Abstract
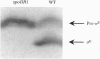
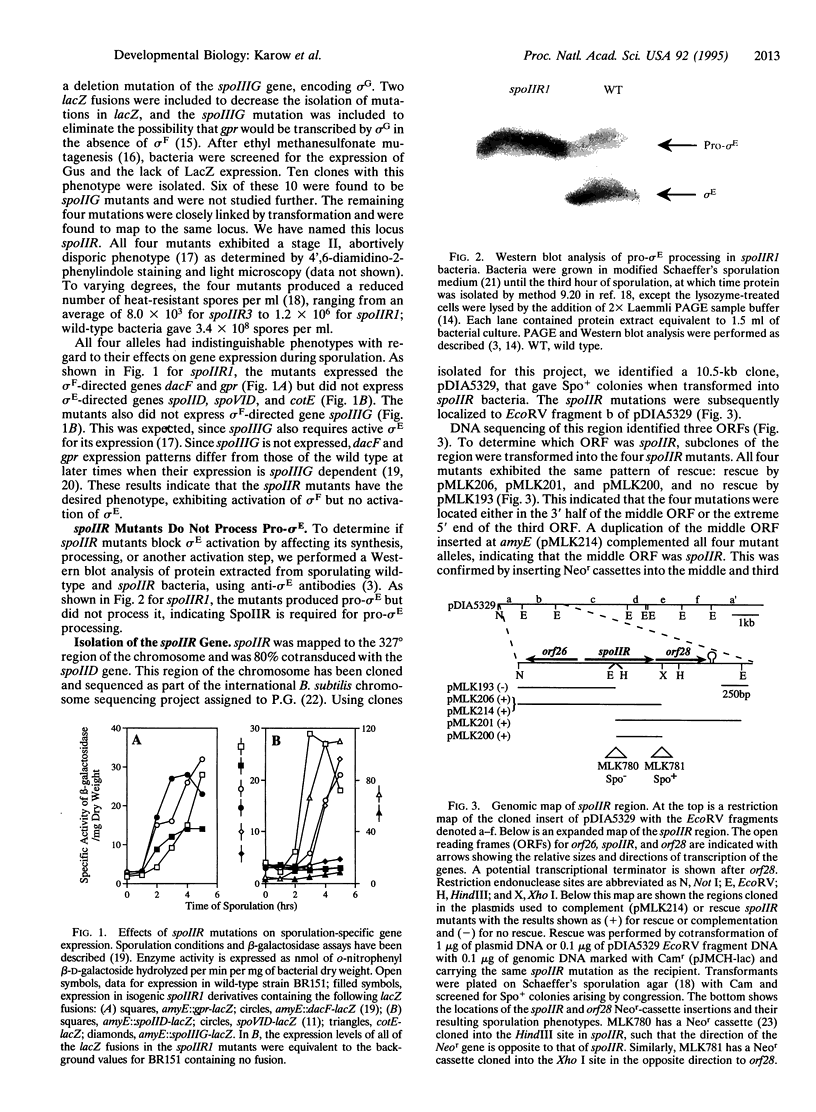
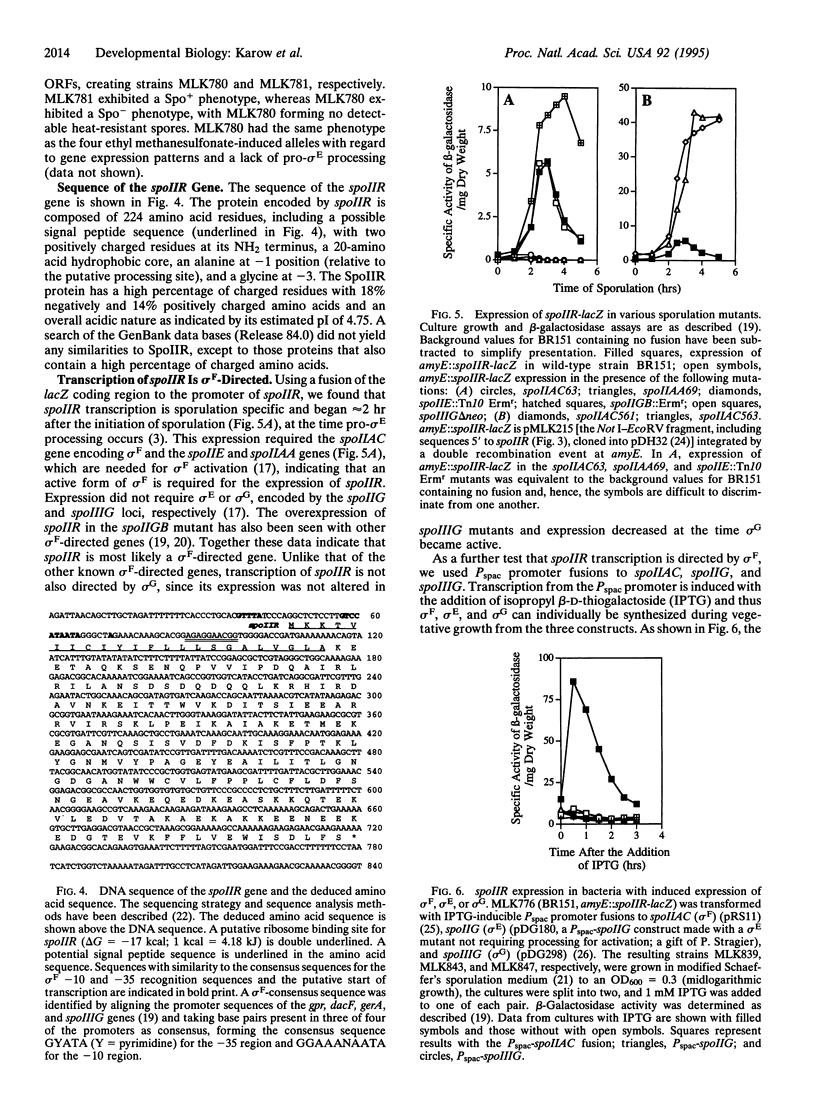
Sporulation of Bacillus subtilis requires the coordinated expression of two separate developmental programs in the mother cell and forespore compartments by sigma E and sigma F, respectively. This coordination is maintained through the action of cross-regulatory factors that control the activities of the various sporulation-specific sigma factors. We present here the isolation and characterization of one such cross-regulatory factor, the spoIIR gene. Using a genetic screen, we have isolated four mutant alleles of spoIIR. These mutants were isolated as expressing sigma F-directed genes but not sigma E-directed genes. The block in sigma E-directed gene expression in spoIIR mutants was caused by an inability to process pro-sigma E to its active form. Cloning and characterization of the spoIIR gene determined that its transcription is directed by sigma F. Thus, SpoIIR is required for linking the activation of sigma E to the activation of sigma F and coordinating the initiation of the two developmental programs required to form a spore.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper S., Duncan L., Losick R. An adenosine nucleotide switch controlling the activity of a cell type-specific transcription factor in B. subtilis. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo V., Alvarez E., Zumstein E., Damiani G., Sgaramella V., Ehrlich S. D., Serror P. An ordered collection of Bacillus subtilis DNA segments cloned in yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6047–6051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall B., Driks A., Losick R., Moran C. P., Jr Cloning and characterization of a gene required for assembly of the Bacillus subtilis spore coat. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1705–1716. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1705-1716.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall B., Lutkenhaus J. Impaired cell division and sporulation of a Bacillus subtilis strain with the ftsA gene deleted. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2398–2403. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2398-2403.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund J. E., Zhang L., Haines M. A., Higgins M. L., Piggot P. J. Analysis by fluorescence microscopy of the development of compartment-specific gene expression during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(10):2898–2905. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.10.2898-2905.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corran J. The induction of supersuppressor mutants of Bacillus subtilis by ethyl methanesulphonate and the posttreatment modification of mutation yield. Mol Gen Genet. 1968;103(1):42–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00271156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Driks A., Schmidt R., Kunkel B., Losick R. Forespore-specific transcription of a gene in the signal transduction pathway that governs Pro-sigma K processing in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):456–466. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting S., Roels S., Losick R. Sporulation operon spoIVF and the characterization of mutations that uncouple mother-cell from forespore gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1237–1256. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90931-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driks A., Losick R. Compartmentalized expression of a gene under the control of sporulation transcription factor sigma E in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9934–9938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. Bacillus subtilis sporulation: regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):1–33. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.1-33.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis in Bacillus subtilis. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:305–320. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya M., Kondo K., Tanaka T. A neomycin resistance gene cassette selectable in a single copy state in the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4410–4410. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas R. M., Haldenwang W. G. Influence of spo mutations on sigma E synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5226–5228. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5226-5228.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin P. A., Losick R. Characterization of a cell division gene from Bacillus subtilis that is required for vegetative and sporulation septum formation. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.5.1451-1459.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Stragier P. Crisscross regulation of cell-type-specific gene expression during development in B. subtilis. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):601–604. doi: 10.1038/355601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis P., Driks A., Losick R. Establishment of cell type by compartmentalized activation of a transcription factor. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1948031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S. R., Errington J. The importance of morphological events and intercellular interactions in the regulation of prespore-specific gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):945–955. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit M. A., Bruand C., Jannière L., Ehrlich S. D. Tn10-derived transposons active in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6736–6740. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6736-6740.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Curtis C. A. Analysis of the regulation of gene expression during Bacillus subtilis sporulation by manipulation of the copy number of spo-lacZ fusions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1260–1266. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1260-1266.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rather P. N., Coppolecchia R., DeGrazia H., Moran C. P., Jr Negative regulator of sigma G-controlled gene expression in stationary-phase Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):709–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.709-715.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santana M., Ionescu M. S., Vertes A., Longin R., Kunst F., Danchin A., Glaser P. Bacillus subtilis F0F1 ATPase: DNA sequence of the atp operon and characterization of atp mutants. J Bacteriol. 1994 Nov;176(22):6802–6811. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.22.6802-6811.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R., Margolis P., Duncan L., Coppolecchia R., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Control of developmental transcription factor sigma F by sporulation regulatory proteins SpoIIAA and SpoIIAB in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9221–9225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stragier P., Bonamy C., Karmazyn-Campelli C. Processing of a sporulation sigma factor in Bacillus subtilis: how morphological structure could control gene expression. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90407-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D. X., Stragier P., Setlow P. Identification of a new sigma-factor involved in compartmentalized gene expression during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):141–149. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Fajardo-Cavazos P., Sussman M. D., Tovar-Rojo F., Cabrera-Martinez R. M., Setlow P. Effect of chromosome location of Bacillus subtilis forespore genes on their spo gene dependence and transcription by E sigma F: identification of features of good E sigma F-dependent promoters. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7867–7874. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7867-7874.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trempy J. E., Morrison-Plummer J., Haldenwang W. G. Synthesis of sigma 29, an RNA polymerase specificity determinant, is a developmentally regulated event in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):340–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.340-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoy B. E., Hoch J. A. Characterization of the spoIVB and recN loci of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1306–1311. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1306-1311.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]