Abstract
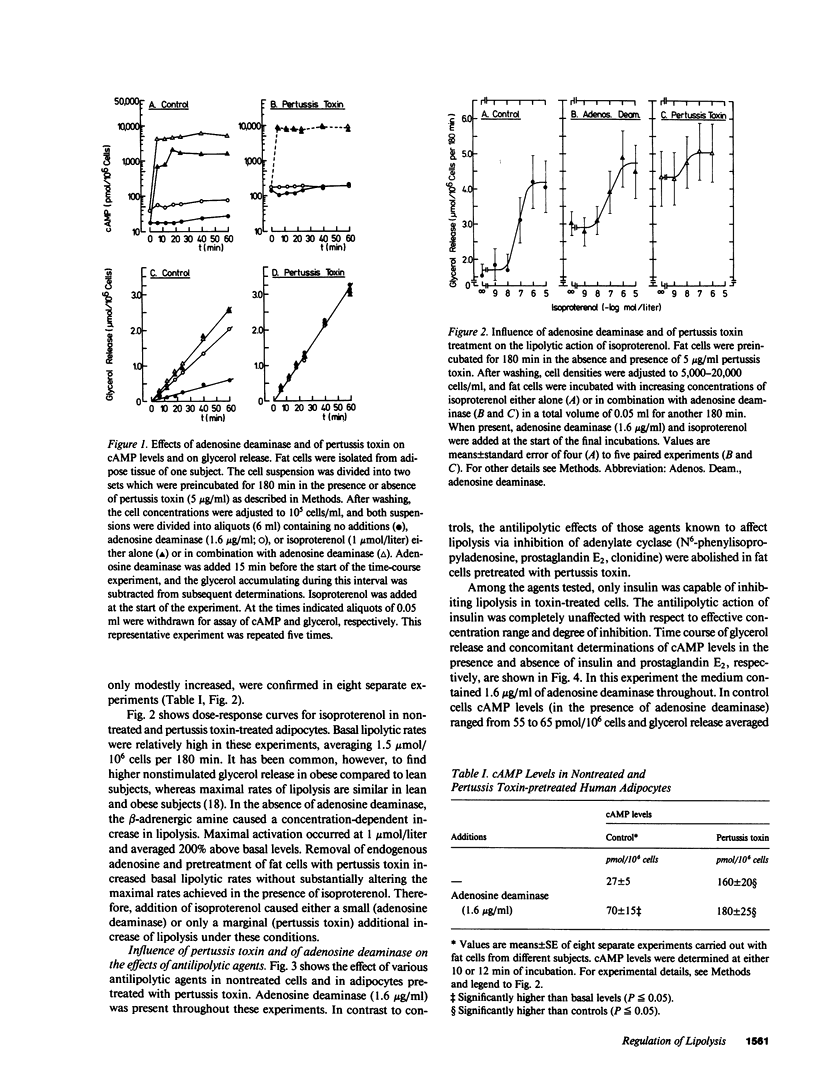
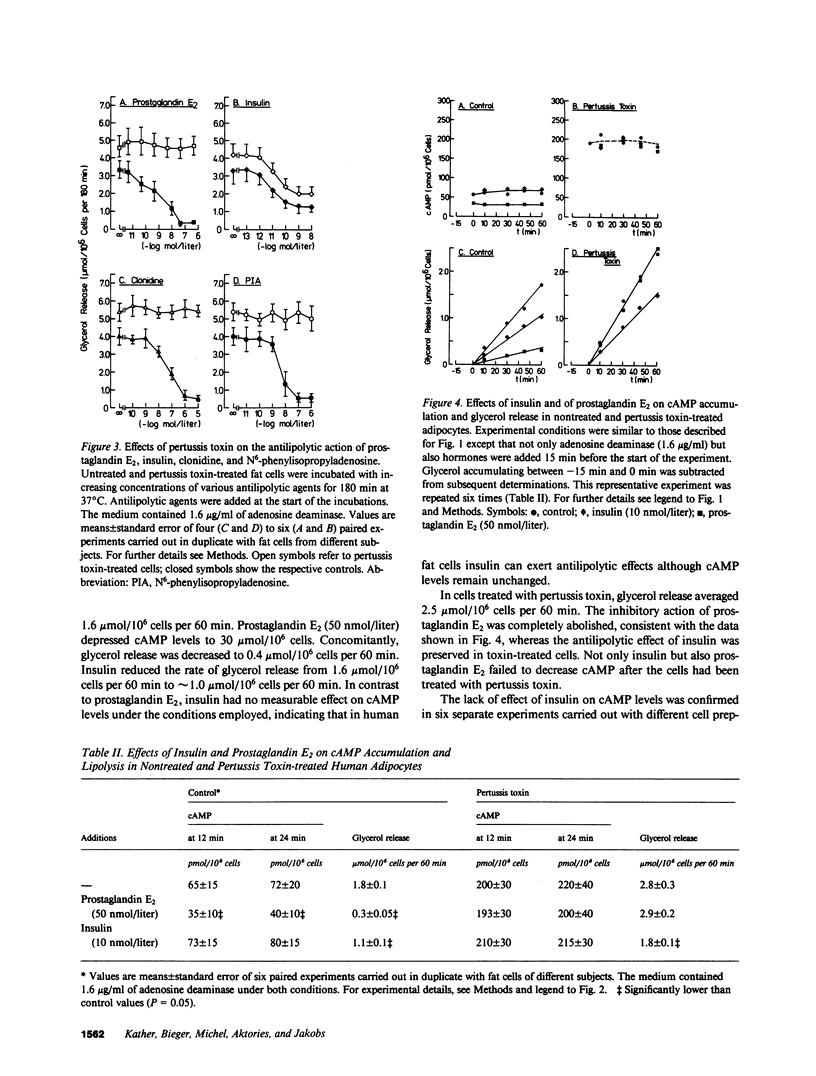
The effects of adenosine deaminase and of pertussis toxin on hormonal regulation of lipolysis were investigated in isolated human fat cells. Adenosine deaminase (1.6 micrograms/ml) caused a two-to threefold increase in cyclic AMP, which was associated with an increase in glycerol release averaging 150-200% above basal levels. Clonidine, N6-phenylisopropyladenosine, prostaglandin E2, and insulin caused a dose-dependent inhibition of glycerol release in the presence of adenosine deaminase. Pretreatment of adipocytes with pertussis toxin (5 micrograms/ml) for 180 min resulted in a five- to sevenfold increase in cyclic AMP. Glycerol release was almost maximal and isoproterenol caused either no further increase or only a marginal additional increase of lipolysis after pretreatment with pertussis toxin, whereas cyclic AMP levels were 500 times higher than in controls. The effects of antilipolytic agents known to affect lipolysis by inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity, i.e., clonidine, N6-phenylisopropyladenosine, and prostaglandin E2, were impaired. In contrast, the antilipolytic action of insulin was preserved in adipocytes pretreated with pertussis toxin. As in controls, the peptide hormone had no detectable effect on cyclic AMP after pertussis toxin treatment. The findings support the view that the antilipolytic effect of insulin does not require adenylate cyclase or phosphodiesterase action. In addition, the results demonstrate that, upon relief of endogenous inhibition, human fat cell lipolysis proceeds at considerable (adenosine deaminase) or almost maximal (pertussis toxin) rates. A certain degree of inhibition, therefore, appears to be necessary for human fat cell lipolysis to be susceptible for hormonal activation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arner P., Bolinder J., Engfeldt P., Hellmér J., Ostman J. Influence of obesity on the antilipolytic effect of insulin in isolated human fat cells obtained before and after glucose ingestion. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI111259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arner P. Relationship between intracellular cyclic AMP and lipolysis in human adipose tissue. Acta Med Scand. 1976;200(3):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb08217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns T. W., Terry B. E., Langley P. E., Robison G. A. Insulin inhibition of lipolysis of human adipocytes: the role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Diabetes. 1979 Nov;28(11):957–961. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.11.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Lewis G. P., Piper P. J. Inhibition by glucocorticoids of prostaglandin release from adipose tissue in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):425–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb08396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J. A partial view of the mechanism of insulin action. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00252681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elks M. L., Watkins P. A., Manganiello V. C., Moss J., Hewlett E., Vaughan M. Selective regulation by pertussis toxin of insulin-induced activation of particulate cAMP phosphodiesterase activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):593–598. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90565-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engfeldt P., Arner P., Ostman J. Influence of adipocyte isolation by collagenase on phosphodiesterase activity and lipolysis in man. J Lipid Res. 1980 May;21(4):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Malbon C. C. Regulation of adenylate cyclase by adenosine. Mol Cell Biochem. 