Abstract
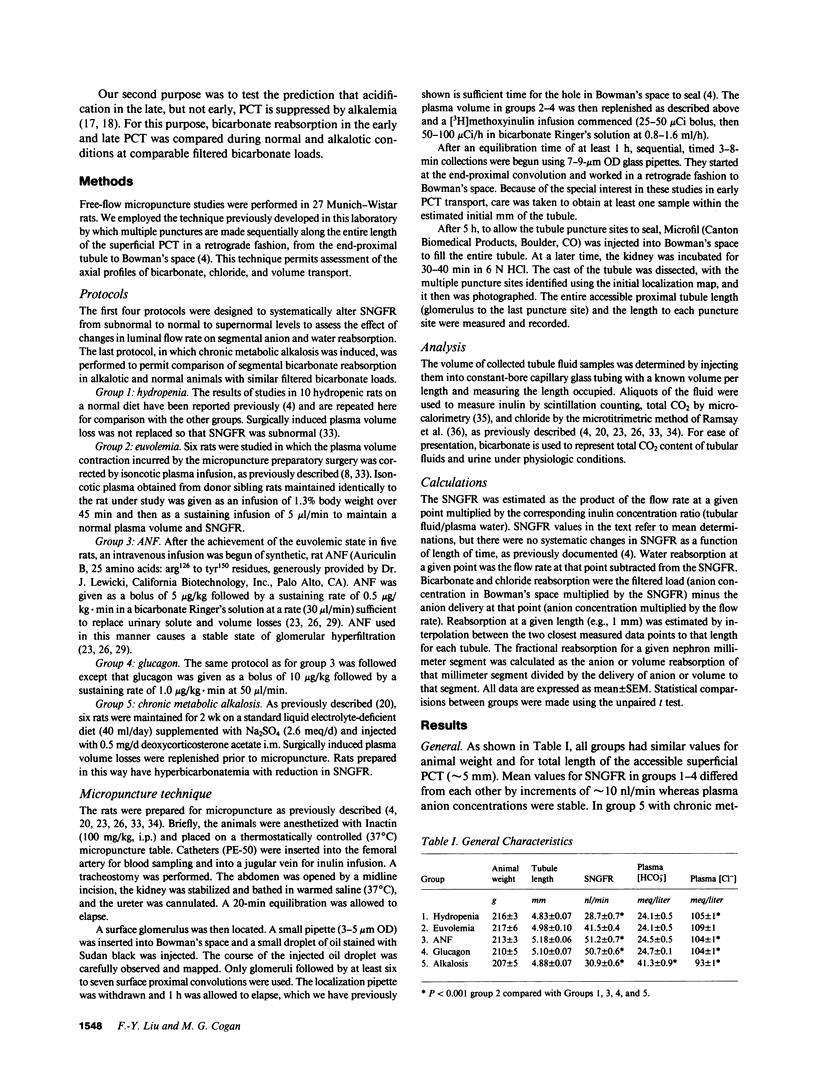
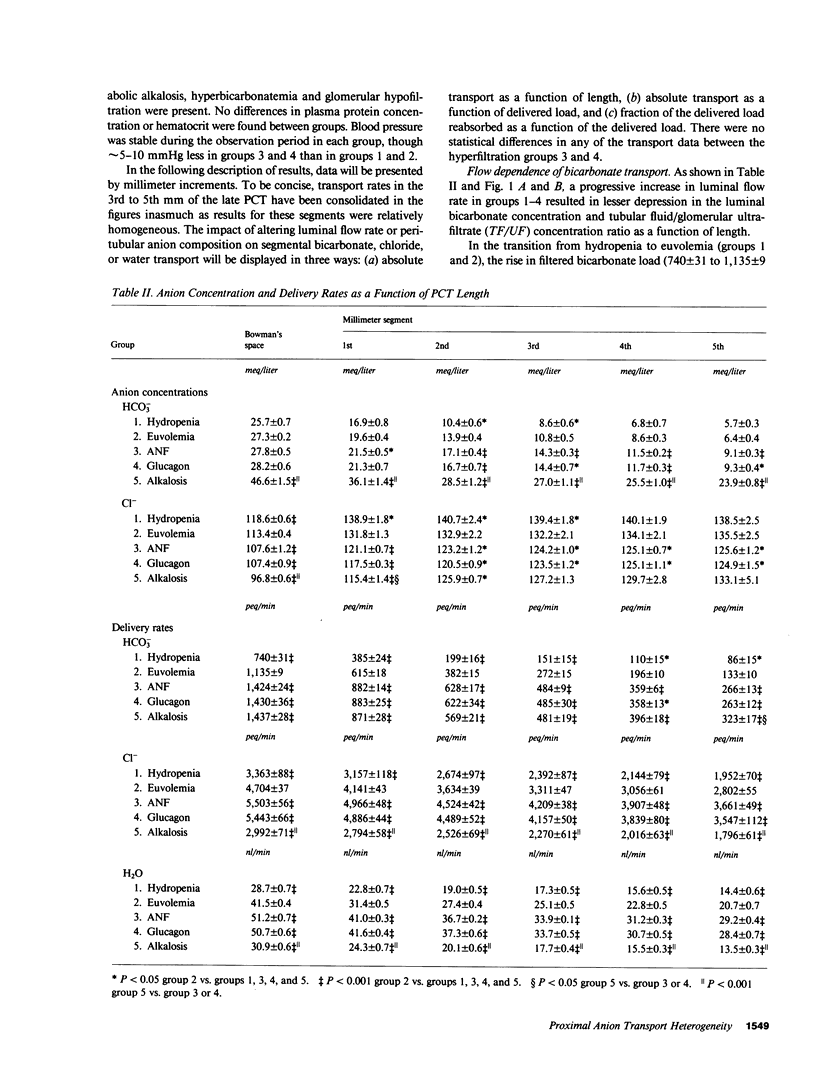
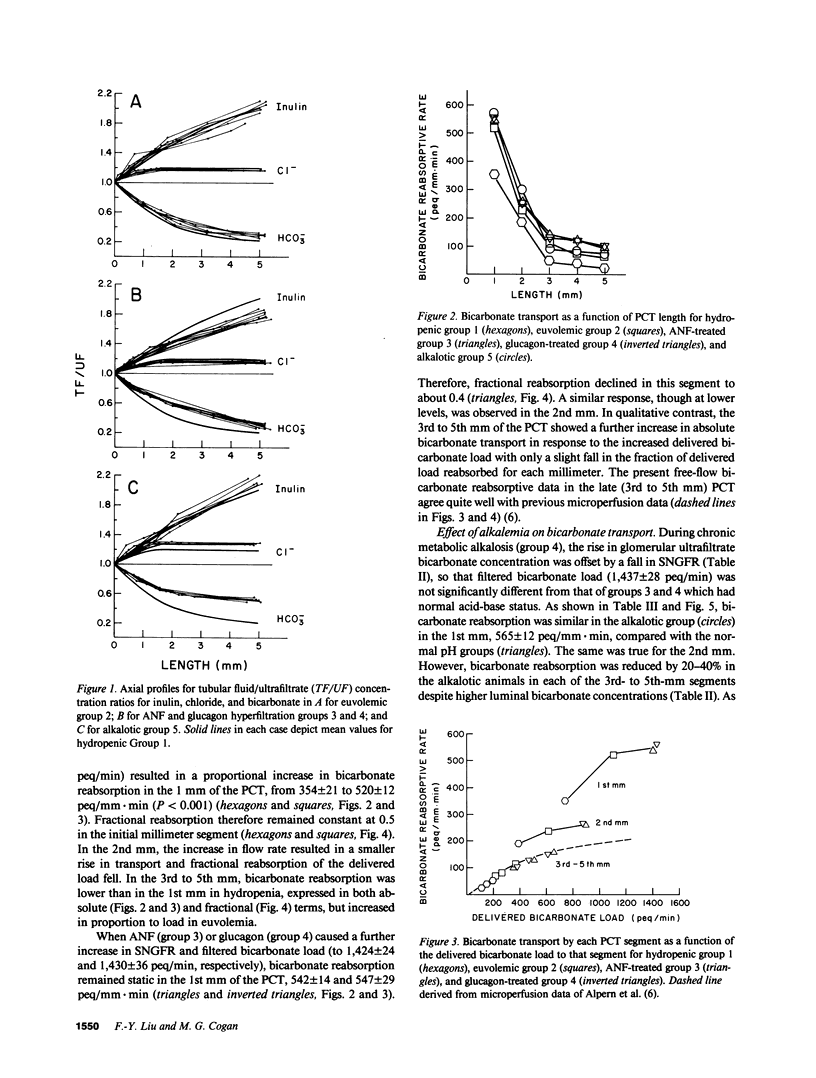
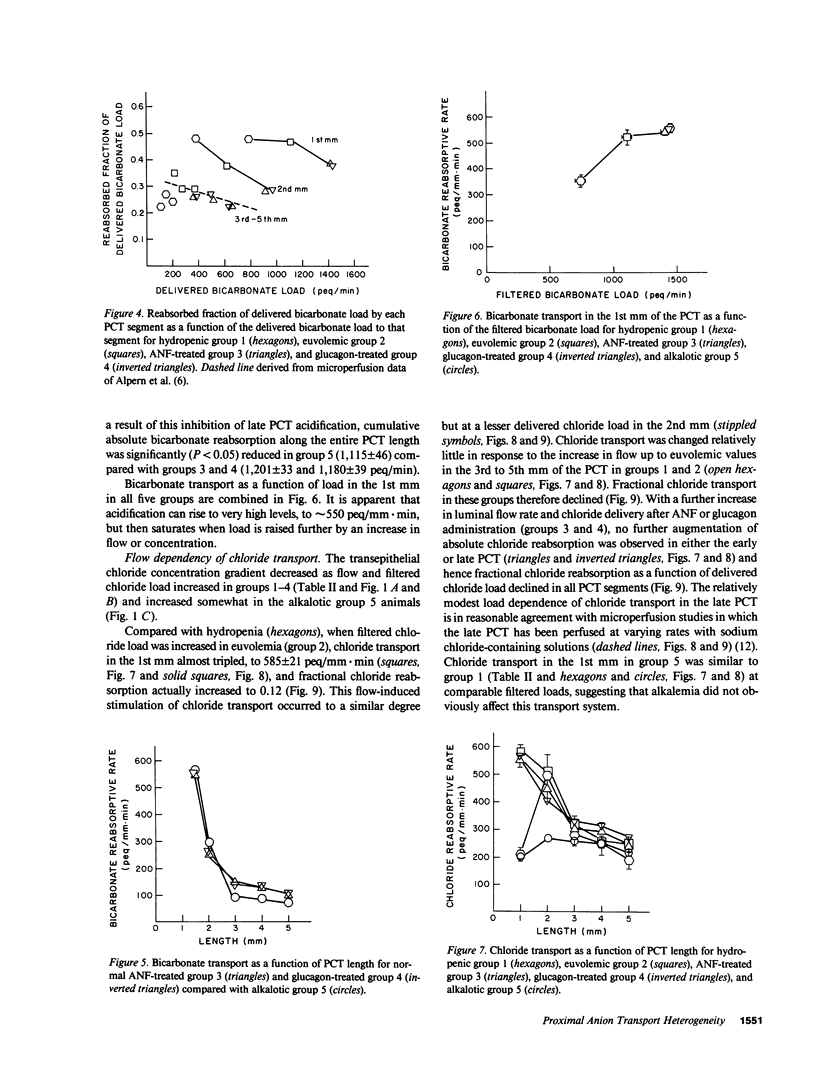
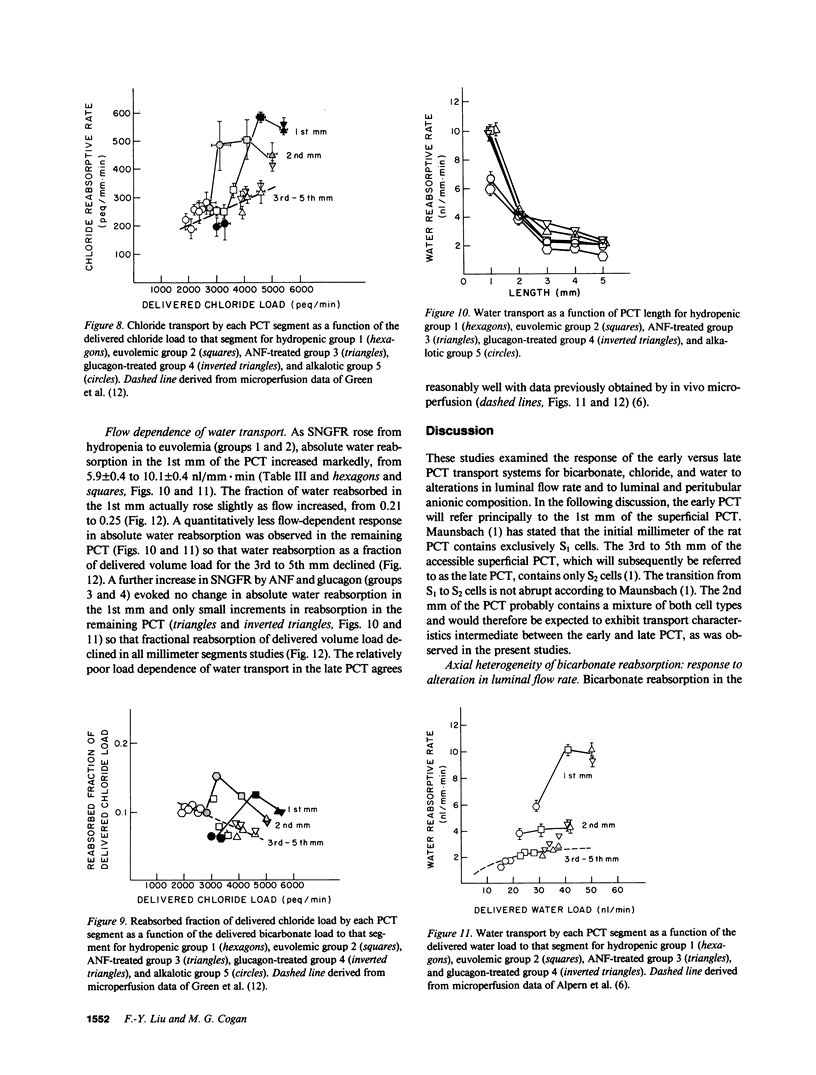
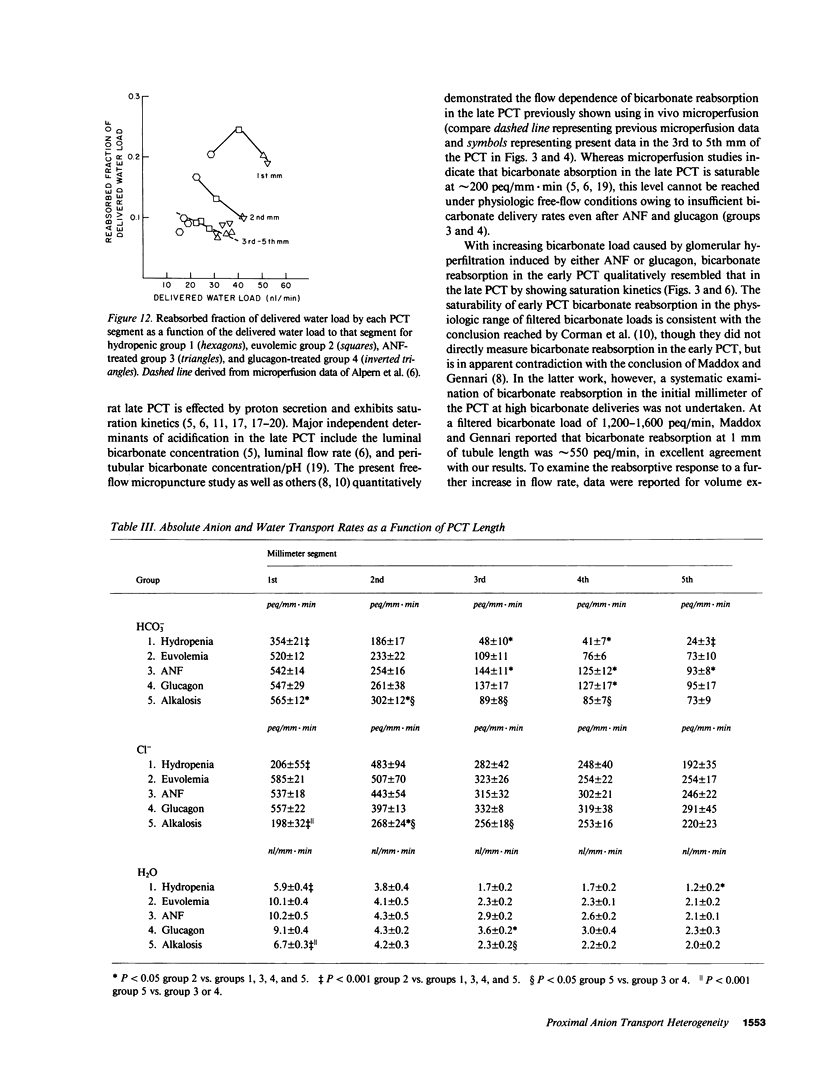
These studies examined regulation of superficial proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) transport as a function of length. When single nephron glomerular filtration rate (SNGFR) increased from 28.7 +/- 0.7 nl/min in hydropenia to 41.5 +/- 0.4 nl/min in euvolemia, bicarbonate, chloride, and water reabsorption in the early (1st mm) PCT increased proportionally: from 354 +/- 21 peq/mm X min, 206 +/- 55 peq/mm X min, and 5.9 +/- 0.4 nl/mm X min to 520 +/- 12 peq/mm X min, 585 +/- 21 peq/mm X min, and 10.1 +/- 0.4 nl/mm X min, respectively. These high transport rates did not increase further, however, when SNGFR went to 51.2 +/- 0.7 or 50.7 +/- 0.6 nl/min after atrial natriuretic factor or glucagon administration. Anion and water transport rates in the late PCT were lower and exhibited less flow dependence. During chronic metabolic alkalosis, acidification was inhibited in the late but not early PCT. In conclusion, the early PCT is distinguished from the late PCT by having high-capacity, flow-responsive but saturable, anion- and water-reabsorptive processes relatively unaffected by alkalemia.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Effect of luminal bicarbonate concentration on proximal acidification in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):F53–F59. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.1.F53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Effects of extracellular fluid volume and plasma bicarbonate concentration on proximal acidification in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):736–746. doi: 10.1172/JCI110821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Flow dependence of proximal tubular bicarbonate absorption. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):F478–F484. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.4.F478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J., Rector F. C., Jr A model of proximal tubular bicarbonate absorption. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F272–F281. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly C., Imbert-Teboul M., Chabardès D., Hus-Citharel A., Montégut M., Clique A., Morel F. The distal nephron of rat kidney: a target site for glucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3422–3424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M., Toto R. D. Lack of a direct effect of atrial natriuretic factor in the rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 2):F66–F69. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.1.F66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. A., Cogan M. G. Influence of peritubular protein on solute absorption in the rabbit proximal tubule. A specific effect on NaCl transport. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):506–516. doi: 10.1172/JCI110282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. A. Heterogeneity of tubular transport processes in the nephron. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:181–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C., Gutkowska J., Thibault G., Garcia R., Genest J., Cantin M. Radioautographic localization of 125I-atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) in rat tissues. Histochemistry. 1985;82(5):441–452. doi: 10.1007/BF02450479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal S. S., Ware R. A., Kleinman J. G. Proximal tubule hydrogen ion transport processes in diuretic-induced metabolic alkalosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jul;106(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs J. P., Steipe B., Schubert G., Schnermann J. Micropuncture studies of the renal effects of atrial natriuretic substance. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00580789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B. Thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. Kidney Int. 1982 Nov;22(5):454–464. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin M., Genest J. The heart and the atrial natriuretic factor. Endocr Rev. 1985 Spring;6(2):107–127. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-2-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G., Alpern R. J. Regulation of proximal bicarbonate reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 2):F387–F395. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.3.F387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G. Atrial natriuretic factor ameliorates chronic metabolic alkalosis by increasing glomerular filtration. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1405–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.2930899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G. Atrial natriuretic factor can increase renal solute excretion primarily by raising glomerular filtration. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 2):F710–F714. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.4.F710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G., Liu F. Y. Metabolic alkalosis in the rat. Evidence that reduced glomerular filtration rather than enhanced tubular bicarbonate reabsorption is responsible for maintaining the alkalotic state. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1141–1160. doi: 10.1172/JCI110864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan M. G., Maddox D. A., Lucci M. S., Rector F. C., Jr Control of proximal bicarbonate reabsorption in normal and acidotic rats. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1168–1180. doi: 10.1172/JCI109570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corman B., Thomas R., McLeod R., de Rouffignac C. Water and total CO2 reabsorption along the rat proximal convoluted tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Dec;389(1):45–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00587927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gessner K. Effect of inhibitors and diuretics on electrical potential differences in rat kidney proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Jun 26;357(3-4):209–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00585976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Moriarty R. J., Giebisch G. Ionic requirements of proximal tubular fluid reabsorption flow dependence of fluid transport. Kidney Int. 1981 Nov;20(5):580–587. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L., Ives H. E., Cogan M. G. In vivo evidence that cGMP is the second messenger for atrial natriuretic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):8015–8018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.8015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L., Lewicki J., Johnson L. K., Cogan M. G. Renal mechanism of action of rat atrial natriuretic factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):769–773. doi: 10.1172/JCI111759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. R. Functional segmentation of the mammalian nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):F203–F218. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.3.F203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniski L. P., Aronson P. S. Chloride/formate exchange with formic acid recycling: a mechanism of active chloride transport across epithelial membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6362–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M., Starr N. L. The mechanism of glucagon-induced natriuresis in dogs. Kidney Int. 1972 Aug;2(2):76–84. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Axial heterogeneity in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. I. Bicarbonate, chloride, and water transport. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):F816–F821. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.5.F816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G., Rector F. C., Jr Axial heterogeneity in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. II. Osmolality and osmotic water permeability. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):F822–F826. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.5.F822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Gennari F. J. Load dependence of HCO3 and H2O reabsorption in the early proximal tubule of the Munich-Wistar rat. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 2):F113–F121. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.1.F113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Gennari F. J. Load dependence of proximal tubular bicarbonate reabsorption in chronic metabolic alkalosis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):709–716. doi: 10.1172/JCI112365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunsbach A. B. Observations on the segmentation of the proximal tubule in the rat kidney. Comparison of results from phase contrast, fluorescence and electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Oct;16(3):239–258. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Murayama Y. Simultaneous measurement of undirectional and net sodium fluxes in microperfused rat proximal tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1970;320(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00588454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Berliner R. W. In vivo perfusion of proximal tubules of the rat: glomerulotubular balance. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):992–997. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector F. C., Jr Sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride absorption by the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):F461–F471. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.5.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Berry C. A., Rector F. C., Jr Effect of luminal and peritubular HCO3(-) concentrations and PCO2 on HCO3(-) reabsorption in rabbit proximal convoluted tubules perfused in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):639–649. doi: 10.1172/JCI110658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senekjian H. O., Knight T. F., Sansom S. C., Weinman E. J. Effect of flow rate and the extracellular fluid volume on proximal urate and water absorption. Kidney Int. 1980 Feb;17(2):155–161. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H., Cupples W. A., de Bold A. J., Veress A. T. Intrarenal localization of the natriuretic effect of cardiac atrial extract. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;60(9):1149–1152. doi: 10.1139/y82-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. J., Jr, McConkey C. L., Jr, Martin K. J. Atriopeptin III increases cGMP in glomeruli but not in proximal tubules of dog kidney. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 2):F27–F31. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.1.F27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vurek G. G., Warnock D. G., Corsey R. Measurement of picomole amounts of carbon dioxide by calorimetry. Anal Chem. 1975 Apr;47(4):765–767. doi: 10.1021/ac60354a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. G., Eveloff J. NaCl entry mechanisms in the luminal membrane of the renal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jun;242(6):F561–F574. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.6.F561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederholt M., Hierholzer K., Windhager E. E., Giebisch G. Microperfusion study of fluid reabsorption in proximal tubules of rat kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1967 Sep;213(3):809–818. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.3.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



