Abstract
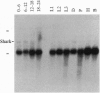
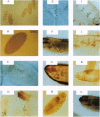
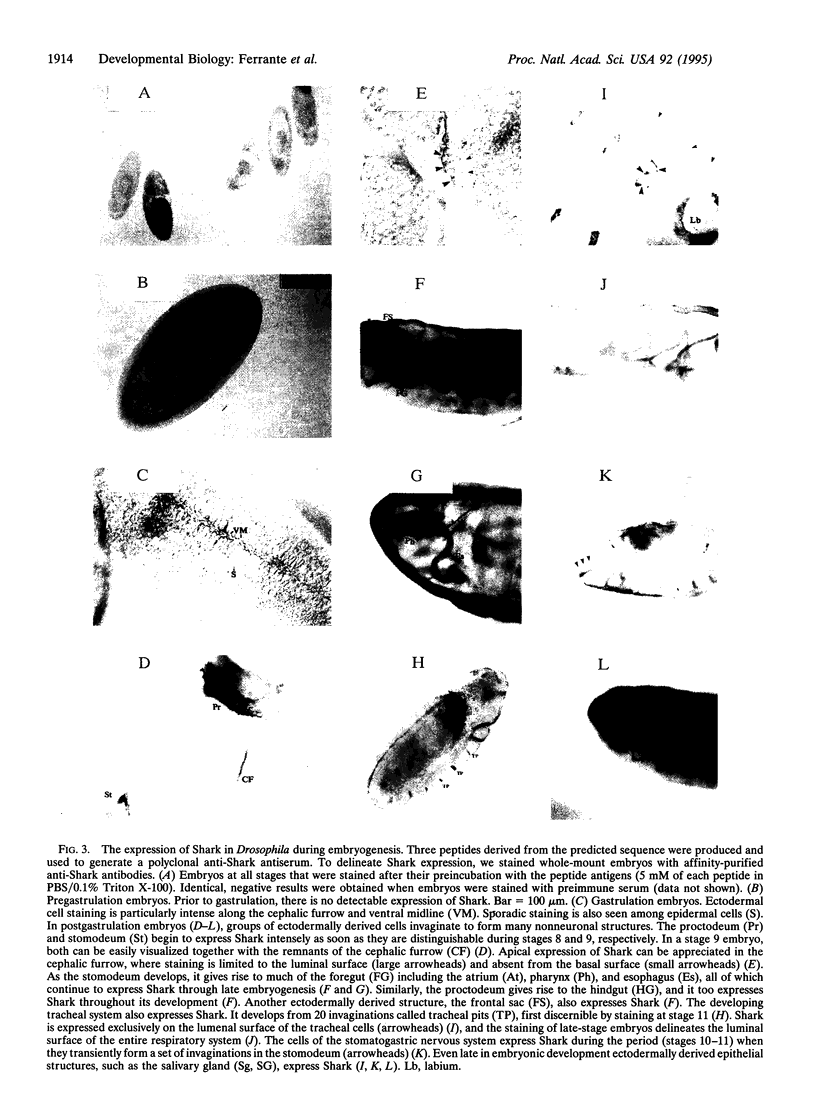
Tyrosine kinases, ankyrin repeats, and Src homology 2 domains play central roles in developmental processes. The cloning of a cDNA for Shark, a single protein that possesses all three domains, is described. During Drosophila embryogenesis, Shark is expressed exclusively by ectodermally derived epithelia and is localized preferentially to the apical surface of these cells. This apical localization persists, even as tissues undergo complex invaginations, moving from the external surface of embryos to form internal structures, but expression is lost when cells lose their polarity. This pattern closely mimics the expression of Crumbs, a protein necessary for proper organization of ectodermal epithelia. Shark's structure and localization pattern suggest that it functions in a signaling pathway for epithelial cell polarity, possibly transducing the Crumbs signal.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. Ankyrins. Adaptors between diverse plasma membrane proteins and the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8703–8706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. C., Iwashima M., Turck C. W., Weiss A. ZAP-70: a 70 kd protein-tyrosine kinase that associates with the TCR zeta chain. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90598-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. A., Chu C. A., Rauen K. A., Kroiher M., Tatarewicz S. M., Steele R. E. Identification of a gene encoding a novel protein-tyrosine kinase containing SH2 domains and ankyrin-like repeats. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1253–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti P., Mayer B. J., Thiel G., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein that binds to the SH3 region of Abl and is similar to Bcr and GAP-rho. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.1379745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman C. R., Skoglund P., Harris W. A., Kintner C. R. Expression of an extracellular deletion of Xotch diverts cell fate in Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):659–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90247-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Ghosh S., Simmons D. L., Tempst P., Liou H. C., Baltimore D., Bose H. R., Jr Rel-associated pp40: an inhibitor of the rel family of transcription factors. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1268–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.1891714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisen L. W., Bird J., West D. C., Soreng A. L., Reynolds T. C., Smith S. D., Sklar J. TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):649–661. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90111-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler R., Bergmann A., Hiromi Y., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a gene involved in dorsoventral pattern formation of Drosophila, is related to the I kappa B gene family of vertebrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Golden A., Han Y., Sternberg P. W. C. elegans lin-45 raf gene participates in let-60 ras-stimulated vulval differentiation. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):133–140. doi: 10.1038/363133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartenstein A. Y., Rugendorff A., Tepass U., Hartenstein V. The function of the neurogenic genes during epithelial development in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):1203–1220. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. Characterization of the Drosophila cactus locus and analysis of interactions between cactus and dorsal proteins. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Signal transduction. How receptors turn Ras on. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):15–16. doi: 10.1038/363015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebay I., Fehon R. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Specific truncations of Drosophila Notch define dominant activated and dominant negative forms of the receptor. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90423-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Blondel B. J., Gallahan D., Callahan R. Mouse mammary tumor gene int-3: a member of the notch gene family transforms mammary epithelial cells. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2594–2599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2594-2599.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruel L., Bourouis M., Heitzler P., Pantesco V., Simpson P. Drosophila shaggy kinase and rat glycogen synthase kinase-3 have conserved activities and act downstream of Notch. Nature. 1993 Apr 8;362(6420):557–560. doi: 10.1038/362557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Fitzgerald K., Greenwald I. Intrinsic activity of the Lin-12 and Notch intracellular domains in vivo. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90424-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Kobayashi T., Kondo J., Takahashi K., Nakamura H., Suzuki J., Nagai K., Yamada T., Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Molecular cloning of a porcine gene syk that encodes a 72-kDa protein-tyrosine kinase showing high susceptibility to proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15790–15796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepass U., Knust E. Crumbs and stardust act in a genetic pathway that controls the organization of epithelia in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1993 Sep;159(1):311–326. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepass U., Theres C., Knust E. crumbs encodes an EGF-like protein expressed on apical membranes of Drosophila epithelial cells and required for organization of epithelia. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):787–799. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90189-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipursky S. L., Rubin G. M. Determination of neuronal cell fate: lessons from the R7 neuron of Drosophila. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:373–397. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]