Abstract
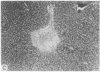
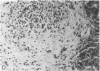
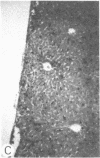
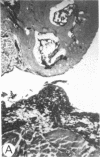
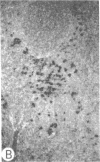
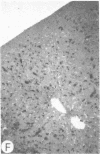
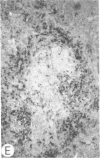
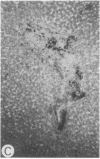
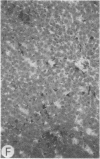
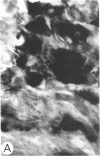
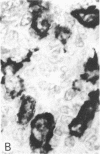
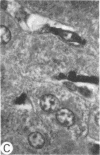
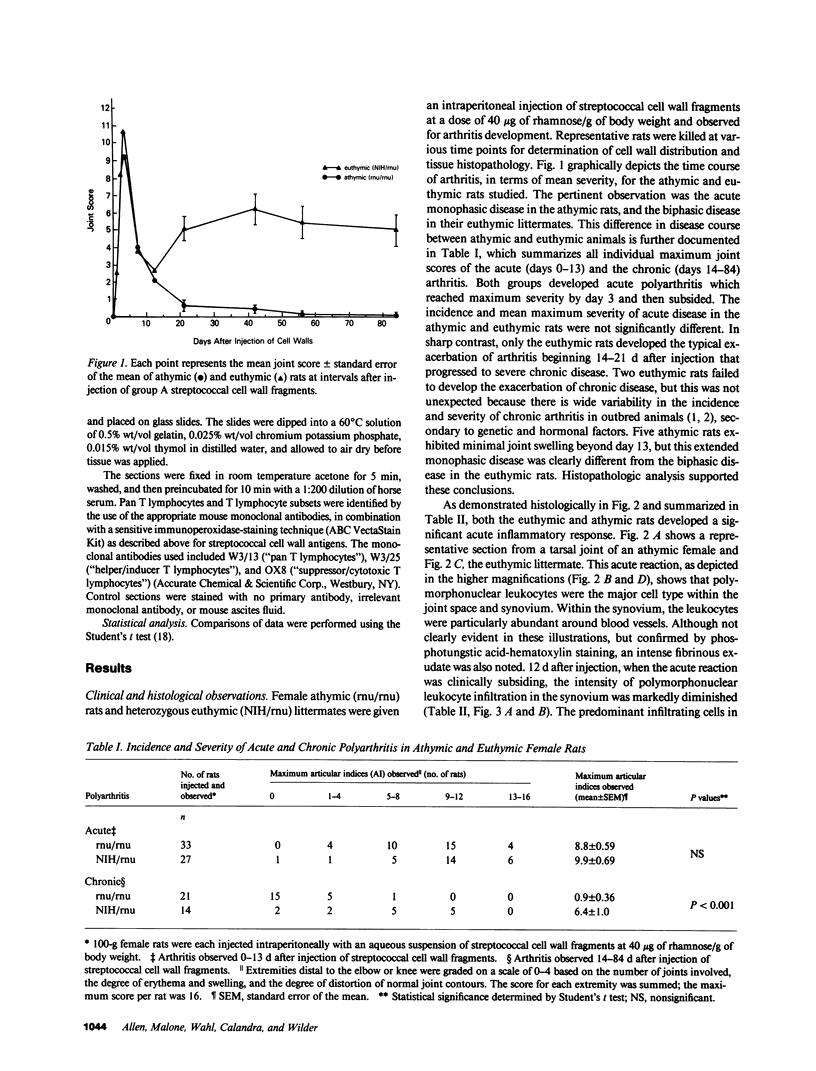
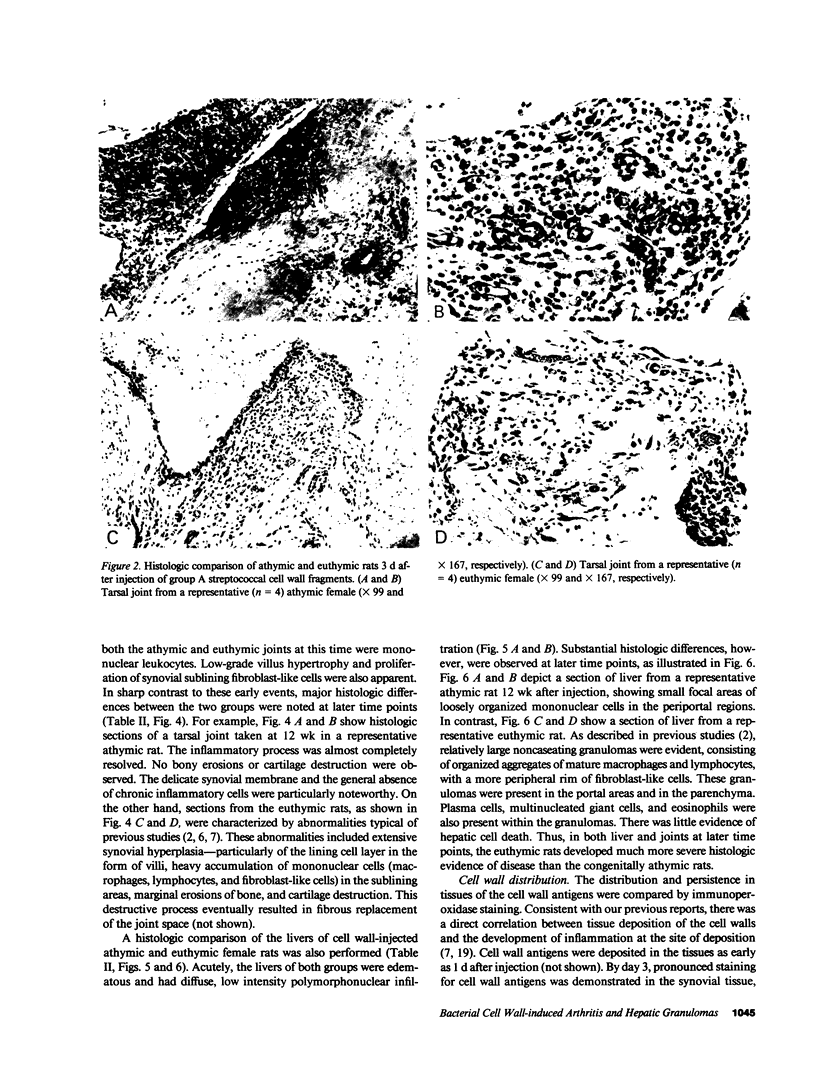
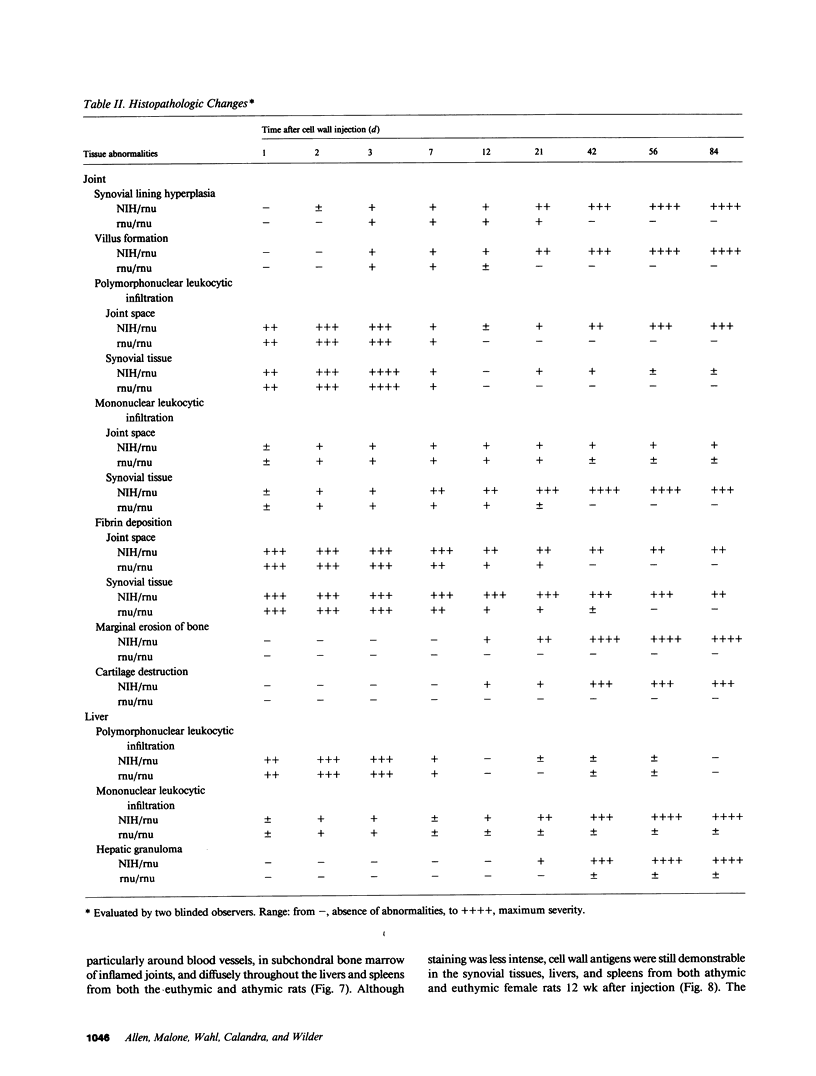
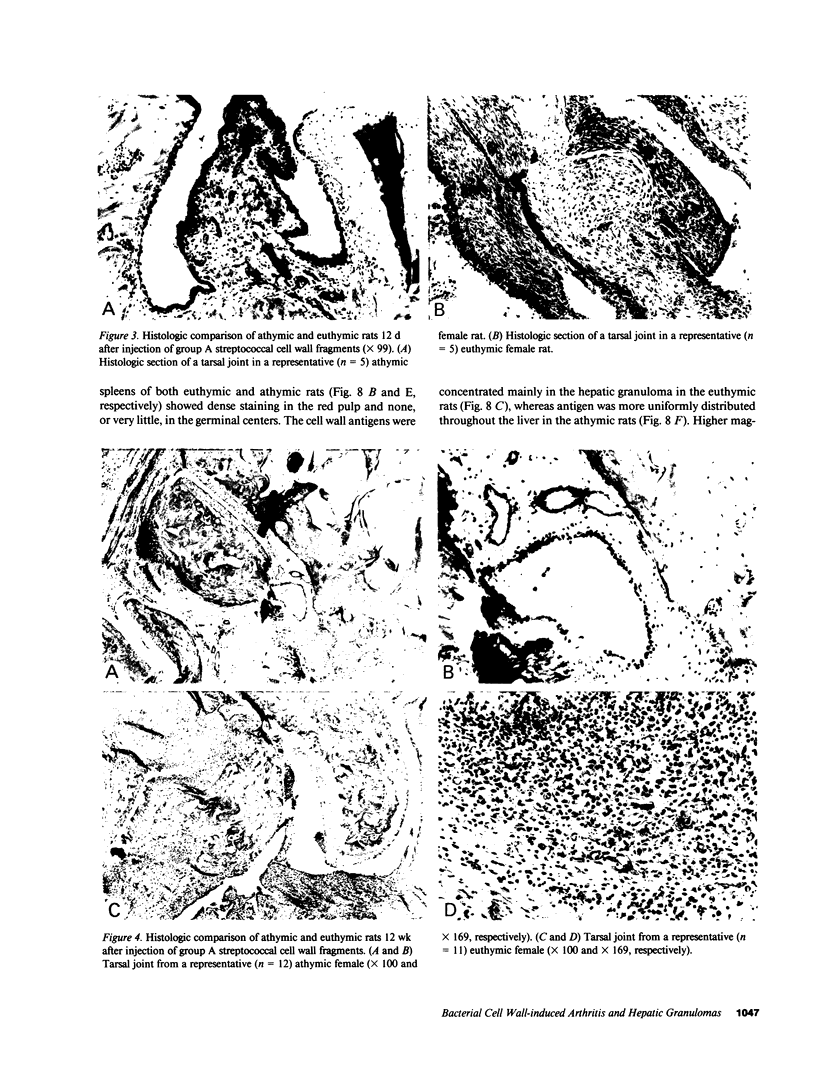
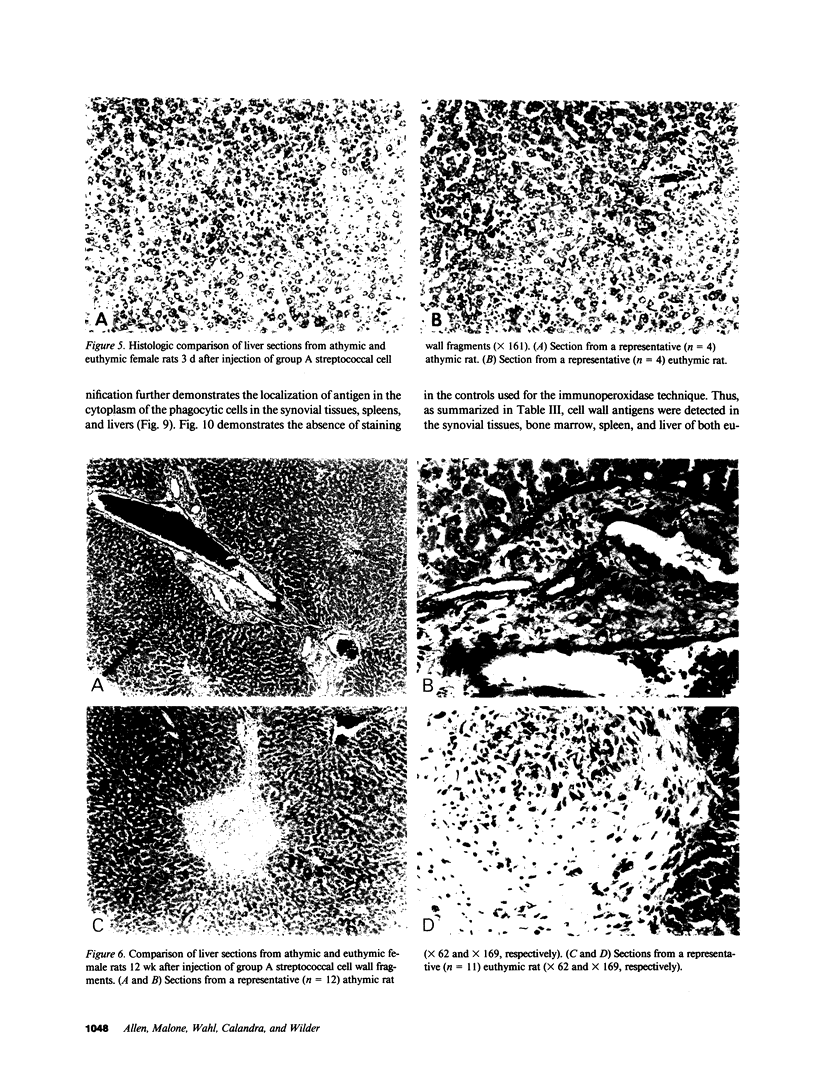
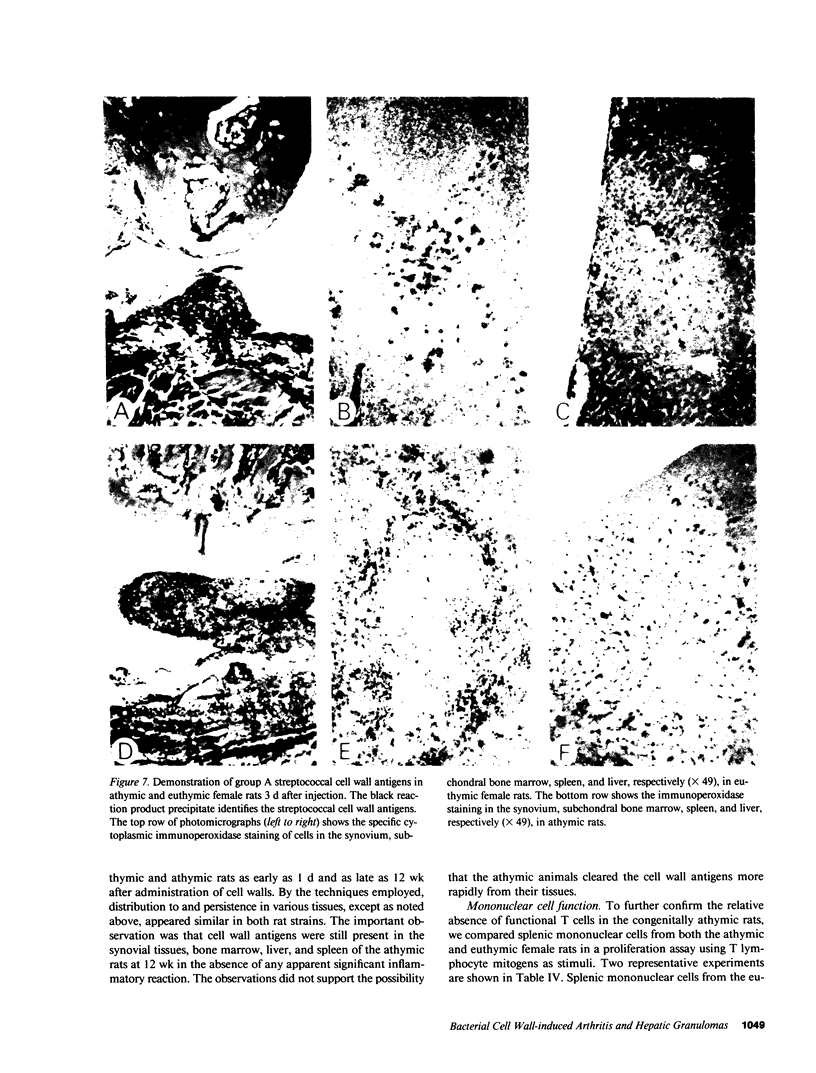
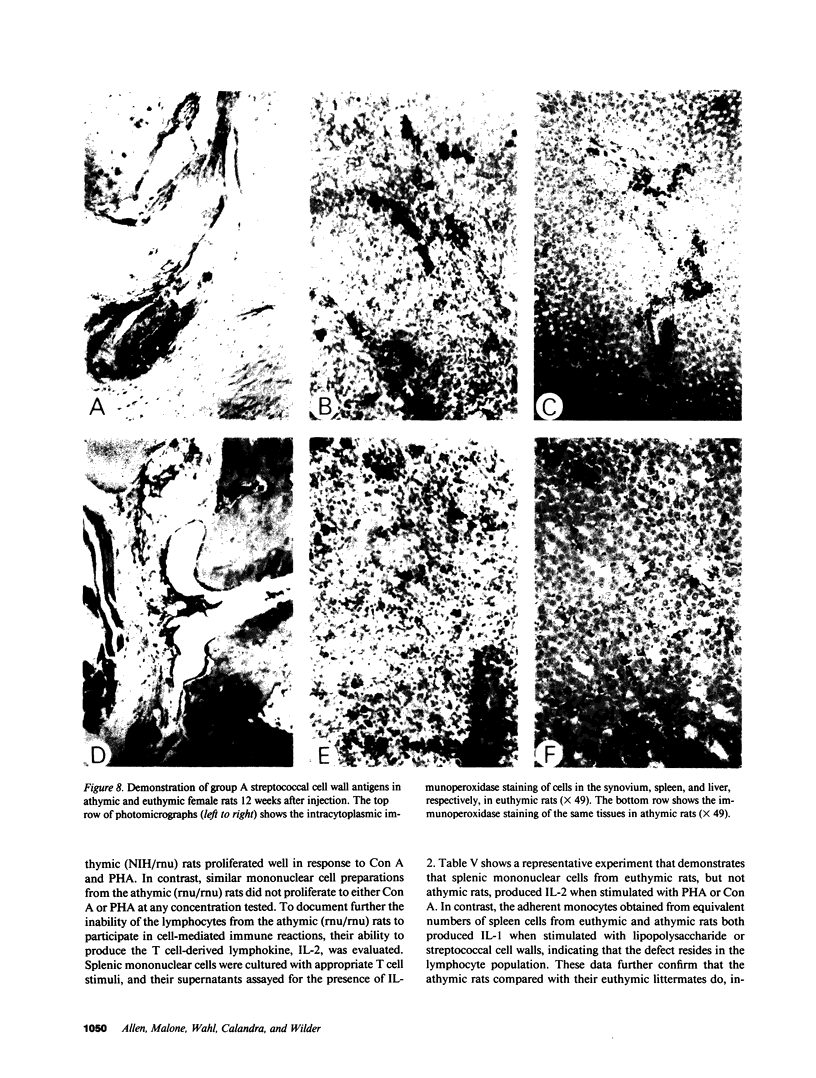
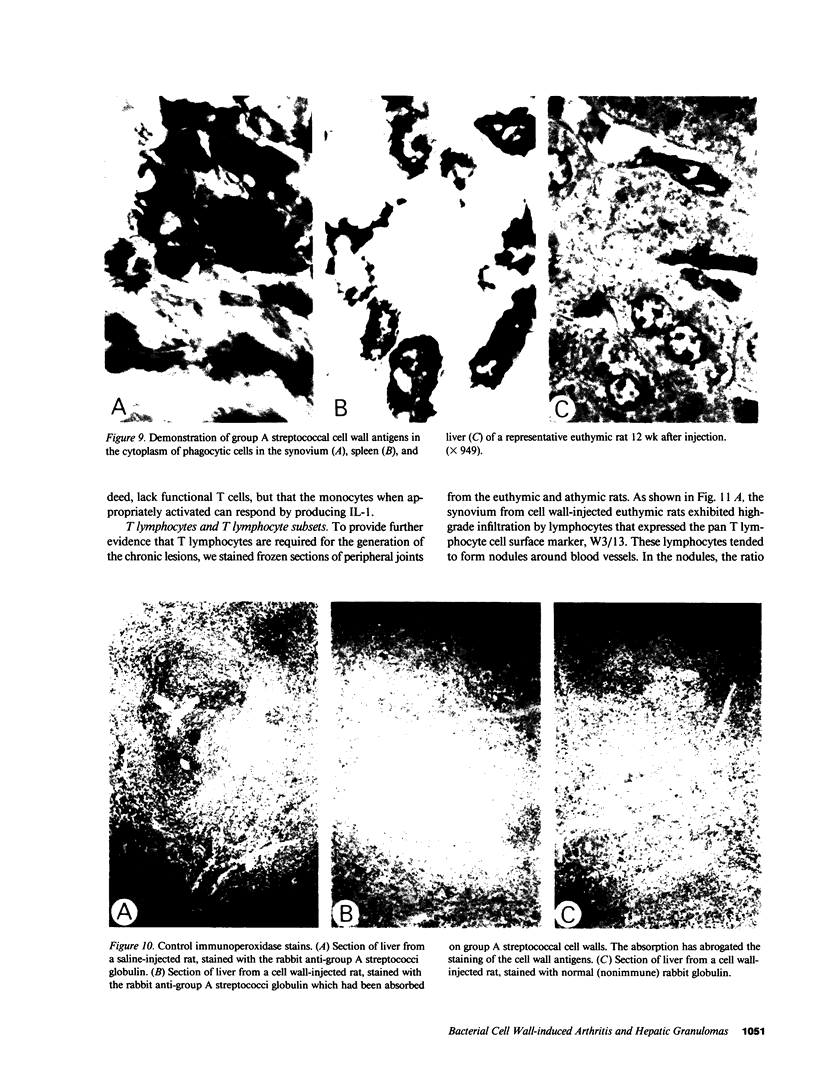
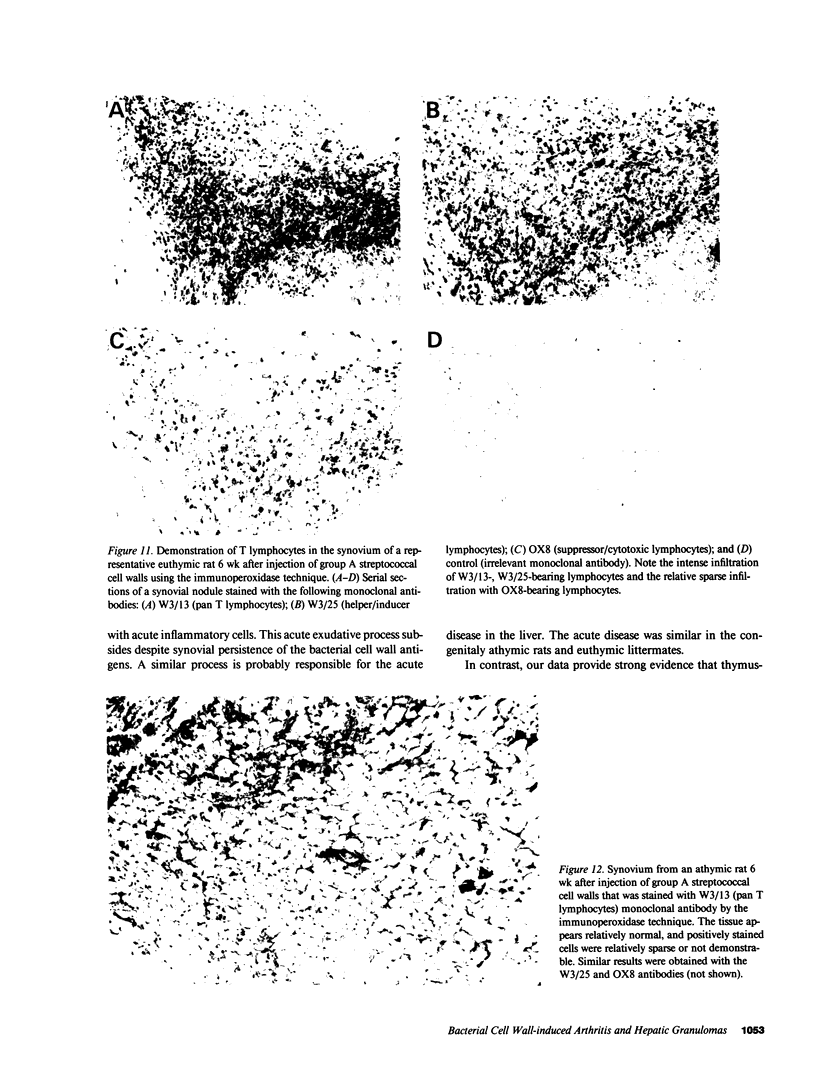
Systemic administration of an aqueous suspension of group A streptococcal cell wall fragments to susceptible rats induces acute and chronic polyarthritis, as well as noncaseating hepatic granulomas. To gain insight into the role of the thymus in the pathogenesis of this experimental model, pathologic responses and cell wall tissue distribution were compared in congenitally athymic rats (rnu/rnu) and their euthymic littermates (NIH/rnu). Within 24 h, both rat strains developed acute arthritis, characterized by polymorphonuclear leukocytic exudate in the synovium and joint spaces. This acute process was maximal