Abstract
Background:
During the progression of periodontal disease, the cementum undergoes alterations in its structure and composition. Understanding the nanostructure of cementum, in terms of its mechanical properties, will provide an insight into the milieu that periodontal ligament cells encounter in health and chronic periodontitis. This study aims to analyze the nanomechanical properties of the cervical third of the cementum (transverse section) in health and chronic periodontitis.
Materials and Methods:
Twenty teeth (10 healthy and 10 periodontally diseased) were collected and the nanomechanical properties of the transverse section of the cervical third cementum were evaluated with depth-sensing nanoindentation technique under dry conditions. A total of 100 nanoindentations were performed to analyze the modulus of elasticity and hardness of cervical third of the cementum.
Results:
The nanomechanical properties of the healthy cervical third cementum sections were significantly higher (P < 0.05) (hardness: 0.720 ± 0.305 GPa; modulus: 15.420 ± 3.902 GPa) than the diseased cementum section (hardness: 0.422 ± 0.157 GPa; modulus: 11.056 ± 3.434 GPa).
Conclusion:
The results of our study indicate that the hardness and modulus of elasticity of the cervical third cementum decreases significantly in chronic periodontitis.
Keywords: Chronic periodontitis, dental cementum, nanoindentation, periodontal regeneration
Introduction
Conventional periodontal regenerative therapies such as bone replacement grafts and guided tissue regeneration have not been able to achieve complete and predictable periodontal regeneration.[1] In spite of allowing progenitor cells to selectively migrate and differentiate as in guided tissue regeneration, the cementum formed is of the cellular type.[2] The possible reason for this could be attributed to the mechanical, physical and chemical changes that take place in the cementum during the progression of periodontitis. Current research has focused on regeneration of acellular extrinsic fiber cementum through functional tissue engineering and, more importantly, the biomimetic approaches.[3] According to the concepts of functional tissue engineering, the cells can sense and respond to mechanical factors and various other environmental cues of the substrate.[4] In addition to this, the regeneration of lost tissue can also be achieved by biomimicking the physical and mechanical properties of the tissue, which serves as a scaffold in nature. Understanding the nanostructure of cementum may aid in designing a biomimetic scaffold that will match with the mechanical properties of the root surface. This will provide a favorable micromechanical environment for progenitor cells and for successful regeneration of acellular extrinsic fiber cementum.
The effect of the physical properties of the extracellular matrix on cell differentiation and proliferation has been well documented.[5] Apart from the components of the cementum matrix, the local microenvironment of the extracellular matrix also plays a major role in periodontal regeneration.[6] In addition to this, various studies[7,8] have reported the importance of the mechanical properties of the matrix in directing stem cell differentiation.
The cementum undergoes numerous physical,[9] chemical,[10] structural[11] and cytotoxic alterations[12] during the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. During the early stage of periodontitis, the acellular extrinsic fiber cementum gets irreversibly damaged[6] as it is found in the cervical third of the root.[2,13] Although various studies have reported the cemental changes that take place during the progression of periodontal disease, the mechanical properties of the cementum are not completely understood.[14] The mechanical properties of the cementum that are commonly analyzed are hardness, modulus of elasticity and surface roughness.[15] Moreover, various studies[16,17] have demonstrated the significance of analyzing the substrate elasticity and its impact on hematopoietic stem cell and progenitor migration and adhesion.
It is now well understood from the available data that the mechanical integrity of a tissue is predominantly a function of its nanostructure.[18] Although the mechanical properties of the cementum have been estimated on macro- and microscales, the nanostructure of the cementum has not yet been characterized in chronic periodontitis in detail.
