Abstract
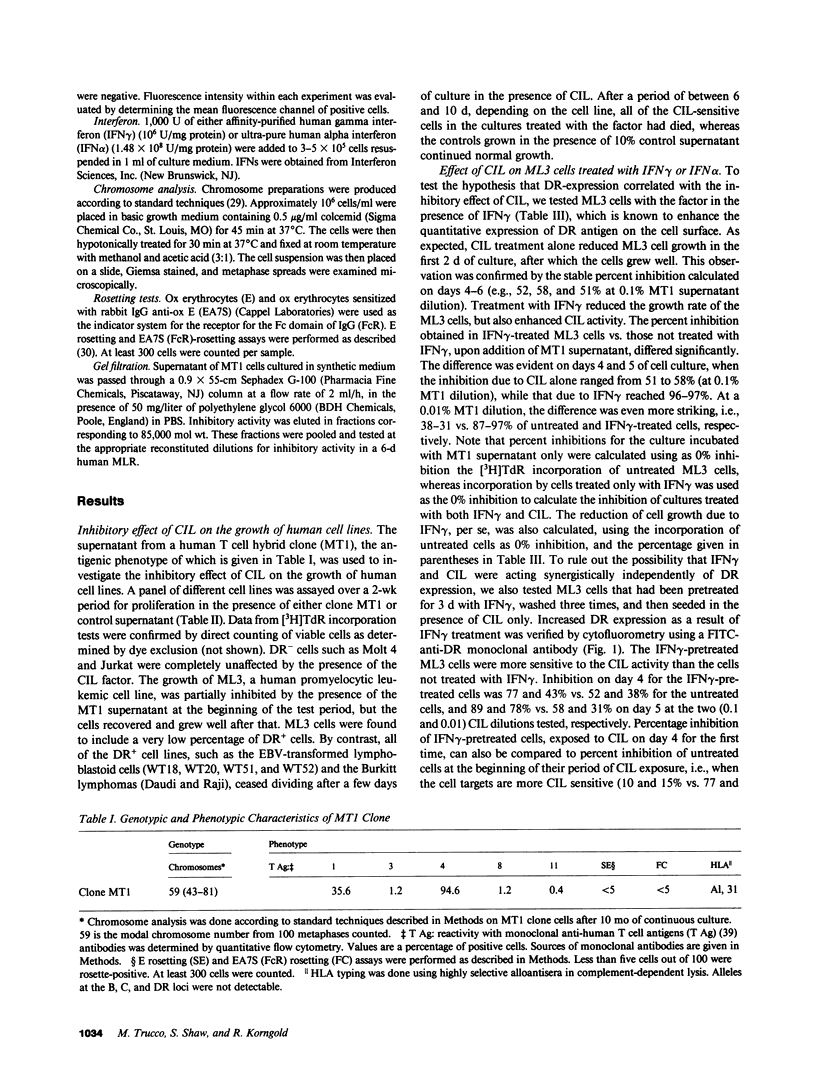
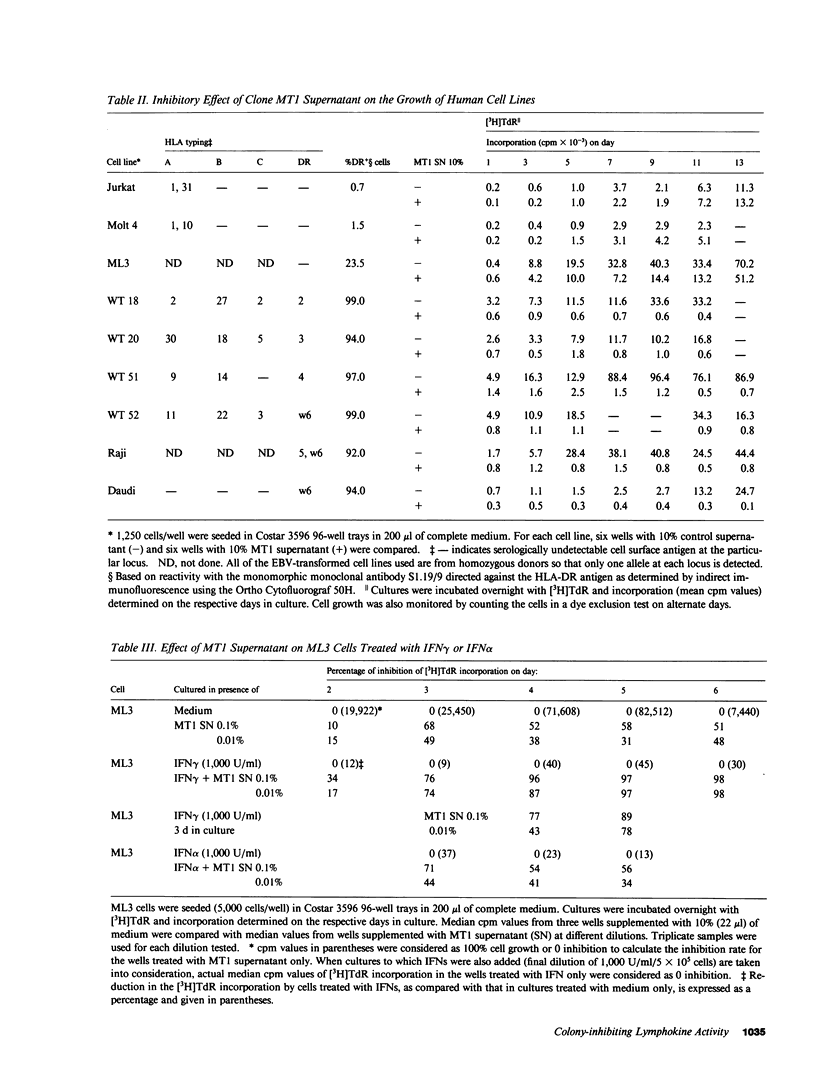
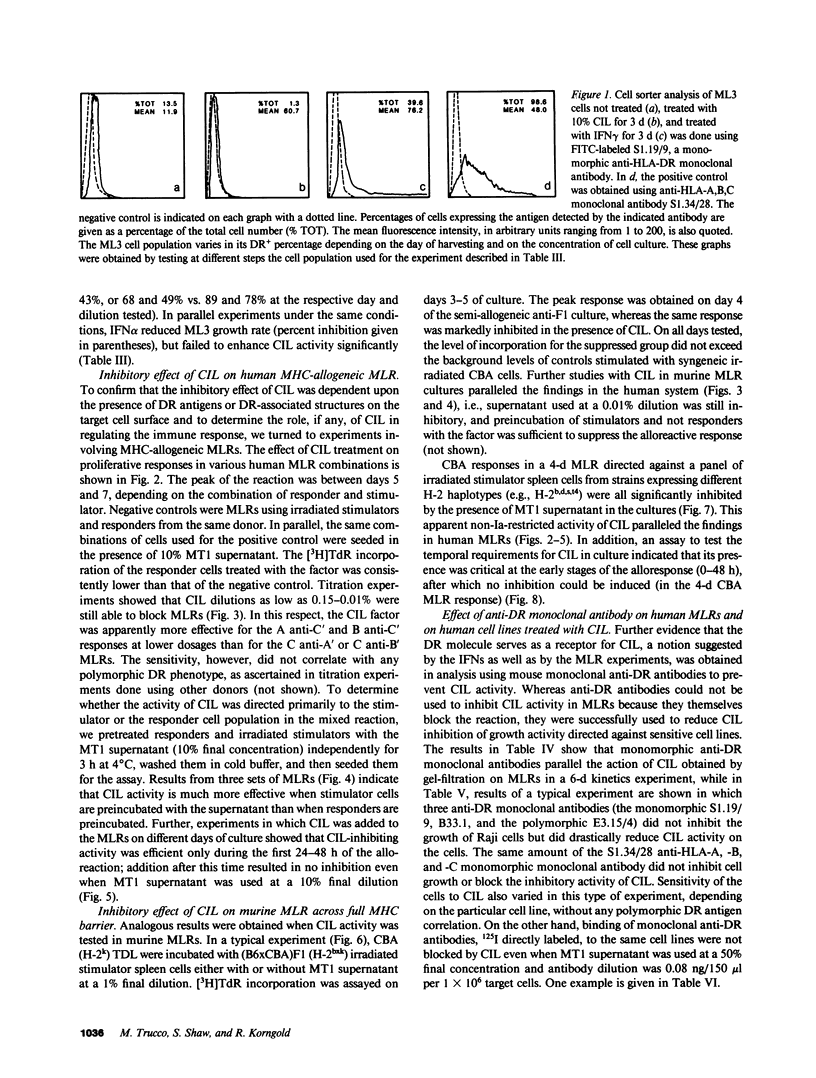
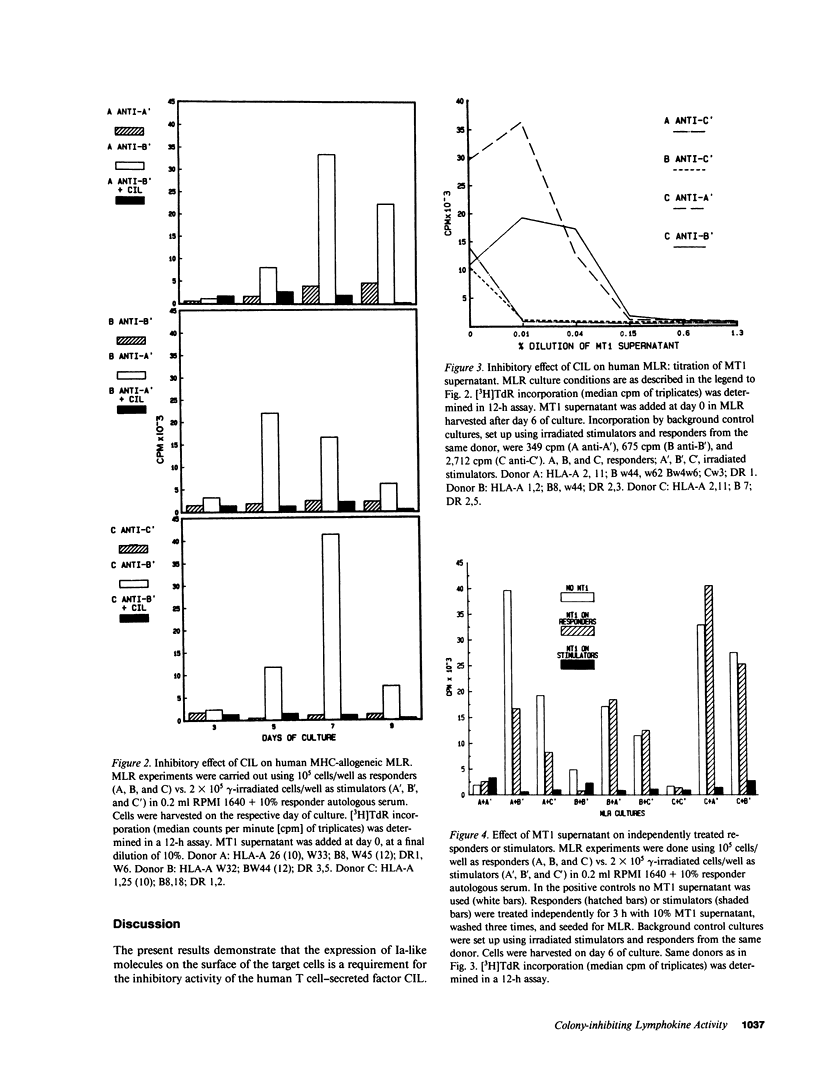
We recently reported the biological activity and some of the biochemical characteristics of a factor produced by a human T cell hybrid clone able to block hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation. This 85-kD protein factor, which we have termed colony-inhibiting lymphokine (CIL), has growth regulatory activity on bone marrow precursors bearing Ia (class II) antigens of either granulocytic-monocytic (CFU-GM) or erythroid lineage (BFU-E and CFU-E). Experiments aimed to investigate the specificity of the inhibitory effect on hematopoietic progenitor cell growth suggested that the expression of HLA-DR surface antigens was required on the target cells. We describe in this communication how DR+ cell lines ceased dividing after a few days of culture in the presence of CIL, whereas DR- cell lines were completely unaffected. The increased DR expression on the ML3 cell surface, mediated by the activity of the gamma interferon (IFN gamma), increases the sensitivity to the growth inhibition factor of the ML3 cell line. To verify the hypothesis that the DR antigens might serve as receptors for the factor, enabling it also to interfere in the immune response, we tested CIL in a mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR), one of the best known in vitro Ia antigen-dependent T cell-mediated immune responses. CIL is able to block major histocompatibility complex-allogeneic MLR both in human and mouse systems. The data indicate that CIL recognizes a nonpolymorphic structure (presumably on all Ia molecules) presented by stimulator cells of either species, and thereby interferes with specific interactions between stimulator and responder cells. Blocking of the alloantigen stimulation stage is also indicated, since CIL is effective only if added to the culture medium during the first 48 h of the MLR. Finally, mouse monoclonal anti-DR antibodies are able to sharply reduce CIL activity on sensitive DR+ cell lines. CIL may act physiologically as a multifunctional mediator in a complex network that links regulation of bone marrow differentiation and the generation of immune responses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacigalupo A., Podesta M., Mingari M. C., Moretta L., Piaggio G., Van Lint M. T., Durando A., Marmont A. M. Generation of CFU-C/suppressor T cells in vitro: an experimental model for immune-mediated marrow failure. Blood. 