Abstract
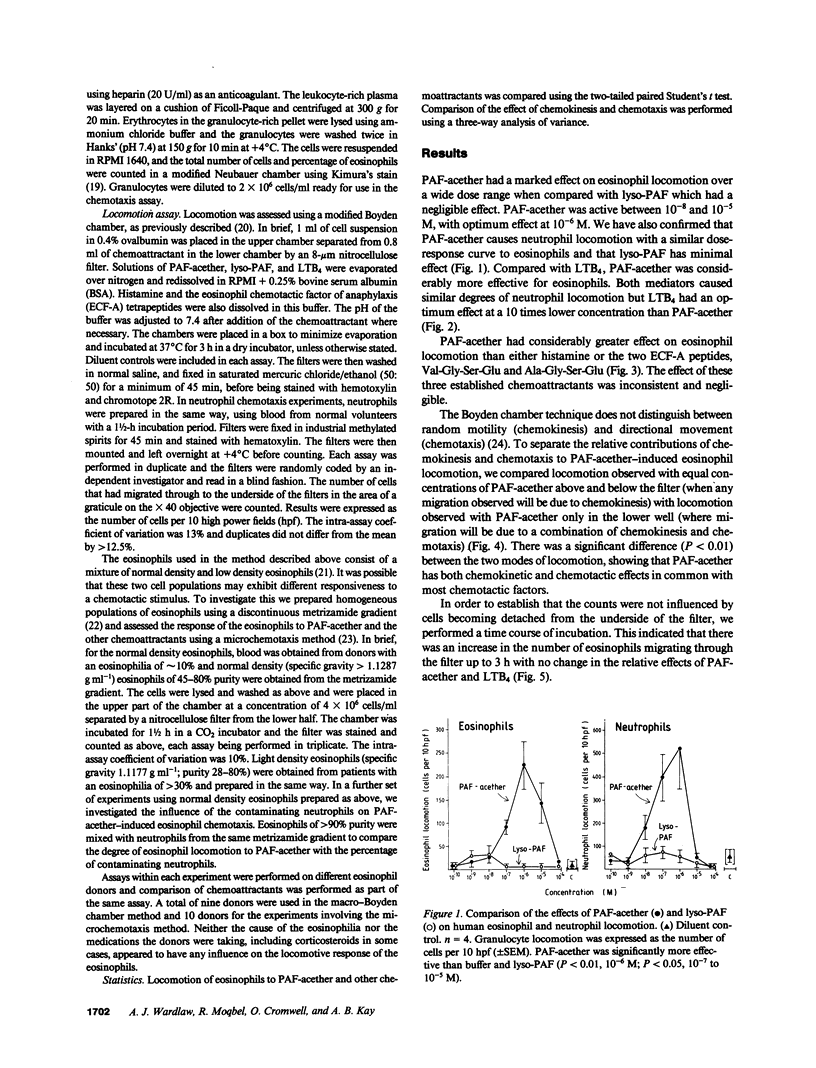
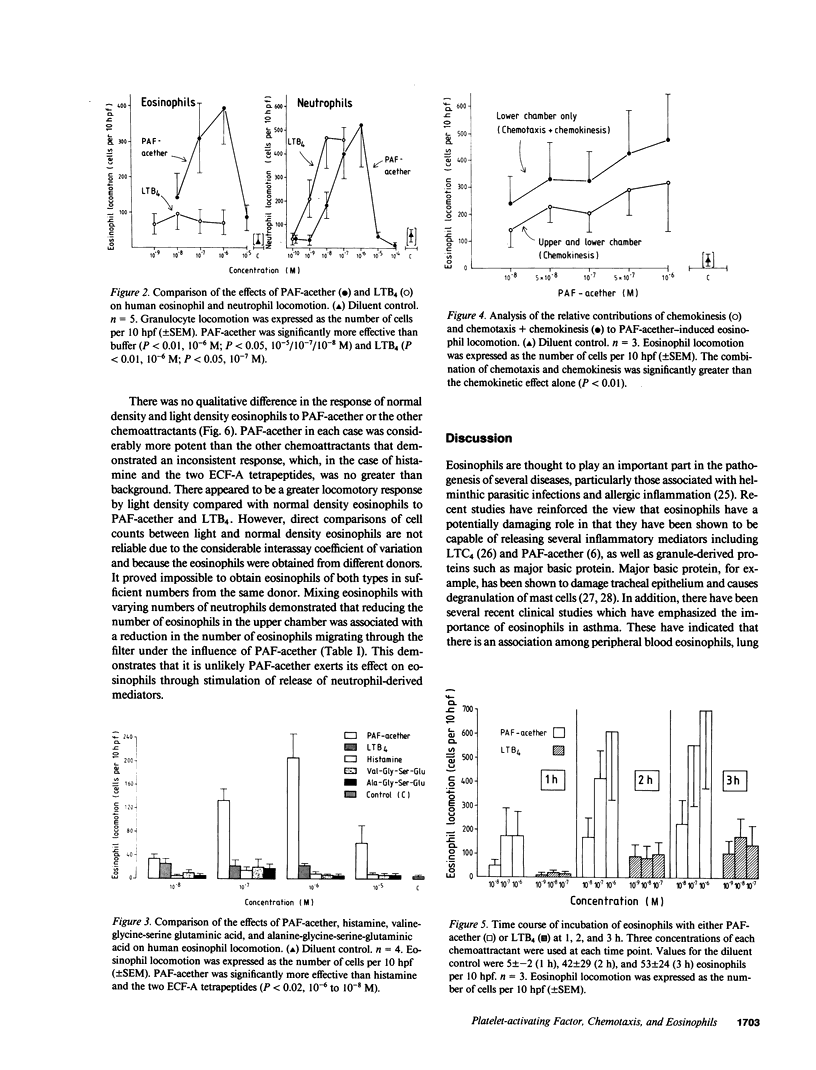
Platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether), an inflammatory mediator with a wide range of biological activities including neutrophil aggregation and chemotaxis, was studied for its effect on human eosinophil locomotion (chemotaxis and chemokinesis). Human eosinophils (25-95% purity) were obtained from donors with a variety of diseases associated with hypereosinophilia. PAF-acether elicited directional locomotion of eosinophils, in a time- and dose-dependent fashion, at concentrations from 10(-5) to 10(-8) M; lyso-PAF had minimal activity over the same dose range. Compared with PAF-acether, the eosinophil locomotory responsiveness of leukotriene B4 (LTB4), histamine, and the valyl- and alanyl-eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A) tetrapeptides was negligible. Conversely, neutrophil responsiveness to PAF-acether (optimum 10(-6) M) was comparable in effect to LTB4 (optimum dose 10(-8) M). It was shown that PAF-acether elicited both chemotaxis and chemokinesis of eosinophils. Comparison of normal density and light density eosinophils revealed no qualitative difference in the response to PAF-acether and the other chemoattractants, although the light density cells seemed to demonstrate a greater degree of locomotion to PAF-acether and LTB4. Thus, PAF-acether appears to be a potent eosinophilotactic agent which may play a role in inflammatory reactions characterized by eosinophil infiltration.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer C. B., Page C. P., Morley J., MacDonald D. M. Accumulation of inflammatory cells in response to intracutaneous platelet activating factor (Paf-acether) in man. Br J Dermatol. 1985 Mar;112(3):285–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1985.tb04855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnoux B., Duval D., Benveniste J. Release of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) from alveolar macrophages by the calcium ionophore A23187 and phagocytosis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;10(6):437–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets. The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1356–1377. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruynzeel P. L., Kok P. T., Hamelink M. L., Kijne A. M., Verhagen J. Exclusive leukotriene C4 synthesis by purified human eosinophils induced by opsonized zymosan. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Aglietta M., Malavasi F., Tetta C., Piacibello W., Sanavio F., Bussolino F. The release of platelet-activating factor from human endothelial cells in culture. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2397–2403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Gallin J. I., Kaplan A. P. The selective eosinophil chemotactic activity of histamine. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1462–1476. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromwell O., Shaw R. J., Walsh G. M., Mallet A. I., Kay A. B. Inhibition of leukotriene C4 and B4 generation by human eosinophils and neutrophils with the lipoxygenase pathway inhibitors U60257 and BW755C. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(5):775–781. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnetzki B. Increased monocyte chemotaxis towards leukotriene B4 and platelet activating factor in patients with inflammatory dermatoses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Nov;54(2):486–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Monchy J. G., Kauffman H. F., Venge P., Koëter G. H., Jansen H. M., Sluiter H. J., De Vries K. Bronchoalveolar eosinophilia during allergen-induced late asthmatic reactions. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):373–376. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz P., Galleguillos F. R., Gonzalez M. C., Pantin C. F., Kay A. B. Bronchoalveolar lavage in asthma: the effect of disodium cromoglycate (cromolyn) on leukocyte counts, immunoglobulins, and complement. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Jul;74(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham S. R., Kay A. B. Eosinophils, bronchial hyperreactivity and late-phase asthmatic reactions. Clin Allergy. 1985 Sep;15(5):411–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1985.tb02290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk W., Goodwin R. H., Jr, Leonard E. J. A 48-well micro chemotaxis assembly for rapid and accurate measurement of leukocyte migration. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Wassom D. L., Steinmuller D. Cytotoxic properties of the eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2925–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godard P., Chaintreuil J., Damon M., Coupe M., Flandre O., Crastes de Paulet A., Michel F. B. Functional assessment of alveolar macrophages: comparison of cells from asthmatics and normal subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Aug;70(2):88–93. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J., Demopoulos C. A., Liehr J., Pinckard R. N. Identification of platelet activating factor isolated from rabbit basophils as acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5514–5516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn B. R., Robin E. D., Theodore J., Van Kessel A. Total eosinophil counts in the management of bronchial asthma. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 29;292(22):1152–1155. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505292922204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson E. M., Mott G. E., Hoppens C., McManus L. M., Weintraub S. T., Ludwig J. C., Pinckard R. N. High performance liquid chromatography of platelet-activating factors. J Lipid Res. 1984 Jul;25(7):753–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Austen K. F. The IgE-mediated release of an eosinophil leukocyte chemotactic factor from human lung. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):899–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B. Eosinophils as effector cells in immunity and hypersensitivity disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Oct;62(1):1–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B. Studies on eosinophil leucocyte migration. II. Factors specifically chemotactic for eosinophils and neutrophils generated from guinea-pig serum by antigen-antibody complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Nov;7(5):723–737. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura I., Moritani Y., Tanizaki Y. Basophils in bronchial asthma with reference to reagin-type allergy. Clin Allergy. 