The aim of this study is to assess and compare the nanomechanical properties of acellular extrinsic fiber cementum at the cervical third of the root in health and in chronic periodontitis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sample collection
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee, Sri Ramachandra University, Chennai. A total of 20 teeth were collected from 12 subjects reporting to the outpatient department, Department of Periodontics. The healthy teeth (n = 10) were collected from six individuals with age ranging from 30 to 40 years for whom orthodontic extractions were indicated. The criteria for selecting healthy teeth samples included absence of dental caries, absence of bleeding on probing and probing depth/attachment loss and no radiographic evidence of bone loss. Periodontally diseased teeth samples (n = 10) were collected from six patients with age ranging from 30 to 40 years diagnosed with generalized severe chronic periodontitis.[19]
Tooth type distribution in the healthy teeth group and diseased teeth group are presented in Table 1. Periodontally compromised teeth were selected if the probing depth and attachment loss was more than 5 mm with radiographic evidence of bone loss up to the apical third.
Table 1.
Distribution of tooth types between the healthy and the diseased group

The exclusion criteria were as follows: Presence of gingival recession around the selected teeth, cigarette/tobacco smoking habit, patients who have undergone periodontal treatment in the last 5 years, patients who have taken any antibiotics for the past 3 months, presence of any systemic disease, root caries, fractured teeth and non-vital teeth and pregnant or lactating women.
Scanning electron microscopy of the cervical third of the cementum
Before nanoindentation, the topography of the sputter-coated outer surface of two healthy and two diseased transverse sections of 3-5-mm-thick cervical third cementum sections [Figures 1a, b and 2] were characterized using FEI quanta FEG 200 – high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (SEM) at various magnifications ranging from ×6500 to ×400. These samples were not used further for characterizing nanomechanical properties as they were sputter coated with gold. The sections were placed on appropriate stubs by fixing them using a double-sided adhesive. The stubs with the sections on top were placed inside the apparatus that was later maintained at a low vacuum of 0.97 Torr throughout the analysis. The specimen sections were examined using an electron energy of 20 keV to obtain the micrographs.[15] Images were recorded using a digital image acquisition software.
Figure 1.
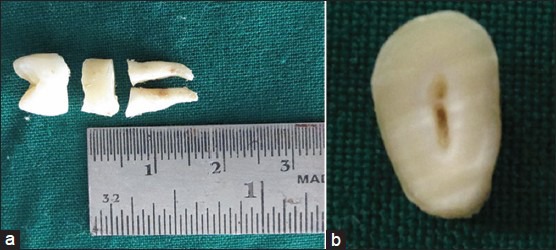
(a) (Color online) Transverse section of the cervical third cementum after decoronation and (b) Transverse section of the cervical third cementum before embedding in resin
Figure 2.
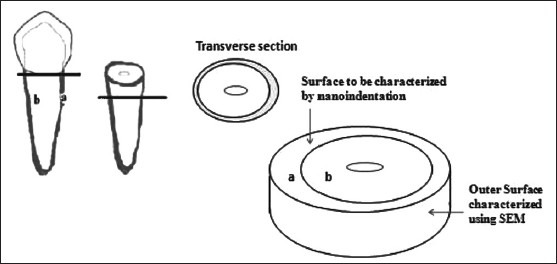
Schematic of the sectioning of the cervical third of the root and the cementum surface characterized using nanoindentation and scanning electron microscopy
Sample preparation for nanoindentation
The depth-sensing nanoindentation technique requires the sample's surface to be flat and even. Because the outer surface of the root is convex, the transverse sections of cementum were characterized for the nanomechanical properties. The sample preparation was performed according to the protocol described by Malek et al.[20] Briefly, the freshly extracted teeth were cleaned and disinfected and the periodontal ligament fragments were removed by using Milton's solution (1% sodium hypochlorite) for 10 min. The crown of the teeth was transversely sectioned at the level of the cement-enamel junction [Figures 1a, b and 2]. The cervical third of the root was sectioned transversely to obtain 5-mm-thick sections [Figure 1a] using a diamond wafering blade on a low-speed cutter under wet conditions. The cervical third sections were stored in deionized water at an ambient temperature of 23 ± 2°C in a polyethylene container until further analysis. The transverse sections of the cervical third of root [Figures 1b and 2] were embedded in epoxy resin and the resin blocks were trimmed and polished using a basic metallography polishing technique.