at day 3 and gradually subsided. Beginning 2-3 wk after injection, the euthymic, but not the athymic, rats developed the typical exacerbation of arthritis, characterized by synovial cell hyperplasia with villus formation and T helper/inducer lymphocyte-rich mononuclear cell infiltration. This process eventually resulted in marginal erosions and destruction of periarticular bone and cartilage. Parallel development of acute and chronic hepatic lesions was observed. Bacterial cell wall antigen distribution and persistence were similar in the athymic and euthymic rats. Cell wall antigens were demonstrated in the cytoplasm of cells within subchondral bone marrow, synovium, liver, and spleen, coincident with the development of the acute lesions, and persisted in these sites, although in decreasing amounts, for the duration of the experiment. Our findings provide evidence that the acute and chronic phases of the experimental model are mechanistically distinct. The thymus and functional thymus derived-lymphocytes appear not to be required for the development of the acute exudative disease but are essential for the development of chronic proliferative and erosive disease. Induction of disease is dependent upon cell wall dissemination to and persistence in the affected tissues.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. B., Blatter D., Calandra G. B., Wilder R. L. Sex hormonal effects on the severity of streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Apr;26(4):560–563. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. B., Calandra G. B., Wilder R. L. Cutaneous inflammatory reactions to group A streptococcal cell wall fragments in Fisher and Lewis inbred rats. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):796–801. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.796-801.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. L., Cuttino J. T., Jr, Anderle S. K., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Radiologic analysis of arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cell walls. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jan;22(1):25–35. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. L., Marr M. C., Schwab J. H., Cromartie W. J. Microangiographic studies of experimental erosive synovitis in rats. Invest Radiol. 1983 May-Jun;18(3):257–263. doi: 10.1097/00004424-198305000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromartie W. J., Craddock J. G., Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Yang C. H. Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1585–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currey H. L., Ziff M. Suppression of adjuvant disease in the rat by heterologous antilymphocyte globulin. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):185–203. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker J. L., Malone D. G., Haraoui B., Wahl S. M., Schrieber L., Klippel J. H., Steinberg A. D., Wilder R. L. NIH conference. Rheumatoid arthritis: evolving concepts of pathogenesis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Dec;101(6):810–824. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-6-810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker J. L., Malone D. G., Haraoui B., Wahl S. M., Schrieber L., Klippel J. H., Steinberg A. D., Wilder R. L. NIH conference. Rheumatoid arthritis: evolving concepts of pathogenesis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Dec;101(6):810–824. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-6-810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Boackle R. J., Schwab J. H. Activation of the alternate complement pathway by peptidoglycan from streptococcal cell wall. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):296–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.296-303.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Ree H. J. Self-sandwich method. An improved immunoperoxidase technic for the detection of small amounts of antigens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Jul;74(1):32–40. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter N., Anderle S. K., Brown R. R., Dalldorf F. G., Clark R. L., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Cell-mediated immune response during experimental arthritis induced in rats with streptococcal cell walls. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Dec;42(3):441–449. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. I. Evidence for the regulatory function of thymus-derived cells in the induction of the disease. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1878–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. II. Different subpopulations of T lymphocytes functioning in the development of the disease. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1127–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Holmdahl R., Larsson E., Wigzell H. Role of T lymphocytes in collagen II induced arthritis in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jan;51(1):117–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Aihara K., Ozawa A., Kotani S., Azuma I. New model of a synthetic adjuvant, N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine- induced arthritis: clinical and histologic studies in athymic nude and euthymic rats. Lab Invest. 1982 Jul;47(1):27–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Pearson C. M., Tamaoki N., Tanaka A., Shimamura K., Ozawa A., Kotani S., Saito M., Hioki K. Role of thymus for N-acetyl muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine-induced polyarthritis and granuloma formation in euthymic and athymic nude rats or in neonatally thymectomized rats. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):758–766. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.758-766.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Pearson C. M., Watanabe Y., Kotani S., Koga T. Structural requirements for arthritogenicity of peptidoglycans from Staphylococcus aureus and Lactobacillus plant arum and analogous synthetic compounds. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1635–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer T., Mizel D., Oppenheim J. J. Independent and synergistic thymocyte proliferative activities of PMA and IL 1. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):939–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Allen J. B., Schwab J. H. In vivo changes in complement induced with peptidoglycan-polysaccharide polymers from streptococcal cell walls. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):377–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.377-380.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. J., Allen J. B., Plotz P. H., Wilder R. L. Lactobacillus casei cell wall-induced arthritis in rats: cell wall fragment distribution and persistence in chronic arthritis-susceptible LEW/N and -resistant F344/N rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):939–942. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. J., Allen J. B., Plotz P. H., Wilder R. L. Polyarthritis in rats following the systemic injection of Lactobacillus casei cell walls in aqueous suspension. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Oct;26(10):1259–1265. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M., WOOD F. D. PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ADJUVANT ARTHRITIS BY LYMPH NODE OR SPLEEN CELLS. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:547–560. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Allen J. B., Anderle S. K., Dalldorf F., Eisenberg R., Cromartie W. J. Relationship of complement to experimental arthritis induced in rats with streptococcal cell walls. Immunology. 1982 May;46(1):83–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler B. M., Dougherty S. F., Farrar J. J., Oppenheim J. J. Relationship of cell cycle to recovery of IL 2 activity from human mononuclear cells, human and mouse T cell lines. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1936–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Sandberg G. P., Mahowald M. L. The cellular basis of adjuvant arthritis. I. Enhancement of cell-mediated passive transfer by concanavalin A and by immunosuppressive pretreatment of the recipient. Cell Immunol. 1983 Feb 1;75(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Sandberg G. P., Mahowald M. L. The cellular basis of adjuvant arthritis. II. Characterization of the cells mediating passive transfer. Cell Immunol. 1983 Aug;80(1):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. G., Kreeftenberg J. G., Kruijt B. C., Kruizinga W., Steerenberg P. The athymic nude rat. II. Immunological characteristics. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Feb;15(2):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., WENNERSTEN C. PASSIVE TRANSFER OF ADJUVANT ARTHRITIS IN RATS WITH LIVING LYMPHOID CELLS OF SENSITIZED DONORS. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1963;23:129–139. doi: 10.1159/000229412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Malone D. G., Wilder R. L. Spontaneous production of fibroblast-activating factor(s) by synovial inflammatory cells. A potential mechanism for enhanced tissue destruction. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):210–222. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse D. J., Whitehouse M. W., Pearson C. M. Passive transfer of adjuvant-induced arthritis and allergic encephalomyelitis in rats using thoracic duct lymphocytes. Nature. 1969 Dec 27;224(5226):1322–1322. doi: 10.1038/2241322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Wahl L. M., Calandra G. B., Wahl S. M. The pathogenesis of group A streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Comparative studies in arthritis resistant and susceptible inbred rat strains. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1442–1451. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Calandra G. B., Garvin A. J., Wright K. D., Hansen C. T. Strain and sex variation in the susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1064–1072. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Ihrie E. J., Dinarello C. A., Cohen P. L. Isolation of an interleukin-1-like factor from human joint effusions. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Aug;26(8):975–983. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]