg D. A., Rauch J., Madaio M. P., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Idiotypic cross-reactions of monoclonal human lupus autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):718–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon G., Schiffenbauer J., Keiser H. D., Diamond B. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify shared idiotypes on human antibodies to native DNA from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):850–854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. The human Ia system. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:221–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Rogers J., Katz D. H. Induction of autoantibodies to thyroglobulin by anti-idiotypic antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):240–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Eyquem A. Idiotype restriction in human autoantibodies to DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol Lett. 1984;7(4):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(84)90041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]