The specimens were polished sequentially using SiC grit papers (200-1000 sizes), then fine polishing using diamond suspension slurries (9 μm, 6 μm, 3 μm and 1 μm) on a polishing cloth. The final polishing process was carried out with colloidal silica suspension (OPS) 0.25 μm for 2 min at a speed of 200 rpm. The specimens were ultrasonificated in deionized water for 10 min between each level of polishing before proceeding to the next level of polishing to remove any abrasives and they were air dried for 3 s prior to mounting the specimens in the nanoindentation specimen holder.
Nanoindentation of the tooth specimens
The local elastic and plastic properties of the cementum were investigated by performing nanoindentation experiments with a three-sided Berkovich-type diamond indenter. These tests were conducted under dry conditions with a CSM nanoindenter (Peseux, Switzerland) [Figure 3]; during indentation, a load-displacement curve was recorded, from which the contact area, hardness and elastic modulus were calculated using the Oliver and Pharr method.[21] The depth calibration to identify the surface to indent was carried out before the nanoindentation process. The determination of elastic modulus from the elastic recovery of the material by measuring the contact stiffness S (=dP/dh) has been achieved by the controlled unloading after indentation. The hardness H and the Young's modulus E were calculated from the following fundamental relations:
Figure 3.
CSM nanoindenter apparatus

where P is the load and A is the projected contact area at that load, and

where Er is the reduced elastic modulus and β is a constant that depends on the geometry of the indenter.
A reduced modulus Er is used in equation (2) to account for the fact that elastic displacements occur in both the indenter and the sample. The elastic modulus of the test material, E, is calculated from Er using

Where n is the Poisson's ratio for the test material and Ei and vr are the elastic modulus and Poisson's ratio, respectively, of the indenter. For diamond, the elastic constant Ei = 1141 GPa and Poisson's ratio vr = 0.07 are often used.[21]
The test zone, maximum force, number of indentations and distance between indentations were programmed into the computer. The testing environment temperature was maintained at 23 ± 1°C.
Indent locations were selected using an optical microscope with a magnification of ×1000. Ten nanoindentations were performed per sample, adding up to 100 nanoindentations in each group. Their locations were selected midway between the cement-dentinal junction and the peripheral cementum to avoid the resin, residual calculus and the cement-dentinal junction [Figure 2]. The optical microscopic image [Figure 4] shows a typical indentation on the cementum (Black arrow), with some striations on the dentin. The parameters set during nanoindentation are presented in Table 2.
Figure 4.
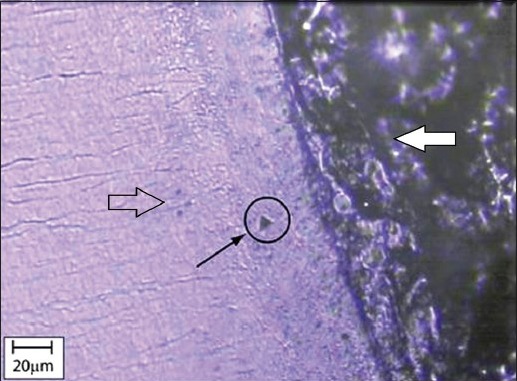
Optical microscope image of the transverse sections of the cervical third cementum Open arrow - Dentin, White arrow - Resin, Black arrow showing the impression of the indent in the middle portion of the cervical cementum
Table 2.
Load/unload cycle parameters used during nanoindentation

Statistical analysis
All the statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistical Software (version 17.0). The mean and standard deviation of the test parameters was estimated for the test and healthy control samples. The intergroup comparison was carried out using a non-parametric test (Mann-Whitney test), and the difference was considered to be statistically significant if the P value was less than 0.05.
RESULTS
Scanning electron microscopy of the cervical third cementum
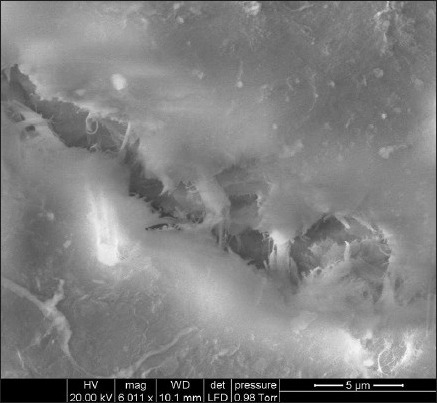
The SEM micrographs of the morphology of the healthy outer surface of the cervical third cementum sections are shown in Figure 5 and those of the diseased sections are shown in Figure 6. SEM characterization revealed the presence of mineralized collagen fibers in the healthy cementum, which were more predominant when compared with the diseased cementum. The SEM micrographs of the diseased cementum showed areas of foreign bodies that could be deposits of calculus.
