Multiple rows have been removed from Table 4 due to a typesetting error. The publisher apologizes for the error. Please view the correct Table 4 here.
Table 4. Parameter estimates and variance components of the HLM models tested (Study 1).
| Fixed effects | Random effects | ||||||||||||
| Model equations |
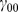
|
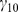
|
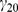
|
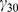
|
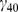
|
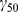
|
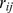
|
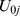
|
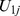
|
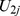
|
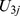
|
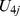
|
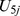
|
| Intercept-only model (empty model) | |||||||||||||
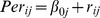
|
5.67** | - | - | - | - | - | .42 | .13 | - | - | - | - | - |
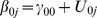
|
|||||||||||||
| Model 1a | |||||||||||||
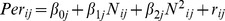
|
5.67** | −.44** | −.03 | - | - | - | .33 | .15 | .17 | ns | - | - | - |
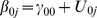
|
|||||||||||||
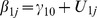
|
|||||||||||||
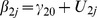
|
|||||||||||||
| Model 1b | |||||||||||||
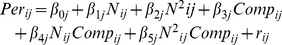
|
5.66** | −.48** | .04 | .05 | −.04 | .11† | .30 | .16 | .14 | ns | .02 | ns | ns |
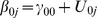
|
|||||||||||||
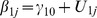
|
|||||||||||||
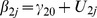
|
|||||||||||||
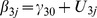
|
|||||||||||||
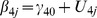
|
|||||||||||||
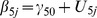
|
|||||||||||||
Note: ** p<.01 (two-tailed);
* p<.05 (two-tailed);
p<.10 (two-tailed).
Per = performance; Comp = task complexity; N = neuroticism.
Reference
- 1. Debusscher J, Hofmans J, De Fruyt F (2014) The Curvilinear Relationship between State Neuroticism and Momentary Task Performance. PLoS ONE 9(9): e106989 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0106989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


