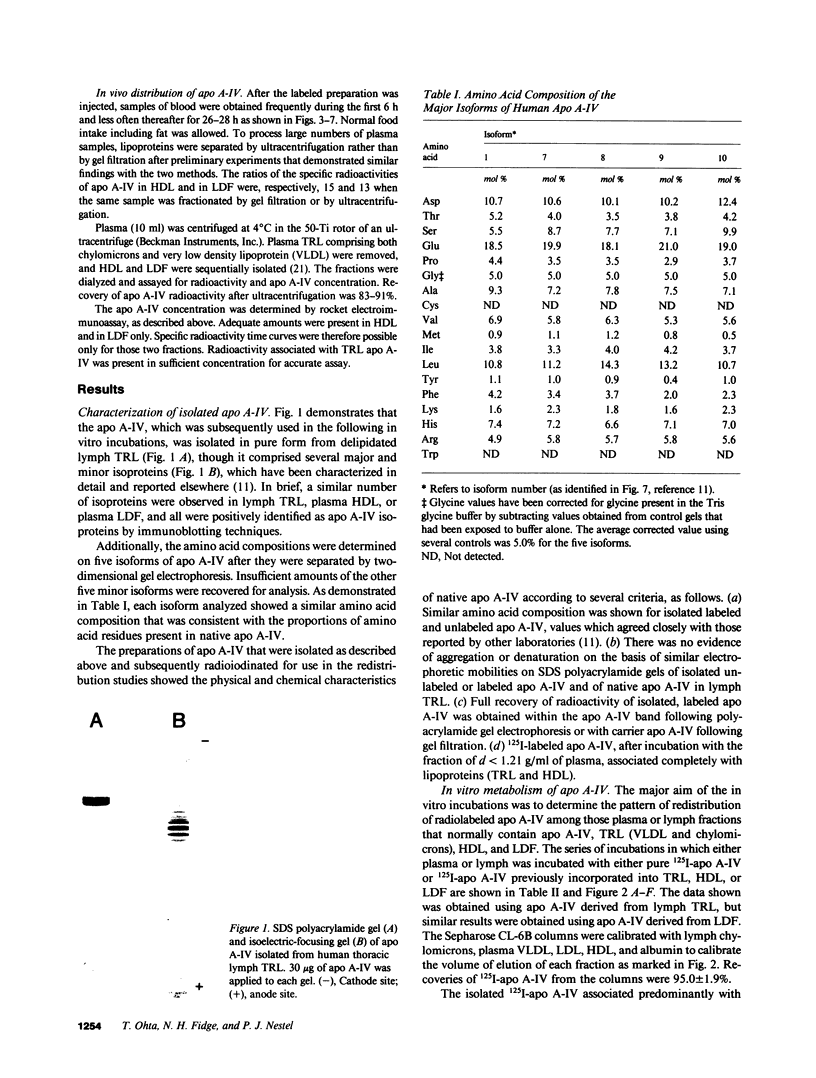
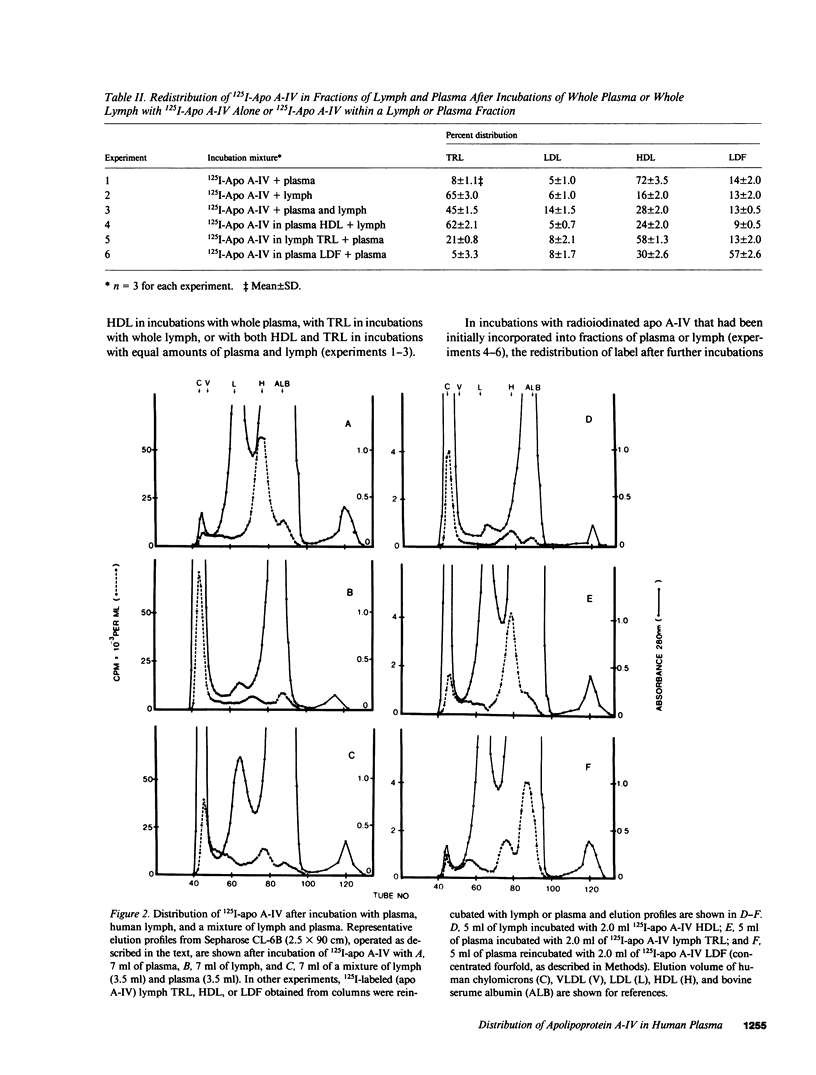
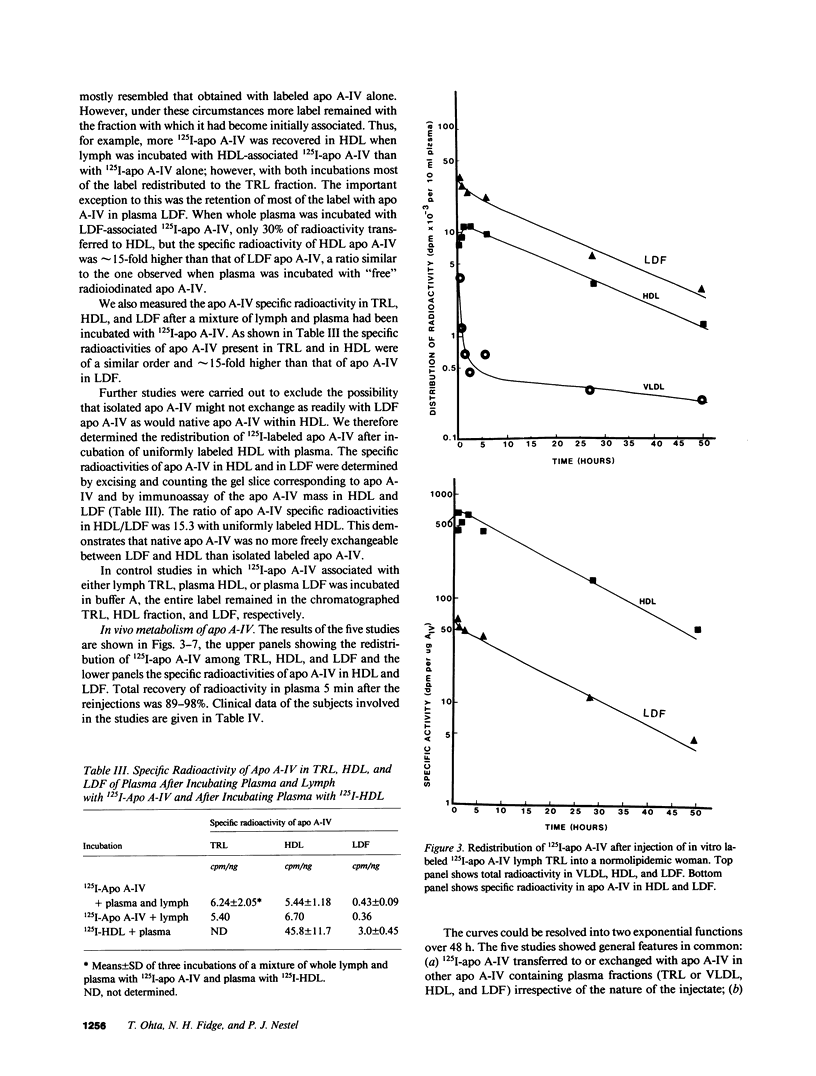
Abstract
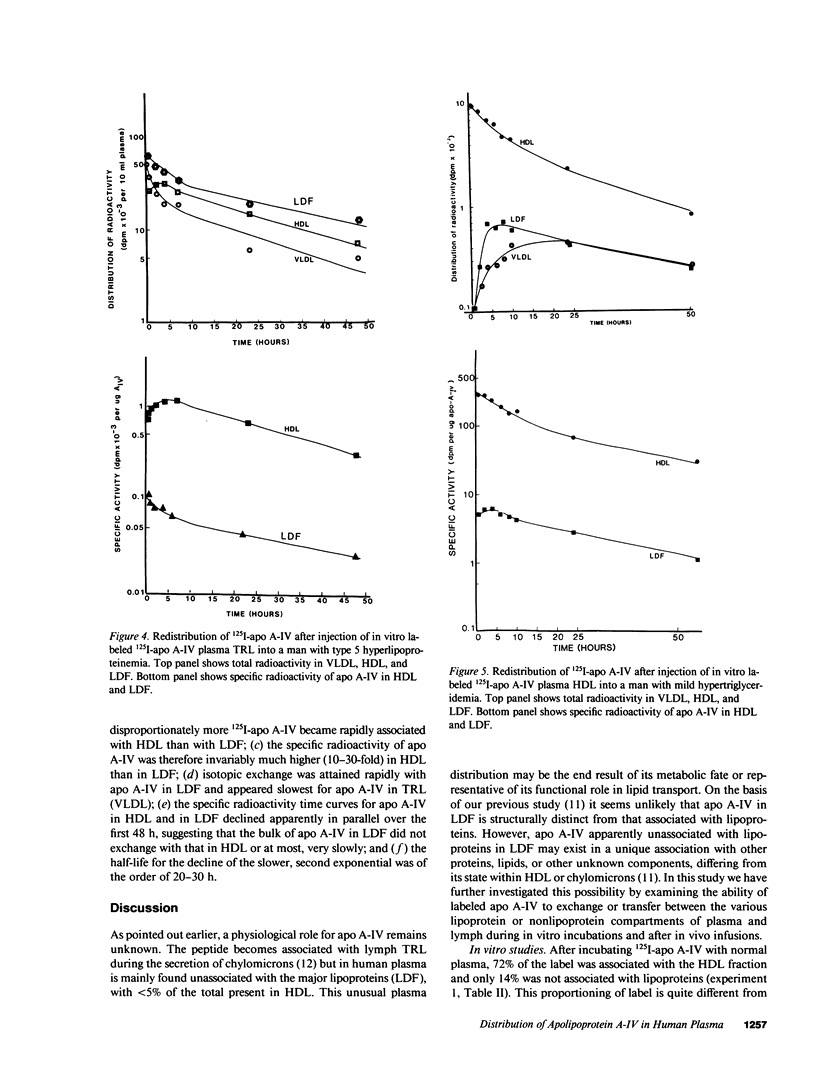
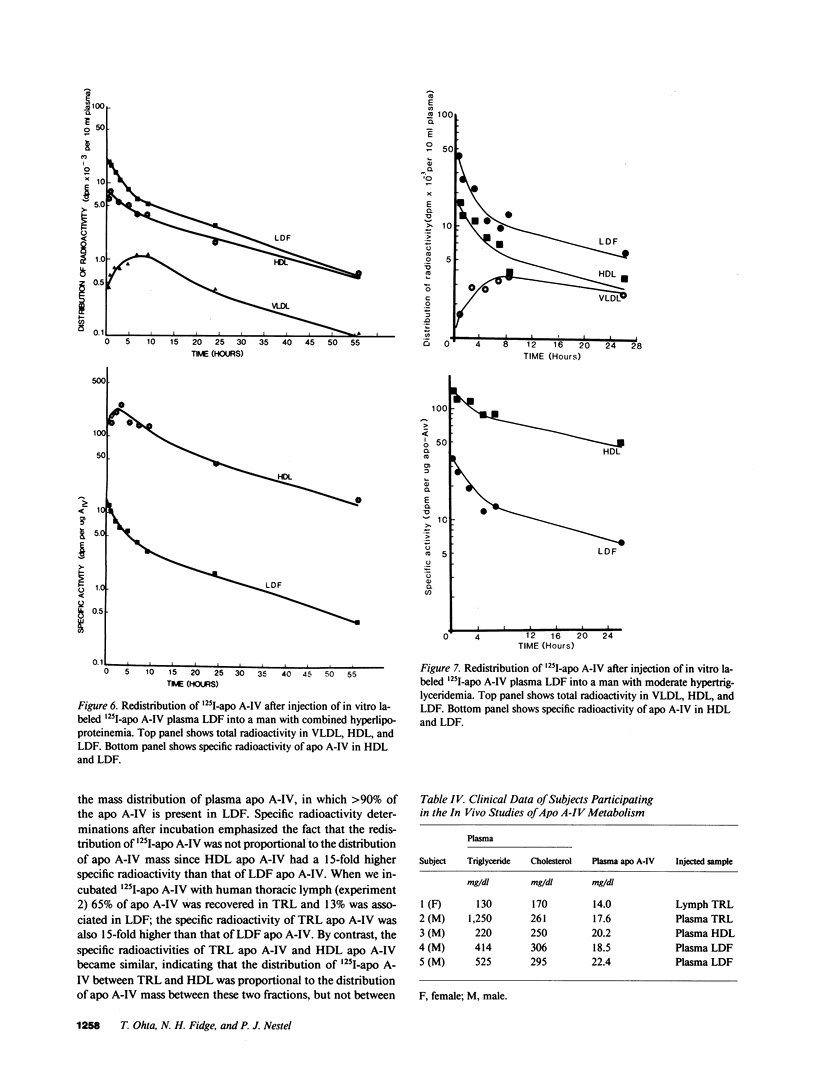
To investigate the unique distribution in plasma of apolipoprotein A-IV (apo A-IV) we have determined, in a series of in vitro and in vivo studies, the redistribution among lipoproteins of 125I-apo A-IV. Free 125I-apo A-IV associated predominantly with high density lipoprotein (HDL) (72 +/- 3.5%) in incubations with plasma, and with triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRL) (65 +/- 3.0%) in incubations with lymph, rather than with the lipoprotein-deficient fraction (LDF) where greater than 90% of apo A-IV resides. Incubations with 125I-apo A-IV (incorporated within HDL or TRL) also resulted in similar redistributions of label. Specific radioactivities of apo A-IV in HDL and in TRL were of a similar order and 15-fold higher than those in LDF. However, when 125I-apo A-IV in LDF was incubated with plasma, 57 +/- 2.6% of label remained in the LDF, though the specific radioactivity of apo A-IV in HDL was 15-fold higher than in LDF. Thus, apo A-IV apparently exchanges freely between TRL, HDL, and a part of apo A-IV in LDF, but most of apo A-IV in LDF is refractive to free exchange or transfer. In vivo experiments carried out in five subjects, in which 125I-apo A-IV was injected within TRL, HDL, or LDF, were consistent with the in vitro data in