Figure 5.

Scanning electron microscopy micrograph of the outer surface of the healthy cervical third cementum (at ×6011 magnification)
Figure 6.
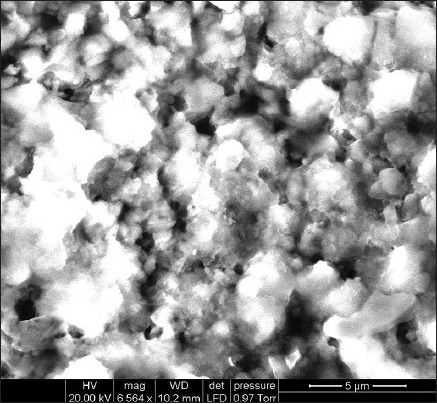
Scanning electron microscopy micrograph of the outer surface of the diseased cervical third cementum section (at ×6011 magnification)
Assessment of the physical property of the cervical third of cementum
Typical indentation profiles of the healthy and diseased cementum cervical sections are shown in Figure 7. These profiles clearly show a penetration depth difference between the healthy and diseased for the same indentation load. This indicates that the healthy sample has higher resistance to plastic deformation.
Figure 7.
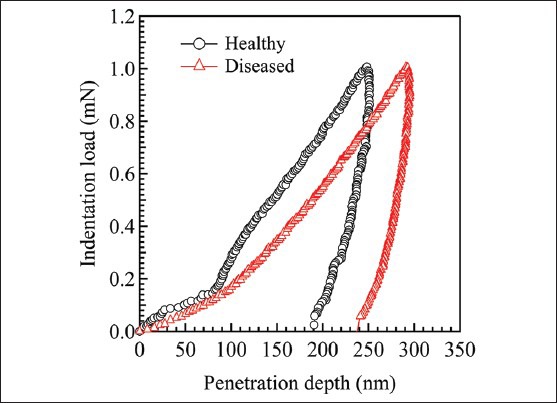
(Color online) Typical nanoindentation profiles of healthy and diseased cervical third cementum
Hardness
The results showed that the hardness values varied between 0.546 and 1.124 GPa for the healthy cementum sections and, for the diseased cementum sections, the values ranged from 0.273 to 0.726 GPa. The mean hardness of the diseased cementum was significantly lower compared with the healthy cementum (P < 0.05) [Table 3]. The mean hardness values for the cementum of the healthy samples and the diseased cementum sample are shown in Figure 8.
Table 3.
Nanomechanical properties of the healthy and the diseased cementum

Figure 8.
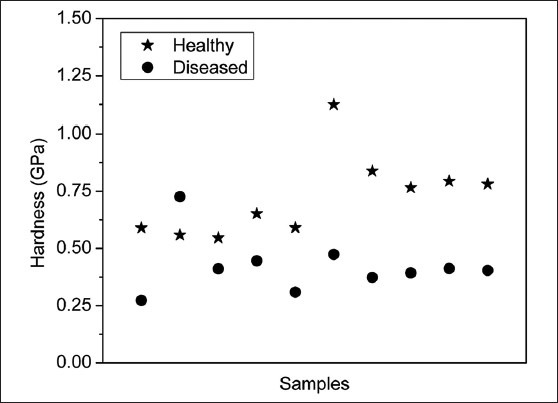
Comparison of hardness values of healthy and diseased cervical third cementum (n = 10)
Modulus of elasticity
The modulus of elasticity of the healthy cementum was observed to be between 12.981 and 21.912 GPa and that of the diseased cementum varied between 6.781 and 13.443 GPa [Figure 5]. The difference between the mean modulus of elasticity of the healthy and diseased cementum [Table 3] was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The mean modulus of elasticity values for the cementum of the healthy samples and the diseased cementum samples are shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9.
