Abstract
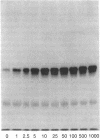
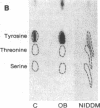
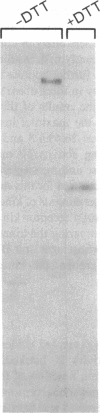
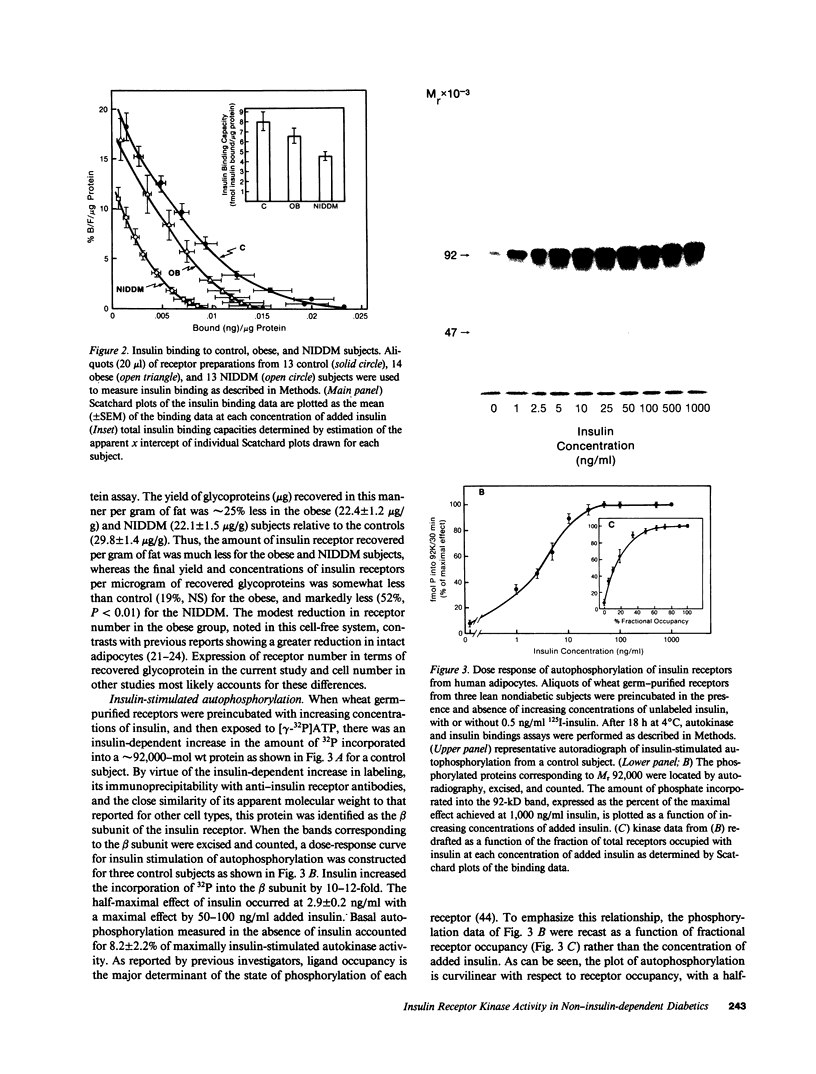
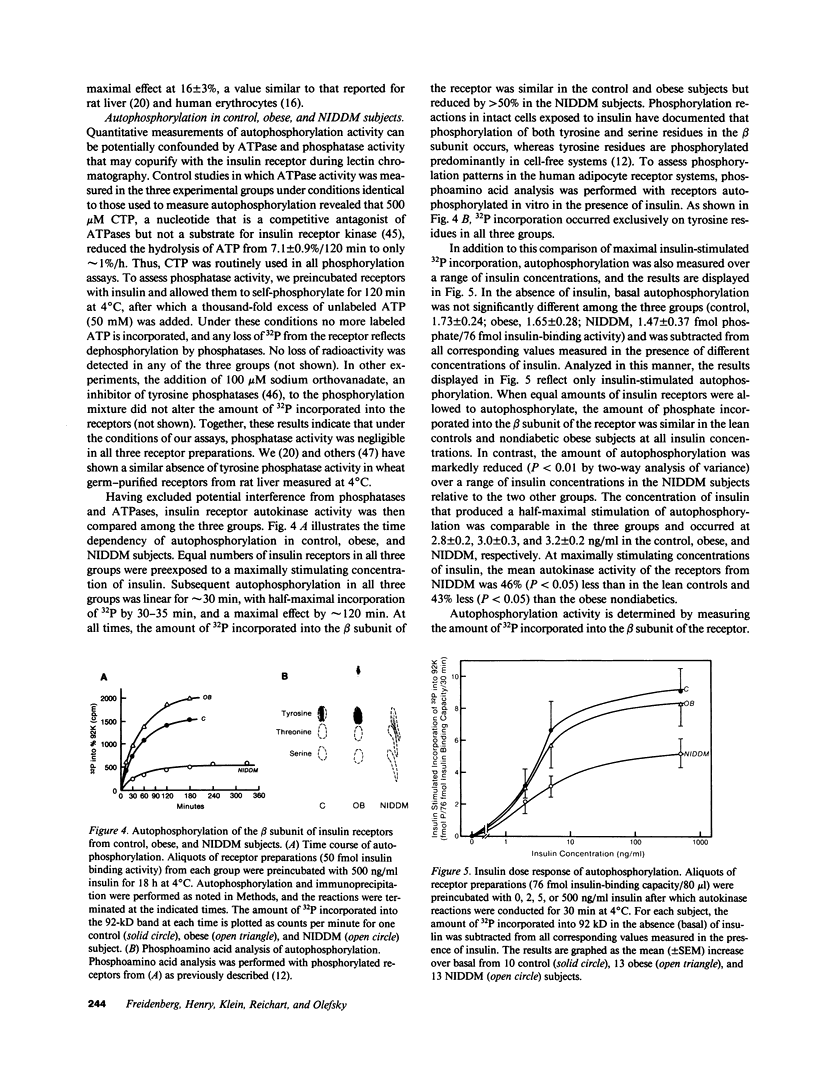
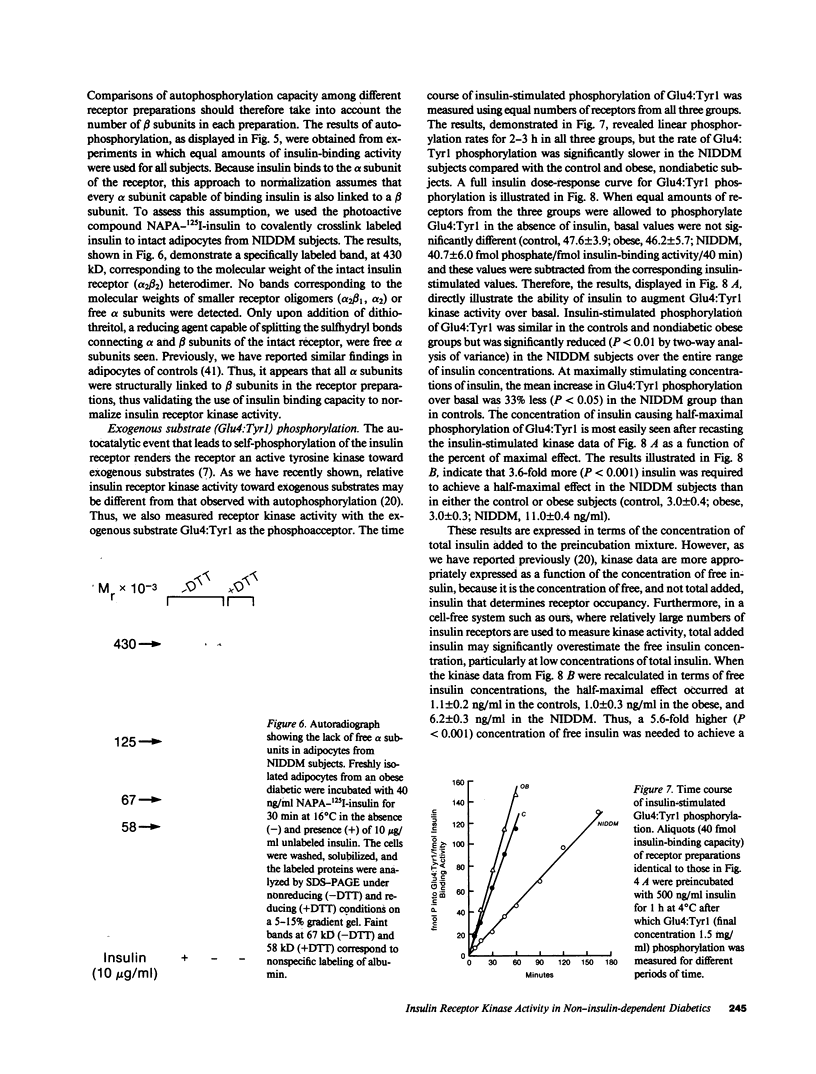
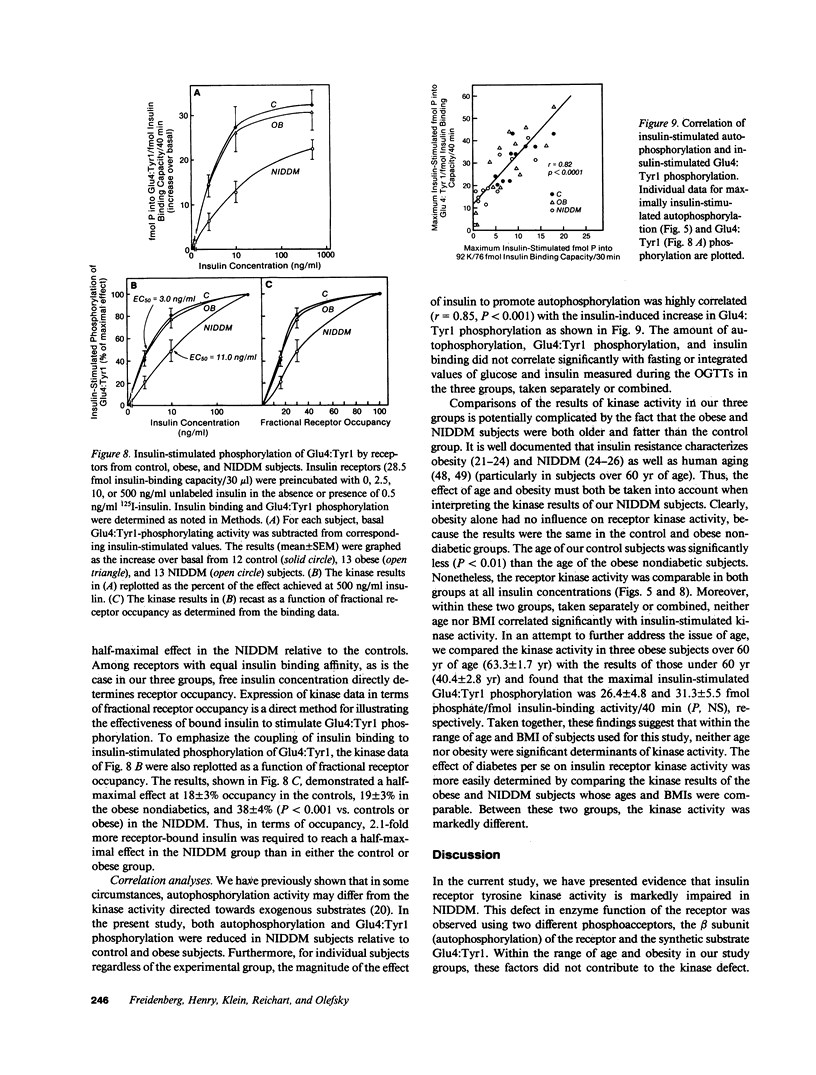
The tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor was examined with partially-purified insulin receptors from adipocytes obtained from 13 lean nondiabetics, 14 obese nondiabetics, and 13 obese subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes (NIDDM). Incubation of receptors at 4 degrees C with [gamma-32P]ATP and insulin resulted in a maximal 10-12-fold increase in autophosphorylation of the 92-kDa beta-subunit of the receptor with a half maximal effect at 1-3 ng/ml free insulin. Insulin receptor kinase activity in the three experimental groups was measured by means of both autophosphorylation and phosphorylation of the exogenous substrate Glu4:Tyr1. In the absence of insulin, autophosphorylation and Glu4:Tyr1 phosphorylation activities, measured with equal numbers of insulin receptors, were comparable among the three groups. In contrast, insulin-stimulated kinase activity was comparable in the control and obese subjects, but was reduced by approximately 50% in the NIDDM group. These findings indicate that the decrease in kinase activity in NIDDM resulted from a reduction in coupling efficiency between insulin binding and activation of the receptor kinase. The insulin receptor kinase defects observed in NIDDM could be etiologically related to insulin resistance in NIDDM and the pathogenesis of the diabetic state.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arsenis G., Livingston J. N. Alterations in the tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor produced by in vitro hyperinsulinemia. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Alexander M. C., Palmer J. L., Pierce M. W., Nemenoff R. A., Blackshear P. J., Tipper J. P., Witters L. A. Role of insulin-stimulated protein phosphorylation in insulin action. Fed Proc. 1982 Aug;41(10):2629–2633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berhanu P., Kolterman O. G., Baron A., Tsai P., Olefsky J. M., Brandenburg D. Insulin receptors in isolated human adipocytes. Characterization by photoaffinity labeling and evidence for internalization and cellular processing. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):1958–1970. doi: 10.1172/JCI111160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Stone K., Mott D. Correlation between muscle glycogen synthase activity and in vivo insulin action in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1185–1190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burant C. F., Treutelaar M. K., Buse M. G. Diabetes-induced functional and structural changes in insulin receptors from rat skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):260–270. doi: 10.1172/JCI112285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Kolterman O. G., Olefsky J. M. Mechanism of the postreceptor defect in insulin action in human obesity. Decrease in glucose transport system activity. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):875–880. doi: 10.1172/JCI110342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R., Deibert D., Hendler R., Felig P., Soman V. Insulin sensitivity and insulin binding to monocytes in maturity-onset diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):939–946. doi: 10.1172/JCI109394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Desbuquois B., Aurbach G. D. Use of polyethylene glycol to separate free and antibody-bound peptide hormones in radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):732–738. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Murray R., Kissebah A. H. Relationship between skeletal muscle insulin resistance, insulin-mediated glucose disposal, and insulin binding. Effects of obesity and body fat topography. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1515–1525. doi: 10.1172/JCI111565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R. I., Kolterman O. G., Griffin J., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in aging. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1523–1535. doi: 10.1172/JCI110908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidenberg G. R., Klein H. H., Cordera R., Olefsky J. M. Insulin receptor kinase activity in rat liver. Regulation by fasting and high carbohydrate feeding. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12444–12453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu F., Flier J. S., Kahn C. R. Characterization of binding and phosphorylation defects of erythrocyte insulin receptors in the type A syndrome of insulin resistance. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):127–138. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu F., Flier J. S., Kahn C. R. Defect in insulin receptor phosphorylation in erythrocytes and fibroblasts associated with severe insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15003–15006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberger G., Zick Y., Gorden P. Defect in phosphorylation of insulin receptors in cells from an insulin-resistant patient with normal insulin binding. Science. 