Abstract
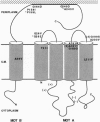
Five proteins (MotA, MotB, FliG, FliM, and FliN) have been implicated in energizing flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. One model for flagellar function envisions that MotA and MotB comprise the stator of a rotary motor and that FliG, FliM, and FliN are part of the rotor. MotA probably functions as a transmembrane proton channel, and MotB has been proposed to anchor MotA to the peptidoglycan of the cell wall. To study interactions between the Mot proteins themselves and between them and other components of the flagellar motor, we attempted to isolate extragenic suppressors of 13 dominant or partially dominant motB missense mutations. Four of these yielded suppressors, which exhibited widely varying efficiencies of suppression. The pattern of suppression was partially alleles-specific, but no suppressor seriously impaired motility in a motB+ strain. Of 20 suppressors from the original selection, 15 were characterized by DNA sequencing. Fourteen of these cause single amino acid changes in MotA. Thirteen alter residues in, or directly adjacent to, the putative periplasmic loops of MotA, and the remaining one alters a residue in the middle of the fourth predicted transmembrane helix of MotA. We conclude that the MotA and MotB proteins form a complex and that their interaction directly involves or is strongly influenced by the periplasmic loops of MotA. The 15th suppressor from the original selection and 2 motB suppressors identified during a subsequent search cause single amino acid substitutions in FliG. This finding suggests that the postulated Mot-protein complex may be in close proximity to FliG at the stator-rotor interface of the flagellar motor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg H. C., Anderson R. A. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature. 1973 Oct 19;245(5425):380–382. doi: 10.1038/245380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Berg H. C. Mutations in the MotA protein of Escherichia coli reveal domains critical for proton conduction. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1433–1442. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90943-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Berg H. C. Restoration of torque in defective flagellar motors. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1678–1681. doi: 10.1126/science.2849208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Berg H. C. The MotA protein of E. coli is a proton-conducting component of the flagellar motor. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):439–449. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90595-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Kim D. Y., Berg H. C. Mutant MotB proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4049–4055. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4049-4055.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F. The bacterial flagellar motor. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;1(2):75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block S. M., Berg H. C. Successive incorporation of force-generating units in the bacterial rotary motor. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):470–472. doi: 10.1038/309470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Mandel G., Simon M. I. Integral membrane proteins required for bacterial motility and chemotaxis. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1982;35:123–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chun S. Y., Parkinson J. S. Bacterial motility: membrane topology of the Escherichia coli MotB protein. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):276–278. doi: 10.1126/science.2447650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mot R., Vanderleyden J. The C-terminal sequence conservation between OmpA-related outer membrane proteins and MotB suggests a common function in both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, possibly in the interaction of these domains with peptidoglycan. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Apr;12(2):333–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Attachment of flagellar basal bodies to the cell envelope: specific attachment to the outer, lipopolysaccharide membrane and the cyoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):396–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.396-407.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean G. E., Macnab R. M., Stader J., Matsumura P., Burks C. Gene sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of the motA protein, a membrane-associated protein required for flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):991–999. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.991-999.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis N. R., Irikura V. M., Yamaguchi S., DeRosier D. J., Macnab R. M. Localization of the Salmonella typhimurium flagellar switch protein FliG to the cytoplasmic M-ring face of the basal body. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6304–6308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis N. R., Sosinsky G. E., Thomas D., DeRosier D. J. Isolation, characterization and structure of bacterial flagellar motors containing the switch complex. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 28;235(4):1261–1270. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glagolev A. N., Skulachev V. P. The proton pump is a molecular engine of motile bacteria. Nature. 1978 Mar 16;272(5650):280–282. doi: 10.1038/272280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irikura V. M., Kihara M., Yamaguchi S., Sockett H., Macnab R. M. Salmonella typhimurium fliG and fliN mutations causing defects in assembly, rotation, and switching of the flagellar motor. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):802–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.802-810.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenal U., White J., Shapiro L. Caulobacter flagellar function, but not assembly, requires FliL, a non-polarly localized membrane protein present in all cell types. J Mol Biol. 1994 Oct 21;243(2):227–244. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Aizawa S. The bacterial flagellum and flagellar motor: structure, assembly and function. Adv Microb Physiol. 1991;32:109–172. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Berg H. C. Isotope and thermal effects in chemiosmotic coupling to the flagellar motor of Streptococcus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Dapice M., Reese T. S. Effects of mot gene expression on the structure of the flagellar motor. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):575–584. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Khan I. H., Reese T. S. New structural features of the flagellar base in Salmonella typhimurium revealed by rapid-freeze electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2888–2896. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2888-2896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Homma M., Kutsukake K., Macnab R. M. Flagellar switch of Salmonella typhimurium: gene sequences and deduced protein sequences. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3247–3257. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3247-3257.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Sequence of the flaA (cheC) locus of Escherichia coli and discovery of a new gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):1007–1012. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.1007-1012.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Adler J., Gargus J. J., Hogg R. W. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malakooti J., Komeda Y., Matsumura P. DNA sequence analysis, gene product identification, and localization of flagellar motor components of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2728–2734. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2728-2734.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D. Bacterial motility and chemotaxis. Adv Microb Physiol. 1992;33:277–346. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson M. D., Tedesco P., Berg H. C., Harold F. M., Van der Drift C. A protonmotive force drives bacterial flagella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsura S., Shioi J., Imae Y. Motility in Bacillus subtilis driven by an artificial protonmotive force. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80581-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Houts S. E. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raha M., Sockett H., Macnab R. M. Characterization of the fliL gene in the flagellar regulon of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(8):2308–2311. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.8.2308-2311.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. G., Silverman M., Simon M. I. Localization of proteins controlling motility and chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):657–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.657-665.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman S. J., Frantz B. B., Matsumura P. Gene sequence, overproduction, purification and determination of the wild-type level of the Escherichia coli flagellar switch protein FliG. Gene. 1993 Oct 29;133(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90232-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Matsumura P., Simon M. The identification of the mot gene product with Escherichia coli-lambda hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3126–3130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Matsumura P., Vacante D., Dean G. E., Macnab R. M. Nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli motB gene and site-limited incorporation of its product into the cytoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):244–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.244-252.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolz B., Berg H. C. Evidence for interactions between MotA and MotB, torque-generating elements of the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):7033–7037. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.7033-7037.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Aizawa S., Kihara M., Isomura M., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M. Genetic evidence for a switching and energy-transducing complex in the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1172–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1172-1179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Fujita H., Ishihara A., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Subdivision of flagellar genes of Salmonella typhimurium into regions responsible for assembly, rotation, and switching. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):187–193. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.187-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]