Abstract
Cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) provides three-dimensional (3D) structural information of bacteria preserved in a native, frozen-hydrated state. The typical low contrast of tilt-series images, a result of both the need for a low electron dose and the use of conventional defocus phase-contrast imaging, is a challenge for high-quality tomograms. We show that Zernike phase-contrast imaging allows the electron dose to be reduced. This limits movement of gold fiducials during the tilt series, which leads to better alignment and a higher-resolution reconstruction. Contrast is also enhanced, improving visibility of weak features. The reduced electron dose also means that more images at more tilt angles could be recorded, further increasing resolution.
Keywords: Defocus phase contrast (DPC), Zernike phase contrast (ZPC), cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET), bacteria, Caulobacter crescentus, Vibrio vulnificus
1. Introduction
Cryo-ET is currently the only method available through which small, unique objects such as bacterial cells can be imaged to produce three-dimensional (3D) structures at ~2 to 10 nm resolution (Milne and Subramaniam, 2009). The rapid freezing of specimens onto EM grids preserves the native arrangement of macromolecules, and eliminates the need for stains, chemical fixation, plastic embedding, and sectioning, which introduce artifacts (Lucic et al., 2008; Murphy and Jensen, 2007). However, several challenges are associated with cryo-ET imaging of bacterial specimens. First, cryo-ET data has an inherently low signal to noise ratio (SNR). Images are acquired under low electron dose conditions in order to preserve specimen integrity. Typically, total electron doses of ~60 to ~200 e−/Å2 are fractionated over an entire tilt series of ~65 to ~130 images, which corresponds to ~1 to ~2 e−/Å2 per image. Many researchers have implemented approaches to improve the SNR of the individual images of the tilt series by using high sensitivity/high resolution CCD cameras (Booth et al., 2006; Faruqi, 1998; Milazzo et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2003), energy filters (Grimm et al., 1997), and post-data collection image processing procedures (Frangakis and Hegerl, 2001; Narasimha et al., 2008). These efforts enable investigators to both record greater numbers of images and improve alignment of the tilt series images, which subsequently result in 3D reconstructions of higher final quality. In addition, due to the low contrast of cryopreserved, unstained biological specimens, micrographs are taken several μm under focus (i.e. a defocus of 4 – 16 μm under focus) in order to enhance the contrast of low-resolution features, including cellular membranes. Unfortunately, the enhanced contrast gained from defocus phase contrast (DPC) is achieved at the expense of reducing information from high-resolution features, such as viral capsid proteins.
To overcome these limitations, Zernike phase contrast transmission electron microscopy (ZPC-TEM) was advanced so that researchers could generate higher contrast images of ice-embedded specimens examined near-to-focus and eliminate the compromise between contrast and resolution. The development and improvement of ZPC cryo-EM tools for 2D image acquisition and single particle analysis of biological specimens has only been recently realized (Danev et al., 2009; Danev and Nagayama, 2001, 2008; Rochat et al., 2011; Shigematsu et al., 2010). The first application of ZPC-TEM for cryo-ET was demonstrated with T4 bacteriophage (Danev et al., 2010). Further studies have shown the technology’s promise when used to examine other small macromolecular complexes such as epsilon15 bacteriophage (Murata et al., 2010), the isolated flagellar hook-basal bodies from Vibrio alginolyticus (Hosogi et al., 2011), as well as the thinnest edges of eukaryotic cells (Fukuda and Nagayama, 2011). All the data presented in our study of bacterial cells was collected with a JEOL JEM-2200FS 200 kV FEG-TEM (JEOL Ltd., Japan) equipped with the Zernike phase plate airlock system located in the back-focal plane of the objective lens, an in-column energy filter (slit width 20 eV), a cryo-transfer specimen holder (Model 914; Gatan, Pleasanton, CA), and a 4k × 4k Gatan Ultrascan CCD camera. Here we present definitive results illustrating the success of ZPC cryo-ET technologies when applied to the generation of tomographic reconstructions of bacteria. Specifically, we have used ZPC cryo-ET to study intact, frozen-hydrated Caulobacter crescentus and Vibrio vulnificus cells.
