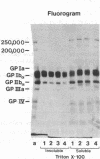
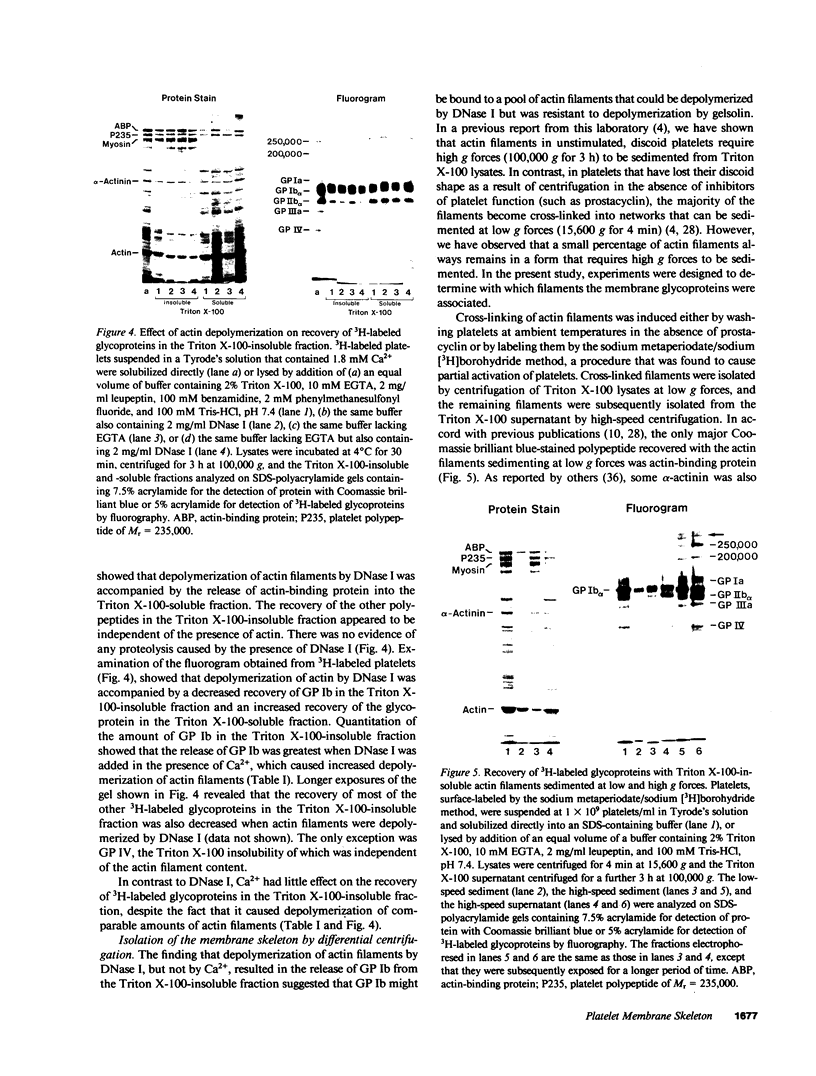
Abstract
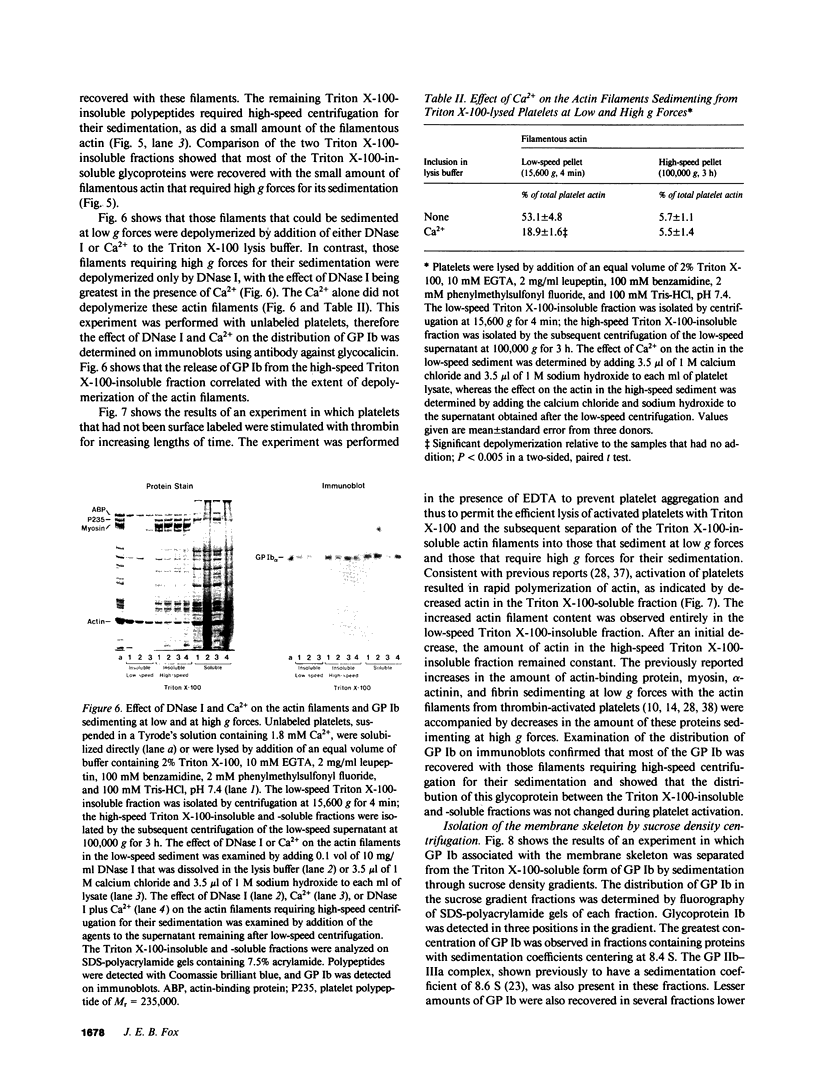
Experiments were performed to determine whether platelets contain a membrane skeleton. Platelets were labeled by a sodium periodate/sodium [3H]borohydride method and lysed with Triton X-100. Much of the filamentous actin could be sedimented at low g forces (15,600 g, 4 min), but some of the actin filaments required high-speed centrifugation for their sedimentation (100,000 g, 3 h). The latter filaments differed from those in the low-speed pellet in that they could not be depolymerized by Ca2+ and could not be sedimented at low g forces even from Triton X-100 lysates of platelets that had been activated with thrombin. Actin-binding protein sedimented with both types of filaments, but 3H-labeled membrane glycoproteins were recovered mainly with the high-speed filaments. The primary 3H-labeled glycoprotein recovered with this "membrane skeleton" was glycoprotein (GP) Ib. Approximately 70% of the platelet GP Ib was present in this skeleton. Several other minor glycoproteins, including greater than 50% of the GP Ia and small amounts of three unidentified glycoproteins of Mr greater than 200,000, were also recovered with the membrane skeleton. The Triton X-100 insolubility of GP Ib, GP Ia, a minor membrane glycoprotein of 250,000 Mr, and actin-binding protein resulted from their association with actin filaments as they were rendered Triton X-100-soluble when actin filaments were depolymerized with deoxyribonuclease I and co-isolated with actin filaments on sucrose gradients. When isolated platelet plasma membranes were extracted with Triton X-100, actin, actin-binding protein, and GP Ib were recovered as the Triton X-100 residue. These studies show that unstimulated platelets contain a membrane skeleton composed of actin filaments and actin-binding protein that is distinct from the rest of the cytoskeleton and is attached to GP Ib, GP Ia, and a minor glycoprotein of 250,000 Mr on the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF



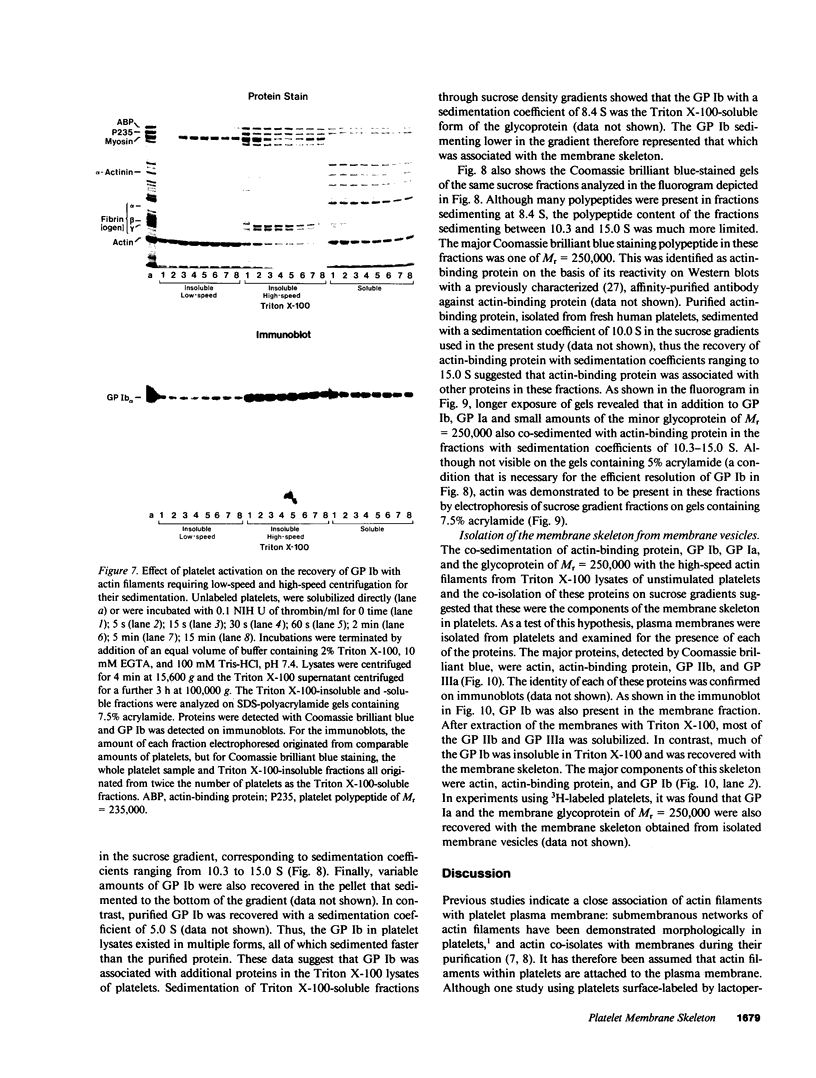
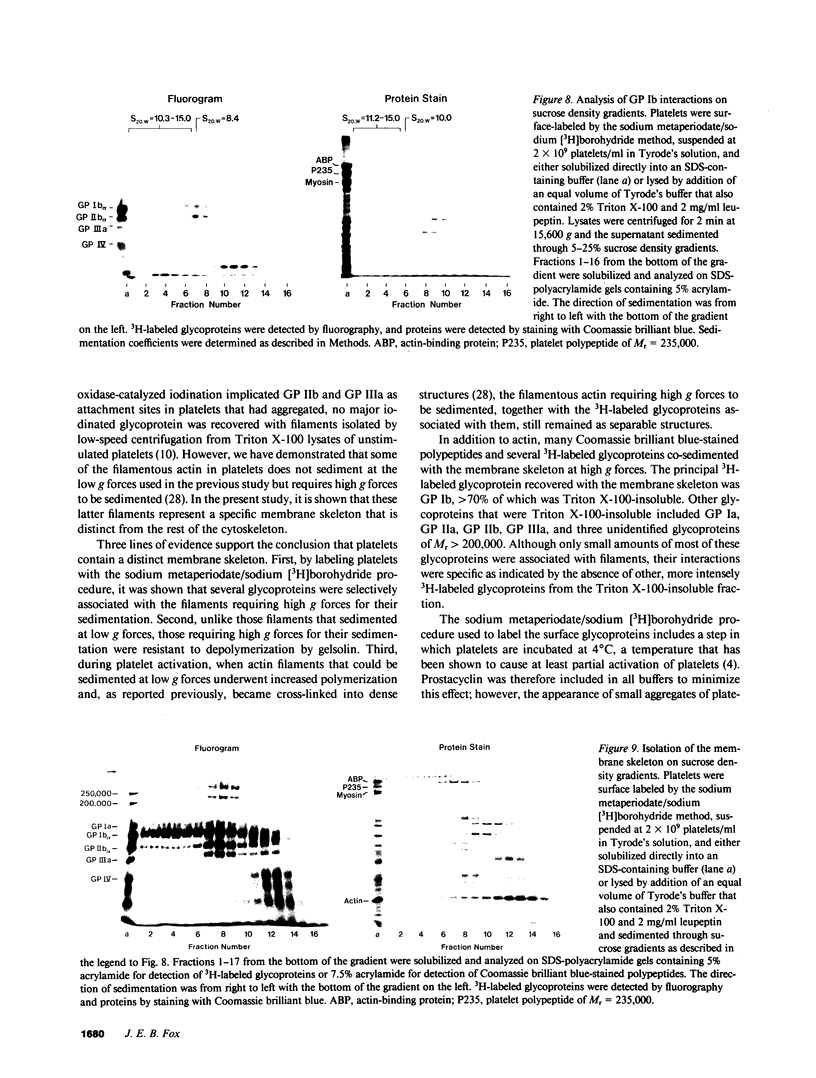
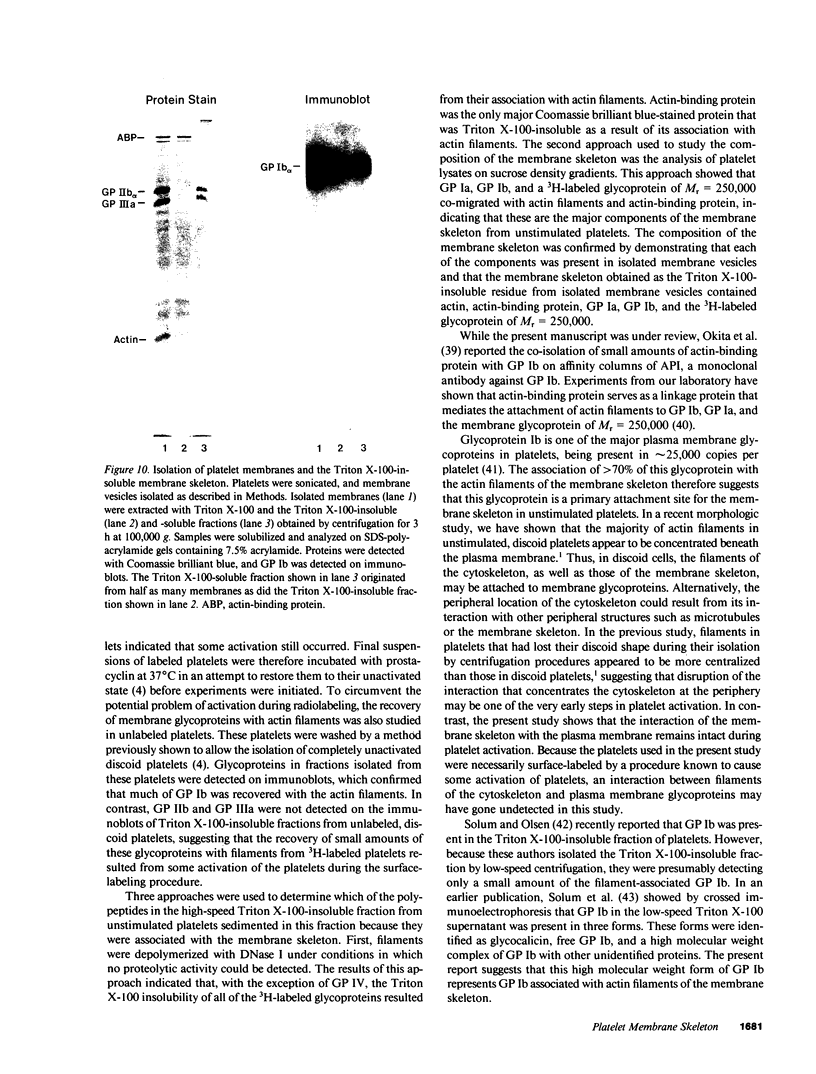


