Abstract
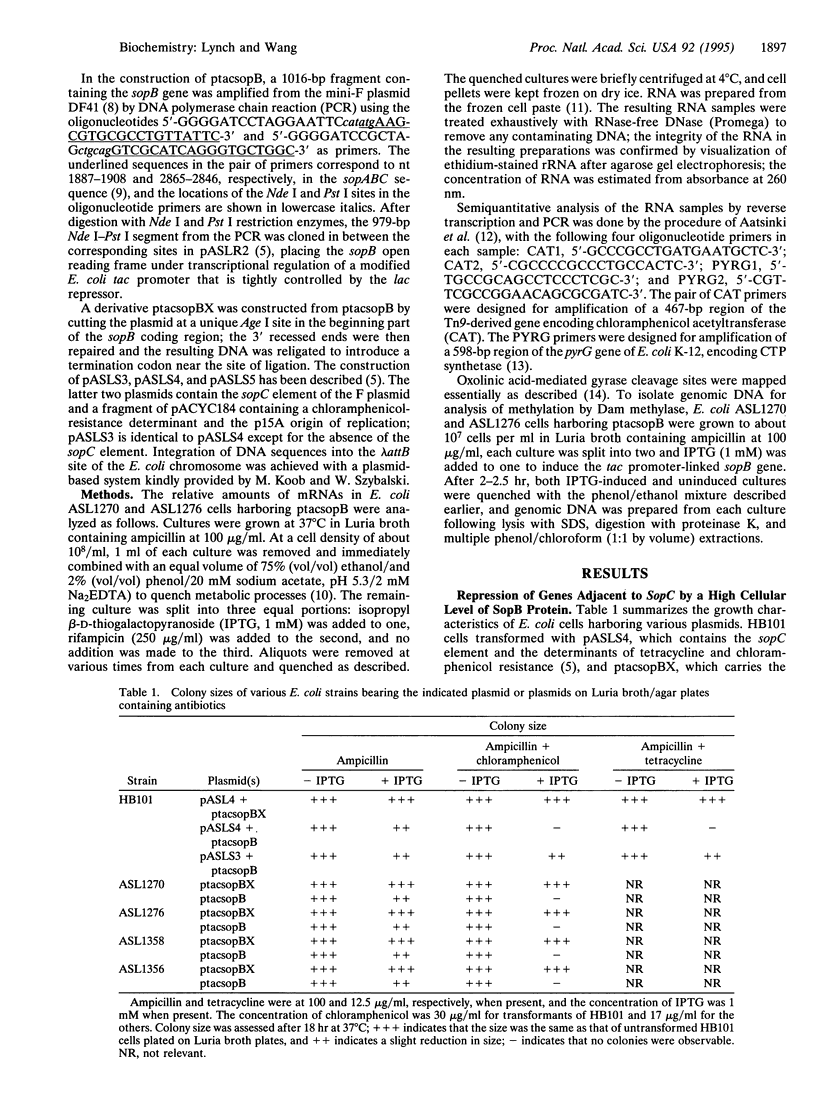
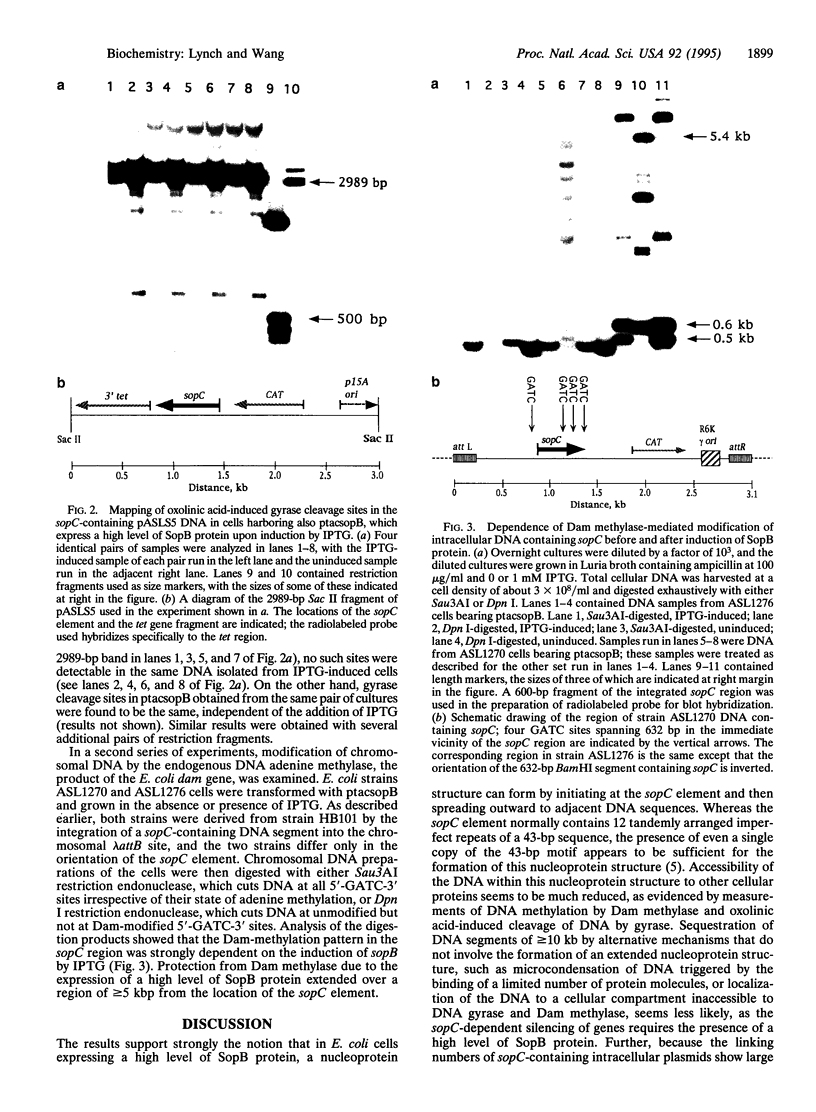
Expression of a high level of F-plasmid-encoded SopB protein in Escherichia coli is found to repress genes linked to sopC, a sequence element of F consisting of 12 tandemly joined imperfect repeats of a 43-bp motif. Repression of a gene can occur over a distance of at least 10 kb from the sopC element and is not affected by the relative orientation of sopC. In the repressed state, accessibility of intracellular DNA to cellular proteins is greatly reduced in the region containing sopC, as monitored by the trapping of the covalent intermediate between DNA and DNA gyrase and by Dam methylase-catalyzed DNA methylation. These results signify the formation of a nucleoprotein structure emanating from sopC and are discussed in terms of position-dependent silencing of genes in general and the IncG type of plasmid incompatibility in particular.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aatsinki J. T., Lakkakorpi J. T., Pietilä E. M., Rajaniemi H. J. A coupled one-step reverse transcription PCR procedure for generation of full-length open reading frames. Biotechniques. 1994 Feb;16(2):282-4, 286-8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allshire R. C., Javerzat J. P., Redhead N. J., Cranston G. Position effect variegation at fission yeast centromeres. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthelemy I., Mellado R. P., Salas M. In vitro transcription of bacteriophage phi 29 DNA: inhibition of early promoters by the viral replication protein p6. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):460–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.460-462.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biek D. P., Shi J. A single 43-bp sopC repeat of plasmid mini-F is sufficient to allow assembly of a functional nucleoprotein partition complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8027–8031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case C. C., Roels S. M., González J. E., Simons E. L., Simons R. W. Analysis of the promoters and transcripts involved in IS10 anti-sense RNA control. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):219–236. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook K. R., Karpen G. H. A rosy future for heterochromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5219–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorer D. R., Henikoff S. Expansions of transgene repeats cause heterochromatin formation and gene silencing in Drosophila. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):993–1002. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsman K., Sondén B., Göransson M., Uhlin B. E. Antirepression function in Escherichia coli for the cAMP-cAMP receptor protein transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9880–9884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Wang J. C. Identification of barriers to rotation of DNA segments in yeast from the topology of DNA rings excised by an inducible site-specific recombinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10514–10518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillén N., Amar M., Hirschbein L. Stabilized non-complementing diploids (Ncd) from fused protoplast products of B. subtilis. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1333–1338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez C., Freire R., Salas M., Hermoso J. M. Assembly of phage phi 29 genome with viral protein p6 into a compact complex. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):269–276. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göransson M., Sondén B., Nilsson P., Dagberg B., Forsman K., Emanuelsson K., Uhlin B. E. Transcriptional silencing and thermoregulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):682–685. doi: 10.1038/344682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa Y., Murotsu T., Matsubara K. Mini-F protein that binds to a unique region for partition of mini-F plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):349–354. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.349-354.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga S. Chromosome and plasmid partition in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:283–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga S. Chromosome partition in Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Oct;3(5):789–801. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Effects of transcription and translation on gyrase-mediated DNA cleavage in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12300–12305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusukawa N., Mori H., Kondo A., Hiraga S. Partitioning of the F plasmid: overproduction of an essential protein for partition inhibits plasmid maintenance. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):365–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00328125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenson P., Rine J. Silencers, silencing, and heritable transcriptional states. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):543–560. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.543-560.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo S., Rine J. Silencers and domains of generalized repression. Science. 1994 Jun 17;264(5166):1768–1771. doi: 10.1126/science.8209257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch A. S., Wang J. C. Use of an inducible site-specific recombinase to probe the structure of protein-DNA complexes involved in F plasmid partition in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 25;236(3):679–684. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kondo A., Ohshima A., Ogura T., Hiraga S. Structure and function of the F plasmid genes essential for partitioning. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90459-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Hughes T. A., Pavitt G. D., Santos D. S., Sidebotham J. M., Hulton C. S., Hinton J. C., Higgins C. F. The chromatin-associated protein H-NS interacts with curved DNA to influence DNA topology and gene expression. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90354-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier D. H., Pillus L. Silencing speaks up. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):963–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Cami B., Hotchkiss R. D. Fusion of bacterial protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2151–2155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M., Iida S. Mutants of Escherichia coli permeable to actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2315–2320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Salas M., Hermoso J. M. Multimeric complexes formed by DNA-binding proteins of low sequence specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jun;18(6):202–206. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90187-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuiver M. H., Bergsma W. G., Arnberg A. C., van Amerongen H., van Grondelle R., van der Vliet P. C. Structural alterations of double-stranded DNA in complex with the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. Implications for its function in DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 20;225(4):999–1011. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng M., Makaroff C. A., Zalkin H. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli pyrG encoding CTP synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5568–5574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley H. R., Ramey W. D., Spiegelman G. B., Holder R. D. Modulation of in vivo and in vitro transcription of bacteriophage phi 29 early genes. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):392–401. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Rowe T. C., Liu L. F. Identification of DNA topoisomerase II as an intracellular target of antitumor epipodophyllotoxins in simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5872–5876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P., Spradling A. C. Insertional mutagenesis of Drosophila heterochromatin with single P elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3539–3543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber F., Kotlarz D., Rimsky S., Buc H. Modulated expression of promoters containing upstream curved DNA sequences by the Escherichia coli nucleoid protein H-NS. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Apr;12(2):231–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]