2. Results and Discussion
The total electron dose employed for cryo-ET data collection depends on the ‘dose sensitivity’ of the biological target. Many of the bacterial species that have been studied using cryo-ET are able to withstand electron doses up to ~200 e−/Å2 with no apparent damage to the cell. However, there are species that are more radiation labile and this may limit studies of their ultrastructure. To establish the dose sensitivity of the two bacterial species in this study, cumulative electron dose series were collected (Figs. 1a and 1b). Each dose series image corresponded to an electron dose of ~5 e−/Å2 with a defocus of 4 μm under focus applied. We determined that the C. crescentus cells could withstand electron doses between 120 and 200 e−/Å2 without observed damage to the cell cytoplasm, cell periphery or flagellum, which is consistent with previous reports (Fig. 1a) (Briegel et al., 2006). However, upon inspection of the images of V. vulnificus cells, while the integrity of the cell membranes and the cytoplasm was stable to a total dose of ~120 e−/Å2, the sheathed bacterial flagellum incurred visible radiation damage (Fig. 1b). Strikingly, radiation damage was first observed in the confines of the sheathed flagellum after a cumulative dose of only ~60 e−/Å2 (Fig. 1b). The restriction of dose sensitivity to only the flagellum of V. vulnificus is unusual and has not been observed with flagella or appendages of other bacterial species examined. Most likely, the reduced dose tolerance is due to the macromolecular crowding within the membranous confines of the flagellar sheath, which limits the diffusion of the beam-induced radiolytic fragments and byproducts. In order to avoid visible radiation damage, the total electron dose for tilt series acquisition of V. vulnificus must be restricted to much less than ~60 e−/Å2. For DPC cryo-ET, the reduced dose would dampen the SNR, hamper the alignment of the images, and diminish quality of the final 3D reconstruction, especially in bacterial cells such as V. vulnificus.
Figure 1.
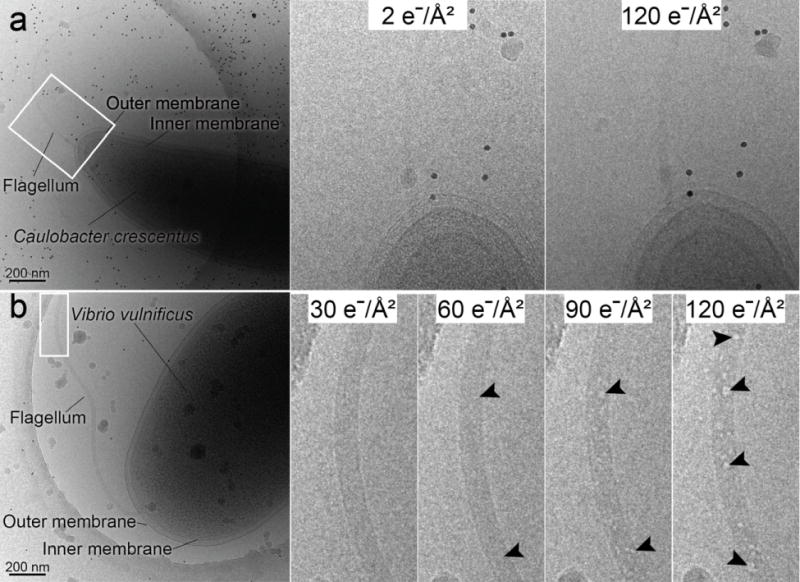
DPC cryo-EM images of frozen-hydrated bacteria. (a) Electron dose series images of C. crescentus. No beam-induced destruction of the cell or its appendages was observed up to doses of ~120 e−/Å2. Magnified views are of the boxed region at 2 e−/Å2 and 120 e−/Å2. (b) Electron dose series images of V. vulnificus. Indications of beam-induced damage to the flagellum noted after a dose of ~60 e−/Å2. Magnified views of the boxed region illustrate the unharmed flagellum structure at a dose of ~30 e−/Å2 and the increase in damage to the flagellum at doses of 60 e−/Å2, 90 e−/Å2, and 120 e−/Å2, arrowheads point to ‘bubbles’. Scale bars, 200 nm.