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Lovrien R. E. Glycophorin is linked by band 4.1 protein to the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):655–658. doi: 10.1038/307655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. Immunoreactive forms of human erythrocyte ankyrin are present in diverse cells and tissues. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):597–599. doi: 10.1038/281597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt M. C., Gregory C., Chong B. H., Zola H., Castaldi P. A. Additional glycoprotein defects in Bernard-Soulier's syndrome: confirmation of genetic basis by parental analysis. Blood. 1983 Oct;62(4):800–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt M. C., Phillips D. R. Purification and preliminary physicochemical characterization of human platelet membrane glycoprotein V. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blikstad I., Markey F., Carlsson L., Persson T., Lindberg U. Selective assay of monomeric and filamentous actin in cell extracts, using inhibition of deoxyribonuclease I. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE J. T. SIMPLIFIED "DISC" (POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL) ELECTROPHORESIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:428–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Markey F., Blikstad I., Persson T., Lindberg U. Reorganization of actin in platelets stimulated by thrombin as measured by the DNase I inhibition assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6376–6380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella J. F., Masiello N. C., Lin S., Bell W., Zucker M. B. Identification of fibrinogen derivatives in the Triton-insoluble residue of human blood platelets. Cell Motil. 1983;3(1):21–30. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemetson K. J., McGregor J. L., James E., Dechavanne M., Lüscher E. F. Characterization of the platelet membrane glycoprotein abnormalities in Bernard-Soulier syndrome and comparison with normal by surface-labeling techniques and high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):304–311. doi: 10.1172/JCI110618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M. The molecular organization of the red cell membrane skeleton. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):141–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. Studies with a murine monoclonal antibody that abolishes ristocetin-induced binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets: additional evidence in support of GPIb as a platelet receptor for von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):99–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E. Association of actin with the platelet membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 16;772(2):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Cohen C. M. Platelets contain proteins immunologically related to red cell spectrin and protein 4.1. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):52–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Boyles J. K., Reynolds C. C., Phillips D. R. Actin filament content and organization in unstimulated platelets. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1985–1991. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Goll D. E., Reynolds C. C., Phillips D. R. Identification of two proteins (actin-binding protein and P235) that are hydrolyzed by endogenous Ca2+-dependent protease during platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1060–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Phillips D. R. Role of phosphorylation in mediating the association of myosin with the cytoskeletal structures of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4120–4126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Reynolds C. C., Phillips D. R. Calcium-dependent proteolysis occurs during platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9973–9981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Nurden A. T., Phillips D. R. Molecular defects in interactions of platelets with the vessel wall. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 25;311(17):1084–1098. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410253111705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröttum K. A., Solum N. O. Congenital thrombocytopenia with giant platelets: a defect in the platelet membrane. Br J Haematol. 1969 Mar;16(3):277–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson B. S. Interaction of the plasma membrane with the cytoskeleton: an overview. Tissue Cell. 1983;15(6):829–852. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(83)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings L. K., Fox J. E., Edwards H. H., Phillips D. R. Changes in the cytoskeletal structure of human platelets following thrombin activation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings L. K., Phillips D. R. Purification of glycoproteins IIb and III from human platelet plasma membranes and characterization of a calcium-dependent glycoprotein IIb-III complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10458–10466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer B. G., Gonnella P. A., Nachmias V. T. alpha-Actinin and vinculin in normal and thrombasthenic platelets. Blood. 