Abstract
The chemotactic activity of human C5a des Arg is enhanced significantly by an anionic polypeptide (cochemotaxin) in normal human serum and plasma. We have found that the cochemotaxin attaches to the oligosaccharide chain of native C5a des Arg to form a complex with potent chemotactic activity for human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Although capable of enhancing the chemotactic activity of native C5a des Arg, the cochemotaxin had no effect on the chemotactic activity of either deglycosylated C5a des Arg, native C5a, or N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Of the known components of the oligosaccharide chain, only sialic acid prevented enhancement by the cochemotaxin of the chemotactic activity exhibited by native C5a des Arg. Sialic acid also prevented the formation of C5a des Arg-cochemotaxin complexes, detected by acid polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, molecular sieve chromatography on polyacrylamide gels, and sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beebe D. P., Ward P. A., Spitznagel J. K. Isolation and characterization of an acidic chemotactic factor from complement-activated human serum. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Jan;15(1):88–105. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxin inactivator of human plasma: its isolation and characterization as a carboxypeptidase. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2427–2436. doi: 10.1172/JCI106462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Goodman M. G., Weigle W. O. Demonstration of a specific receptor for human C5a anaphylatoxin on murine macrophages. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):68–78. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Hugli T. E. Demonstration of specific C5a receptor on intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3943–3947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Henson P. M., Otani A., Hugli T. E. Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Primary structural analysis of the polypeptide portion of human C5a anaphylatoxin. Polypeptide sequence determination and assignment of the oligosaccharide attachment site in C5a. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6955–6964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., Chenoweth D. E., Hugli T. E. Response of human neutrophils to C5a: a role for the oligosaccharide moiety of human C5ades Arg-74 but not of C5a in biologic activity. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1978–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., Hugli T. E. Identification of classical anaphylatoxin as the des-Arg form of the C5a molecule: evidence of a modulator role for the oligosaccharide unit in human des-Arg74-C5a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Gerard C., Kawahara M., Scheetz M. E., 2nd, Barton R., Briggs S., Koppel G., Russell S. Isolation of three separate anaphylatoxins from complement-activated human serum. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Dec 4;41:59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00225297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxins: C3a and C5a. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- José P. J., Forrest M. J., Williams T. J. Human C5a des Arg increases vascular permeability. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2376–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller H. U., Hess M. W., Cottier H. The chemokinetic effect of serum albumin. Experientia. 1977 Oct 15;33(10):1386–1387. doi: 10.1007/BF01920196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., Kunkel S., Ward P. A., Showell H., McLean R. H. Preservation of C3, C5, and C5a functional activities by a new radiolabeling method; demonstration of C5 products in complement-activated serum. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2278–2282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maderazo E. G., Woronick C. L. Micropore filter assay of human granulocyte locomotion: problems and solutions. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Oct;11(2):196–211. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. D., Goldstein I. M., Chernoff D., Webster R. O., Henson P. M. Chemotactic activity of C5ades Arg: evidence of a requirement for an anionic peptide 'helper factor' and inhibition by a cationic protein in serum from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Immunol. 1980 Feb;17(2):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
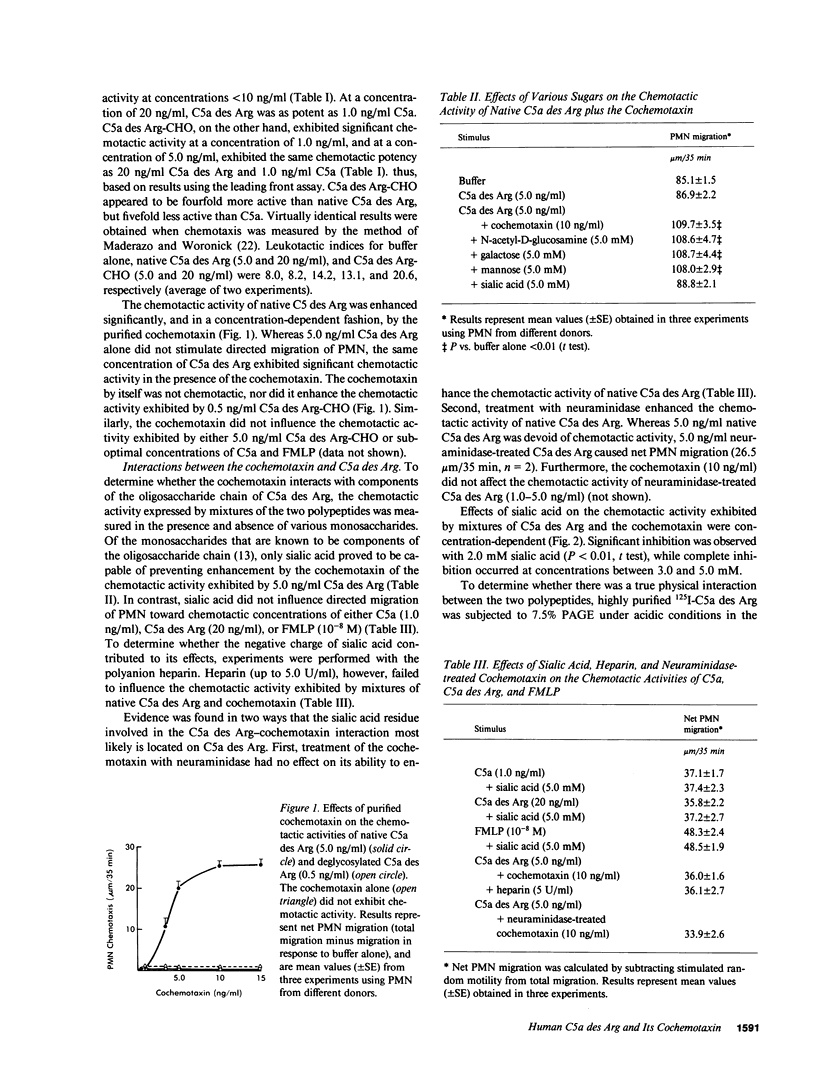
- Perez H. D., Goldstein I. M., Webster R. O., Henson P. M. Enhancement of the chemotactic activity of human C5a des Arg by an anionic polypeptide ("cochemotaxin") in normal serum and plasma. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):800–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. D., Lipton M., Goldstein I. M. A specific inhibitor of complement (C5)-derived chemotactic activity in serum from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):29–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI109110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. D., Ong R. R., Elfman F. Removal or oxidation of surface membrane sialic acid inhibits formyl-peptide-induced polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1902–1908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. D., Wooten S. K., Miller M. E. Partial characterization of in vivo chemotactic activity: comparison to human C5a. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 May;59(5):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Newman L. J. A neutrophil chemotactic factor from human C'5. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. O., Hong S. R., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M. Biologial effects of the human complement fragments C5a and C5ades Arg on neutrophil function. Immunopharmacology. 1980 Jun;2(3):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(80)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]