Abstract
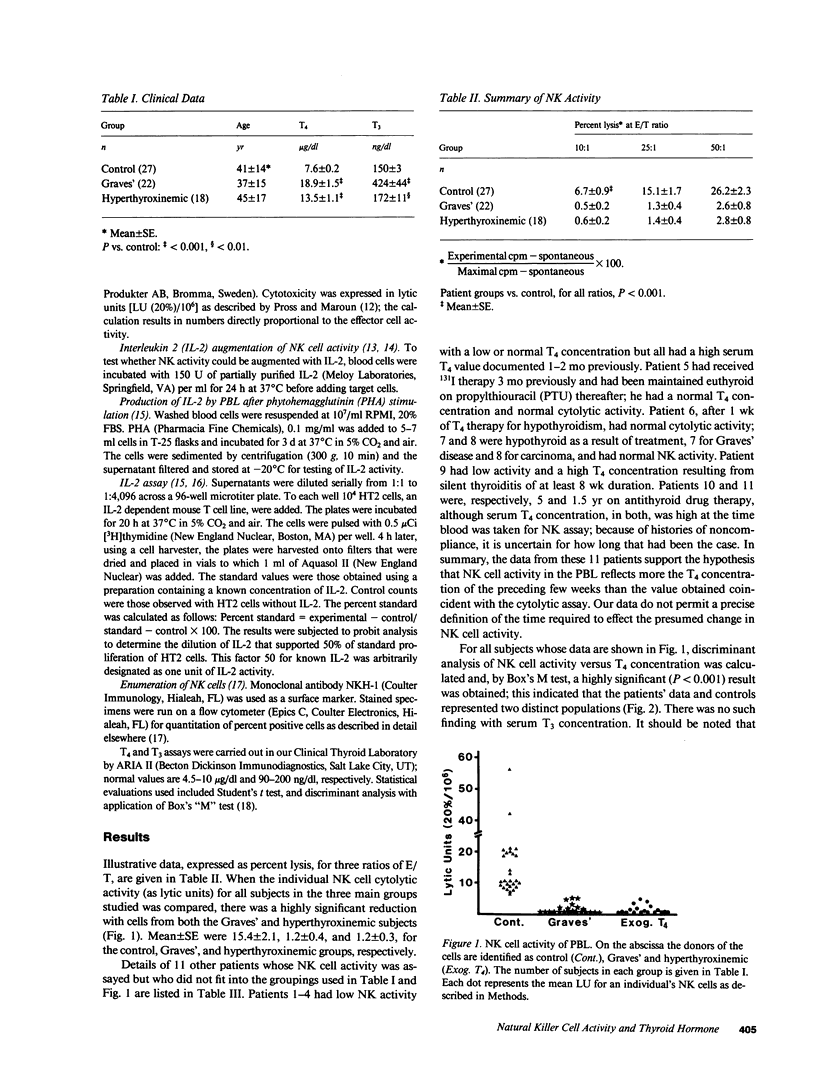
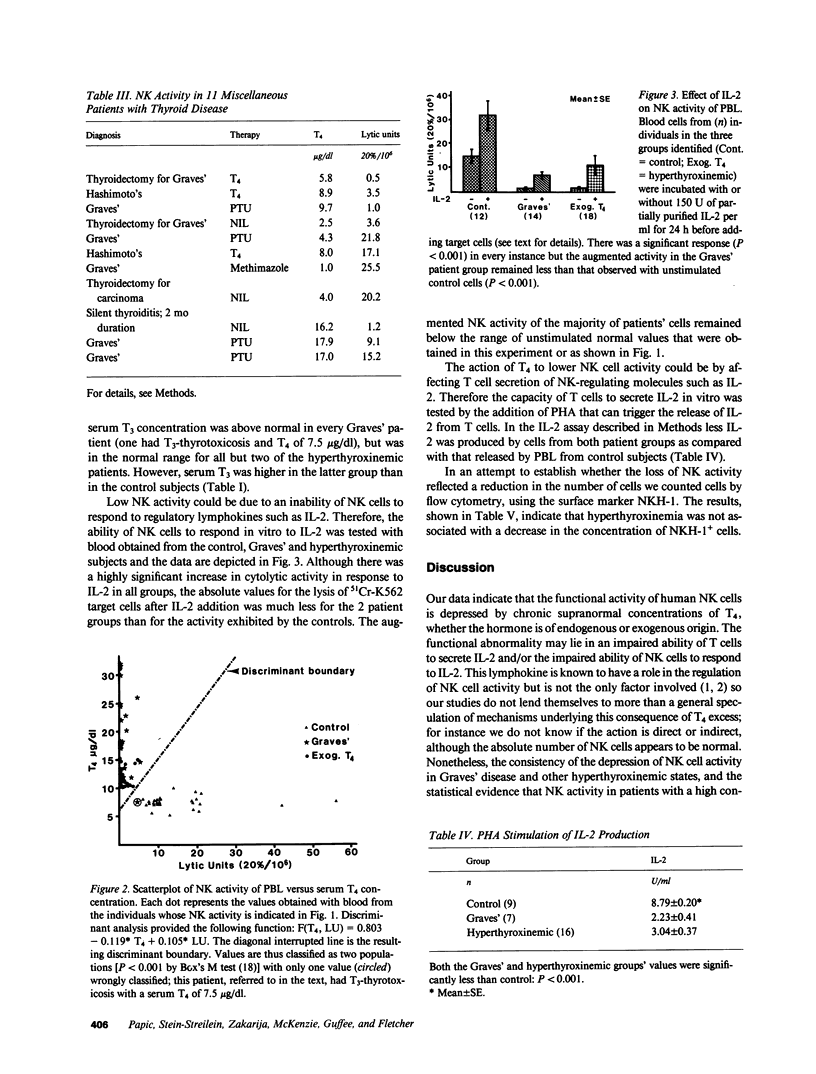
Natural killer (NK) cells were assessed in patients with hyperthyroxinemia due to Graves' disease or treatment with thyroxine (T4). Cytolytic activity was measured with 51Cr-labeled K562 tumor cells and NK enumeration was by flow cytometry using NKH-1 monoclonal antibody to identify the relevant surface marker. Activity was uniformly decreased in association with hyperthyroxinemia, regardless of the underlying pathology; however, there was no reduction in the number of NKH-1+ cells. NK activity was enhanced by addition of interleukin 2 (IL-2) in both control and patients' cells although the value in the latter instance failed to reach the basal control level. Production of IL-2 by lymphocytes from hyperthyroxinemic subjects, in response to phytohemagglutinin, was also reduced. Since NK cells are thought to act as a defense against viral infections and some malignancies and may play a role in autoregulation of the immune system, this effect of T4 may have significant biological implications.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amino N., Mori H., Iwatani Y., Asari S., Izumiguchi Y., Miyai K. Peripheral K lymphocytes in autoimmune thyroid disease: decrease in Graves' disease and increase in Hashimoto's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Mar;54(3):587–591. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-3-587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Biron C. A., Welsh R. M. Elevated natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity, plasma interferon, and tumor cell rejection in mice persistently infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):991–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Irvine W. J., Davidson N. M., Wu F. T, B and K cells in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):17–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Kiessling R., Andersson B. Human fetal thymus and bone marrow contain target cells for natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jan;11(1):8–12. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey P., Edwards A., Honeyman M., McCarthy W. H. Low natural-killer-cell activity in familial melanoma patients and their relatives. Br J Cancer. 1979 Jul;40(1):113–122. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey P., Hobbs A., Edwards A., McCarthy W. H., McGovern V. J. Relationship between natural killer cell activity and histological features of lymphocyte infiltration and partial regression of the primary tumor in melanoma patients. Cancer Res. 1982 Jan;42(1):363–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar J. C., Borges M., Iflah S., Kleinmann R. E., Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H. Elevated serum thyroxine concentration in patients receiving "replacement" doses of levothyroxine. J Endocrinol Invest. 1982 Mar-Apr;5(2):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF03350495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatani Y., Amino N., Kabutomori O., Mori H., Tamaki H., Motoi S., Izumiguchi Y., Miyai K. Decrease of peripheral large granular lymphocytes in Graves' disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jan;55(1):239–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Civin C. I., Loken M. R., Phillips J. H. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4480–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Heterogeneity of natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:359–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhof P. C., Morales A., Baines M. G. Quantitation of a whole blood assay for human natural killer cell activity. J Immunol Methods. 