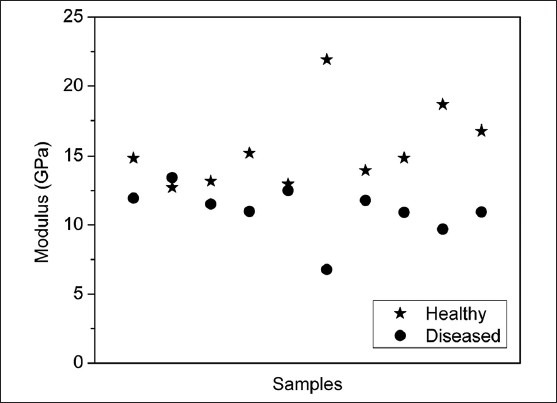
Comparison of modulus of elasticity values of healthy and diseased cervical third cementum (n = 10)
DISCUSSION
The presence of a healthy cementum is pivotal for periodontal regeneration.[22] Even though regeneration of alveolar bone can be accomplished by the presently available therapeutic modalities, the regeneration of the acellular extrinsic fiber cementum still remains elusive.[23] Functional tissue engineering strategies using scaffolds, cells and growth factors may offer more predictable avenues for periodontal regeneration. An important principle in functional tissue engineering is the determination of the biomechanical properties of the native tissue in health and in diseased conditions.[24] In the case of periodontal tissue engineering, this information can be obtained by analyzing the mechanical properties of both the healthy and the diseased root surface. This study was undertaken to investigate the effect of chronic periodontitis on the nanomechanical properties of the cervical third of the cementum within a periodontal pocket environment.
In order to evaluate the changes in the morphology of the diseased cementum, SEM was performed prior to nanoindentation. The topography of the outer surface of the healthy and diseased transverse sections of the cervical third of the cementum was characterized using high-resolution SEM. SEM revealed morphological changes in the outer surface of the diseased cementum such as the absence of mineralized cemental collagen fibers that were a predominant feature in the healthy cementum sections. However, these samples were not characterized for nanoindentation as the sputtering may itself influence the nanomechanical properties. Hence, it was not possible to correlate the finding of SEM micrographs with nanoindentation measurements as both these analyses were performed on two different cementum surfaces.
Previous studies have estimated hardness and modulus of elasticity of healthy cementum.[25] To the best our knowledge, this is the first study comparing the hardness and modulus of elasticity between healthy and diseased transverse sections of the cervical third cementum using depth-sensing nanoindentation techniques. The results of our study revealed a statistically significant difference in the hardness of the diseased cementum as compared with the healthy cementum (P < 0.05). This decrease in hardness of the diseased cementum could be due to the softening of the cementum induced by demineralization by organic acids of inflammatory exudates and resorption of collagen and protein polysaccharide matrix via enzyme activities within the confines of the periodontal pocket.[25] In order to avoid the hypermineralized layer[10] of cementum that forms when the root surface becomes exposed to the oral cavity due to gingival recession, periodontally compromised teeth with absence of gingival recession were selected.
Another important factor that must be taken into account is the total duration each of these diseased cementum sections had been exposed to the periodontal pocket environment since the onset of the periodontitis. As it was difficult to obtain this information, it could be considered as a limitation of this study.
There was a statistically significant (P < 0.05) difference in the modulus of elasticity of the diseased cervical third cementum as compared with the healthy cementum. There was a decrease in the modulus of elasticity of the diseased cementum sections. This could be due to the organic acids and enzymes of inflammatory exudates within the periodontal pocket that result in dissolution of mineral contents and proteolytic breakdown of collagen fibers.[25,26]
The results of our study are in agreement with various other studies[3,14,27] that have characterized similar cemental sections from healthy teeth under similar conditions. In the study by Gungormus et al.,[3] a cementum-like biomineralized microlayer was constructed using amelogenin-derived peptides and the authors compared the mechanical properties, namely modulus of elasticity and hardness using nanoindentation, with that of the native cementum. The hardness and modulus of elasticity values for the native healthy cementum obtained in their study are in accordance to the values observed in our study.