1981 Mar;57(3):491–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacigalupo A., Podestà M., Mingari M. C., Moretta L., Van Lint M. T., Marmont A. Immune suppression of hematopoiesis in aplastic anemia: activity of T-gamma lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1449–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Bognacki J., Dorner M. H., de Sousa M. Identification of leukemia-associated inhibitory activity as acidic isoferritins. A regulatory role for acidic isoferritins in the production of granulocytes and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1426–1444. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E. Lactoferrin acts on Ia-like antigen-positive subpopulations of human monocytes to inhibit production of colony stimulatory activity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1717–1720. doi: 10.1172/JCI109635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Lu L., Bognacki J. Transferrin, derived from an OKT8-positive subpopulation of T lymphocytes, suppresses the production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulatory factors from mitogen-activated T lymphocytes. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):37–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E. Relationship of cell-cycle expression of Ia-like antigenic determinants on normal and leukemia human granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells to regulation in vitro by acidic isoferritins. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):632–642. doi: 10.1172/JCI110490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Smithyman A., Eger R. R., Meyers P. A., de Sousa M. Identification of lactoferrin as the granulocyte-derived inhibitor of colony-stimulating activity production. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1052–1067. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J. F., Brennan J. K., Lichtman M. A., Abboud C. N., Kirkpatrick F. H. The fractionation, characterization, and subcellular localization of colony-stimulating activities released by the human monocyte-like cell line, GCT. Blood. 1980 Oct;56(4):717–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg P. L., Mosny S. A. Cytotoxic effects of interferon in vitro on granulocytic progenitor cells. Cancer Res. 1977 Jun;37(6):1794–1799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Senn J. S., Till J. E., McCulloch E. A. Colony formation by normal and leukemic human marrow cells in culture: effect of conditioned medium from human leukocytes. Blood. 