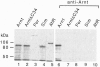
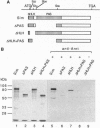
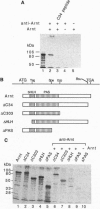
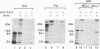Abstract
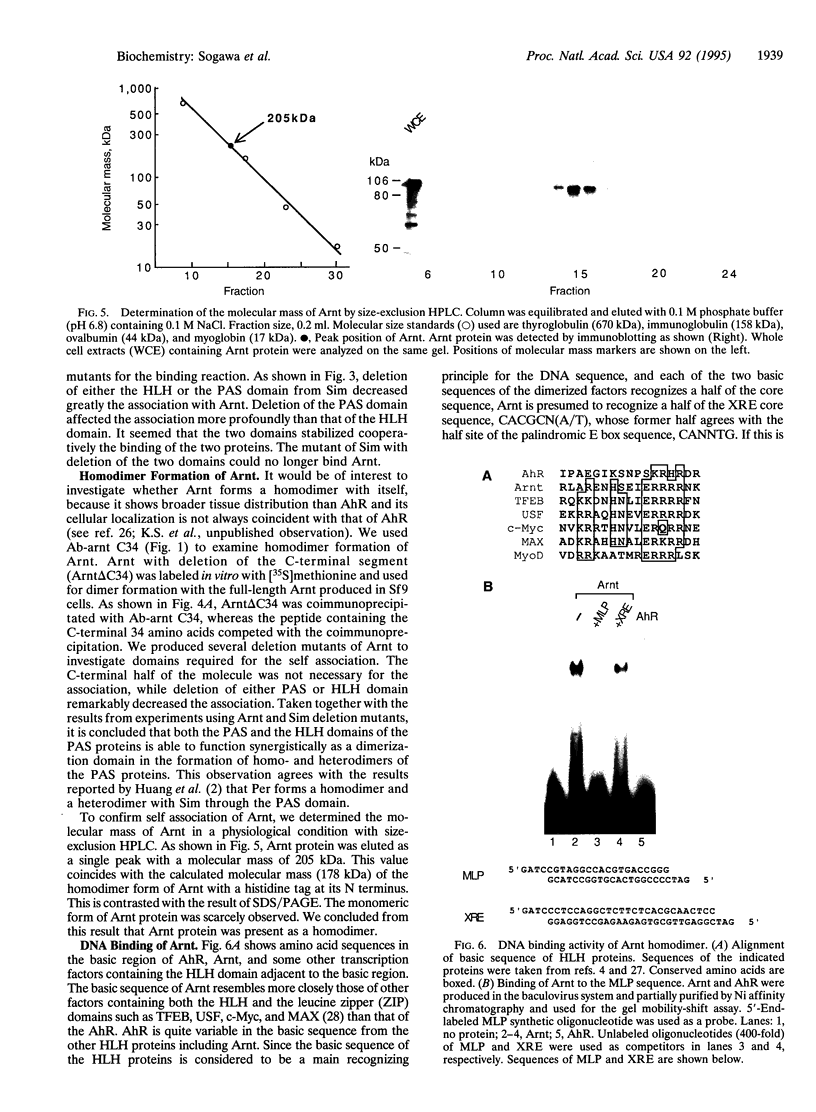
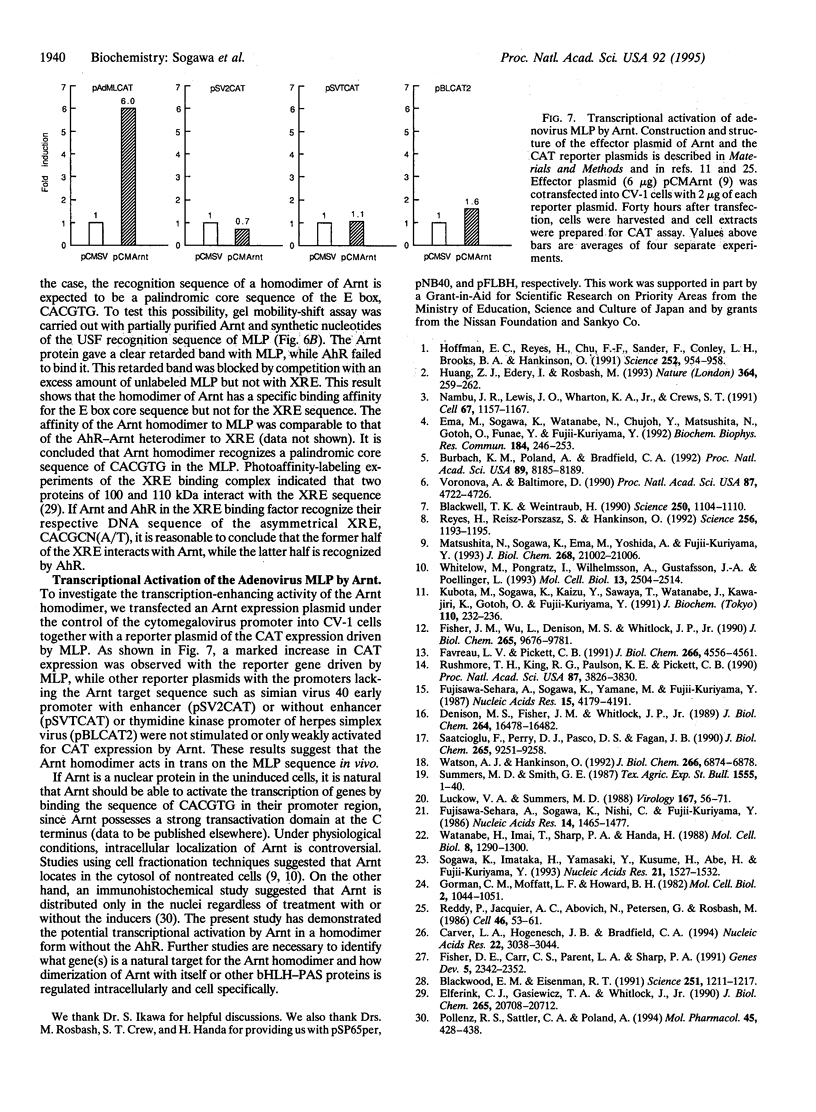
Arnt (Ah receptor nuclear translocator) is a member of a transcription factor family having characteristic motifs designated bHLH (basic helix-loop-helix) and PAS and was originally found as a factor forming a complex with Ah receptor (AhR) to bind the specific xenobiotic responsive element (XRE) sequence for induction of drug-metabolizing P4501A1. We have examined interaction of Arnt with other PAS proteins--Drosophila Per, Sim, and AhR--by the coimmunoprecipitation method. Arnt formed a homodimer with itself as well as heterodimers with the others by means of the PAS and HLH domains in a cooperative way. The Arnt homodimer binds the sequence of adenovirus major late promoter (MLP) with the E box core sequence CACGTG, suggesting that the CAC half of the XRE, CACGCN(A/T), recognized by the AhR-Arnt heterodimer is a target for Arnt. Cotransfection experiments using CV-1 cells with an Arnt expression plasmid and a MLP chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter plasmid revealed that Arnt markedly activated CAT expression, indicative of a newly discovered regulatory role of Arnt.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbach K. M., Poland A., Bradfield C. A. Cloning of the Ah-receptor cDNA reveals a distinctive ligand-activated transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8185–8189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver L. A., Hogenesch J. B., Bradfield C. A. Tissue specific expression of the rat Ah-receptor and ARNT mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):3038–3044. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.3038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Protein-DNA interactions at recognition sites for the dioxin-Ah receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16478–16482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink C. J., Gasiewicz T. A., Whitlock J. P., Jr Protein-DNA interactions at a dioxin-responsive enhancer. Evidence that the transformed Ah receptor is heteromeric. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20708–20712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ema M., Sogawa K., Watanabe N., Chujoh Y., Matsushita N., Gotoh O., Funae Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. cDNA cloning and structure of mouse putative Ah receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91185-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favreau L. V., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat NAD(P)H:quinone reductase gene. Identification of regulatory elements controlling basal level expression and inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds and phenolic antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4556–4561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. E., Carr C. S., Parent L. A., Sharp P. A. TFEB has DNA-binding and oligomerization properties of a unique helix-loop-helix/leucine-zipper family. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2342–2352. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. M., Wu L., Denison M. S., Whitlock J. P., Jr Organization and function of a dioxin-responsive enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9676–9681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Nishi C., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Regulatory DNA elements localized remotely upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1465–1477. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Characterization of xenobiotic responsive elements upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene: a similarity to glucocorticoid regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4179–4191. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. C., Reyes H., Chu F. F., Sander F., Conley L. H., Brooks B. A., Hankinson O. Cloning of a factor required for activity of the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Science. 