Abstract
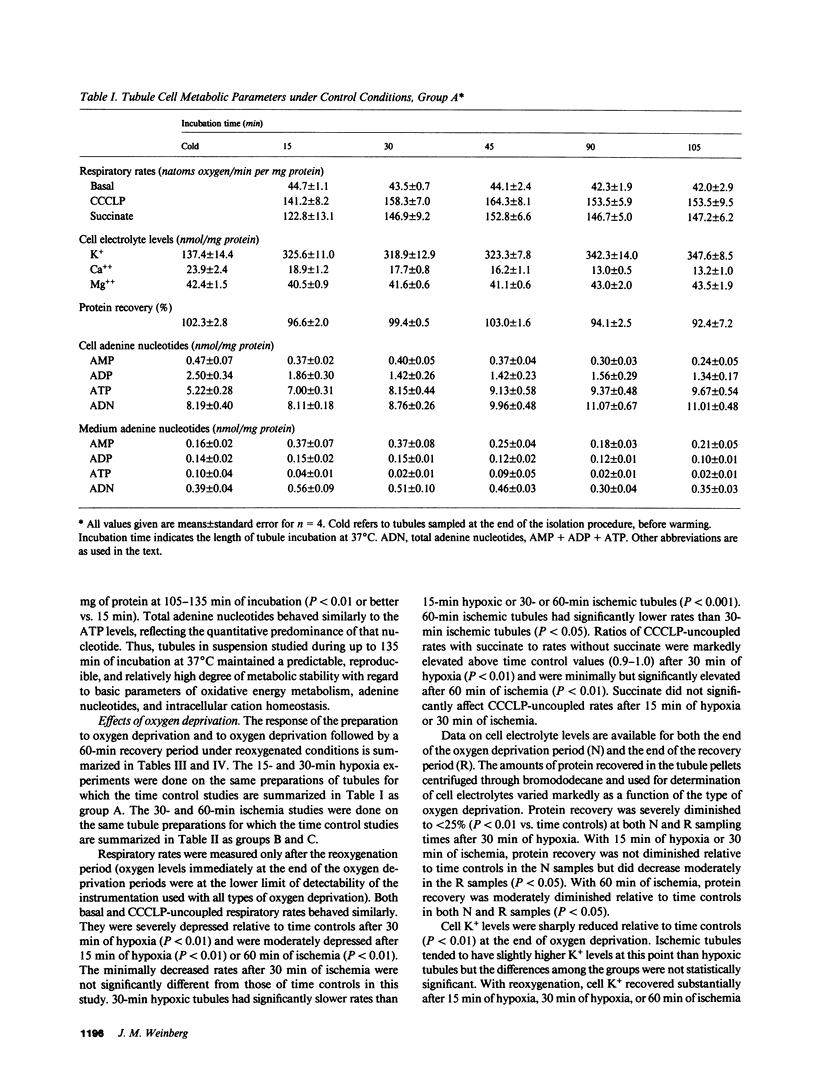
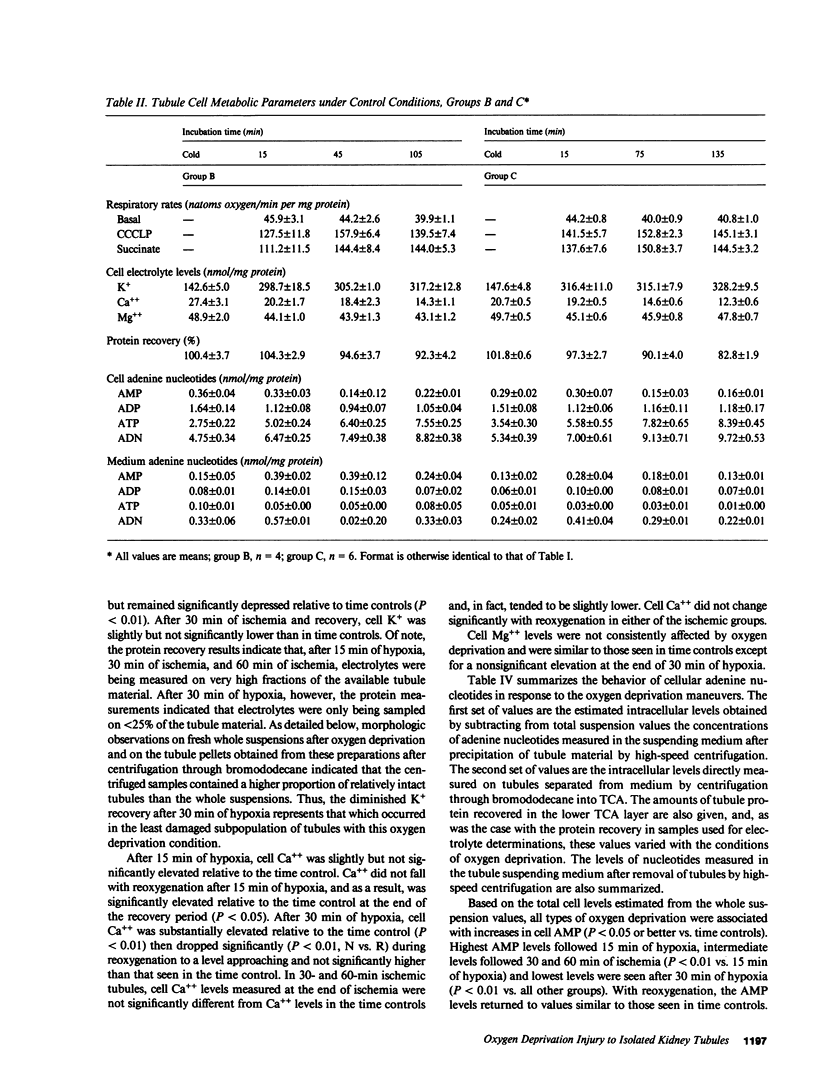
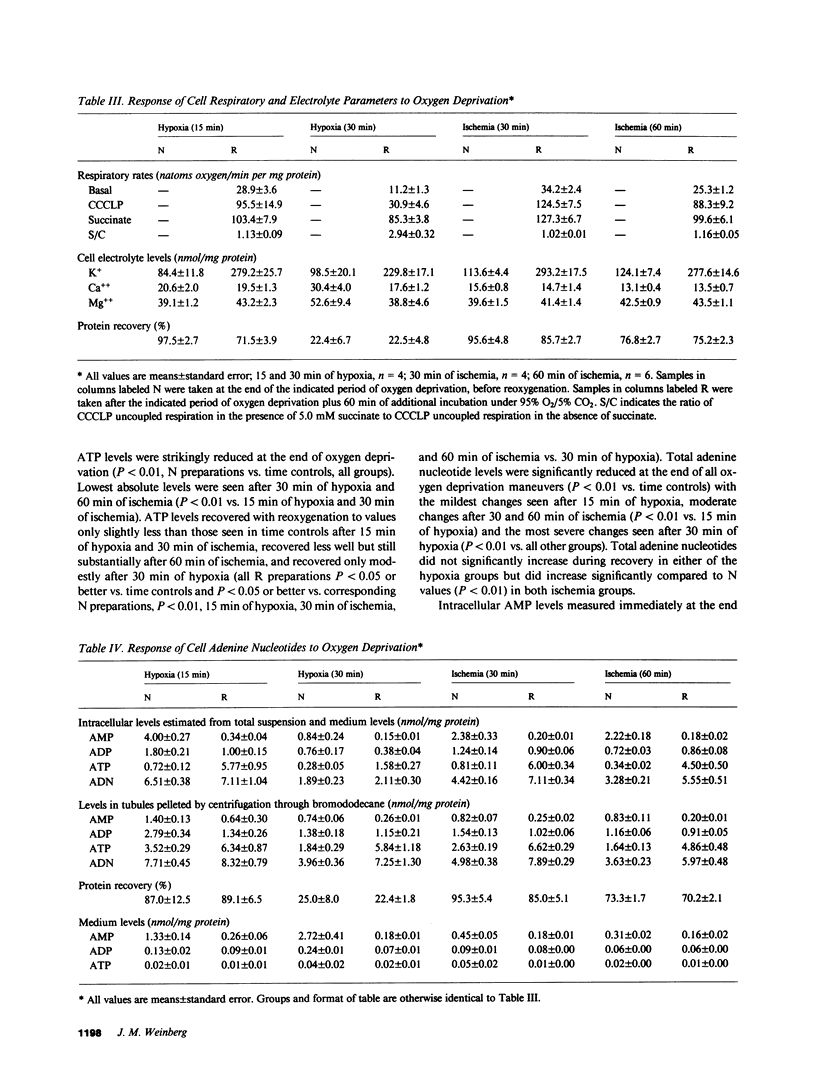
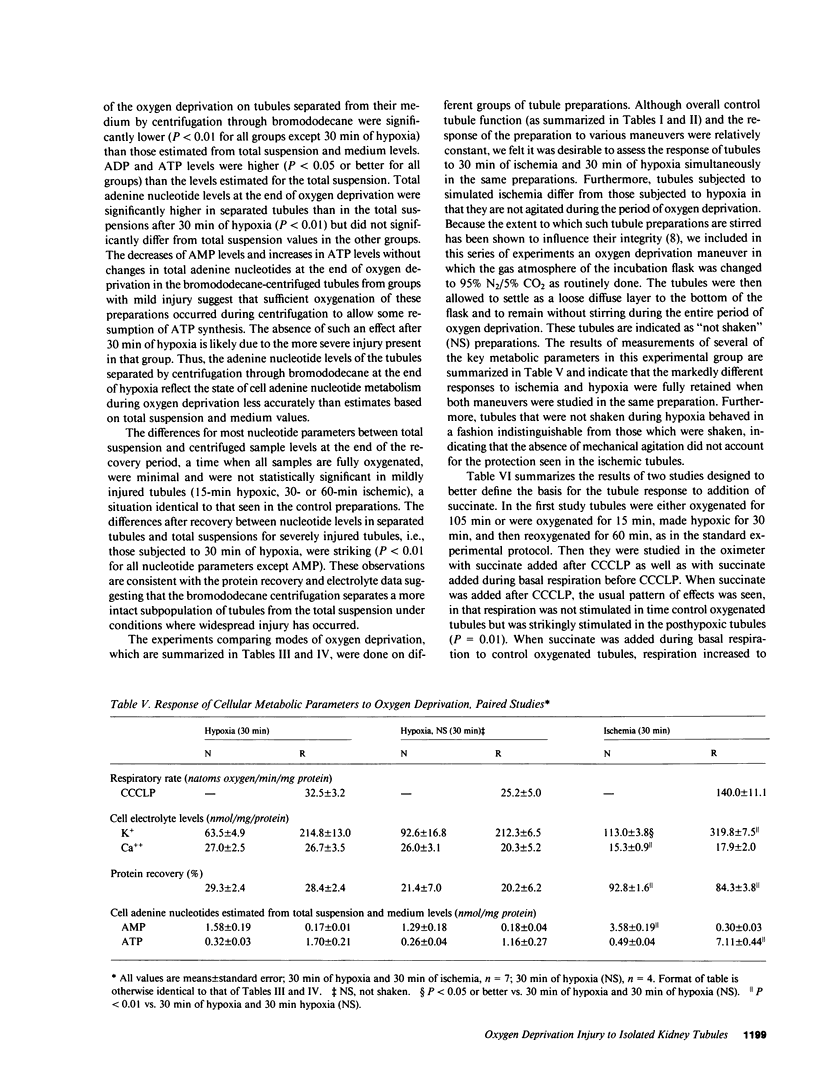
The utility of freshly isolated suspensions of rabbit tubules enriched in proximal segments for studying the pathogenesis of oxygen deprivation-induced renal tubular cell injury was evaluated. Oxygenated control preparations exhibited very good stability of critical cell injury-related metabolic parameters including oxygen consumption, cell cation homeostasis, and adenine nucleotide metabolism for periods in excess of 2 h. Highly reproducible models of oxygen deprivation-induced injury and recovery were developed and alterations of injury-related metabolic parameters in these models were characterized in detail. When oxygen deprivation was produced under hypoxic conditions, tubules sustained widespread lethal cell injury and associated metabolic alterations within 15-30 min. However, when oxygen deprivation was produced under simulated ischemic conditions, tubules tolerated 30-60 min with only moderate amounts of lethal cell injury occurring, a situation similar to that seen with ischemia in vivo. Like ischemia in vivo, simulated ischemia in vitro was characterized by a fall in pH during oxygen deprivation. No such fall in pH occurred in the hypoxic model. To test whether this fall in pH could contribute to the protection seen during simulated ischemia in vitro, tubules were subjected to hypoxia at medium pHs ranging from 7.45 to 6.41. Striking protection from hypoxic injury was seen as pH was reduced with maximal protection occurring in tubules made hypoxic at pHs below 7.0. Measurements of injury-associated metabolic parameters suggested that the protective effect of reduced pH may be mediated by pH-induced alterations of tubule cell Ca++ metabolism. This study has, thus, defined and characterized in detail a new and extremely versatile model system for the study of oxygen deprivation-induced cell injury in the kidney and has established that pH alterations play a major role in modulating such injury.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S., Shoubridge E., Radda G. K. Estimation of cellular pH gradients with 31P-NMR in intact rabbit renal tubular cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 1):C188–C196. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.247.3.C188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschuld R. A., Hostetler J. R., Brierley G. P. Response of isolated rat heart cells to hypoxia, re-oxygenation, and acidosis. Circ Res. 1981 Aug;49(2):307–316. doi: 10.1161/01.res.49.