In order to assess the application of ZPC for tilt series image acquisition, we acquired sequential images of multiple individual bacterial cells. One image was collected with standard DPC conditions and the other was acquired using ZPC settings. The ZPC data was collected near-to-focus using a Zernike-style phase plate with a thin amorphous carbon film applied to a 5 × 5 array phase plate aperture disc. The carbon film thickness of the phase plate was ~27 nm, which corresponded to a π/2 phase shift (Danev et al., 2009), and a central hole dimension of ~0.75 μm (cut on periodicity of ~35 nm). Each recorded image was limited to an electron dose of ~1.5 or less e−/Å2, which matches the dose of a single tilt series image. After examining the DPC and ZPC images (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Fig. 1), we concluded that the ZPC images had improved SNR that allowed us to resolve features that were either barely discernable or undetectable in the equivalent DPC image. Some of the complexes unambiguously identified in the ZPC images include: individual pili, the core filament of the sheathed flagellum, macromolecular complexes throughout the cytoplasm, and outer membrane vesicles and their cargo. In addition, we quantified membrane intensity peaks from linear density profiles derived from measurements taken across the membranes of V. vulnificus cells (Figs. 3a, 3b and 3c). From the measurements, we concluded that the improvement in image contrast of the ZPC data was beneficial for achieving greater clarity of the measured spacing between the inner and outer membranes of the bacterial cell wall. In addition, the peak associated with the peptidoglycan layer (* in Figs. 3b, 3c) was also resolved in the ZPC data, whereas it was imperceptible in the DPC data.
Figure 2.
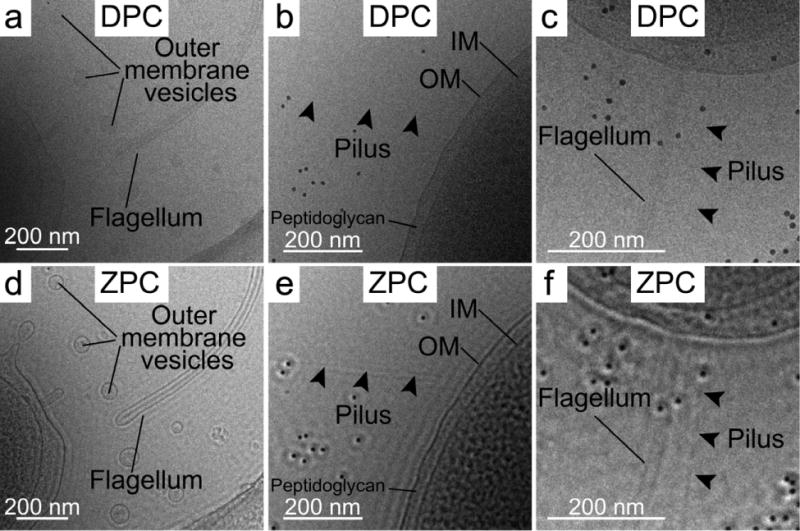
Enlarged views of DPC and ZPC cryo-EM images of V. vulnificus cells (whole cell images, Supplementary Figure 1). Single low dose (~1.5 e−/Å2) DPC (a, b, and c) and ZPC (d, e, and f) images of portions of individual V. vulnificus cells. Each image set highlights the improvement in image contrast and visibility of the flagellum, outer membrane vesicles, and pilus that was obtained with ZPC (d, e, and f) versus DPC (a, b, and c). Scale bars, 200 nm.
Figure 3.
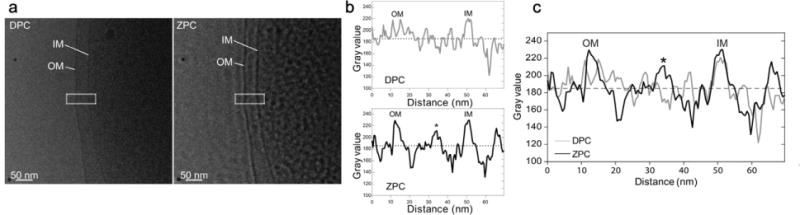
DPC and ZPC cryo-EM images and linear profiles through the cell wall envelope of a V. vulnificus cell. (a) Enlarged views from single low dose (~1.5 e−/Å2) DPC (left) and ZPC (right) images of the same V. vulnificus cell (OM: outer membrane; IM: inner membrane). (b) Linear profiles through the V. vulnificus envelope from regions highlighted with dashed boxes in a; OM: outer membrane peak; IM: inner membrane peak; the star (*) represents the peak in the ZPC profile corresponding to the discernible peptidoglycan layer. (c) Overlaid linear profiles through the V. vulnificus envelope from regions highlighted in a. OM: outer membrane peak; IM: inner membrane peak; the star (*) represents the peak in the ZPC profile corresponding to the peptidoglycan layer. Scale bars, 200 nm.
