Abstract
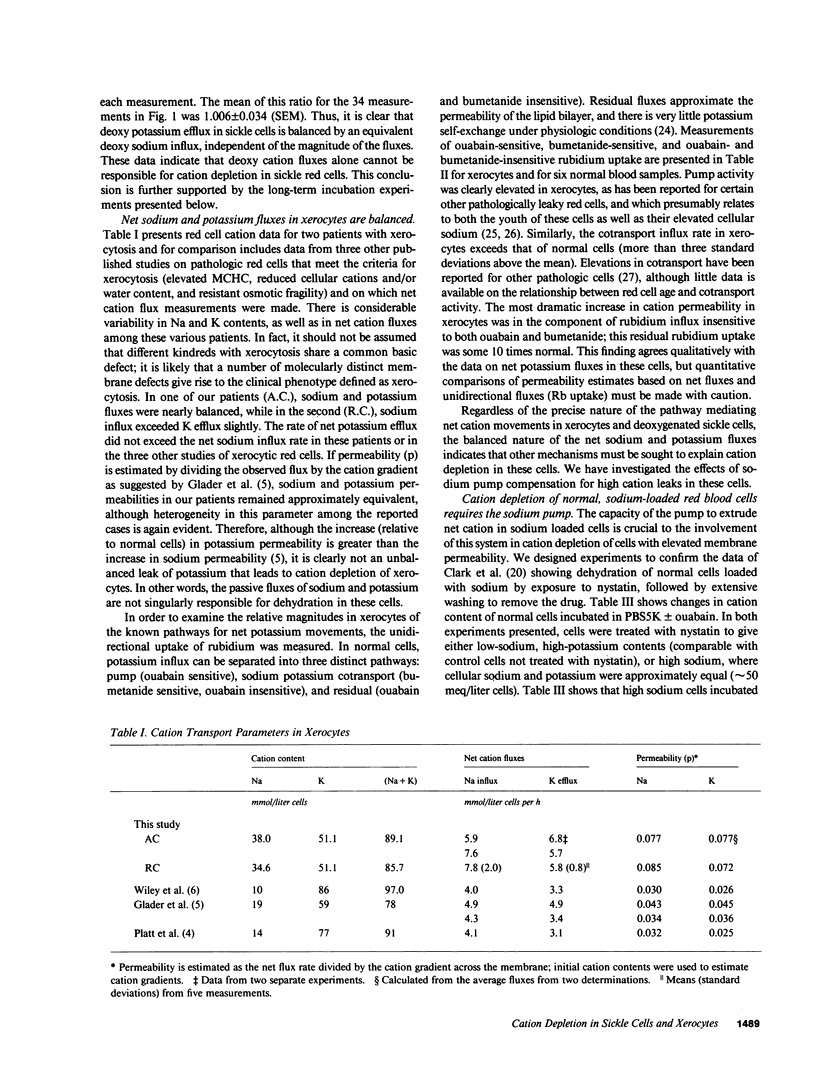
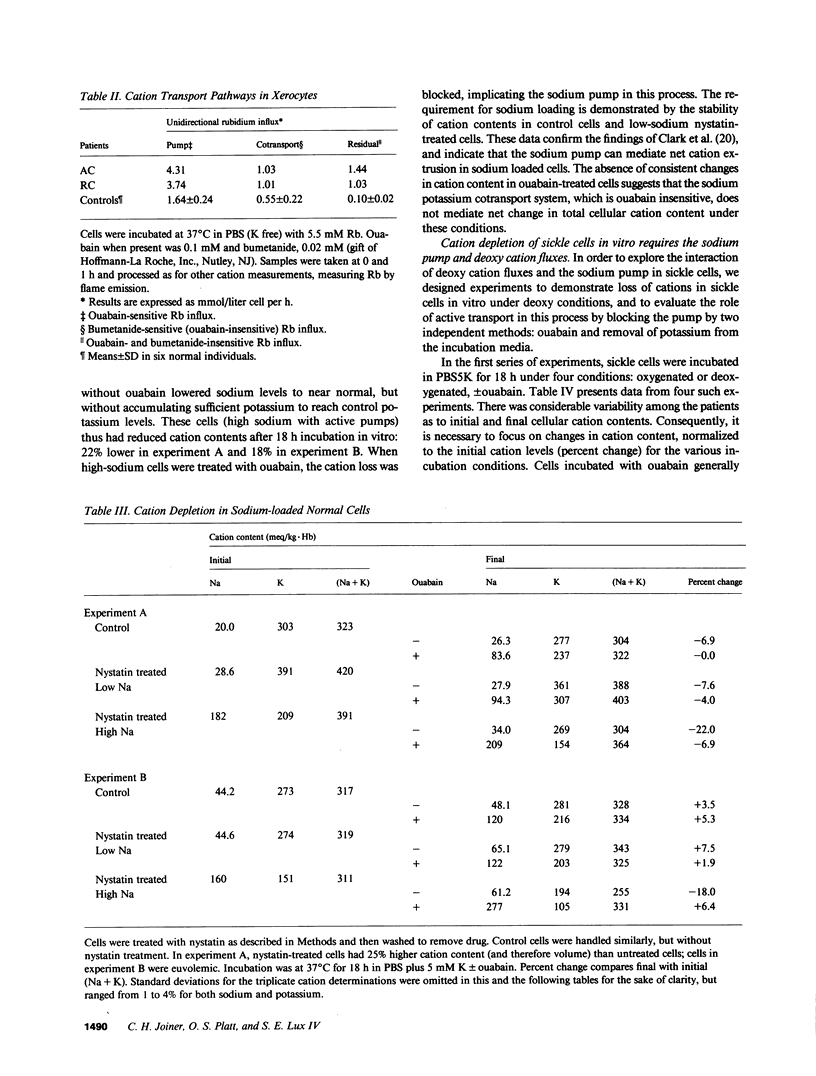
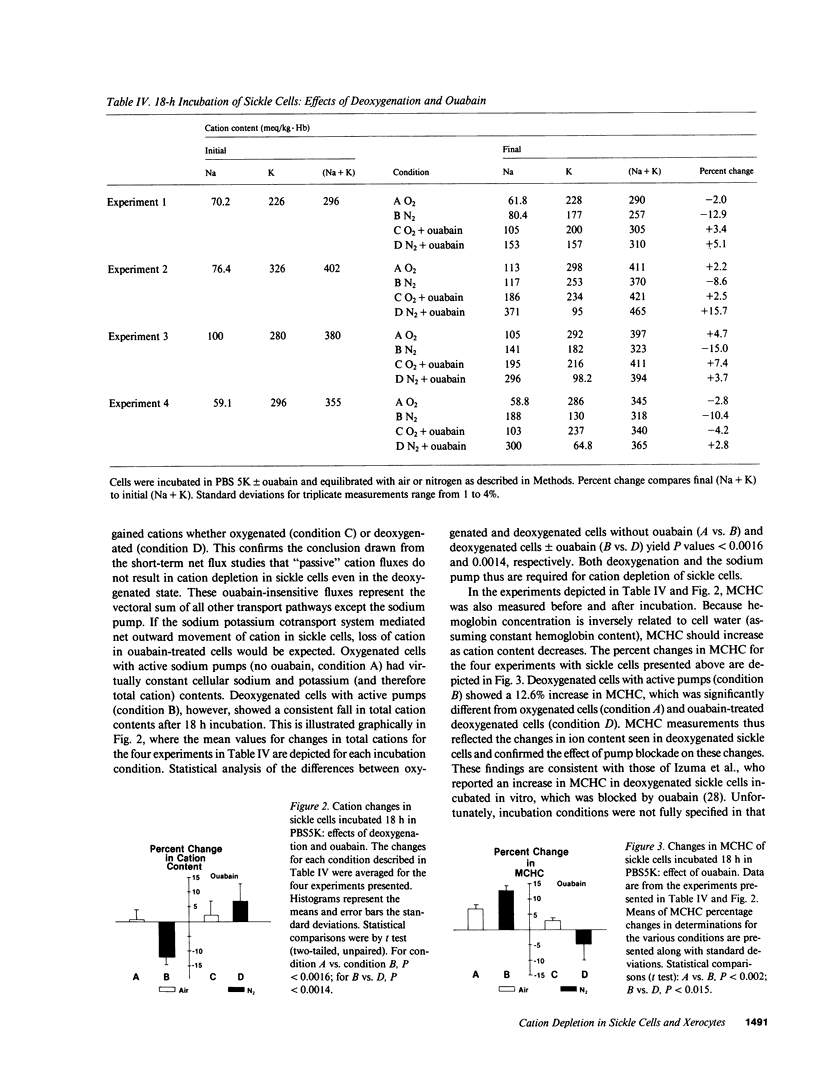
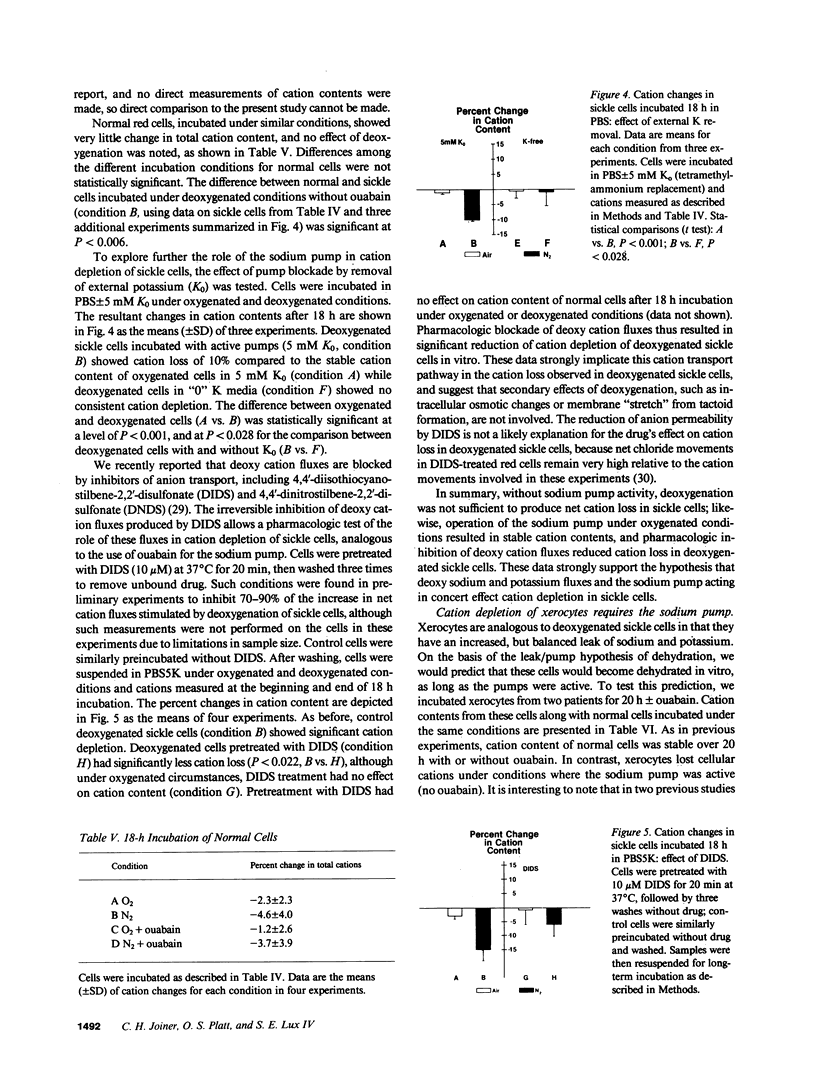
The mechanism by which sickle cells and xerocytic red cells become depleted of cations in vivo has not been identified previously. Both types of cells exhibit elevated permeabilities to sodium and potassium, in the case of sickle cells, when deoxygenated. The ouabain-insensitive fluxes of sodium and potassium were equivalent, however, in both cell types under these conditions. When incubated 18 hours in vitro, sickle cells lost cations but only when deoxygenated. This cation depletion was blocked by ouabain, removal of external potassium, or pretreatment with 4,4'-diisothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulfonate, which blocks the increase in cation permeability induced by deoxygenation. The loss of cation exhibited by oxygenated xerocytes similarly incubated was also blocked by ouabain. These data support the hypothesis that the elevated "passive" cation fluxes of xerocytes and deoxygenated sickle cells are not directly responsible for cation depletion of these cells; rather, these pathologic leaks interact with the sodium pump to produce a net loss of cellular cation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkowitz L. R., Orringer E. P. Passive sodium and potassium movements in sickle erythrocytes. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C208–C214. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertles J. F., Milner P. F. Irreversibly sickled erythrocytes: a consequence of the heterogeneous distribution of hemoglobin types in sickle-cell anemia. J Clin Invest. 1968 Aug;47(8):1731–1741. doi: 10.1172/JCI105863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Balazs T., Landau L. C. Determinants of red cell sickling. Effects of varying pH and of increasing intracellular hemoglobin concentration by osmotic shrinkage. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Apr;87(4):597–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Lew V. L. Effect of a 'sickling pulse' on calcium and potassium transport in sickle cell trait red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:265–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugnara C., Bunn H. F., Tosteson D. C. Regulation of erythrocyte cation and water content in sickle cell anemia. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):388–390. doi: 10.1126/science.3961486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugnara C., Kopin A. S., Bunn H. F., Tosteson D. C. Regulation of cation content and cell volume in hemoglobin erythrocytes from patients with homozygous hemoglobin C disease. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1608–1617. doi: 10.1172/JCI111867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chailley B., Feo C., Garay R., Dagher G., Bruckdorfer R., Fischer S., Piau J. P., Delaunay J. Evidence for imbalanced furosemide-sensitive Na+, K+ cotransport in hereditary stomatocytosis. Scand J Haematol. 1981 Nov;27(5):365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1981.tb00498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Guatelli J. C., White A. T., Shohet S. B. Study on the dehydrating effect of the red cell Na+/K+-pump in nystatin-treated cells with varying Na+ and water contents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 7;646(3):422–432. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90311-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Caggiano V., Shohet S. B. Effects of abnormal cation transport on deformability of desiccytes. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(4):521–532. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Deformability of oxygenated irreversibly sickled cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):189–196. doi: 10.1172/JCI109650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Hydration of sickle cells using the sodium ionophore Monensin. A model for therapy. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1074–1080. doi: 10.1172/JCI110695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Morrison C. E., Shohet S. B. Monovalent cation transport in irreversibly sickled cells. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):329–337. doi: 10.1172/JCI109133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coletta M., Hofrichter J., Ferrone F. A., Eaton W. A. Kinetics of sickle haemoglobin polymerization in single red cells. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):194–197. doi: 10.1038/300194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANON D., MARIKOVSKY V. DETERMINATION OF DENSITY DISTRIBUTION OF RED CELL POPULATION. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Oct;64:668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton J. W., Jacob H. S., White J. G. Membrane abnormalities of irreversibly sickled cells. Semin Hematol. 1979 Jan;16(1):52–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embury S. H., Backer K., Glader B. E. Monovalent cation changes in sickle erythrocytes: a direct reflection of alpha-globin gene number. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jul;106(1):75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry M. E., Nagel R. L. Heterogeneity of red cells in the sickler: a characteristic with practical clinical and pathophysiological implications. Blood Cells. 1982;8(1):9–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry M. E., Nagel R. L. The effect of deoxygenation on red cell density: significance for the pathophysiology of sickle cell anemia. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1370–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fales F. W. Water distribution in blood during sickling of erythrocytes. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):703–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich O., Leibson C., Gunn R. B. Chloride net efflux from intact erythrocytes under slippage conditions. Evidence for a positive charge on the anion binding/transport site. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):127–152. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Garrahan P. J. The interaction of sodium and potassium with the sodium pump in red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):297–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R., Adragna N., Canessa M., Tosteson D. Outward sodium and potassium cotransport in human red cells. J Membr Biol. 1981;62(3):169–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01998162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The stoicheiometry of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):217–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glader B. E., Fortier N., Albala M. M., Nathan D. G. Congenital hemolytic anemia associated with dehydrated erythrocytes and increased potassium loss. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 5;291(10):491–496. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409052911003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glader B. E., Nathan D. G. Cation permeability alterations during sickling: relationship to cation composition and cellular hydration of irreversibly sickled cells. Blood. 