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURG M. B., ORLOFF J. Oxygen consumption and active transport in separated renal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1962 Aug;203:327–330. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.2.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balaban R. S., Soltoff S. P., Storey J. M., Mandel L. J. Improved renal cortical tubule suspension: spectrophotometric study of O2 delivery. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):F50–F59. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.1.F50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur H., Kasperek S., Pfaff E. Criteria of viability of isolated liver cells. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Jun;356(6):827–838. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.s1.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell M. L., Lazarus H. M., Herman A. H., Egdahl R. H., Rutenburg A. M. pH dependent changes in cell membrane stability. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jan;136(1):298–299. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bing O. H., Brooks W. W., Messer J. V. Heart muscle viability following hypoxia: protective effect of acidosis. Science. 1973 Jun 22;180(4092):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4092.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bore P. J., Sehr P. A., Chan L., Thulborn K. R., Ross B. D., Radda G. K. The importance of pH in renal preservation. Transplant Proc. 1981 Mar;13(1 Pt 2):707–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B. Isolated perfused tubule. Introduction: background and development of microperfusion technique. Kidney Int. 1982 Nov;22(5):417–424. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Effect of temperature and medium K on Na and K fluxes in separated renal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):1005–1010. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke T. J., Arnold P. E., Gordon J. A., Bulger R. E., Dobyan D. C., Schrier R. W. Protective effect of intrarenal calcium membrane blockers before or after renal ischemia. Functional, morphological, and mitochondrial studies. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1830–1841. doi: 10.1172/JCI111602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke T. J., Cronin R. E., Duchin K. L., Peterson L. N., Schrier R. W. Ischemia and tubule obstruction during acute renal failure in dogs: mannitol in protection. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):F305–F314. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.4.F305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busa W. B., Nuccitelli R. Metabolic regulation via intracellular pH. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 2):R409–R438. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.4.R409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung J. Y., Thompson I. G., Bonventre J. V. Effects of extracellular calcium removal and anoxia on isolated rat myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):C184–C190. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.3.C184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunarro J. A., Schultz S. E., Johnson W. A., Weiner M. W. Effects of ischemia on metabolite concentrations in dog renal cortex. Ren Physiol. 1982;5(3):143–155. doi: 10.1159/000172850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goracci G., Porcellati G., Woelk H. Subcellular localization and distribution of phospholipases A in liver and brain tissue. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1978;3:55–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guder W. G., Wieland O. H. Metabolism of isolated kidney tubules. Additive effects of parathyroid hormone and free-fatty acids on renal gluconeogenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 21;31(1):69–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullans S. R., Brazy P. C., Dennis V. W., Mandel L. J. Interactions between gluconeogenesis and sodium transport in rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F859–F869. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanley M. J. Isolated nephron segments in a rabbit model of ischemic acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):F17–F23. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.1.F17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris S. I., Balaban R. S., Barrett L., Mandel L. J. Mitochondrial respiratory capacity and Na+- and K+-dependent adenosine triphosphatase-mediated ion transport in the intact renal cell. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10319–10328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems R., Stubbs M., Krebs H. A. Restricted permeability of rat liver for glutamate and succinate. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(6):807–815. doi: 10.1042/bj1070807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochachka P. W., Mommsen T. P. Protons and anaerobiosis. Science. 