Abstract
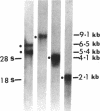
We have characterized the messenger RNAs (mRNAs) coding for procollagen alpha 1(I), elastin, fibronectin, and actin in the lungs of Syrian golden hamsters by Northern blot analyses. While elastin, fibronectin, and beta-actin were each coded for by a single mRNA species of 4.1 kilobases (kb), 9.1 kb, and 2.1 kb in size, respectively, we identified a major (5.4 kb) and a minor (6.5 kb) procollagen alpha 1(I) mRNA species in the hamster lungs. The mRNAs for the three extracellular matrix proteins showed increased accumulation followed by steady decline in the bleomycin-treated lungs. There were significant differences among the three mRNAs in the relative increase and the time of maximum accumulation. After reaching the peak levels between 2-3 wk posttreatment, the levels of procollagen alpha 1(I) and elastin mRNAs declined to near normal values around the fourth week. In contrast, the accumulation of fibronectin mRNA was maximum in the first week after bleomycin treatment. The procollagen alpha 1(I) mRNA accumulated most dramatically (sevenfold above the levels in the untreated animals) compared with a five-fold increase in mRNA coding for fibronectin. Elastin mRNA increased approximately twofold above the control values. Nuclear runoff transcription experiments demonstrated a selective increase in the rates of transcription of genes coding for procollagen alpha 1(I), fibronectin, and elastin; the extent of transcriptional stimulation of procollagen alpha 1(I) and fibronectin genes was significantly greater than that of elastin. Since the amount of actin mRNA, as well as the rate of transcription of actin gene(s), varied only slightly after bleomycin treatment, we conclude that the metabolism of mRNAs coding for extracellular matrix proteins may be preferentially perturbed during pulmonary fibrosis.
Full text
PDF

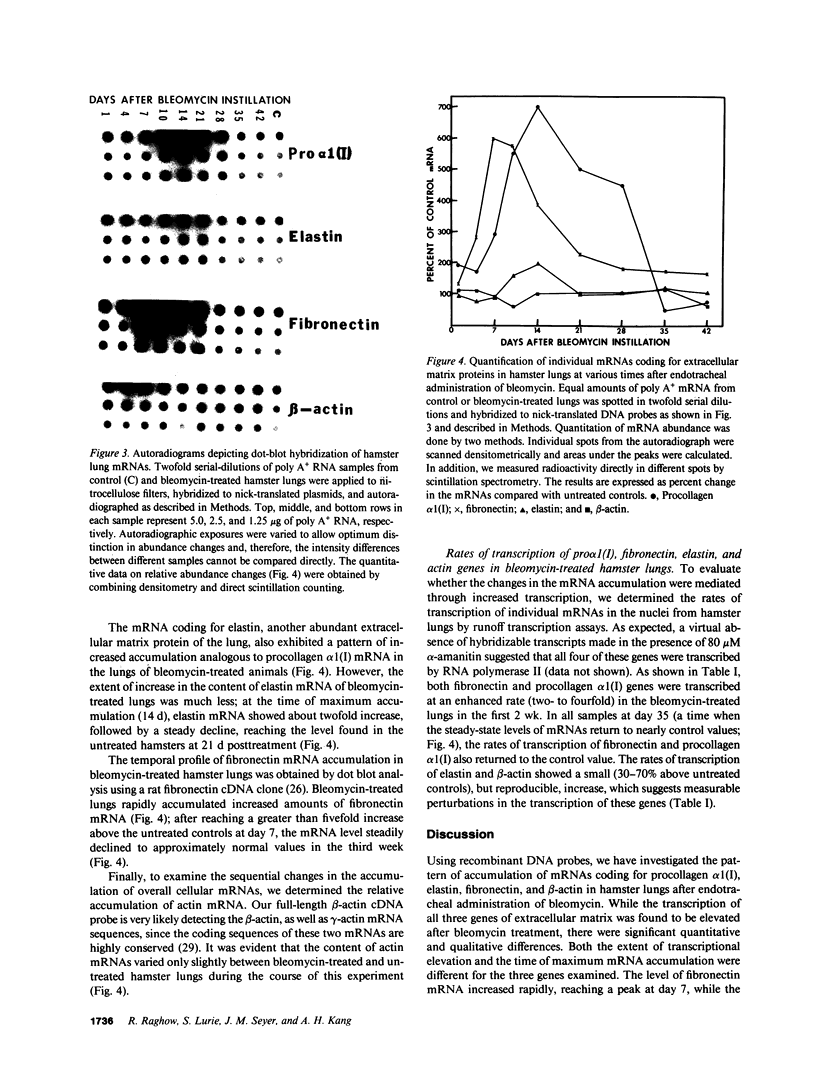
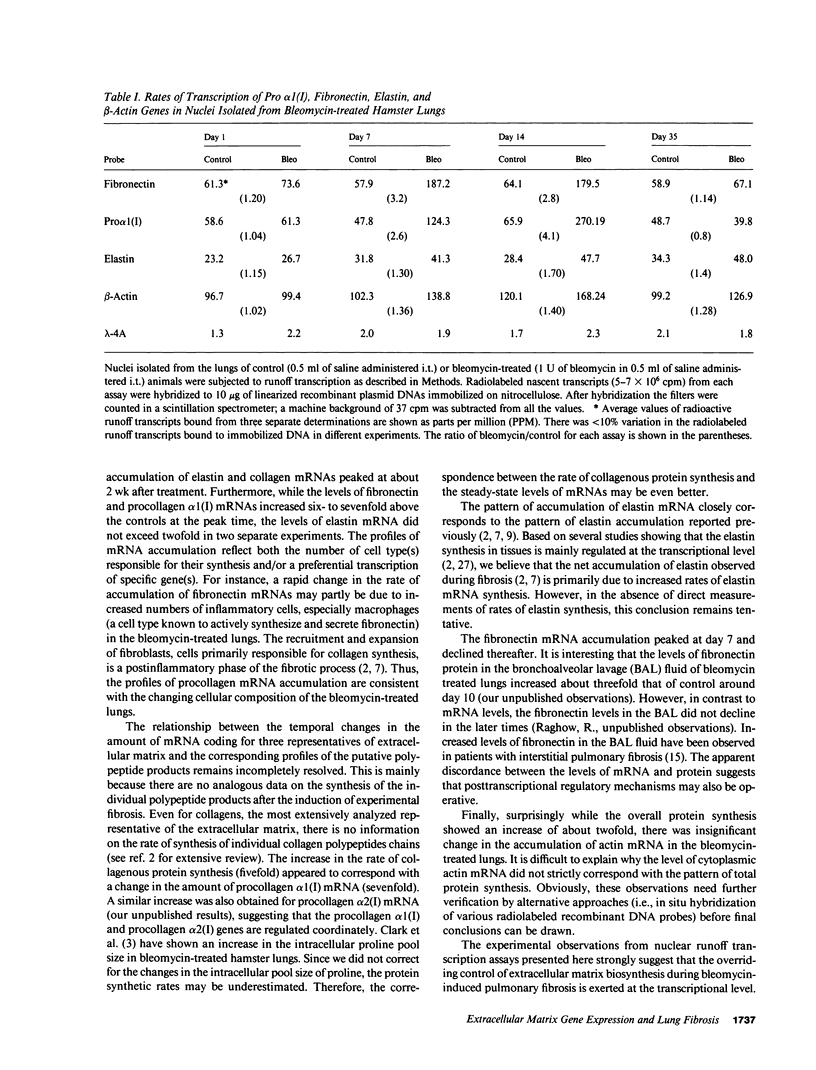


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji S. S., Theodorakis N. G., Morimoto R. I. Heat shock-induced translational control of HSP70 and globin synthesis in chicken reticulocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2437–2448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Adelberg S., Crystal R. G. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Spontaneous release of the alveolar macrophage-derived growth factor in the interstitial lung disorders. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1801–1813. doi: 10.1172/JCI111140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor J. O., Bray B. A., Ryan S. F., Mandl I., Turino G. M. Glycosaminoglycan and collagen synthesis in N-nitroso-N-methylurethane induced pulmonary fibrosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 May;164(1):1–8. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor J. O., Osman M., Cerreta J. M., Mandl I., Turino G. M. Glycosaminoglycan synthesis in explants derived from bleomycin-treated fibrotic hamster lungs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Jul;173(3):362–366. doi: 10.3181/00379727-173-41657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Bernard M. P., Ding J. F., Ramirez F. Cloning and characterization of five overlapping cDNAs specific for the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5925–5934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Kostal K. M., Marino B. A. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. An alveolar macrophage product increases fibroblast prostaglandin E2 and cyclic adenosine monophosphate and suppresses fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2082–2091. doi: 10.1172/JCI111173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Kostal K. M., Marino B. A. Modulation of collagen production following bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. Presence of a factor in lung that increases fibroblast prostaglandin E2 and cAMP and suppresses fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8098–8105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Kuhn C., 3rd, McDonald J. A., Mecham R. P. Lung connective tissue. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1983;10:249–331. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363710-9.50011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Overton J. E., Marino B. A., Uitto J., Starcher B. C. Collagen biosynthesis in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Dec;96(6):943–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Shibahara S., Boyd C., Mason M. L., Tolstoshev P., Crystal R. G. Elastin mRNA levels during foetal development of sheep nuchal ligament and lung. Hybridization to complementary and cloned DNA. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):653–663. doi: 10.1042/bj2200653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Shibahara S., Schafer M. P., Harrison M., Leach C., Tolstoshev P., Crystal R. G. Sheep elastin genes. Isolation and preliminary characterization of a 9.9-kilobase genomic clone. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):643–652. doi: 10.1042/bj2200643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Wan K. M., Ben-Ze'ev A., Penman S. Regulation of actin mRNA levels and translation responds to changes in cell configuration. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):182–189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Boedtker H. Sequence determination and analysis of the 3' region of chicken pro-alpha 1(I) and pro-alpha 2(I) collagen messenger ribonucleic acids including the carboxy-terminal propeptide sequences. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):996–1006. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulmer J. D., Bienkowski R. S., Cowan M. J., Breul S. D., Bradley K. M., Ferrans V. J., Roberts W. C., Crystal R. G. Collagen concentration and rates of synthesis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Aug;122(2):289–301. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. H., Lucey E. C., Franzblau C., Snider G. L. Failure of mechanical properties to parallel changes in lung connective tissue composition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jul;120(1):67–73. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlinsky J. B. Glycosaminoglycans in emphysematous and fibrotic hamster lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jan;125(1):85–88. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madri J. A., Furthmayr H. Collagen polymorphism in the lung. An immunochemical study of pulmonary fibrosis. Hum Pathol. 