1981;42(3):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkston P., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous release of interleukin-2 by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 7;308(14):793–800. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304073081401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Maroun J. A. The standardization of NK cell assays for use in studies of biological response modifiers. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 30;68(1-2):235–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Ruscetti F. W., Neubauer R. H., Brown R. L., Kawakami T. G. Spontaneous release of a factor with properties of T cell growth factor from a continuous line of primate tumor T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Leitman S., Chang A. E., Ettinghausen S. E., Matory Y. L., Skibber J. M., Shiloni E., Vetto J. T. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1485–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon D., Rendell M., Williams J., Smith C., Ross D. A., Waud J. M., Howard J. E. Chemical hyperthyroidism: serum triiodothyronine levels in clinically euthyroid individuals treated with levothyroxine. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Mar;142(3):571–573. doi: 10.1001/archinte.142.3.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Lief F. S. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity against virus-infected target cells in humans. I. Characterization of the effector lymphocyte. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-Streilein J., Bennett M., Mann D., Kumar V. Natural killer cells in mouse lung: surface phenotype, target preference, and response to local influenza virus infection. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2699–2704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-Streilein J., Guffee J. In vivo treatment of mice and hamsters with antibodies to asialo GM1 increases morbidity and mortality to pulmonary influenza infection. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1435–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Human natural killer cells: biologic and pathologic aspects. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):489–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. R., Baur R., Schleusener H., Bandy-Dafoe P. Peripheral blood and intrathyroidal mononuclear cell populations in patients with autoimmune thyroid disorders enumerated using monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jan;56(1):164–169. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-1-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Zarling J. M. Autologous herpes simplex virus-infected cells are lysed by human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2011–2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarija M., McKenzie J. M., Banovac K. Clinical significance of assay of thyroid-stimulating antibody in Graves' disease. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):28–32. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Prete G. F., Maggi E., Mariotti S., Tiri A., Vercelli D., Parronchi P., Macchia D., Pinchera A., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Cytolytic T lymphocytes with natural killer activity in thyroid infiltrate of patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis: analysis at clonal level. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jan;62(1):52–57. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-1-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