1973 Jun;3(2):195–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T., Lenihan D. J., Malone B., Roddy L. L., Wasserman S. I. Increased biosynthesis of platelet-activating factor in activated human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5526–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Human platelet stimulation by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):903–906. doi: 10.1172/JCI110108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W. J., Hunninghake G. W., Richerson H. B. Late asthmatic responses: inquiry into mechanisms and significance. Clin Rev Allergy. 1985 May;3(2):145–165. doi: 10.1007/BF02992980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy L., Lee T. H., Goetzl E. J., Pickett W. C., Kay A. B. Complement receptor enhancement and chemotaxis of human neutrophils and eosinophils by leukotrienes and other lipoxygenase products. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):541–547. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. C., Ackerman S. J., Gleich G. J., Thomas L. L. Activation of basophil and mast cell histamine release by eosinophil granule major basic protein. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1981–1991. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L. Biology and biochemistry of platelet-activating factor. Clin Rev Allergy. 1983 Sep;1(3):353–367. doi: 10.1007/BF02991226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Satouchi K., Yasunaga K., Saito K. Molecular species of platelet-activating factor generated by human neutrophils challenged with ionophore A23187. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1090–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipkorn U., Karlsson G., Bake B. Effect of platelet activating factor on the human nasal mucosa. Allergy. 1984 Feb;39(2):141–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1984.tb01946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prin L., Capron M., Tonnel A. B., Bletry O., Capron A. Heterogeneity of human peripheral blood eosinophils: variability in cell density and cytotoxic ability in relation to the level and the origin of hypereosinophilia. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1983;72(4):336–346. doi: 10.1159/000234893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Pinckard R. N., Ferrigni K. S., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J. Activation of human neutrophils with 1-O-hexadecyl/octadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine (platelet activating factor). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1250–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. J., Walsh G. M., Cromwell O., Moqbel R., Spry C. J., Kay A. B. Activated human eosinophils generate SRS-A leukotrienes following IgG-dependent stimulation. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):150–152. doi: 10.1038/316150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Crespo M., Alonso F., Egido J. Platelet-activating factor in anaphylaxis and phagocytosis. I. Release from human peripheral polymorphonuclears and monocytes during the stimulation by ionophore A23187 and phagocytosis but not from degranulating basophils. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):645–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., David J. R., Butterworth A., Pisani N. T., Siongok T. A. A new method for the purification of human eosinophils and neutrophils, and a comparison of the ability of these cells to damage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P. F. Eosinophilia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Jan;73(1 Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90474-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