1980 Jul;11(4):353–366. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80031-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough B., Collins J. F., Johanson W. G., Jr, Grover F. L. Bleomycin-induced diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis in baboons. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):79–88. doi: 10.1172/JCI108928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dickson L. A., de Wet W. J., Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Di Liberto M., Pepe G., Sangiorgi F. O., Ramirez F. Analysis of the 3' end of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Utilization of multiple polyadenylation sites in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10128–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Thrall R. S., Williams C. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Effects of steroid on lung collagen metabolism. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Oct;124(4):428–434. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.4.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Harding J. D., Pictet R. L., Rutter W. J. Accumulation of the predominant pancreatic mRNAs during embryonic development. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2154–2159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Gossage D., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Transcriptional regulation of type I collagen genes in cultured fibroblasts by a factor isolated from thioacetamide-induced fibrotic rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12718–12723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Granoff A. Cell-free translation of frog virus 3 messenger RNAs. Initiation factors from infected cells discriminate between early and late viral mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Crystal R. G. Fibronectin in human bronchopulmonary lavage fluid. Elevation in patients with interstitial lung disease. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):113–122. doi: 10.1172/JCI110421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer J. M., Hutcheson E. T., Kang A. H. Collagen polymorphism in idiopathic chronic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1498–1507. doi: 10.1172/JCI108420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider G. L., Celli B. R., Goldstein R. H., O'Brien J. J., Lucey E. C. Chronic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis produced in hamsters by endotracheal bleomycin. Lung volumes, volume-pressure relations, carbon monoxide uptake, and arterial blood gas studied. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Feb;117(2):289–297. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolstoshev P., Haber R., Trapnell B. C., Crystal R. G. Procollagen messenger RNA levels and activity and collagen synthesis during the fetal development of sheep lung, tendon, and skin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9672–9679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapol W. M., Trelstad R. L., Coffey J. W., Tsai I., Salvador R. A. Pulmonary fibrosis in severe acute respiratory failure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Apr;119(4):547–554. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]