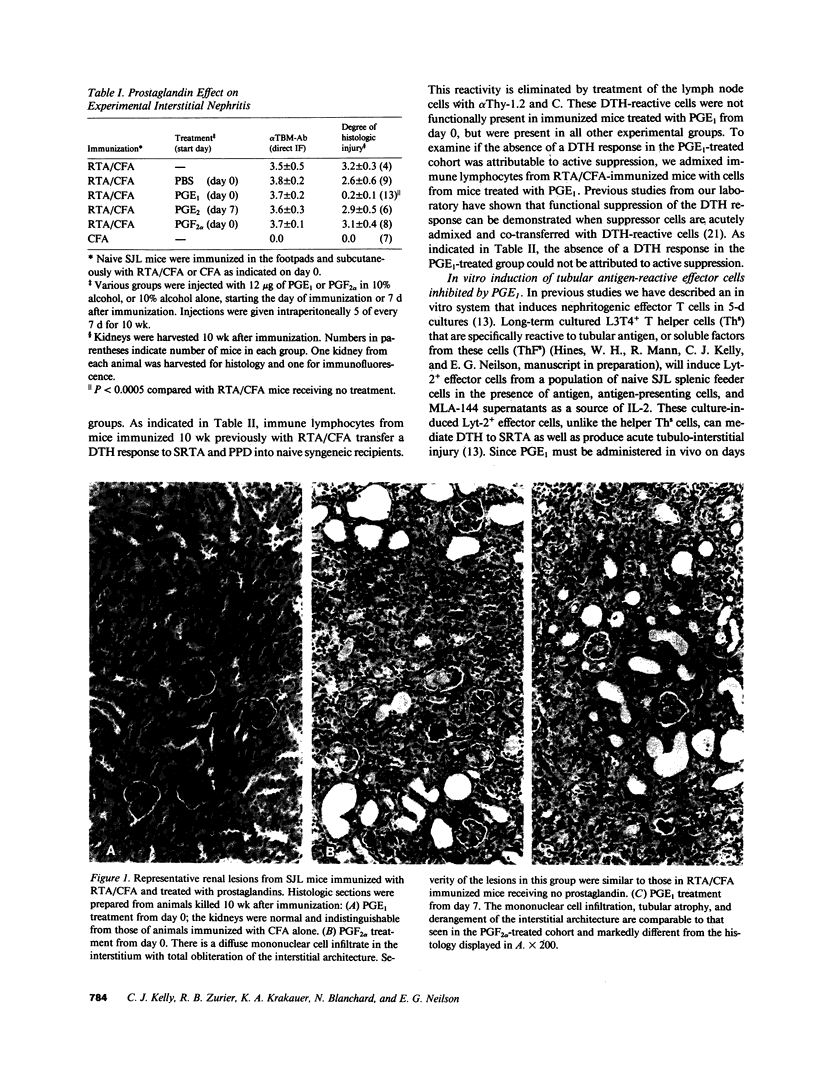
Abstract
Immunosuppressive effects of E-series prostaglandins have been demonstrated in many in vitro assays of immune responsiveness as well as in autoimmune diseases. To explore the mechanisms underlying prostaglandin E1 (PGE1)-associated immunosuppression in autoimmunity, we treated SJL mice immunized to produce immune-mediated interstitial nephritis with PGE1, PGF2 alpha, or vehicle alone. Mice receiving PGE1 treatment do not develop interstitial nephritis, nor do they display delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) to the immunizing renal tubular antigen preparation. The observed immunosuppression is critically dependent on PGE1 administration during the period of effector T cell induction. We therefore investigated the effect of PGE1 on the in vitro induction of DTH effector T cells reactive to renal tubular antigens (SRTA). PGE1 inhibits effector T cell induction in a dose-dependent, reversible manner, but has no inhibitory effect on fully differentiated DTH effector cells or SRTA-reactive cell lines. The PGE1 effect is indirect and mediated via nonspecific suppressor lymphokines. This suppression can be overcome by recombinant interleukin 1 (IL-1), which suggests a mechanism related to either diminished IL-1 secretion or target cell sensitivity to IL-1.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abehsira-Amar O., Damais C., Parant M., Chedid L. Strain dependence of muramyl dipeptide-induced LAF(IL 1) release by murine-adherent peritoneal cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):365–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agus D., Mann R., Clayman M., Kelly C., Michaud L., Cohn D., Neilson E. G. The effects of daily cyclophosphamide administration on the development and extent of primary experimental interstitial nephritis in rats. Kidney Int. 1986 Mar;29(3):635–640. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agus D., Mann R., Cohn D., Michaud L., Kelly C., Clayman M., Neilson E. G. Inhibitory role of dietary protein restriction on the development and expression of immune-mediated antitubular basement membrane-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):930–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI112092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. E., Fahey J. V., Munck A. Prostaglandin inhibition of T-cell proliferation is mediated at two levels. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jun;61(1):52–61. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J., Symington F. W., McKearn T. J., Sprent J. A monoclonal antibody discriminating between subsets of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. C. The distribution and initial characterization of oligosaccharide units on the COOH-terminal propeptide extensions of the pro-alpha 1 and pro-alpha 2 chains of type I procollagen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10798–10802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Webb D. R. Regulation of the immune response by prostaglandins. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Jan;15(1):106–122. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Askenase P. W. Reconstitution of an inactive antigen-specific T cell suppressor factor by incubation of the factor with prostaglandins. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2025–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Winkelstein A., Izui S., Dixon F. J. Prostaglandin E1 inhibits T-cell proliferation and renal disease in MRL/1 mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Nov;21(2):190–203. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Winkelstein A., Izui S. Effect of prostaglandin E on immune complex nephritis in NZB/W mice. Lab Invest. 1979 Dec;41(6):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. J., Clayman M. D., Neilson E. G. Immunoregulation in experimental interstitial nephritis: immunization with renal tubular antigen in incomplete Freund's adjuvant induces major histocompatibility complex-restricted, OX8+ suppressor T cells which are antigen-specific and inhibit the expression of disease. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):903–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. J., Silvers W. K., Neilson E. G. Tolerance to parenchymal self. Regulatory role of major histocompatibility complex-restricted, OX8+ suppressor T cells specific for autologous renal tubular antigen in experimental interstitial nephritis. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1892–1903. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer K. A., Torrey S. B., Zurier R. B. Prostaglandin E1 treatment of NZB/W mice. III. Preservation of spleen cell concentrations and mitogen-induced proliferative responses. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Nov;11(3):256–266. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L. Levels of 13,14-dihydro-15-keto-PGE2 in some biological fluids as measured by radioimmunoassay. Prostaglandins. 1977;14(6):1125–1139. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. V. The auto-induction of antigen-specific Lyt-2+ suppressor T cells diminishes the expression of interstitial nephritis in mice with antitubular basement membrane disease. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):908–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Zakheim B., Clayman M., McCafferty E., Michaud L., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. IV. Long-term cultured L3T4+ T cell lines transfer delayed expression of disease as I-A-restricted inducers of the effector T cell repertoire. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):286–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeish K. R., Stelzer G. T., Eades D. S., Cohen R., Wallace J. H. Serial changes in humoral and cellular immunity induced by prostaglandin E2 treatment of murine immune complex glomerulonephritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Nov;106(5):517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., McCafferty E., Mann R., Michaud L., Clayman M. Murine interstitial nephritis. III. The selection of phenotypic (Lyt and L3T4) and idiotypic (RE-Id) T cell preferences by genes in Igh-1 and H-2K characterizes the cell-mediated potential for disease expression: susceptible mice provide a unique effector T cell repertoire in response to tubular antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2375–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., McCafferty E., Mann R., Michaud L., Clayman M. Tubular antigen-derivatized cells induce a disease-protective, antigen-specific, and idiotype-specific suppressor T cell network restricted by I-J and Igh-V in mice with experimental interstitial nephritis. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):215–230. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Phillips M. Suppression of interstitial nephritis by auto-anti-idiotypic immunity. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):179–189. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Phillips S. M. Cell-mediated immunity in interstitial nephritis. I. T lymphocyte systems in nephritic guinea pigs: the natural history and diversity of the immune response. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2373–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Phillips S. M. Murine interstitial nephritis. I. Analysis of disease susceptibility and its relationship of pleiomorphic gene products defining both immune-response genes and a restrictive requirement for cytotoxic T cells at H-2K. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Ruscetti F. W., Neubauer R. H., Brown R. L., Kawakami T. G. Spontaneous release of a factor with properties of T cell growth factor from a continuous line of primate tumor T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. S., Dodge G. R. Prostaglandin E inhibits the production of human interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):943–948. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. J., Campbell L., Calhoun K., Nowowiejski I., Webb D. R. Suppression of B-cell and T-cell responses by the prostaglandin-induced T-cell-derived suppressor (PITS). I. Analysis of the PITS beta factor. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jan 15;66(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. J., DeHaven J. I., Donnelly R. P., Lamb B. Suppression of B-cell and T-cell responses by the prostaglandin-induced T-cell-derived suppressor (PITS). II. Resolution of multiple PITS beta factors. Cell Immunol. 1984 Sep;87(2):703–707. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. J., Nowowiejski I., Webb D. R. Partial characterization of a prostaglandin-induced suppressor factor. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 1;50(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Beller D. I., Unanue E. R. Prostaglandins modulate macrophage Ia expression. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):163–165. doi: 10.1038/299163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Kristensen F., Bettens F., deWeck A. L. Lymphokine regulation of activated (G1) lymphocytes. I. Prostaglandin E2-induced inhibition of interleukin 2 production. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1770–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D. R., Wieder K. J., Rogers T. J., Healy C. T., Nowowiejski-Wieder I. Chemical identification of a prostaglandin-induced T suppressor (PITS). Lymphokine Res. 1985 Spring;4(2):139–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakheim B., McCafferty E., Phillips S. M., Clayman M., Neilson E. G. Murine interstitial nephritis. II. The adoptive transfer of disease with immune T lymphocytes produces a phenotypically complex interstitial lesion. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):234–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Damjanov I., Sayadoff D. M., Rothfield N. F. Prostaglandin E1 treatment of NZB/NZW F1 hybrid mice. II. Prevention of glomerulonephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Nov-Dec;20(8):1449–1456. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]