Abstract
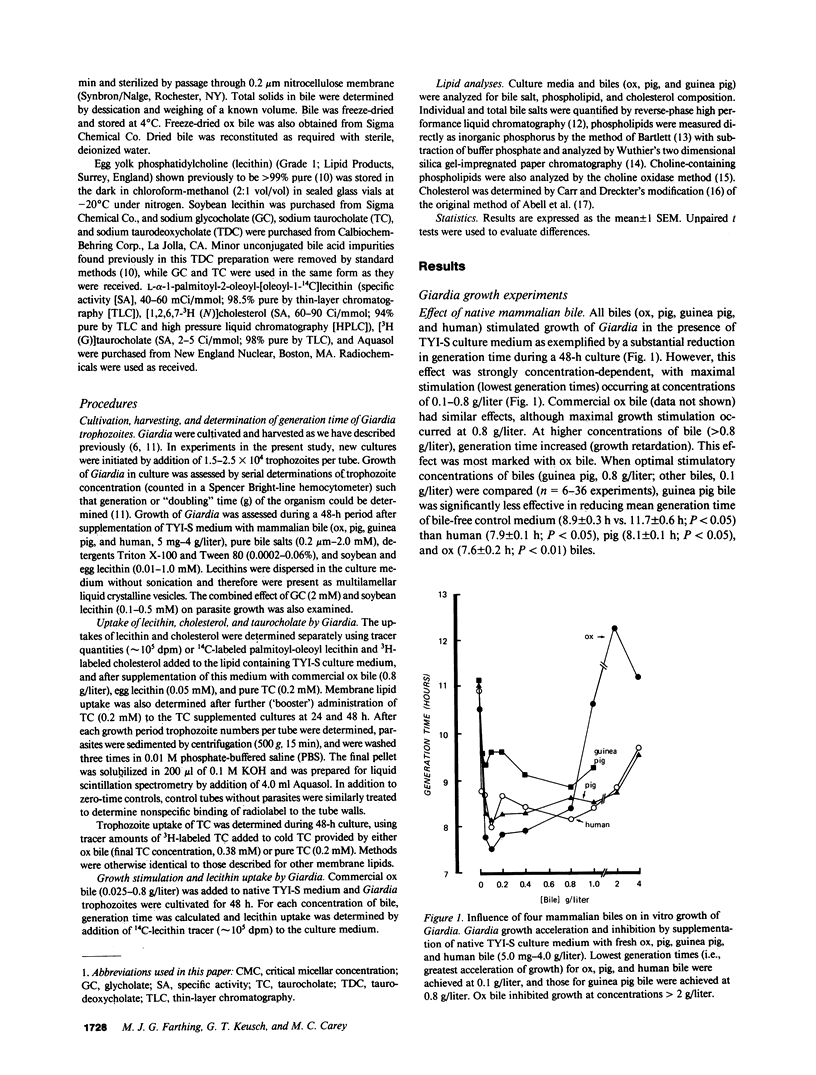
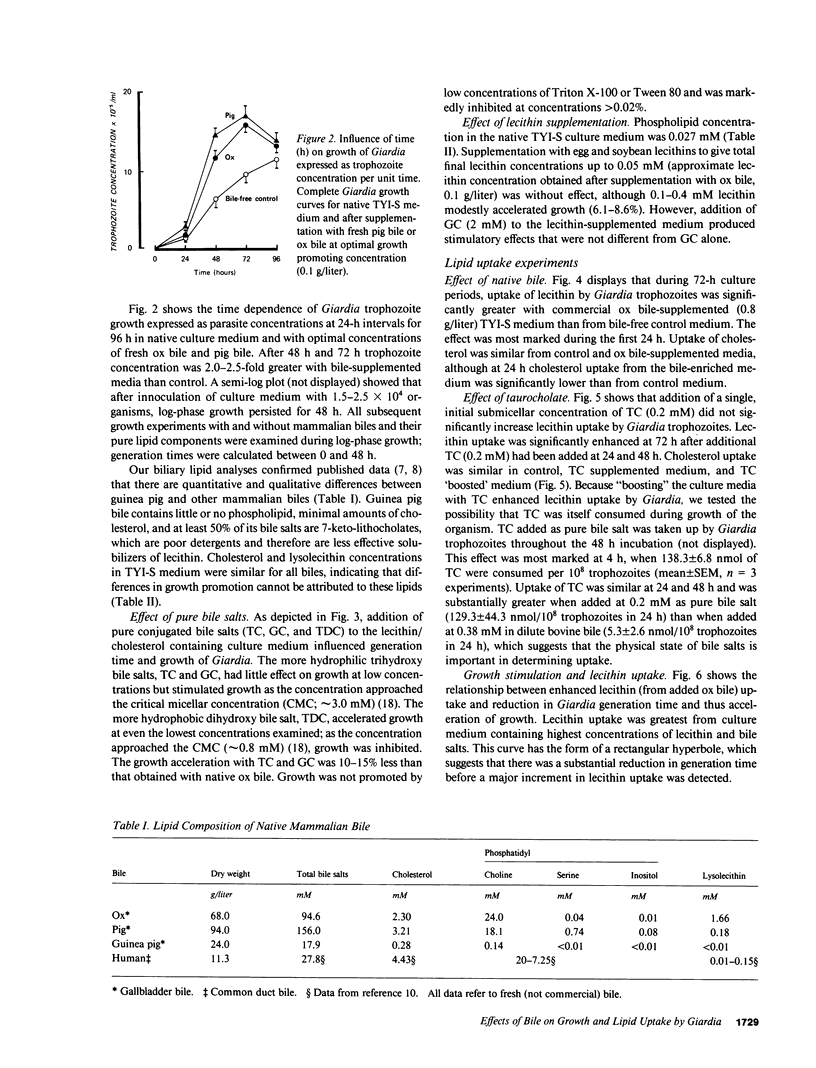
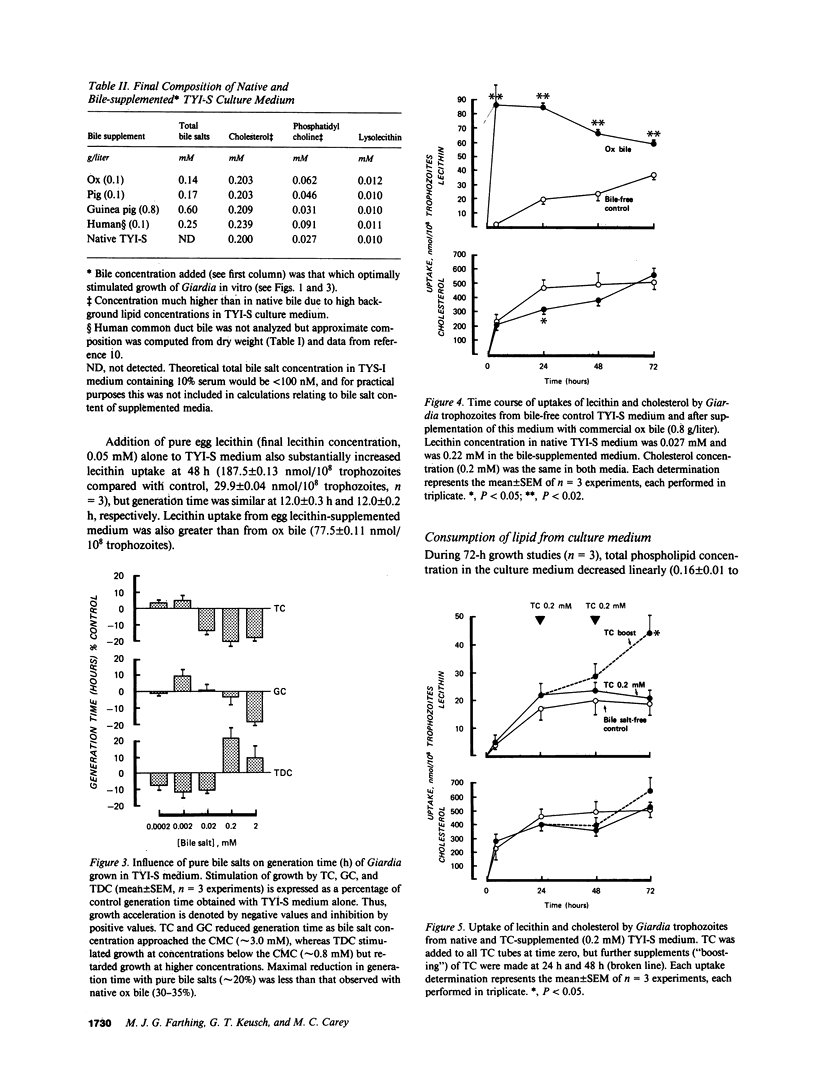
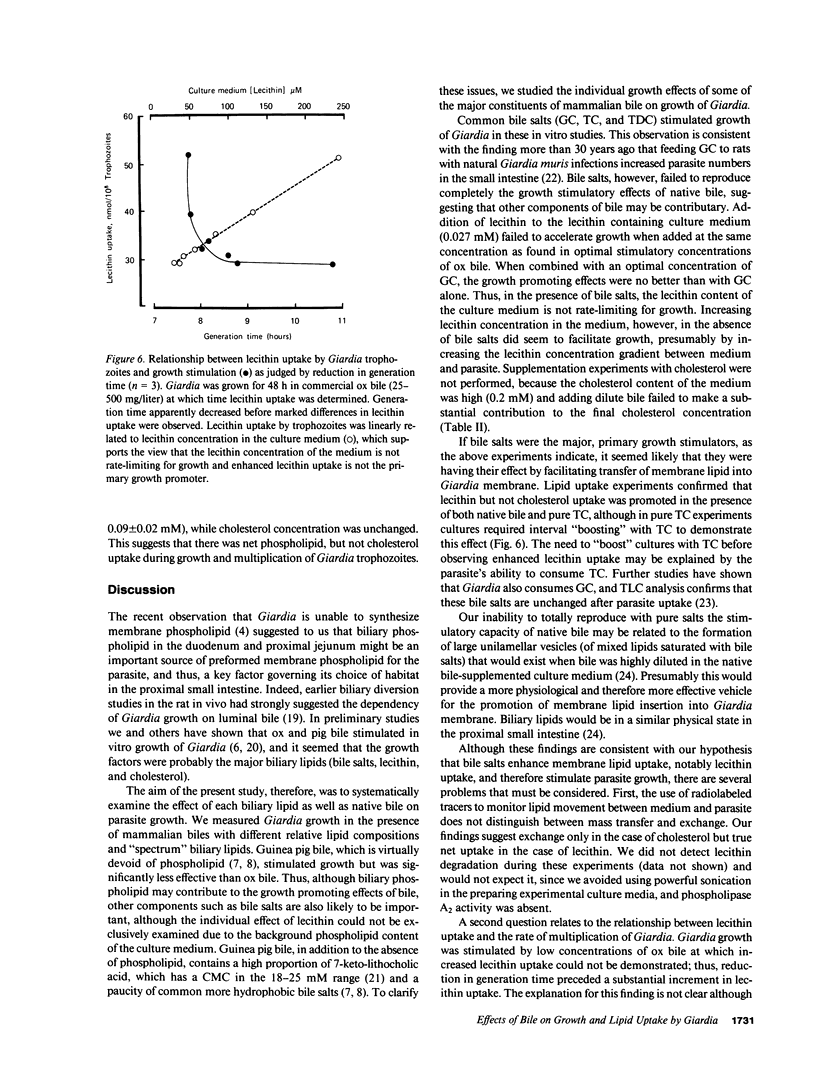
We have shown previously that ox and pig bile accelerate in vitro growth of Giardia lamblia. We have now investigated the possible mechanisms by which mammalian biles promote parasite growth. Growth effects of (a) ox, pig, guinea pig, and human biles, (b) pure bile salts, and (c) egg and soybean lecithins were studied in the presence of a lecithin-containing growth medium. Individually, dilute native bile and pure sodium taurocholate (TC), glycocholate (GC), and taurodeoxycholate (TDC) promoted parasite growth; growth was most marked with biles of high phospholipid content, with biles enriched in more hydrophobic bile salts (ox approximately equal to human greater than pig greater than guinea pig) and with micellar concentrations of GC and submicellar concentrations of TC and TDC. By measuring uptake of radiolabeled biliary lipids from bile and bile salt-supplemented growth medium, we showed that the parasite consumed bile lipids, with the rank order lecithin greater than bile salts. Apparent net uptake of cholesterol was considered to be due to exchange, since net loss of cholesterol from the growth medium was not detected. Although bile and bile salt-stimulated parasite growth was associated with enhanced lecithin uptake, reduction in generation time was observed at low bile and bile salt concentrations when lecithin uptake was similar to bile free controls. Thus, bile salts may stimulate Giardia growth initially by a mechanism independent of enhanced membrane phospholipid uptake. However, since Giardia has no capacity to synthesize membrane lipid, biliary lecithin may be a major source of phospholipid for growth of this parasite.