Abstract
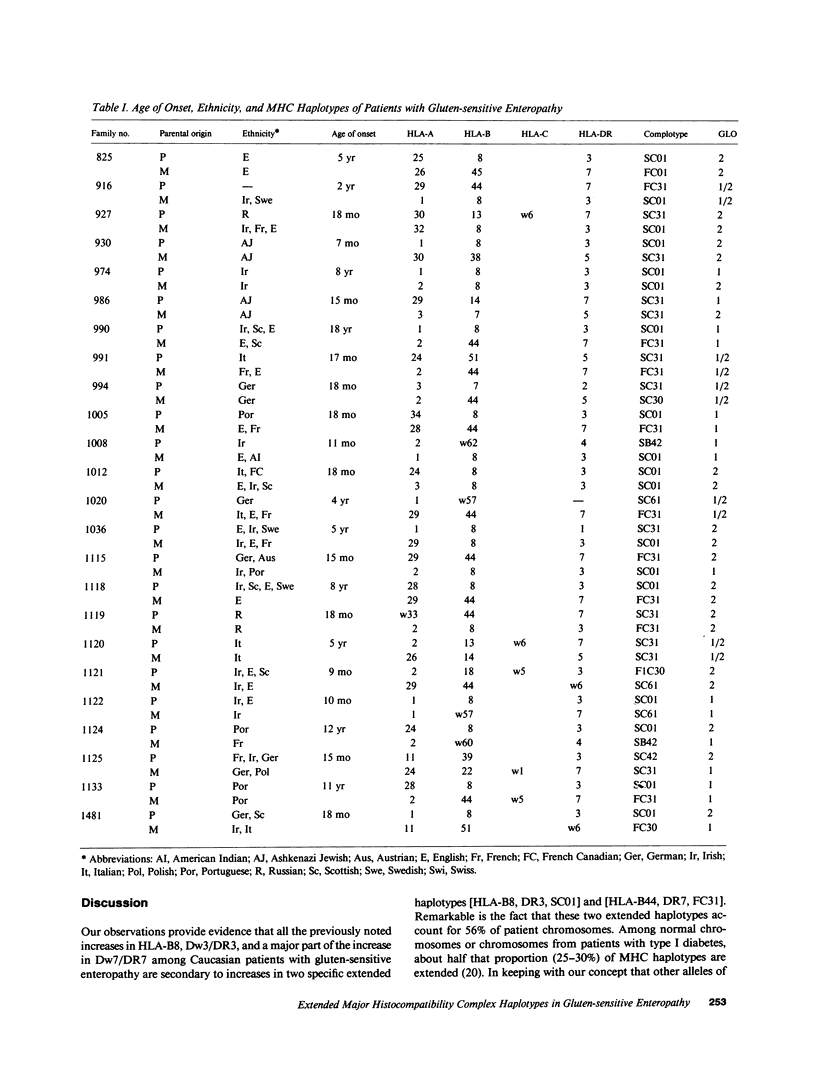
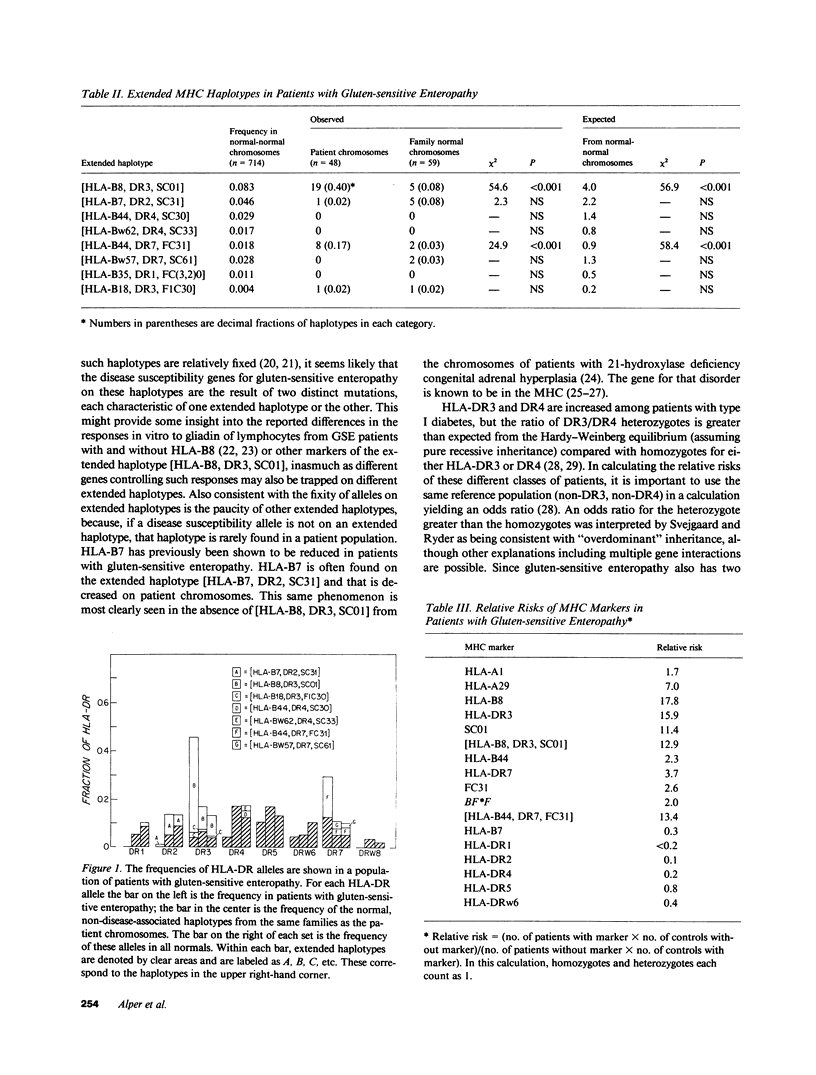
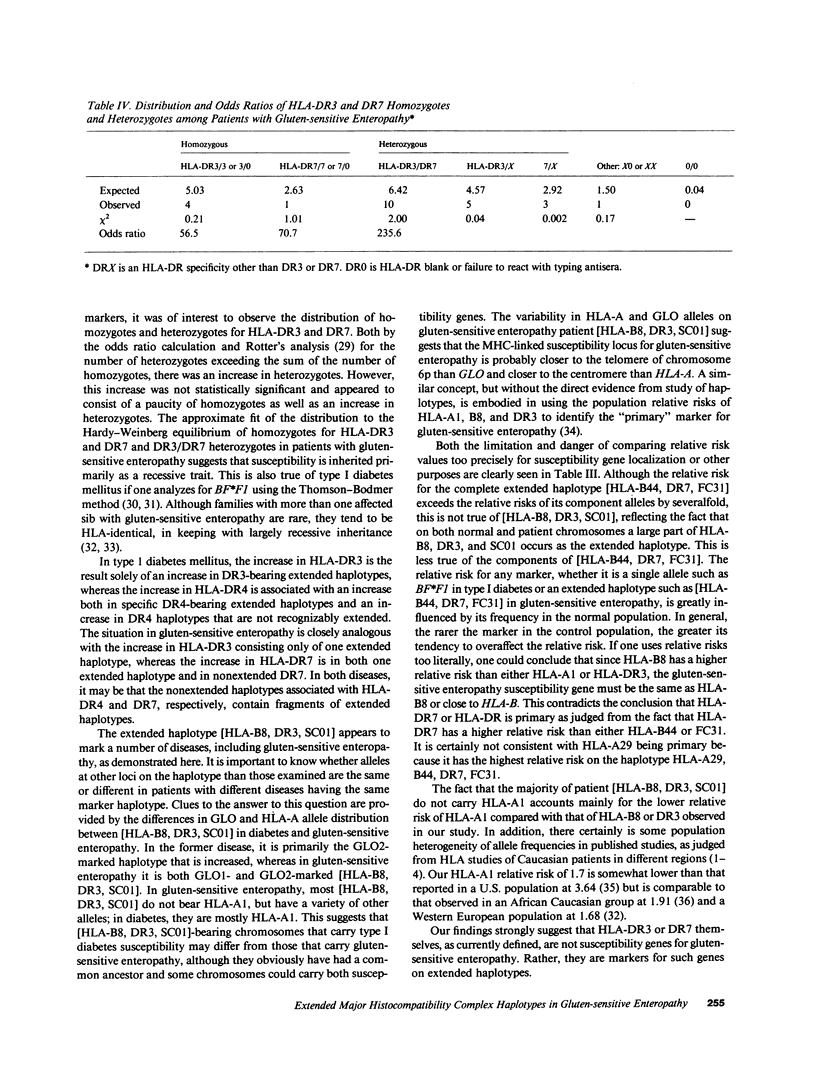
We have studied major histocompatibility complex markers in randomly ascertained Caucasian patients with gluten-sensitive enteropathy and their families. The frequencies of extended haplotypes, defined as haplotypes of specific HLA-B, DR, BF, C2, C4A, and C4B allelic combinations, occurring more frequently than expected, were compared on patient chromosomes, on normal chromosomes from the study families, and on chromosomes from normal families. Over half of patient chromosomes consisted almost entirely of two extended haplotypes [HLA-B8, DR3, SC01] and [HLA-B44, DR7, FC31] which, with nonextended HLA-DR7, accounted for the previously observed HLA markers of this disease: HLA-B8, DR3, and DR7. There was no increase in HLA-DR3 on nonextended haplotypes or in other extended haplotypes with HLA-DR3 or DR7. The distribution of homozygotes and heterozygotes for HLA-DR3 and DR7 was consistent with recessive inheritance of the major histocompatibility complex-linked susceptibility gene for gluten-sensitive enteropathy. On the other hand, by odds ratio analysis and from the sum of DR3 and DR7 homozygotes compared with DR3/DR7 heterozygotes, there was an increase in heterozygotes and a decrease in homozygotes suggesting the presence of modifying phenomena.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Awdeh Z. L., Raum D. D., Yunis E. J. Extended major histocompatibility complex haplotypes in man: role of alleles analogous to murine t mutants. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Aug;24(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Boenisch T., Watson L. Genetic polymorphism in human glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):68–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism in human C2: evidence for genetic linkage between C2 and Bf. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Raum D., Karp S., Awdeh Z. L., Yunis E. J. Serum complement 'supergenes' of the major histocompatibility complex in man (complotypes). Vox Sang. 1983;45(1):62–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb04124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Alper C. A. Genetic polymorphism of human complement C4 and detection of heterozygotes. Nature. 