Abstract
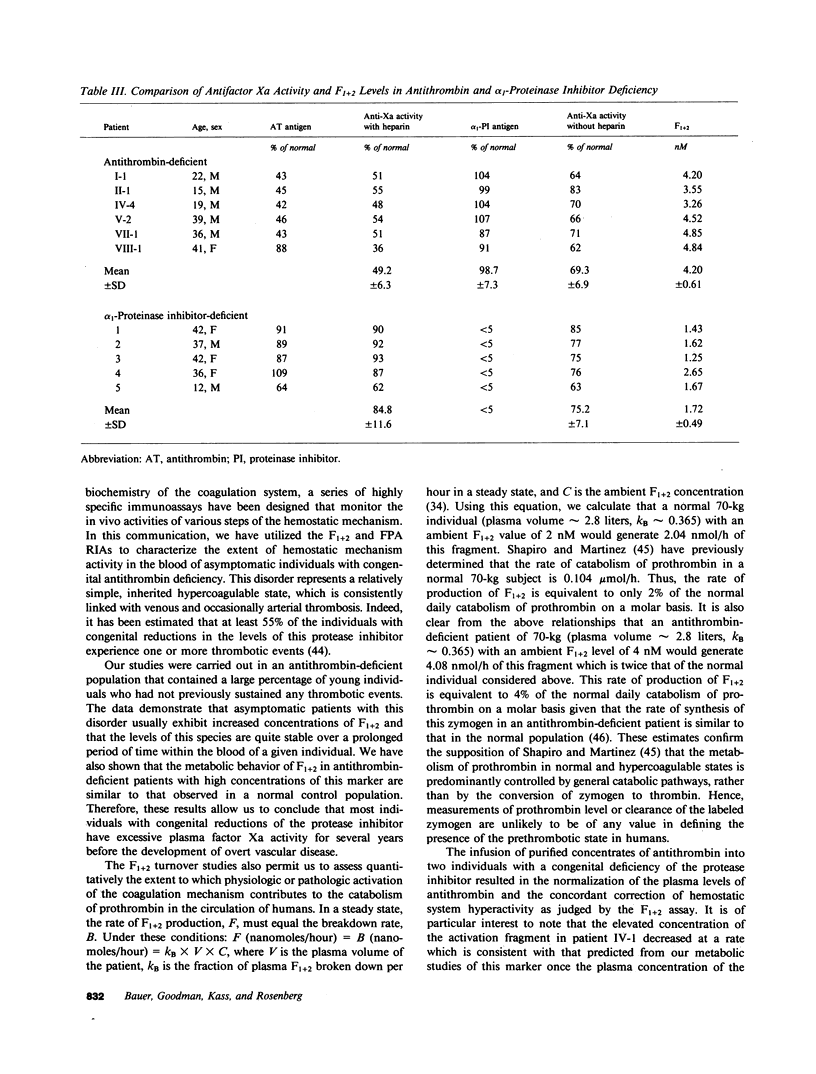
The presence of congenital antithrombin deficiency has been consistently shown to predispose patients to venous thrombosis. We have utilized the prothrombin fragment F1+2 radioimmunoassay to quantitate factor Xa activity in the blood of 22 asymptomatic individuals with this clinical disorder not receiving antithrombotic therapy. The mean level of F1+2 was significantly elevated in these patients as compared to normal controls (3.91 vs. 1.97 nM, P less than 0.001). The metabolic behavior of 131 I-F1+2 was found to be similar in antithrombin-deficient subjects and normal individuals. The hemostatic system hyperactivity as measured by the F1+2 assay could be specifically corrected by raising the plasma antithrombin levels of the above asymptomatic individuals into the normal range. This study provides the first demonstration that the prethrombotic state can be biochemically defined as an imbalance between the production and inhibition of factor Xa enzymatic activity within the human circulation. It is known that antithrombin and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor (PI) are the major inhibitors of factor Xa in human plasma in the absence of heparin. To further evaluate the mechanism by which antithrombin functions as an inhibitor of factor Xa in humans, we studied five patients who exhibited severe congenital deficiencies of alpha 1-PI. Our results indicated that the plasma of these subjects showed virtually identical decreases in plasma antifactor Xa activity in the absence of heparin when compared to antithrombin-deficient individuals, but the plasma F1+2 levels in the alpha 1-PI deficient population were not significantly different than normal. This data suggests that alpha 1-PI does not function as a major inhibitor of factor Xa in vivo, and that a tonically active heparin-dependent mechanism exists in humans for accelerating the neutralization of this enzyme by antithrombin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abildgaard U., Lie M., Odegård O. R. Antithrombin (heparin cofactor) assay with "new" chromogenic substrates (S-2238 and Chromozym TH). Thromb Res. 1977 Oct;11(4):549–553. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambruso D. R., Leonard B. D., Bies R. D., Jacobson L., Hathaway W. E., Reeve E. B. Antithrombin III deficiency: decreased synthesis of a biochemically normal molecule. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson D. L., Stevan L., Ball A. P., Franza B. R., Jr, Finlayson J. S. Generation of the combined prothrombin activation peptide (F1-2) during the clotting of blood and plasma. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1410–1418. doi: 10.1172/JCI108902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowcliffe T. W. Studies of heparin binding to antithrombin III by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Feb 29;42(5):1434–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. A., Ashenhurst J. B., Chediak J., Rosenberg R. D. Antithrombin "Chicago": a functionally abnormal molecule with increased heparin affinity causing familial thrombophilia. Blood. 1983 Dec;62(6):1242–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. A., Rosenberg R. D. Thrombin generation in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):791–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekmans A. W., Veltkamp J. J., Bertina R. M. Congenital protein C deficiency and venous thromboembolism. A study of three Dutch families. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 11;309(6):340–344. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308113090604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson T. H., Atencio A. C., Simon T. L. In vivo behavior of radioiodinated rabbit antithrombin III. Demonstration of a noncirculating vascular compartment. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):191–199. doi: 10.1172/JCI111401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho A., Ellman L. Hereditary antithrombin III deficiency. Effect of antithrombin III deficiency on platelet function. Am J Med. 1976 Aug;61(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Schetz J., de Cock F., Holmer E., Verstraete M. Metabolism of antithrombin III (heparin cofactor) in man: effects of venous thrombosis and of heparin administration. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;7(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Esmon C. T. Activated protein C inhibits platelet prothrombin-converting activity. Blood. 1979 Dec;54(6):1272–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Nixon R. R., Cooper M. R., Esmon C. T. Familial protein S deficiency is associated with recurrent thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2082–2088. doi: 10.1172/JCI111632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damus P. S., Hicks M., Rosenberg R. D. Anticoagulant action of heparin. Nature. 1973 Dec 7;246(5432):355–357. doi: 10.1038/246355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damus P. S., Rosenberg R. D. Antithrombin-heparin cofactor. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:653–669. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing M. R., Bloom J. W., Mann K. G. Comparison of the inhibition of thrombin by three plasma protease inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2649–2653. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L., Harris K. W. Complex formation between thrombin and thrombomodulin inhibits both thrombin-catalyzed fibrin formation and factor V activation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7944–7947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G. Identification of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitel S. N., Medina V. M., Wessler S. Inhibition of human activated Factor X by antithrombin III and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor in human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6890–6895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J., Wideman C. Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1370–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI110385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J. C., Smallridge R. C., Rosenberg R. D. Inherited antithrombin-III deficiency causing mesenteric venous infarction: a new clinical entity. Ann Surg. 1975 Jun;181(6):791–794. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197506000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handin R. I., Cohen H. J. Purification and binding properties of human platelet factor four. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4273–4282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan R. E., Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Rosenberg R. D. The kinetics of hemostatic enzyme-antithrombin interactions in the presence of low molecular weight heparin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10081–10090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Canfield W. M., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5824–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau H. K., Rosenberg J. S., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. The isolation and characterization of a specific antibody population directed against the prothrombin activation fragments F2 and F1 + 2. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8751–8761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau H. K., Rosenberg R. D. The isolation and characterization of a specific antibody population directed against the thrombin antithrombin complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5885–5893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. A., Fritze L., Galli S. J., Karp G., Rosenberg R. D. Microvascular heparin-like species with anticoagulant activity. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):H725–H733. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.5.H725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. A., McKenney J. B., Rosenberg R. D. Acceleration of thrombin-antithrombin complex formation in rat hindquarters via heparinlike molecules bound to the endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):341–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI111429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. A., Rosenberg R. D. Heparinlike molecules with anticoagulant activity are synthesized by cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90615-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlar R. A., Kleiss A. J., Griffin J. H. Mechanism of action of human activated protein C, a thrombin-dependent anticoagulant enzyme. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):1067–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massé F. X., Bolton M. M., Jr Experience with a low-cost chair-type detector system for the determination of radioactive body burdens of M.I.T. radiation workers. Health Phys. 1970 Jul;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197007000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Interaction of coagulation factor Xa with human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Ti M., Kaplan K. L., Spanondis K., Soland T., Butler V. P., Jr The generation of fibrinopeptide A in clinical blood samples: evidence for thrombin activity. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1136–1144. doi: 10.1172/JCI108566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Younger L. R., Wilner G. D., Procupez T., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2350–2353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosslin B. Analysis of disappearance time-curves after single injection of labelled proteins. Ciba Found Symp. 1972;9:113–130. doi: 10.1002/9780470719923.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odegård O. R., Lie M., Abildgaard U. Antifactor Xa activity measured with amidolytic methods. Haemostasis. 1976;5(5):265–275. doi: 10.1159/000214145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosta G. M., Favreau L. V., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Purification and properties of human platelet heparitinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11249–11255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J., Kvam D., Nossel H. L., Kaplan K. L., Kernoff P. B. Thrombin and plasmin activity and platelet activation in the development of venous thrombosis. Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Functional properties of an endothelial cell cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5532–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve E. B., Leonard B., Wentland S. H., Damus P. Studies with 131I-labelled antithrombin III in dogs. Thromb Res. 1980 Nov 15;20(4):375–389. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie R. F., Alper C. A., Graves J., Pearson N., Larson C. Automated quantitation of proteins in serum and other biologic fluids. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Feb;59(2):151–159. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Lenox R. H., Wray H. L., Ramseth D. Statistical characterization of the random errors in the radioimmunoassay dose--response variable. Clin Chem. 1976 Mar;22(3):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D. Statistical quality control and routine data processing for radioimmunoassays and immunoradiometric assays. Clin Chem. 1974 Oct;20(10):1255–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. M., Shuman M. A. Prothrombin is activated on vascular endothelial cells by factor Xa and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):7001–7005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.7001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. S., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Activation of human prothrombin by highly purified human factors V and X-a in presence of human antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1607–1617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. S., McKenna P. W., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of human factor IXa by human antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):8883–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVITT S., GALLAGHER N. G. Prevention of venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in injured patients. A trial of anticoagulant prophylaxis with phenindione in middle-aged and elderly patients with fractured necks of femur. Lancet. 1959 Dec 5;2(7110):981–989. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Curriden S., Lawrence D., Griffin J. H., Loskutoff D. J. Activated protein C stimulates the fibrinolytic activity of cultured endothelial cells and decreases antiactivator activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1121–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz H. P., Fischer M., Hopmeier P., Batard M. A., Griffin J. H. Plasma protein S deficiency in familial thrombotic disease. Blood. 1984 Dec;64(6):1297–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Martinez J. Human prothrombin metabolism in normal man and in hypocoagulable subjects. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1292–1298. doi: 10.1172/JCI106095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Waugh D. F. The purification of human prothrombin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Dec 1;16(3):468–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead N., Kaplan A. P., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of activated factor XII by antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6481–6488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. M., Nawroth P. P., Kisiel W., Handley D., Drillings M., Bartos J. A coagulation pathway on bovine aortic segments leading to generation of Factor Xa and thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):1910–1921. doi: 10.1172/JCI111611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D., Nawroth P., Marcum J., Handley D., Kisiel W., Rosenberg R., Stern K. Interaction of antithrombin III with bovine aortic segments. Role of heparin in binding and enhanced anticoagulant activity. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):272–279. doi: 10.1172/JCI111685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Stenflo J., Dahlbäck B., Teodorsson B. Inactivation of human coagulation factor V by activated protein C. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1914–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor E., Murano G., Snoy P., Gerety R. J. Inactivation of hepatitis B virus by heat in antithrombin III stabilized with citrate. Thromb Res. 1981 Apr 1;22(1-2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(81)90326-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitel J. M., Bauer K. A., Lau H. K., Rosenberg R. D. Studies of the prothrombin activation pathway utilizing radioimmunoassays for the F2/F1 + 2 fragment and thrombin--antithrombin complex. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):1086–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaler E., Lechner K. Antithrombin III deficiency and thromboembolism. Clin Haematol. 1981 Jun;10(2):369–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Coordinate binding of factor Va and factor Xa to the unstimulated platelet. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):743–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Rohrbach M. S., Mann K. G. Functional prothrombinase complex assembly on isolated monocytes and lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7264–7267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11128–11131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Sexton P. W., Esmon C. T. The inhibition of blood coagulation by activated Protein C through the selective inactivation of activated Factor V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 7;571(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Wessler S., Stoll P. J. Rabbit plasma inhibitor of the activated species of blood coagulation factor X. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 10;246(11):3694–3702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]