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABEL L. L., LEVY B. B., BRODIE B. B., KENDALL F. E. A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ament M. E., Rubin C. E. Relation of giardiasis to abnormal intestinal structure and function in gastrointestinal immunodeficiency syndromes. Gastroenterology. 1972 Feb;62(2):216–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong M. J., Carey M. C. The hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of bile salts. Inverse correlation between reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatographic mobilities and micellar cholesterol-solubilizing capacities. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):70–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEMRICK W. J. THE EFFECT OF BILE FLOW ON GIARDIA DUODENALIS RACE SIMONI IN THE INTESTINE OF A LABORATORY STRAIN OF RATTUS NORVEGICUS. J Parasitol. 1963 Dec;49:956–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARR J. J., DREKTER I. J. Simplified rapid technic for the extraction and determination of serum cholesterol without saponification. Clin Chem. 1956 Oct;2(5):353–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. Micelle formation by bile salts. Physical-chemical and thermodynamic considerations. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Oct;130(4):506–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. C., Small D. M. The physical chemistry of cholesterol solubility in bile. Relationship to gallstone formation and dissolution in man. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):998–1026. doi: 10.1172/JCI109025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing M. J., Pereira M. E., Keusch G. T. Giardia lamblia: evaluation of roller bottle cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Dec;54(3):410–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing M. J., Varon S. R., Keusch G. T. Mammalian bile promotes growth of Giardia lamblia in axenic culture. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):467–469. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurantz D., Laker M. F., Hofmann A. F. Enzymatic measurement of choline-containing phospholipids in bile. J Lipid Res. 1981 Feb;22(2):373–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartong W. A., Gourley W. K., Arvanitakis C. Giardiasis: clinical spectrum and functional--structural abnormalities of the small intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jul;77(1):61–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarroll E. L., Muller P. J., Meyer E. A., Morse S. A. Lipid and carbohydrate metabolism of Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Feb;2(3-4):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamath K. R., Murugasu R. A comparative study of four methods for detecting Giardia lamblia in children with diarrheal disease and malabsorption. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jan;66(1):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. B. Axenic culture of Giardia lamblia in TYI-S-33 medium supplemented with bile. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):487–488. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazer N. A., Carey M. C. Quasi-elastic light-scattering studies of aqueous biliary lipid systems. Cholesterol solubilization and precipitation in model bile solutions. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):426–442. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olveda R. K., Andrews J. S., Jr, Hewlett E. L. Murine giardiasis: localization of trophozoites and small bowel histopathology during the course of infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 Jan;31(1):60–66. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERIC-GOLIA L., JONES R. S. Cholesterol-4-C 14 and bile acids in the guinea pig. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jan;106:177–180. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roda A., Hofmann A. F., Mysels K. J. The influence of bile salt structure on self-association in aqueous solutions. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6362–6370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Brown W. R. In vitro studies on bile acid deconjugation and lipolysis inhibition by Giardia lamblia. Dig Dis Sci. 1981 Aug;26(8):700–704. doi: 10.1007/BF01316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon B. N., Tandon R. K., Satpathy B. K., Shriniwas Mechanism of malabsorption in giardiasis: a study of bacterial flora and bile salt deconjugation in upper jejunum. Gut. 1977 Mar;18(3):176–181. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.3.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari S. G., Tandon B. N. Functional and histological changes of small bowel in patients with giardia lamblia infestation. Indian J Med Res. 1974 May;62(5):689–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins A. M., Wright S. G., Drasar B. S., James W. P. Bacterial colonization of jejunal mucosa in giardiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90294-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthier R. E. Two-dimensional chromatography on silica gel-loaded paper for the microanalysis of polar lipids. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):544–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