1979 Nov 8;282(5735):205–207. doi: 10.1038/282205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Extended HLA/complement allele haplotypes: evidence for T/t-like complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):259–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahams D. Medicine and the law. Consent to medical treatment in prison. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1269–1269. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92711-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Mapping of steroid 21-hydroxylase genes adjacent to complement component C4 genes in HLA, the major histocompatibility complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G., Woodrow J. C. Genetic susceptibility in diabetes mellitus: analysis of the HLA association. Br Med J. 1976 Oct 9;2(6040):846–848. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6040.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi M., Borelli I., Olivetti E., Richiardi P., Wright P., Ansaldi N., Barbera C., Santini B. Two HLA-D and DR alleles are associated with coeliac disease. Tissue Antigens. 1979 Oct;14(4):309–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb00854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont B., Oberfield S. E., Smithwick E. M., Lee T. D., Levine L. S. Close genetic linkage between HLA and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (21-hydroxylase deficiency). Lancet. 1977 Dec 24;2(8052-8053):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Nelson D. L., Katz A. J., Bernardin J. E., Kasarda D. D., Hague N. E., Strober W. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Influence of histocompatibility type on gluten sensitivity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):227–233. doi: 10.1172/JCI109848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Rogentine G. N., Strober W. Predominance of histocompatibility antigen HL-A8 in patients with gluten-sensitive enteropathy. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1602–1605. doi: 10.1172/JCI106958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Strober W. HL-A antigens and adult coeliac disease. Lancet. 