1979 Jun 15;25(3):143–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00235364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay R. A., Lardy H. A. The antilipolytic effect of insulin does not require adenylate cyclase or phosphodiesterase action. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A. Decreased sensitivity to alpha 2 adrenergic amines, adenosine and prostaglandins in white fat cells from hamsters treated with pertussis vaccine. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 20;126(2):306–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Luzio J. P., Siddle K. Hormonal control of adipose-tissue lipolysis. Biochem Soc Symp. 1978;(43):97–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Cronin M. J., Moss J., Anderson H., Myers G. A., Pearson R. D. Pertussis toxin: lessons from biological and biochemical effects in different cells. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:173–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Chang H., Farahbakhsh Z., Reaven G. Inhibition of lipolysis by adenosine is potentiated with age. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1750–1755. doi: 10.1172/JCI111593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kather H., Aktories K., Schulz G., Jakobs K. H. Islet-activating protein discriminates the antilipolytic mechanism of insulin from that of other antilipolytic compounds. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 5;161(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80749-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kather H., Schröder F., Simon B. Microdetermination of glycerol using bacterial NADH-linked luciferase. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Apr 23;120(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90370-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kather H., Simon B. Adrenoceptor of the alpha 2-subtype mediating inhibition of the human fat cell adenylate cyclase. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;11(2 Suppl 1):111–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb02047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kather H., Simon B. Biphasic effects of prostaglandin E2 on the human fat cell adenylate cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):609–612. doi: 10.1172/JCI109500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kather H., Wieland E., Fischer B., Wirth A., Schlierf G. Adrenergic regulation of lipolysis in abdominal adipocytes of obese subjects during caloric restriction: reversal of catecholamine action caused by relief of endogenous inhibition. Eur J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;15(1):30–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1985.tb00140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooney R. A., Ebersohl R. D., McDonald J. M. Insulin-mediated antilipolysis in permeabilized rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7701–7704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno F. J., Mills I., García-Sáinz J. A., Fain J. N. Effects of pertussis toxin treatment on the metabolism of rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10938–10943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Loss of the inhibitory function of the guanine nucleotide regulatory component of adenylate cyclase due to its ADP ribosylation by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in adipocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3319–3326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohisalo J. J. Effects of adenosine on lipolysis in human subcutaneous fat cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Feb;52(2):359–363. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-2-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohisalo J. J., Stouffer J. E. Adenosine, thyroid status and regulation of lipolysis. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):249–251. doi: 10.1042/bj1780249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olansky L., Myers G. A., Pohl S. L., Hewlett E. L. Promotion of lipolysis in rat adipocytes by pertussis toxin: reversal of endogenous inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6547–6551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenqvist U., Efendić S. Stimulatory effect in vitro of prostaglandin E 1 on noradrenaline-induced lipolysis in subcutaneous adipose tissue from hypothyroid subjects. Acta Med Scand. 1971 Nov;190(5):341–345. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1971.tb07440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D. Increased antilipolytic effect of the adenosine 'R-site' agonist N6-(phenylisopropyl)adenosine in adipocytes from adrenalectomized rats. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 16;115(1):127–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80741-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel R. J. Stimulation of cAMP accumulation and lipolysis in hamster adipocytes with forskolin. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):C63–C68. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.1.C63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe U., Schönhöfer P. S., Ebert R. Facilitation by adenosine of the action of insulin on the accumulation of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate, lipolysis, and glucose oxidation in isolated fat cells. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 1;46(3):537–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y. Differential effects of two phosphodiesterase inhibitors on fat cell metabolism. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):1787–1791. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-1787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Yajima M., Ase K., Ui M. A role of the B-oligomer moiety of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in development of the biological effects on intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6756–6761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ui M., Katada T., Murayama T., Kurose H., Yajima M., Tamura M., Nakamura T., Nogimori K. Islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin: a specific uncoupler of receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G., Finley E., Taylor E. Adenosine and the control of lipolysis in rat adipocytes during pregnancy and lactation. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 15;216(1):121–128. doi: 10.1042/bj2160121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Loten E. G. The antilipolytic action of insulin on adrenocorticotrophin-stimulated rat adipocytes. The roles of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and the protein kinase dependent on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):17–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yajima M., Hosoda K., Kanbayashi Y., Nakamura T., Takahashi I., Ui M. Biological properties of islets-activating protein (IAP) purified from the culture medium of Bordetella pertussis. J Biochem. 1978 Jan;83(1):305–312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Is increased basal lipolysis in adipose tissue of fasted-refed rats related to cyclic-AMP-dependent mechanisms? Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(3):453–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