Nanoindentation has been used in dentistry to evaluate the mechanical properties of the dental hard tissues for the past two decades.[18] It has been used in the field of endodontics to determine the nanomechanical properties of endodontically treated teeth and carious human teeth,[28,29] in implantology to study the elasticity of the alveolar bone near the dental implant[30] and in orthodontics.[31] In the field of periodontics, nanoindentation has been used to determine the nanomechanical properties of the cement-dentinal junction,[14,15] cementum in Ank/Ank mutant mouse[32] bone-periodontal ligament and cementum complex.[33]
This technique was utilized in our study as it is more accurate when compared with other conventional mechanical tests.[34] In addition, it allows the measurement of the mechanical properties of a very small selected region of the cementum.[18]
Although there are few reports in the literature that have assessed the hardness of the cementum, most of these studies have used micromechanical testing techniques.[35,36] Evaluation of mechanical properties using microindentation found no statistically significant difference between microhardness of the cementum in teeth with and without periodontal involvement.[35] Also, healthy human dental cementum of premolar teeth analyzed using microindentation showed no significant differences in the hardness and elastic modulus of the cementum between the buccal and the lingual surfaces or between the upper and the lower teeth.[36]
The importance of cervical third of the cementum is that it contains acellular extrinsic fiber cementum[37] and its regeneration is considered to be the gold standard for periodontal regeneration.[6] Because predictable regeneration of new acellular extrinsic fiber cementum on a diseased root surface is yet to be achieved, current research on periodontal regeneration has focused on inducing the formation of an acellular extrinsic fiber cementum.[23] However, the cementum formed after treatment with guided tissue regeneration,[38] bone grafts[39] and a derivative of enamel matrix proteins[40] is of the cellular type. The local environmental factors, especially the substrate stiffness, plays a crucial role in recruitment and function of cementum-forming cells.[41] The mechanical signals, for example stiffness of the substrate, can have a significant influence on the adhesion, migration, proliferation and differentiation of numerous cell types such as fibroblasts and osteoblasts.[42,43] It is now well documented that the elastic properties of the substrate plays a role in the differentiation of adult and embryonic stem cells.[44,45,46] This can be extrapolated to the cementum, wherein an alteration of the nanomechanical properties during the progression of periodontal disease process may impede complete periodontal regeneration.
The prime objective of this study was to determine the changes in the nanomechanical properties of the cervical third of the cementum in chronic periodontitis based on the values obtained from a total of 200 nanoindentations. Because only 10 healthy cementum sections and 10 diseased cementum sections were taken for nanoindentation, a tooth-type statistical comparison was not possible. However, further studies can focus on comparing the nanomechanical properties based on tooth type/upper arch and lower arch.
The values obtained in the present study for the diseased cervical third cementum are found to be lesser than the healthy cementum sections, indicating a change in the nanostructure and mechanical integrity. This may have an effect on the recruitment on progenitor cells and formation of new attachment. Thus, the understanding of the nanomechanical properties of the cervical third cementum may not only aid in determining the influence of mechanical signals of cementum in health and in chronic periodontitis on progenitor cells but also help in devising various nanomechanical design parameters required for engineering acellular extrinsic fiber cementum.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, there is a decrease in the nanomechanical properties of the diseased cervical third cementum. Further analysis of the diseased root surface in wet conditions may help in understanding the nanostructural changes occurring in the cervical third of the root during periodontitis.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Aichelmann-Reidy ME, Reynolds MA. Predictability of clinical outcomes following regenerative therapy in intrabony defects. J Periodontol. 2008;79:387–93. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.060521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.MacNeil RL, Somerman MJ. Development and regeneration of the periodontium: Parallels and contrasts. Periodontol 2000. 1999;19:8–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.1999.tb00144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gungormus M, Oren EE, Horst JA, Fong H, Hnilova M, Somerman MJ, et al. Cementomimetics-constructing a cementum-like biomineralized microlayer via amelogenin-derived peptides. Int J Oral Sci. 2012;4:69–77. doi: 10.1038/ijos.2012.