To test the utility and potential of ZPC cryo-ET for the structural characterization of bacteria, we collected and analyzed multiple data sets of C. crescentus and V. vulnificus cells collected under both DPC and ZPC conditions at total electron doses of between ~30 e−/Å2 and ~120 e−/Å2. We determined several important points. First, using ZPC approaches, we reduced the total electron dose used to acquire a tilt series by 75%, in other words, from ~120 e−/Å2 to ~30 e−/Å2 and generated high contrast, high SNR 3D reconstructions of bacterial cells. A decrease in electron dose combined with ZPC will enable cryo-ET to be applied to radiation sensitive samples, such as the sheathed flagellum of V. vulnificus. In addition, reduction of the electron dose for tomography is important because the ice and the specimens embedded within the ice move due to repeated exposure to the beam (Brilot et al., 2012; Wright et al., 2006). The motion of objects in the ice can substantially limit the generation of higher resolution 3D maps and volumes. For single particle analysis, groups have improved data collection strategies in order to minimize movement and utilized electron detection devices that allow for the sub-selection and alignment of image frames to reduce blurring (Brilot et al., 2012; Li et al., 2013). In our study, we sought to define the impact of ice mobility on the 10 nm gold particles commonly used to align the tilt series images used for construction of the 3D tomogram. We observed that gold particles in a higher dose (~120 e−/Å2) tilt series were displaced by up to 3 nm in the x-y plane (Fig. 4a, 4c), whereas the gold particles in lower dose (~30 e−/Å2) tilt series were displaced by no more than 1.25 nm in the x–y plane (Fig. 4b, 4c). This illustrates that fiducial movement within the ice layer can be reduced by ~50% when a lower electron dose of ~30 e−/Å2 is used for data collection, which equates to an overall better alignment of the images for the generation of higher-quality tomographic reconstructions.
Figure 4.
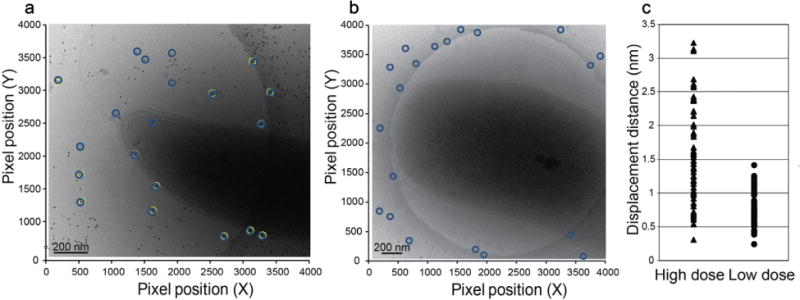
Gold fiducial positions overlaid on pre- and post-cryo-ET tilt series data acquisition images of frozen-hydrated bacteria. (a) Overlaid fiducial positions on an image of a C. crescentus cell acquired after a tilt series collected at high total dose (~120 e−/Å2). (b) Overlaid fiducial positions on an image of a V. vulnificus cell acquired after a tilt series collected at low total dose (~30 e−/Å2). Fiducial positions before (yellow open circles) and after (blue open circles) tilt series collection are presented. (c) Displacement in the x–y plane of 10 nm gold particles after exposure to high (~120 e−/Å2, filled triangle) and low (~30 e−/Å2, filled circle) electron doses used for cryo-ET data collection. Scale bars, 200 nm.