1972 Dec 16;2(7790):1310–1310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92680-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Hodge S. E., Rotter J. I. Evidence for recessive and against dominant inheritance at the HLA-"linked" locus in coeliac disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):263–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keuning J. J., Peña A. S., van Leeuwen A., van Hooff J. P., va Rood J. J. HLA-DW3 associated with coeliac disease. Lancet. 1976 Mar 6;1(7958):506–508. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90294-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kömpf J., Bissbort S., Gussmann S., Ritter H. Polymorphism of red cell glyoxalase I (EI: 4.4.1.5); a new genetic marker in man. Investigation of 169 mother-child combinations. Humangenetik. 1975;27(2):141–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00273329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauff G., Alper C. A., Awdeh Z., Batchelor J. R., Bertrams J., Bruun-Petersen G., Dawkins R. L., Démant P., Edwards J., Grosse-Wilde H. Statement on the nomenclature of human C4 allotypes. Immunobiology. 1983 Mar;164(2):184–191. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(83)80009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann V. J., McCluskey J., Kay P. H., Zilko P. J., Christiansen F. T., Dawkins R. L. HLA and complement genetic markers in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia. 1983 Mar;24(3):221–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00250171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Green A., Dunsworth T., Svejgaard A., Barbosa J., Rich S. S., Iselius L., Platz P., Ryder L. P. Heterozygous expression of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) determinants in the HLA system. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Mar;35(2):201–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougenot J. F., Hors J., Schmid M., Cathelineau L., Navarro J., Polonovski C. Les antigènes HLA dans la maladie caeliaque et l'intolérance digestive aux protéines du lait de vache chez l'enfant. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1977 Jun-Jul;1(6-7):507–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerup J., Platz P., Andersen O. O., Christy M., Lyngsoe J., Poulsen J. E., Ryder L. P., Nielsen L. S., Thomsen M., Svejgaard A. HL-A antigens and diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1974 Oct 12;2(7885):864–866. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Alper C. A., Stein R., Gabbay K. H. Genetic marker for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1979 Jun 9;1(8128):1208–1210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91895-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Awdeh Z., Alper C. A. BF types and the mode of inheritance of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Immunogenetics. 1981;12(1-2):59–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01561651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Awdeh Z., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A., Gabbay K. H. Extended major histocompatibility complex haplotypes in type I diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):449–454. doi: 10.1172/JCI111441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Anderson C. E., Rubin R., Congleton J. E., Terasaki P. I., Rimoin D. L. HLA genotypic study of insulin-dependent diabetes the excess of DR3/DR4 heterozygotes allows rejection of the recessive hypothesis. Diabetes. 1983 Feb;32(2):169–174. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singal D. P., Blajchman M. A. Histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens, lymphocytotoxic antibodies and tissue antibodies in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1973 Jun;22(6):429–432. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.6.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes P. L., Asquith P., Holmes G. K., MacKintosh P., Cooke W. T. Inheritance and influence of histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens in adult coeliac disease. Gut. 1973 Aug;14(8):627–630. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.8.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Ryder L. P. HLA genotype distribution and genetic models of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann Hum Genet. 1981 Jul;45(Pt 3):293–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1981.tb00340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Chaplin D. D., Weis J. H., Dupont B., New M. I., Seidman J. G. Two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes are located in the murine S region. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):465–467. doi: 10.1038/312465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



