Abstract
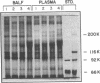
Small amounts of plasma protein normally reach the alveolar epithelial surface by a size-selective process that restricts the passage of very large molecules. Size selectivity may be compromised in the lungs of patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). To assess this question, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from normal volunteers (n = 11), cardiac edema patients (n = 3), and ARDS patients (n = 8) was compared. Mean total protein in ARDS BALF was greater than 12 times the levels in normals or cardiac edema patients. BALF/plasma total protein ratios and measurements of epithelial lining fluid protein also separated the patients groups. The large proteins IgM and alpha 2-macroglobulin were found in ARDS BALF at greater than 90 times the concentrations of normal or cardiac edema fluid. The relationship of distribution coefficient vs. log molecular weight for seven proteins (54,000-900,000 mol wt) hyperbolically increased in normals but was flat in ARDS patients. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed a paucity of high molecular weight proteins in normal and cardiac edema BALF, but demonstrated the full spectrum of plasma proteins in ARDS BALF. We conclude that normal size selectivity is preserved in cardiac edema but is destroyed by the alveolar-capillary injury of ARDS.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. R., Holliday R. L., Driedger A. A., Lefcoe M., Reid B., Sibbald W. J. Documentation of pulmonary capillary permeability in the adult respiratory distress syndrome accompanying human sepsis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jun;119(6):869–877. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.6.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachofen M., Weibel E. R. Structural alterations of lung parenchyma in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Chest Med. 1982 Jan;3(1):35–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell D. Y., Haseman J. A., Spock A., McLennan G., Hook G. E. Plasma proteins of the bronchoalveolar surface of the lungs of smokers and nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):72–79. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignon J., Chahinian P., Feldmann G., Sapin C. Ultrastructural immunoperoxidase demonstration of autologous albumin in the alveolar capillary membrane and in the alveolar lining material in normal rats. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):503–509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham K. L., Woolverton W. C., Blake L. H., Staub N. C. Increased sheep lung vascular permeability caused by pseudomonas bacteremia. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):792–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI107819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Schaeffer R. C., Jr, Michaels S. G., Weil M. H. Pulmonary edema fluid. Spectrum of features in 37 patients. Circulation. 1979 Nov;60(5):1161–1169. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.60.5.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall E. D., Staub N. C., Goldberg H. S., Effros R. M. Recent developments in pulmonary edema. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):808–822. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauber I. M., Pluss W. T., VanGrondelle A., Trow R. S., Weil J. V. Specificity and sensitivity of noninvasive measurement of pulmonary vascular protein leak. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Aug;59(2):564–574. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.2.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Rennard S. I., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Early reversible changes in human alveolar structures induced by hyperoxia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 13;309(15):878–883. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310133091502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFouw D. O. Ultrastructural features of alveolar epithelial transport. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5 Pt 2):S9–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Effros R. M., Mason G. R. Measurements of pulmonary epithelial permeability in vivo. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5 Pt 2):S59–S65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann A. J., 3rd, Vaughan T. R., Jr, Brigham K. L., Woolverton W. C., Staub N. C. Effect of increased vascular pressure on lung fluid balance in unanesthetized sheep. Circ Res. 1975 Sep;37(3):271–284. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.3.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein A., Grossman R. F., Jones J. G., Overland E., Pitts L., Murray J. F., Staub N. C. The value of edema fluid protein measurement in patients with pulmonary edema. Am J Med. 1979 Jul;67(1):32–38. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb A. F., Klein E. Hemodynamic and alveolar protein studies in noncardiac pulmonary edema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Nov;114(5):831–835. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.5.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin A. B., Kohler J., DeNardo G. Noninvasive measurement of pulmonary transvascular protein flux in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):869–877. doi: 10.1172/JCI109953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin A. B., Stewart P. A. Differential permeability of endothelial and epithelial barriers to albumin flux. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Dec;47(6):1315–1324. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.6.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. N., Taylor A. E. Permeability of intestinal capillaries to endogenous macromolecules. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):H457–H464. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.238.4.H457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Inflammatory and immune processes in the human lung in health and disease: evaluation by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):149–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. G., Minty B. D., Lawler P., Hulands G., Crawley J. C., Veall N. Increased alveolar epithelial permeability in cigarette smokers. Lancet. 1980 Jan 12;1(8159):66–68. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. B., Davis G. S., Giancola M. S. Biochemical analyses of bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of healthy human volunteer smokers and nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Nov;118(5):863–875. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macart M., Gerbaut L. An improvement of the Coomassie Blue dye binding method allowing an equal sensitivity to various proteins: application to cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Jun 16;122(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason G. R., Effros R. M., Uszler J. M., Mena I. Small solute clearance from the lungs of patients with cardiogenic and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. Chest. 1985 Sep;88(3):327–334. doi: 10.1378/chest.88.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason G. R., Uszler J. M., Effros R. M., Reid E. Rapidly reversible alterations of pulmonary epithelial permeability induced by smoking. Chest. 1983 Jan;83(1):6–11. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill W. W., Naegel G. P., Olchowski J. J., Reynolds H. Y. Immunoglobulin G subclass proteins in serum and lavage fluid of normal subjects. Quantitation and comparison with immunoglobulins A and E. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):584–587. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnear F. L., Barie P. S., Malik A. B. Lung fluid and protein exchange in the acute sheep preparation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jun;50(6):1358–1361. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.6.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. C., Parker R. E., Granger D. N., Taylor A. E. Vascular permeability and transvascular fluid and protein transport in the dog lung. Circ Res. 1981 Apr;48(4):549–561. doi: 10.1161/01.res.48.4.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L., Fowler A. A., 3rd Another look at ARDS. Chest. 1982 Jul;82(1):98–104. doi: 10.1378/chest.82.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J., Suelter C. H. An evaluation of the Coomassie brillant blue G-250 dye-binding method for quantitative protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1977 Aug;81(2):478–480. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90723-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenrath R., Zimmermann I. Blood plasma contamination of the lung alveolar surfactant obtained by various sampling techniques. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jul;18(2):238–248. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Basset G., Lecossier D., O'Donnell K. M., Pinkston P., Martin P. G., Crystal R. G. Estimation of volume of epithelial lining fluid recovered by lavage using urea as marker of dilution. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):532–538. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht J., Shapiro L., Krauthammer M., Taplin G., Wasserman K., Uszler J. M., Effros R. M. Accelerated clearance of small solutes from the lungs in interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jan;121(1):105–117. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutili G., Kvietys P., Martin D., Parker J. C., Taylor A. E. Increased pulmonary microvasuclar permeability induced by alpha-naphthylthiourea. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 May;52(5):1316–1323. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.5.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger-Keeley E. E., Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of alveolar-capillary membrane permeability to peroxidase used as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):781–793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E. Structural basis for some permeability properties of the air--blood barrier. Fed Proc. 1978 Sep;37(11):2471–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbald W. J., Driedger A. A., Moffat J. D., Myers M. L., Reid B. A., Holliday R. L. Pulmonary microvascular clearance of radiotracers in human cardiac and noncardiac pulmonary edema. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jun;50(6):1337–1347. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.6.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprung C. L., Rackow E. C., Fein I. A., Jacob A. I., Isikoff S. K. The spectrum of pulmonary edema: differentiation of cardiogenic, intermediate, and noncardiogenic forms of pulmonary edema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Dec;124(6):718–722. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C., Bland R. D., Brigham K. L., Demling R., Erdmann A. J., 3rd, Woolverton W. C. Preparation of chronic lung lymph fistulas in sheep. J Surg Res. 1975 Nov;19(5):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(75)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. E., Gaar K. A., Jr Estimation of equivalent pore radii of pulmonary capillary and alveolar membranes. Am J Physiol. 1970 Apr;218(4):1133–1140. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.4.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vreim C. E., Snashall P. D., Staub N. C. Protein composition of lung fluids in anesthetized dogs with acute cardiogenic edema. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1466–1469. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr G. A., Martin R. R., Sharp P. M., Rossen R. D. Normal human bronchial immunoglobulins and proteins: effects of cigarette smoking. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jul;116(1):25–30. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]