showing rapid exchange of label among plasma apo A-IV containing fractions with much higher specific radioactivities in HDL than in LDF (10-30-fold). However, the small fraction of apo A-IV in LDF that did become labeled was removed from plasma in a biexponential fashion and at the same rate as from HDL. Thus, only a small fraction of the bulk of apo A-IV in plasma LDF exchanges freely with apo A-IV in TRL and HDL, suggesting that apo A-IV in LDF exists in at least two pools. This is consistent with our previous findings that apo A-IV in plasma is present in two distinct complexes with lipids and other peptides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-On H., Roheim P. S., Eder H. A. Serum lipoproteins and apolipoproteins in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI108329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Utermann G. An apolipoprotein homolog of rat apolipoprotein A-IV in human plasma. Isolation and partial characterisation. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 1;93(3):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLamatre J. G., Hoffmeier C. A., Lacko A. G., Roheim P. S. Distribution of apolipoprotein A-IV between the lipoprotein and the lipoprotein-free fractions of rat plasma: possible role of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. J Lipid Res. 1983 Dec;24(12):1578–1585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delamatre J. G., Roheim P. S. The response of apolipoprotein A-IV to cholesterol feeding in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 13;751(2):210–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H. The redistribution and metabolism of iodinated apolipoprotein A-IV in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 14;619(1):129–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N., Poulis P. Studies on the metabolism of rat serum very low density apolipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1975 Sep;16(5):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidez L. I., Swaney J. B., Murnane S. Analysis of rat serum apolipoproteins by isoelectric focusing. I. Studies on the middle molecular weight subunits. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jan;18(1):59–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Glickman R. M., Riley J. W., Quinet E. Human apolipoprotein A-IV. Intestinal origin and distribution in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI109745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff M. W., Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J., Billington T., Watson B. Metabolism of C-apolipoproteins: kinetics of C-II, C-III1 and C-III2, and VLDL-apolipoprotein B in normal and hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. J Lipid Res. 1981 Nov;22(8):1235–1246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Fidge N. H., Tan M. H. Increased lipoprotein-remnant formation in chronic renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1982 Aug 5;307(6):329–333. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198208053070601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J. Characterization of apolipoprotein A-IV complexes and A-IV isoforms in human lymph and plasma lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14888–14893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Braithwaite F., Eder H. A. Characterization of the apolipoproteins of rat plasma lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 25;16(2):271–278. doi: 10.1021/bi00621a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Beisiegel U. Apolipoprotein A-IV: a protein occurring in human mesenteric lymph chylomicrons and free in plasma. Isolation and quantification. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(2):333–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lenten B. J., Roheim P. S. Changes in the concentrations and distributions of apolipoproteins of the aging rat. J Lipid Res. 1982 Nov;23(8):1187–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W. Isolation and characterization of an apoprotein from the d less than 1.006 lipoproteins of human and canine lymph homologous with the rat A-IV apoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):287–292. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Relative contributions by liver and intestine to individual plasma apolipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7316–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]