To characterize the improvement in tomogram SNR and the definition of cellular structures, DPC and ZPC cryo-ET data was analyzed from the same C. crescentus cell. Tomographic reconstructions were generated using IMOD (Kremer et al., 1996). As shown in Fig. 5, each 2.2 nm slice through the ZPC cryo-ET 3D volume had significantly higher SNR and clarity of the cell membranes (white arrows), s-layer periodicity (white arrowheads), and macromolecules within the cytoplasm when compared to individual 2.2 nm or averaged 11 nm slices from the DPC data. In our current and previous investigations (Guerrero-Ferreira et al., 2011) as well as in Fig. 5 and Supplementary Movies 1, 2, and 3, we have analyzed features such as the cell membranes, flagellum, flagellar basal body, bacteriophage capsid, and bacteriophage head filament, which typically require enhancement through the application of a defocus. All of these structures were more evident in the ZPC data because they were represented as uniform projections of the object mass density.
Figure 5.
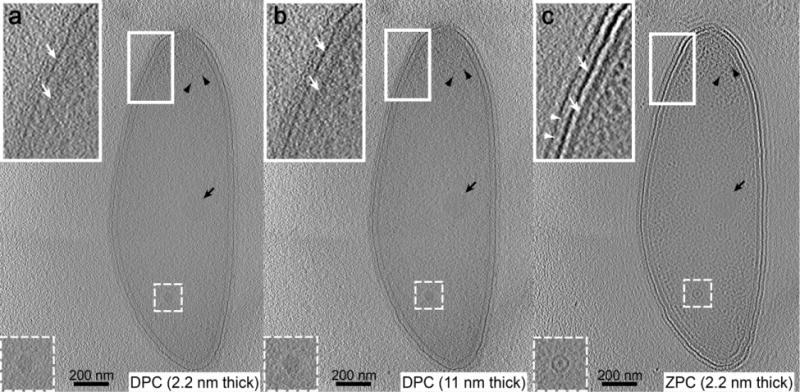
Cryo-electron tomograms of the same C. crescentus cells. Tomographic slices through the same C. crescentus cell. Single 2.2 nm DPC slice (a), averaged 11 nm DPC slice (b), single 2.2 nm ZPC slice (c). Insets are magnified views of the boxed region (bacterial envelope) highlighting the outer and inner membranes (white arrows) and s-layer periodicity (white arrowhead). Other complexes are noted including, a macromolecular complex (dashed-boxed region), storage granule (black arrow), and ribosomes (black arrowheads). Scale bars, 200 nm.
To further assess the resolution of low electron dose (~35 e−/Å2) tomography data of bacterial cells collected using either DPC or ZPC methods, we utilized the noise-compensated leave-one-out in two dimensions (NLOO-2D) method (Cardone et al., 2005) as implemented in Bsoft (Heymann et al., 2008) to determine the in-plane resolution of the full tomograms. The in-plane resolution of the DPC tomograms was estimated as ~25 nm (0.3 threshold) and the in-plane resolution of the ZPC tomograms was estimated as ~12 nm (0.3 threshold). The percent improvement in resolution of the ZPC tomograms as compared to the DPC tomograms was ~50%. However, it should be noted that due to sample geometry and thickness; the angular increment or step-size used for data collection; and the number of images acquired, the quantification of tomogram resolution is extremely variable and might be misleading. Nevertheless, resolution calculations are valuable first appraisals of tomogram quality prior to additional processing and analysis. Further increases in data resolution could be realized as sub-tomogram averaging methods are optimized and microscope hardware is upgraded with direct-electron detectors that will permit the collection of data with higher SNR.
During the analysis of the DPC and ZPC tomography data, we studied the impact of the defringing algorithm (Danev et al., 2010) on the quality of final reconstructions. We used the algorithm as described before but varied the power coefficient in the exponent of the filter function to between 5 and 10. When we examined slices from the DPC, ZPC, and tomograms generated with defringed ZPC tilt series (Supplementary Fig. 2), we observed that defringing reduced some of the fringe artifact associated with the cut on frequency of the phase plate. However, its use also reduced and flattened signal associated with bacterial membrane components and macromolecular complexes within the cytoplasm in individual 2D images. Upon examining the effect of defringing on the FFT of individual images and the radial average of the FFT (Supplementary Fig. 3), we observed the reduction of the fringe background in the FFT as well as the reduced peak height of the cut on frequency in the radial average. In the 2D FFTs and the radial averages we noted a marked decrease in the intensity of the frequency domains surrounding the peak of the cut on frequency that was reduced by the defringing program. However, reconstructions of ZPC tilt series processed for fringe reduction generated good quality tomograms with reduced fringe artifacts, no loss of resolution, and maintained improved ZPC contrast, as previously reported (Danev et al., 2010).