1983 Mar 25;219(4591):1391–1397. doi: 10.1126/science.6298937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoek J. B., Nicholls D. G., Williamson J. R. Determination of the mitochondrial protonmotive force in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1458–1464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khym J. X. An analytical system for rapid separation of tissue nucleotides at low pressures on conventional anion exchangers. Clin Chem. 1975 Aug;21(9):1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapes J. P., Harris R. A. On the oxidation of succinate by parenchymal cells isolated from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):80–83. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80858-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medzihradsky F., Marks M. J. Measures of viability in isolated cells. Biochem Med. 1975 Jun;13(2):164–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(75)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiitsutsuji-Uwo J. M., Ross B. D., Krebs H. A. Metabolic activities of the isolated perfused rat kidney. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):852–862. doi: 10.1042/bj1030852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrenius S., Thor H., Rajs J., Berggren M. Isolated rat hepatocytes as an experimental tool in the study of cell injury. Effect of anoxia. Forensic Sci. 1976 Nov-Dec;8(3):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0300-9432(76)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttila A., Trump B. F. Extracellular acidosis protects Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and rat renal cortex against anoxic injury. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):277–278. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttila A., Trump B. F. Studies on modification on the cellular response to injury. Lab Invest. 1975 Jun;32(6):690–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole-Wilson P. A. Measurement of myocardial intracellular pH in pathological states. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1978 Jun;10(6):511–526. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(78)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer K. A., Ganote C. E., Jennings R. B. Alterations in renal cortex following ischemic injury. 3. Ultrastructure of proximal tubules after ischemia or autolysis. Lab Invest. 1972 Apr;26(4):347–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorive G., Nielsen R., Kleinzeller A. Effect of pH on the water and electrolyte content of renal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):376–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwertz D. W., Kreisberg J. I., Venkatachalam M. A. Characterization of rat kidney proximal tubule brush border membrane-associated phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 15;224(2):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel N. J., Glazier W. B., Chaudry I. H., Gaudio K. M., Lytton B., Baue A. E., Kashgarian M. Enhanced recovery from acute renal failure by the postischemic infusin of adenine nucleotides and magnesium chloride in rats. Kidney Int. 1980 Mar;17(3):338–349. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. H., Lifschitz M. D., Barnes L. D. Current concepts on the pathophysiology of acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):F171–F181. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.3.F171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struyvenberg A., Morrison R. B., Relman A. S. Acid-base behavior of separated canine renal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):1155–1162. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecki T., Thomas J. A., Koch C. D., LaNoue K. F. The effect of hormones on proton compartmentation in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4122–4129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain J. L., Sabina R. L., McHale P. A., Greenfield J. C., Jr, Holmes E. W. Prolonged myocardial nucleotide depletion after brief ischemia in the open-chest dog. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):H818–H826. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.242.5.H818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trump B. F., Bulger R. E. Studies of cellular injury in isolated flounder tubules. 3. Light microscopic and functional changes due to cyanide. Lab Invest. 1968 Jun;18(6):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinay P., Gougoux A., Lemieux G. Isolation of a pure suspension of rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F403–F411. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S., Sperelakis N. Blockade of myocardial slow inward current at low pH. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):C99–103. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1977.233.3.C99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M., Scherphof G. L., Boshouwers F. M., van Deenen L. L. Differentiation of phospholipases A in mitochondria and lysosomes of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jul;10(4):411–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. M., Harding P. G., Humes H. D. Alterations in renal cortex cation homeostasis during mercuric chloride and gentamicin nephrotoxicity. Exp Mol Pathol. 1983 Aug;39(1):43–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(83)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. H., Kippen I., Wright E. M. Stoichiometry of Na+-succinate cotransport in renal brush-border membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1773–1778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