1971 Jan;37(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Sieber F., Winterhalter K. H. Erythroid colony formation in cultures of mouse and human bone marrow: analysis of the requirement for erythropoietin by gel filtration and affinity chromatography on agarose-concanavalin A. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Apr;83(2):309–320. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R., Dresch C., Metcalf D. Heterogeneity in human neutrophil, macrophage and eosinophil progenitor cells demonstrated by velocity sedimentation separation. Blood. 1977 Nov;50(5):823–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Ranyard J., Yelton L., Billing R., Bohman R. Gamma-interferon induces expression of the HLA-D antigens on normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4080–4084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korngold R., Sprent J. Negative selection of T cells causing lethal graft-versus-host disease across minor histocompatibility barriers. Role of the H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1114–1124. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland J. I., Bockman R. S., Broxmeyer H. E., Moore M. A. Limitation of excessive myelopoiesis by the intrinsic modulation of macrophage-derived prostaglandin E. Science. 1978 Feb 3;199(4328):552–555. doi: 10.1126/science.304600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. A., Broxmeyer H. E., Sheridan A. P., Meyers P. A., Jacobsen N., Winchester R. J. Continuous human bone marrow culture: Ia antigen characterization of probable pluripotential stem cells. Blood. 1980 Apr;55(4):682–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Olofsson T., Mauritzon N. Characterization of mononuclear blood cell-derived differentiation inducing factors for the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Dec;67(6):1225–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. W., Metcalf D. Production of colony-stimulating factor in mitogen-stimulated lymphocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelus L. M. Association between colony forming units-granulocyte macrophage expression of Ia-like (HLA-DR) antigen and control of granulocyte and macrophage production. A new role for prostaglandin E. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):568–578. doi: 10.1172/JCI110649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Acuto O., Terhorst C., Faust J., Lazarus R., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. II. Studies of B73.1 antibody-antigen interaction on the lymphocyte membrane. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2142–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. The differentiation and function of human T lymphocytes. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone-Wolff D. S., Yip Y. K., Kelker H. C., Le J., Henriksen-Destefano D., Rubin B. Y., Rinderknecht E., Aggarwal B. B., Vilcek J. Interrelationships of human interferon-gamma with lymphotoxin and monocyte cytotoxin. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):828–843. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepperman A. D., Curtis J. E., McCulloch E. A. Erythropietic colonies in cultures of human marrow. Blood. 1974 Nov;44(5):659–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torok-Storb B., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A. Regulation of in vitro erythropoiesis by normal T cells: evidence for two T-cell subsets with opposing function. Blood. 1981 Jul;58(1):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucco M. M., Garotta G., Stocker J. W., Ceppellini R. Murine monoclonal antibodies against HLA structures. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:219–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucco M. M., Stocker J. W., Caeppellini R. Monoclonal antibodies against human lymphocyte antigens. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):666–668. doi: 10.1038/273666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucco M. M., Stocker J. W., Ceppellini R. Monoclonal antibodies to human lymphocyte membrane antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:66–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucco M., Galfrè G., De Marchi M., Varetto O., Carbonara A. O. "tb 9", a new HLA-D specificity defined by two homozygous typing cells. Tissue Antigens. 1977 Oct;10(4):343–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1977.tb00767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucco M., Rovera G., Ferrero D. A novel human lymphokine that inhibits haematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):166–168. doi: 10.1038/309166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Kunkel H. G. The human Ia system. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:221–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Ross G. D., Jarowski C. I., Wang C. Y., Halper J., Broxmeyer H. E. Expression of Ia-like antigen molecules on human granulocytes during early phases of differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4012–4016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