1991 May 17;252(5008):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.1852076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Z. J., Edery I., Rosbash M. PAS is a dimerization domain common to Drosophila period and several transcription factors. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):259–262. doi: 10.1038/364259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota M., Sogawa K., Kaizu Y., Sawaya T., Watanabe J., Kawajiri K., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Xenobiotic responsive element in the 5'-upstream region of the human P-450c gene. J Biochem. 1991 Aug;110(2):232–236. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow V. A., Summers M. D. Signals important for high-level expression of foreign genes in Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus expression vectors. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):56–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita N., Sogawa K., Ema M., Yoshida A., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. A factor binding to the xenobiotic responsive element (XRE) of P-4501A1 gene consists of at least two helix-loop-helix proteins, Ah receptor and Arnt. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21002–21006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambu J. R., Lewis J. O., Wharton K. A., Jr, Crews S. T. The Drosophila single-minded gene encodes a helix-loop-helix protein that acts as a master regulator of CNS midline development. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1157–1167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollenz R. S., Sattler C. A., Poland A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor and aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator protein show distinct subcellular localizations in Hepa 1c1c7 cells by immunofluorescence microscopy. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):428–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Jacquier A. C., Abovich N., Petersen G., Rosbash M. The period clock locus of D. melanogaster codes for a proteoglycan. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90859-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Reisz-Porszasz S., Hankinson O. Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., King R. G., Paulson K. E., Pickett C. B. Regulation of glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene expression: identification of a unique xenobiotic-responsive element controlling inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3826–3830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saatcioglu F., Perry D. J., Pasco D. S., Fagan J. B. Aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor DNA-binding activity. Sequence specificity and Zn2+ requirement. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9251–9258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Imataka H., Yamasaki Y., Kusume H., Abe H., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. cDNA cloning and transcriptional properties of a novel GC box-binding protein, BTEB2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1527–1532. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A., Baltimore D. Mutations that disrupt DNA binding and dimer formation in the E47 helix-loop-helix protein map to distinct domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4722–4726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Imai T., Sharp P. A., Handa H. Identification of two transcription factors that bind to specific elements in the promoter of the adenovirus early-region 4. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1290–1300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson A. J., Hankinson O. Dioxin- and Ah receptor-dependent protein binding to xenobiotic responsive elements and G-rich DNA studied by in vivo footprinting. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6874–6878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw M., Pongratz I., Wilhelmsson A., Gustafsson J. A., Poellinger L. Ligand-dependent recruitment of the Arnt coregulator determines DNA recognition by the dioxin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2504–2514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]