1978 May;51(5):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofrichter J., Ross P. D., Eaton W. A. Supersaturation in sickle cell hemoglobin solutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner C. H., Lauf P. K. Modulation of ouabain binding and potassium pump fluxes by cellular sodium and potassium in human and sheep erythrocytes. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:177–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner C. H., Lauf P. K. The effect of anti-L on ouabain binding to sheep erythrocytes. J Membr Biol. 1975 Apr 23;21(1-2):99–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01941064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul D. K., Fabry M. E., Windisch P., Baez S., Nagel R. L. Erythrocytes in sickle cell anemia are heterogeneous in their rheological and hemodynamic characteristics. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):22–31. doi: 10.1172/JCI110960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kregenow F. M. Osmoregulatory salt transporting mechanisms: control of cell volume in anisotonic media. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:493–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Celle P. L., Weed R. I. The contribution of normal and pathologic erythrocytes to blood rheology. Prog Hematol. 1971;7(0):1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masys D. R., Bromberg P. A., Balcerzak S. P. Red cells shrink during sickling. Blood. 1974 Dec;44(6):885–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy P. R., Sherman A. S. Irreversibly sickled cells and red cell survival in sickle cell anemia: a study with both DF32P and 51CR. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. R., Rickles F. R., Lichtman M. A., La Celle P. L., Bates J., Weed R. I. A new variant of hereditary hemolytic anemia with stomatocytosis and erythrocyte cation abnormality. Blood. 1971 Aug;38(2):184–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi C. T., Dover G. J., Rodgers G. P., Serjeant G. R., Antonarakis S. E., Anagnou N. P., Higgs D. R., Weatherall D. J., Schechter A. N. Alpha thalassemia changes erythrocyte heterogeneity in sickle cell disease. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1632–1637. doi: 10.1172/JCI111870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt O. S. Exercise-induced hemolysis in sickle cell anemia: shear sensitivity and erythrocyte dehydration. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):1055–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt O. S., Lux S. E., Nathan D. G. Exercise-induced hemolysis in xerocytosis. Erythrocyte dehydration and shear sensitivity. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):631–638. doi: 10.1172/JCI110297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. P., Schechter A. N., Noguchi C. T. Cell heterogeneity in sickle cell disease: quantitation of the erythrocyte density profile. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jul;106(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth E. F., Jr, Nagel R. L., Bookchin R. M. pH dependency of potassium efflux from sickled red cells. Am J Hematol. 1981;11(1):19–27. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830110104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Schlegel R. A., Williamson P. Endocytosis in sickle erythrocytes: a mechanism for elevated intracellular Ca2+ levels. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jan;126(1):53–59. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSTESON D. C., CARLSEN E., DUNHAM E. T. The effects of sickling on ion transport. I. Effect of sickling on potassium transport. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Sep 20;39(1):31–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSTESON D. C., SHEA E., DARLING R. C. Potassium and sodium of red blood cells in sickle cell anemia. J Clin Invest. 1952 Apr;31(4):406–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI102623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S. Co-ordinated increase of sodium leak and sodium pump in hereditary spherocytosis. Br J Haematol. 1972 May;22(5):529–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb05700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S., Ellory J. C., Shuman M. A., Shaller C. C., Cooper R. A. Characteristics of the membrane defect in the hereditary stomatocytosis syndrome. Blood. 1975 Sep;46(3):337–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S., Shaller C. C. Selective loss of calcium permeability on maturation of reticulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1113–1119. doi: 10.1172/JCI108735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