1984 Mar;63(3):606–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind S. E., Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Human platelets contain gelsolin. A regulator of actin filament length. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1384–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI110578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey F., Persson T., Lindberg U. Characterization of platelet extracts before and after stimulation with respect to the possible role of profilactin as microfilament precursor. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A. A new solid-state reagent to iodinate proteins. I. Conditions for the efficient labeling of antiserum. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 15;125(2):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menashi S., Weintroub H., Crawford N. Characterization of human platelet surface and intracellular membranes isolated by free flow electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4095–4101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Kinoshita T., Ferris B. Structural analysis of human platelet membrane glycoprotein I complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2952–2954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman P. J., Knipp M. A., Kahn R. A. Extraction and identification of human platelet integral membrane proteins using Triton X-114. Thromb Res. 1982 Jul 15;27(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. Specific roles for platelet surface glycoproteins in platelet function. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):720–722. doi: 10.1038/255720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita J. R., Pidard D., Newman P. J., Montgomery R. R., Kunicki T. J. On the association of glycoprotein Ib and actin-binding protein in human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):317–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura I., Lombart C., Jamieson G. A. Platelet glycocalicin. II. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5950–5955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet membrane defects in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Evidence for decreased amounts of two major glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):535–545. doi: 10.1172/JCI108805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Evidence for the presence of nonequivalent disulfide bonds using nonreduced-reduced two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Edwards H. H. Identification of membrane proteins mediating the interaction of human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):77–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A. The essential role of Ca2+ in the activity of bovine pancreatic deoxyribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):1981–1986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S., Stracher A., Burridge K. Isolation and characterization of a calcium-sensitive alpha-actinin-like protein from human platelet cytoskeletons. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12986–12991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P. Membrane skeletal dynamics: role in modulation of red cell deformability, mobility of transmembrane proteins, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):175–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solum N. O., Hagen I., Filion-Myklebust C., Stabaek T. Platelet glycocalicin. Its membrane association and solubilization in aqueous media. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 10;597(2):235–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solum N. O., Olsen T. M. Glycoprotein Ib in the Triton-insoluble (cytoskeletal) fraction of blood platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 29;799(3):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solum N. O., Olsen T. M., Gogstad G. O., Hagen I., Brosstad F. Demonstration of a new glycoprotein Ib-related component in platelet extracts prepared in the presence of leupeptin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 23;729(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Burris S. M., Hasegawa D., Johnson M. Micropipette aspiration of human blood platelets: a defect in Bernard-Soulier's syndrome. Blood. 1984 May;63(5):1249–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Burris S. M., Tukey D., Smith C., 2nd, Clawson C. C. Micropipette aspiration of human platelets: influence of microtubules and actin filaments on deformability. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):210–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]