3. Conclusions
Here we demonstrated that the thin carbon film ZPC technology allows one to reduce the electron dose applied to the specimen and maintain high contrast; improve image alignment due to the greater SNR of each image and the reduction of fiducial displacement; and achieve higher contrast and resolution in each tilt series image and in the final 3D reconstruction. One challenge associated with ZPC TEM is the charging and ageing of the phase plate over time that necessitates phase plate exchange (Danev et al., 2009). We are working to determine the utility of other materials for the thin film of the phase plate when used for cryo-ET applications. We continue to improve and streamline the cryo-ET data collection scheme in order to extend the usable lifetime of the thin carbon film phase plate. In the current study, we have successfully collected up to eight individual tilt series using one phase plate aperture by employing SerialEM (Mastronarde, 2005). SerialEM was used to automate data acquisition, reduce the time taken to obtain a tilt series from the 90 minutes reported by Danev et al. (Danev et al., 2010) to 45 to 60 minutes, and lower the total electron dose applied to the phase plate during the collection of each data set to less than 240 e−/Å2. Several teams are engineering phase plate airlock systems that can be retrofitted onto existing microscopes in order to offer the ZPC technology to a larger group of investigators. Due to the significant improvements that employing thin carbon film ZPC affords to cryo-ET data, the technology should be advantageous to structural studies of a wide-range of biological specimens.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Figure 1. DPC and ZPC cryo-EM images of V. vulnificus cells (region of interest views in Figure 2). Single low dose (~1.5 e−/Å2) DPC (top) and ZPC (bottom) images of individual V. vulnificus cells. Each image set highlights the improvement in image contrast and visibility of the cell and cellular appendages and secretions that was obtained with ZPC. Scale bars, 200 nm.
Supplementary Figure 2. DPC, ZPC, and defringed ZPC slices from cryo-electron tomograms of the same C. crescentus cell. From left to right: single 2.2 nm DPC slice, single non-defringed 2.2 nm ZPC slice, single defringed 2.2 nm ZPC slice (power of 5), and single defringed 2.2 nm ZPC slice (power of 10). Note the absence of the fringe-artifact in the DPC data and the presence of the fringe artifact in the ZPC data. The two applications of the defringing algorithm reduced the fringe along cell membranes and some macromolecular complexes. The signal associated with some cytoplasmic complexes was reduced with defringing, whereas overall contrast was improved. Scale bars, 200 nm.
Supplementary Figure 3. FFT and radial plots from DPC, ZPC, and defringed ZPC cryo-EM 2D images of the same C. crescentus cell. From left to right: DPC FFT and radial profile, non-defringed ZPC FFT and radial profile, defringed ZPC FFT and radial profile (power of 5), and defringed ZPC FFT and radial profile (power of 10). Note the absence of the ZPC cut on frequency peak in the DPC data and the presence of the cut on frequency peak in the raw ZPC data. The application of the defringing algorithm reduced the fringe in the FFT that was also illustrated as a decrease in the intensity of the cut on frequency peak. Scale bars, 200 nm.
Supplementary Movie 1. The movie is of a series of 2.2 nm slices from the DPC cryo-electron tomogram of the C. crescentus cell from Figure 5a. The total electron dose of the DPC tomogram is ~70 e−/Å2. Scale bar, 200 nm.
Supplementary Movie 2. The movie is of a series of 11 nm slices from the DPC cryo-electron tomogram of the C. crescentus cell from Figure 5b. The total electron dose of the DPC tomogram is ~70 e−/Å2. Scale bar, 200 nm.
