Abstract
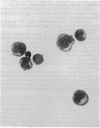
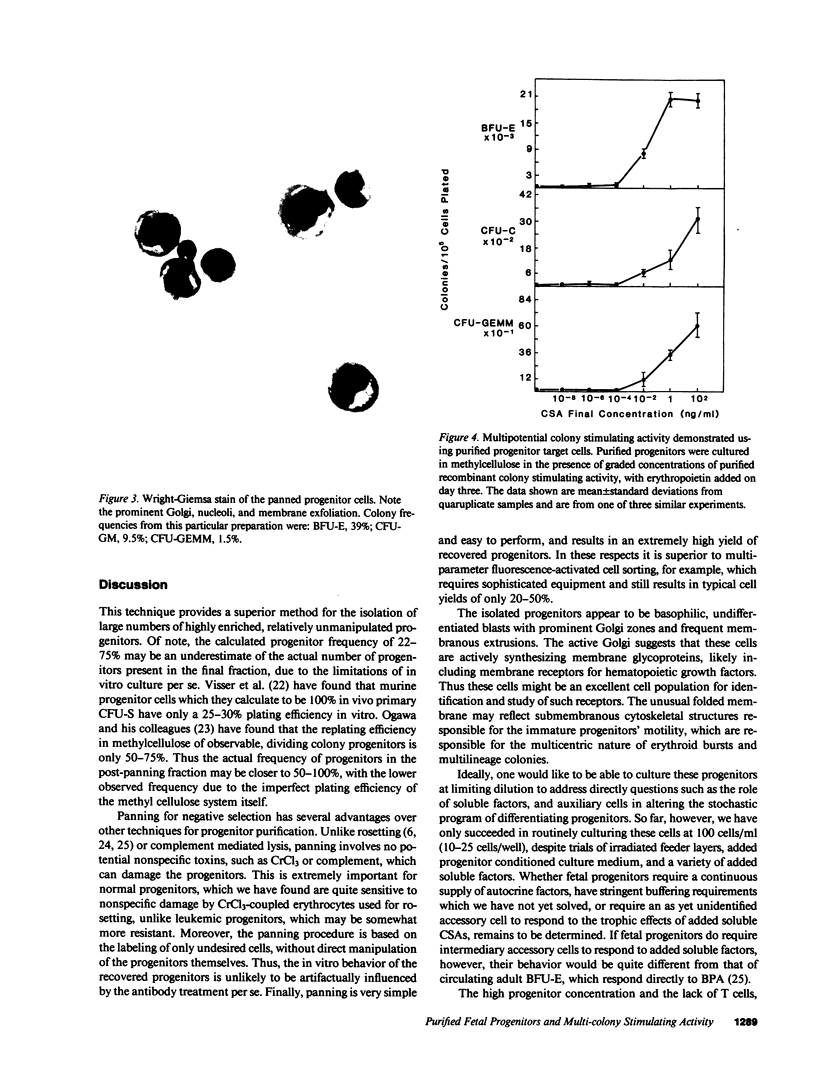
To facilitate the direct study of progenitor cell biology, we have developed a simple and efficient procedure based upon negative selection by panning to purify large numbers of committed erythroid and myeloid progenitors from human fetal liver. The nonadherent, panned cells constitute a highly enriched population of progenitor cells, containing 30.4 +/- 13.1% erythrocyte burst forming units (BFU-E), 5.5 +/- 1.9% granulocyte-macrophage colony forming units (CFU-GM), and 1.4 +/- 0.7% granulocyte-erythroid-macrophage-megakaryocyte colony forming units (CFU-GEMM) as assayed in methylcellulose cultures. These cells are morphologically immature blasts with prominent Golgi. This preparative method recovers 60-100% of the committed progenitors detectable in unfractionated fetal liver and yields 2-30 X 10(6) progenitors from each fetal liver sample, and thus provides sufficient numbers of enriched progenitors to allow direct biochemical and immunologic manipulation. Using this technique, a purified recombinant protein previously thought to have only granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating activity (GM-CSA) is shown to have both burst promoting activity and multipotential colony stimulating activity. Progenitor purification by panning thus appears to be a simple, efficient method that should facilitate the direct study of committed hematopoietic progenitors and their differentiation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beverley P. C., Linch D., Delia D. Isolation of human haematopoietic progenitor cells using monoclonal antibodies. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):332–333. doi: 10.1038/287332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Sharrow S. O., Shearer G. M. T cell subpopulations required for the human cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to influenza virus: evidence for T cell help. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):487–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodger M. P., Francis G. E., Delia D., Granger S. M., Janossy G. A monoclonal antibody specific for immature human hemopoietic cells and T lineage cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2269–2274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Metcalf D. The growth of mouse bone marrow cells in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):287–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukes P. P., Ma A., Clemons G. K., Meytes D. Measurement of human erythroid burst-promoting activity by a specific cell culture assay. Exp Hematol. 1985 Jan;13(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A. Monoclonal antibodies that bind to the human erythrocyte-membrane glycoproteins glycophorin A and Band 3 [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):334–335. doi: 10.1042/bst0080334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauser A. A., Messner H. A. Granuloerythropoietic colonies in human bone marrow, peripheral blood, and cord blood. Blood. 1978 Dec;52(6):1243–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauser A. A., Messner H. A. Granuloerythropoietic colonies in human bone marrow, peripheral blood, and cord blood. Blood. 1978 Dec;52(6):1243–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. The chromic chloride method of coupling antigens to erythrocytes: definition of some important parameters. J Immunol Methods. 1976;10(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg P. L., Baker S., Link M., Minowada J. Immunologic selection of hemopoietic precursor cells utilizing antibody-mediated plate binding ("panning"). Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):190–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Beveridge R. P., Schlossman S. F. Isolation of myeloid progenitor cells from peripheral blood of chronic myelogenous leukemia patients. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann I. M., Bodger M. P., Hoffbrand A. V. Development of pluripotent hematopoietic progenitor cells in the human fetus. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):118–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan M. W., Lutton J. D., Levere R. D., Rieder R. F., Cederqvist L. L. In vitro culture of erythroid colonies from human fetal liver and umbilical cord blood. Br J Haematol. 1979 Apr;41(4):477–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb05885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Sieber F., Winterhalter K. H. Erythroid colony formation in cultures of mouse and human bone marrow: analysis of the requirement for erythropoietin by gel filtration and affinity chromatography on agarose-concanavalin A. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Apr;83(2):309–320. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linch D. C., Nathan D. G. T cell and monocyte-derived burst-promoting activity directly act on erythroid progenitor cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):775–777. doi: 10.1038/312775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Metcalf D., von Melchner H., Burgess A. W. Isolation of murine fetal hemopoietic progenitor cells and selective fractionation of various erythroid precursors. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):376–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platsoucas C. D., Beck J. D., Kapoor N., Good R. A., Gupta S. Separation of human bone marrow cell populations by density gradient electrophoresis: differential mobilities of myeloid (CFU-C), monocytoid, and lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1981 Apr;59(2):345–354. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley P. T., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B. M., Farley B. A. Erythroid colony formation from human fetal liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):984–988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. L., Rup D., Lodish H. F. Difficulties in the quantification of asialoglycoprotein receptors on the rat hepatocyte. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9033–9036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Axelrad A. A., McLeod D. L., Shreeve M. M. Induction of colonies of hemoglobin-synthesizing cells by erythropoietin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1542–1546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Suda J., Ogawa M. Disparate differentiation in mouse hemopoietic colonies derived from paired progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2520–2524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser J. W., Bauman J. G., Mulder A. H., Eliason J. F., de Leeuw A. M. Isolation of murine pluripotent hemopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1576–1590. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. R., Opelz G., Cline M. J. Characterization of functionally distinct lymphoid and myeloid cells from human blood and bone marrow. I. Separation by a buoyant density gradient technique. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(1-2):63–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90159-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welte K., Platzer E., Lu L., Gabrilove J. L., Levi E., Mertelsmann R., Moore M. A. Purification and biochemical characterization of human pluripotent hematopoietic colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]