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Guilak F, Butler DL, Goldstein SA. Functional tissue engineering: The role of biomechanics in articular cartilage repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;391:295–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Huang NF, Li S. Regulation of the matrix microenvironment for stem cell engineering and regenerative medicine. Ann Biomed Eng. 2011;39:1201–14. doi: 10.1007/s10439-011-0297-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grzesik WJ, Narayanan AS. Cementum and periodontal wound healing and regeneration. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13:474–84. doi: 10.1177/154411130201300605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Engler AJ, Sen S, Sweeney HL, Discher DE. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell. 2006;126:677–89. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Evans ND, Minelli C, Gentleman E, LaPointe V, Patankar SN, Kallivretaki M, et al. Substrate stiffness affects early differentiation events in embryonic stem cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2009;18:1–13. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v018a01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Emslie RD, Stack MV. The micro hardness of roots of teeth with periodontal disease. Dent Pract Dent Rec. 1958;9:101–13. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Selvig KA, Hals E. Periodontally diseased cementum studied by correlated microradiography, electron probe analysis and electron microscopy. J Periodontal Res. 1977;12:419–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb00137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Selvig KA. Biological changes at the tooth-saliva interface in periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1969;48:846–55. doi: 10.1177/00220345690480053901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Aleo JJ. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced depression of cellular proliferation by ascorbic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980;164:248–51. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bosshardt DD, Schroeder HE. Establishment of acellular extrinsic fiber cementum on human teeth. A light- and electron-microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res. 1991;263:325–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00318774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ho SP, Balooch M, Goodis HE, Marshall GW, Marshall SJ. Ultrastructure and nanomechanical properties of cementum dentin junction. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;68:343–51. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.20061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ho SP, Goodis HE, Balooch M, Nonomura G, Marshall SJ, Marshall GW. The effect of sample preparation technique on determination of structure and nanomechanical properties of human cementum hard tissue. Biomaterials. 2004;25:4847–57. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.11.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Holst J, Watson S, Lord MS, Eamegdool SS, Bax DV, Nivison-Smith LB, et al. Substrate elasticity provides mechanical signals for the expansion of hemopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:1123–8. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee-Thedieck C, Rauch N, Fiammengo R, Klein G, Spatz JP. Impact of substrate elasticity on human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell adhesion and motility. J Cell Sci. 2012;15:3765–75. doi: 10.1242/jcs.095596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Angker L, Swain MV. Nanoindentation: Application to dental hard tissue Investigations. J Mater Res. 2006;21:1893–905. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Armitage GC. Development of classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol. 1999;4:1–6. doi: 10.1902/annals.1999.4.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Malek S, Darendeliler MA, Rex T, Kharbanda OP, Srivicharnkul P, Swain MV, et al. Physical properties of root cementum: Part 2. Effect of different storage methods. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003;124:561–70. doi: 10.1016/s0889-5406(03)00398-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Oliver WC, Pharr GM. Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J Mater Res. 2004;19:3–20. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gonçalves PF, Lima LL, Sallum EA, Casati MZ, Nociti FH., Jr Root cementum may modulate gene expression during periodontal regeneration: A preliminary study in humans. J Periodontol. 2008;79:323–31. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.070327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zeichner-David M. Regeneration of periodontal tissues: Cementogenesis revisited. Periodontol 2000. 2006;41:196–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2006.00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Butler DL, Goldstein SA, Guilak F. Functional tissue engineering: The role of biomechanics. J Biomech Eng. 2000;122:570–5. doi: 10.1115/1.1318906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ruben MP, Shapiro A. An analysis of root surface changes in periodontal disease a review. J Periodontol. 1978;49:89–91. doi: 10.1902/jop.1978.49.2.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rylander H, Lindhe J. Cause related periodontal therapy. In: Lindhe J, Karring T, Lang NP, editors. Clinical Periodontology and Implant Dentistry. 3rd ed. Copenhagen: Munksgaard; 1998. pp. 450–1. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Srivicharnkul P, Kharbanda OP, Swain MV, Petocz P, Darendeliler MA. Physical properties of root cementum: Part 3. Hardness and elastic modulus after application of light and heavy forces. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2005 doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2003.12.021. 127-168-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cheron RA, Marshall SJ, Goodis HE, Peters OA. Nanomechanical properties of endodontically treated teeth. J Endod. 2011;37:1562–5. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2011.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Marshall GW, Habelitz S, Gallagher R, Balooch M, Balooch G, Marshall SJ. Nanomechanical properties of hydrated carious human dentin. J Dent Res. 2001;80:1768–71. doi: 10.1177/00220345010800081701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chang MC, Ko CC, Liu CC, Douglas WH, DeLong R, Seong WJ, et al. Elasticity of alveolar bone near dental implant-bone interfaces after one month's healing. J Biomech. 2003;36:1209–14. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9290(03)00113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Alcock JP, Barbour ME, Sandy JR, Ireland AJ. Nanoindentation of orthodontic archwires: The effect of decontamination and clinical use on hardness, elastic modulus and surface roughness. Dent Mater. 2009;25:1039–43. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2009.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fong H, Foster BL, Sarikaya M, Somerman MJ. Structure and mechanical properties of Ank/Ank mutant mouse dental tissues-an animal model for studying periodontal regeneration. Arch Oral Biol. 2009;54:570–6. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2009.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hurng JM, Kurylo MP, Marshall GW, Webb SM, Ryder MI, Ho SP. Discontinuities in the human bone-PDL-cementum complex. Biomaterials. 2011;32:7106–17. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.06.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Waters NE. Some mechanical and physical properties of teeth. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1980;34:99–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ratiola CA, Craig RG. The microhardness of cementum; Underlying dentine of normal teeth and teeth exposed to periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1961;32:113–23. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Clark GJ. Australia: University of Sydney; 1997. An Analysis of the Physical Properties of Human Dental Cementum of Premolar Teeth using Micro-indentation, Thesis. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schroeder HE. Biological problems of regenerated cementogenesis: Synthesis and attachment of collagenous matrices on growing and established root surfaces. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;142:1–58. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Luder HU, Zappa U. Nature and attachment of cementum formed under guided conditions in human teeth. An electron microscopic study. J Periodontol. 1998;69:889–98. doi: 10.1902/jop.1998.69.8.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dragoo MR, Sullivan HC. A clinical and histological evaluation of autogenous iliac bone grafts in humans I Wound healing 2 to 8 months. J Periodontol. 1973;44:599–613. doi: 10.1902/jop.1973.44.10.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bosshardt DD, Sculean A, Windisch P, Pjetursson BE, Lang NP. Effects of enamel matrix proteins on tissue formation along the roots of human teeth. J Periodontal Res. 2005;40:158–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2005.00785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Evans ND, Minelli C, Gentleman E, LaPointe V, Patankar SN, Kallivretaki M, et al. Substrate stiffness affects early differentiation events in embryonic stem cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2009;18:1–13. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v018a01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Discher DE, Mooney DJ, Zandstra PW. Growth factors, matrices, and forces combine and control stem cells. Science. 2009;324:1673–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1171643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chen CS, Tan J, Tien J. Mechanotransduction at cell–matrix and cell–cell contacts. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2004;6:275–302. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bioeng.6.040803.140040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gilbert PM, Havenstrite KL, Magnusson KE, Sacco A, Leonardi NA, Kraft P, et al. Substrate elasticity regulates skeletal muscle stem cell self-renewal in culture. Science. 2010;329:1078–81. doi: 10.1126/science.1191035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Holst J, Watson S, Lord MS, Eamegdool SS, Bax DV, Nivison-Smith LB, et al. Substrate elasticity provides mechanical signals for the expansion of hemopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:1123–8. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Huebsch N, Arany PR, Mao AS, Shvartsman D, Ali OA, Bencherif SA, et al. Harnessing traction-mediated manipulation of the cell/matrix interface to control stem-cell fate. Nat Mater. 2010;9:518–26. doi: 10.1038/nmat2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