1984 Mar 2;223(4639):932–934. doi: 10.1126/science.6141638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., King-Roach A. P. Insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue in vitro and the response to exogenous insulin in obese human subjects. Metabolism. 1976 Oct;25(10):1095–1101. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffetz D., Zick Y. Receptor aggregation is necessary for activation of the soluble insulin receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):889–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kasuga M., Akanuma Y., Ezaki O., Takaku F. Decreased autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor-kinase in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14208–14216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwagi A., Verso M. A., Andrews J., Vasquez B., Reaven G., Foley J. E. In vitro insulin resistance of human adipocytes isolated from subjects with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1246–1254. doi: 10.1172/JCI111080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Hedo J. A., Yamada K. M., Kahn C. R. The structure of insulin receptor and its subunits. Evidence for multiple nonreduced forms and a 210,000 possible proreceptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10392–10399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Sasaki N., Kahn C. R., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Antireceptor antibodies as probes of insulinlike growth factor receptor structure. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1459–1469. doi: 10.1172/JCI111102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. H., Freidenberg G. R., Cordera R., Olefsky J. M. Substrate specificities of insulin and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):254–263. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. H., Freidenberg G. R., Kladde M., Olefsky J. M. Insulin activation of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in intact rat adipocytes. An in vitro system to measure histone kinase activity of insulin receptors activated in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4691–4697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M. Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):957–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI110350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Insel J., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in human obesity: evidence for receptor and postreceptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1272–1284. doi: 10.1172/JCI109790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A. Insulin and glucagon regulation of protein phosphorylation in isolated hepatocytes. Persistence, reversibility, and concentration dependence of hormonal effect. Evidence for common phosphorylation sites for both hormones on the Mr = 46,000 protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8376–8389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Grémeaux T., Ballotti R., Van Obberghen E. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is defective in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):676–679. doi: 10.1038/315676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth P., Smith U. Aging enhances the insulin resistance in obesity through both receptor and postreceptor alterations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Feb;62(2):433–437. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Pike L. J., Freidenberg G. R., Cordera R., Stith B. J., Olefsky J. M., Krebs E. G. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 following microinjection of insulin receptor-kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):459–461. doi: 10.1038/320459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino L. J., Campbell P. J., Gottesman I. S., Gerich J. E. Abnormal coupling of insulin receptor binding in noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 1):E688–E692. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.5.E688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Kwok Y. C., Shulman G. I., Blackshear P. J., Osathanondh R., Avruch J. Insulin-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase. Characterization and relation to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5058–5065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe E., Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Epidermal growth factor. Characteristics of specific binding in membranes from liver, placenta, and other target tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):518–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Decreased insulin binding to adipocytes and circulating monocytes from obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1165–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI108384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. LIlly lecture 1980. Insulin resistance and insulin action. An in vitro and in vivo perspective. Diabetes. 1981 Feb;30(2):148–162. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.2.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Decreased insulin binding to lymphocytes from diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1172/JCI107878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Predominance of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptors during the initial response of intact cells to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7131–7136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Hjøllund E., Sørensen N. S. Insulin receptor binding and insulin action in human fat cells: effects of obesity and fasting. Metabolism. 1982 Sep;31(9):884–895. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Gitomer W., Oka Y., Oppenheimer C. L., Czech M. P. beta-Adrenergic regulation of insulin and epidermal growth factor receptors in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7386–7394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ D., ZIERLER K. L. Forearm metabolism in obesity and its response to intra-arterial insulin. Characterization of insulin resistance and evidence for adaptive hyperinsulinism. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2173–2181. doi: 10.1172/JCI104676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Mechanism and significance of insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):990–995. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., White M. F., Lauris V., Kahn C. R. Phorbol esters modulate insulin receptor phosphorylation and insulin action in cultured hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7797–7801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Haring H. U., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R. Kinetic properties and sites of autophosphorylation of the partially purified insulin receptor from hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Takayama S., Kahn C. R. Differences in the sites of phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9470–9478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor beta subunit activates the receptor-associated tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5277–5286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Characterization of insulin-mediated phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):75–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Sasaki N., Rees-Jones R. W., Grunberger G., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) stimulates tyrosine kinase activity in purified receptors from a rat liver cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91610-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Whittaker J., Roth J. Insulin stimulated phosphorylation of its own receptor. Activation of a tyrosine-specific protein kinase that is tightly associated with the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3431–3434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]