Supplementary Movie 3. The movie is of a series of 2.2 nm slices from the ZPC cryo-electron tomogram of the C. crescentus cell from Figure 5c. The total electron dose of the ZPC tomogram is ~70 e−/Å2. Scale bar, 200 nm.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Paul Gulig for providing the Vibrio vulnificus strains, and the Robert P. Apkarian Integrated Electron Microscopy Core, Emory University for microscopy services and support. We thank Dr. Bernard Heymann and Dr. Giovanni Cardone for their help and guidance with the calculation of tomogram resolution. This work was supported in part by Emory University, Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta, and the Georgia Research Alliance to E.R.W.; the Center for AIDS Research at Emory University (P30 AI050409); HFSP grant RGP0051 to E.R.W.; public health service grant GM104540 to E.R.W. from the NIH/NIGMS, and NSF grant 0923395 to E.R.W.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- Booth CR, Jakana J, Chiu W. Assessing the capabilities of a 4k×4k CCD camera for electron cryo-microscopy at 300kV. J Struct Biol. 2006;156:556–563. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2006.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briegel A, Dias DP, Li Z, Jensen RB, Frangakis AS, et al. Multiple large filament bundles observed in Caulobacter crescentus by electron cryotomography. Mol Microbiol. 2006;62:5–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brilot AF, Chen JZ, Cheng A, Pan J, Harrison SC, et al. Beam-induced motion of vitrified specimen on holey carbon film. J Struct Biol. 2012;177:630–637. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardone G, Grunewald K, Steven AC. A resolution criterion for electron tomography based on cross-validation. J Struct Biol. 2005;151:117–129. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2005.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danev R, Glaeser RM, Nagayama K. Practical factors affecting the performance of a thin-film phase plate for transmission electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 2009;109:312–325. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2008.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danev R, Kanamaru S, Marko M, Nagayama K. Zernike phase contrast cryo-electron tomography. J Struct Biol. 2010;171:174–181. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2010.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danev R, Nagayama K. Transmission electron microscopy with Zernike phase plate. Ultramicroscopy. 2001;88:243–252. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3991(01)00088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danev R, Nagayama K. Single particle analysis based on Zernike phase contrast transmission electron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 2008;161:211–218. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2007.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faruqi AR. Design principles and applications of a cooled CCD camera for electron microscopy. Adv Exper Med Biol. 1998;453:63–72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6039-1_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana J, Cardone G, Heymann JB, Winkler DC, Steven AC. Structural changes in Influenza virus at low pH characterized by cryo-electron tomography. J Vir. 2012;86:2919–2929. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06698-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana J, Steven AC. At low pH, influenza virus matrix protein M1 undergoes a conformational change prior to dissociating from the membrane. J Vir. 2013;87:5621–5628. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00276-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangakis AS, Hegerl R. Noise reduction in electron tomographic reconstructions using nonlinear anisotropic diffusion. J Struct Biol. 2001;135:239–250. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.2001.4406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda Y, Nagayama K. Zernike phase contrast cryo-electron tomography of whole mounted frozen cells. J Struct Biol. 2011;177:484–489. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2011.11.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm R, Barmann M, Hackl W, Typke D, Sackmann E, et al. Energy filtered electron tomography of ice-embedded actin and vesicles. Biophys J. 1997;72:482–489. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78689-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Ferreira RC, Viollier PH, Ely B, Poindexter JS, Georgieva M, Jensen GJ, Wright ER. Alternative mechanism for bacteriophage adsorption to the motile bacterium Caulobacter crescentus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108:9963–9968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012388108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann JB, Cardone G, Winkler DC, Steven AC. Computational resources for cryo-electron tomography in Bsoft. J Struct Biol. 2008;161:232–242. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2007.08.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosogi N, Shigematsu H, Terashima H, Homma M, Nagayama K. Zernike phase contrast cryo-electron tomography of sodium-driven flagellar hook-basal bodies from Vibrio alginolyticus. J Struct Biol. 2011;173:67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2010.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller PW, Adamson CS, Heymann JB, Freed EO, Steven AC. HIV-1 maturation inhibitor bevirimat stabilizes the immature Gag lattice. J Vir. 2011;85:1420–1428. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01926-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer JR, Mastronarde DN, McIntosh JR. Computer visualization of three-dimensional image data using IMOD. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:71–76. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X, Mooney P, Zheng S, Booth CR, Braunfeld MB, et al. Electron counting and beam-induced motion correction enable near-atomic-resolution single-particle cryo-EM. Nat Methods. 2013;10:584–590. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucic V, Leis A, Baumeister W. Cryo-electron tomography of cells: connecting structure and function. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;130:185–196. doi: 10.1007/s00418-008-0459-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastronarde DN. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J Struct Biol. 2005;152:36–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2005.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milazzo AC, Cheng A, Moeller A, Lyumkis D, Jacovetty E, et al. Initial evaluation of a direct detection device detector for single particle cryo-electron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 2011;176:404–408. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2011.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne JL, Subramaniam S. Cryo-electron tomography of bacteria: progress, challenges and future prospects. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7:666–675. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata K, Liu X, Danev R, Jakana J, Schmid MF, et al. Zernike phase contrast cryo-electron microscopy and tomography for structure determination at nanometer and subnanometer resolutions. Structure. 2010;18:903–912. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2010.06.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy GE, Jensen GJ. Electron cryotomography. Biotechniques. 2007;43:413–421. doi: 10.2144/000112568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narasimha R, Aganj I, Bennett AE, Borgnia MJ, Zabransky D, et al. Evaluation of denoising algorithms for biological electron tomography. J Struct Biol. 2008;164:7–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2008.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochat RH, Liu X, Murata K, Nagayama K, Rixon FJ, et al. Seeing the portal in herpes simplex virus type 1 B capsids. J Vir. 2011;85:1871–1874. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01663-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigematsu H, Sokabe T, Danev R, Tominaga M, Nagayama K. A 3.5-nm structure of rat TRPV4 cation channel revealed by Zernike phase-contrast cryoelectron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:11210–11218. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.090712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright ER, Iancu CV, Tivol WF, Jensen GJ. Observations on the behavior of vitreous ice at ~82 and ~12 K. J Struct Biol. 2006;153:241–252. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2005.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P, Borgnia MJ, Mooney P, Shi D, Pan M, et al. Automated image acquisition and processing using a new generation of 4K × 4K CCD cameras for cryo electron microscopic studies of macromolecular assemblies. J Struct Biol. 2003;143:135–144. doi: 10.1016/s1047-8477(03)00124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Figure 1. DPC and ZPC cryo-EM images of V. vulnificus cells (region of interest views in Figure 2). Single low dose (~1.5 e−/Å2) DPC (top) and ZPC (bottom) images of individual V. vulnificus cells. Each image set highlights the improvement in image contrast and visibility of the cell and cellular appendages and secretions that was obtained with ZPC. Scale bars, 200 nm.
Supplementary Figure 2. DPC, ZPC, and defringed ZPC slices from cryo-electron tomograms of the same C. crescentus cell. From left to right: single 2.2 nm DPC slice, single non-defringed 2.2 nm ZPC slice, single defringed 2.2 nm ZPC slice (power of 5), and single defringed 2.2 nm ZPC slice (power of 10). Note the absence of the fringe-artifact in the DPC data and the presence of the fringe artifact in the ZPC data. The two applications of the defringing algorithm reduced the fringe along cell membranes and some macromolecular complexes. The signal associated with some cytoplasmic complexes was reduced with defringing, whereas overall contrast was improved. Scale bars, 200 nm.
Supplementary Figure 3. FFT and radial plots from DPC, ZPC, and defringed ZPC cryo-EM 2D images of the same C. crescentus cell. From left to right: DPC FFT and radial profile, non-defringed ZPC FFT and radial profile, defringed ZPC FFT and radial profile (power of 5), and defringed ZPC FFT and radial profile (power of 10). Note the absence of the ZPC cut on frequency peak in the DPC data and the presence of the cut on frequency peak in the raw ZPC data. The application of the defringing algorithm reduced the fringe in the FFT that was also illustrated as a decrease in the intensity of the cut on frequency peak. Scale bars, 200 nm.
Supplementary Movie 1. The movie is of a series of 2.2 nm slices from the DPC cryo-electron tomogram of the C. crescentus cell from Figure 5a. The total electron dose of the DPC tomogram is ~70 e−/Å2. Scale bar, 200 nm.
Supplementary Movie 2. The movie is of a series of 11 nm slices from the DPC cryo-electron tomogram of the C. crescentus cell from Figure 5b. The total electron dose of the DPC tomogram is ~70 e−/Å2. Scale bar, 200 nm.
Supplementary Movie 3. The movie is of a series of 2.2 nm slices from the ZPC cryo-electron tomogram of the C. crescentus cell from Figure 5c. The total electron dose of the ZPC tomogram is ~70 e−/Å2. Scale bar, 200 nm.


