Abstract
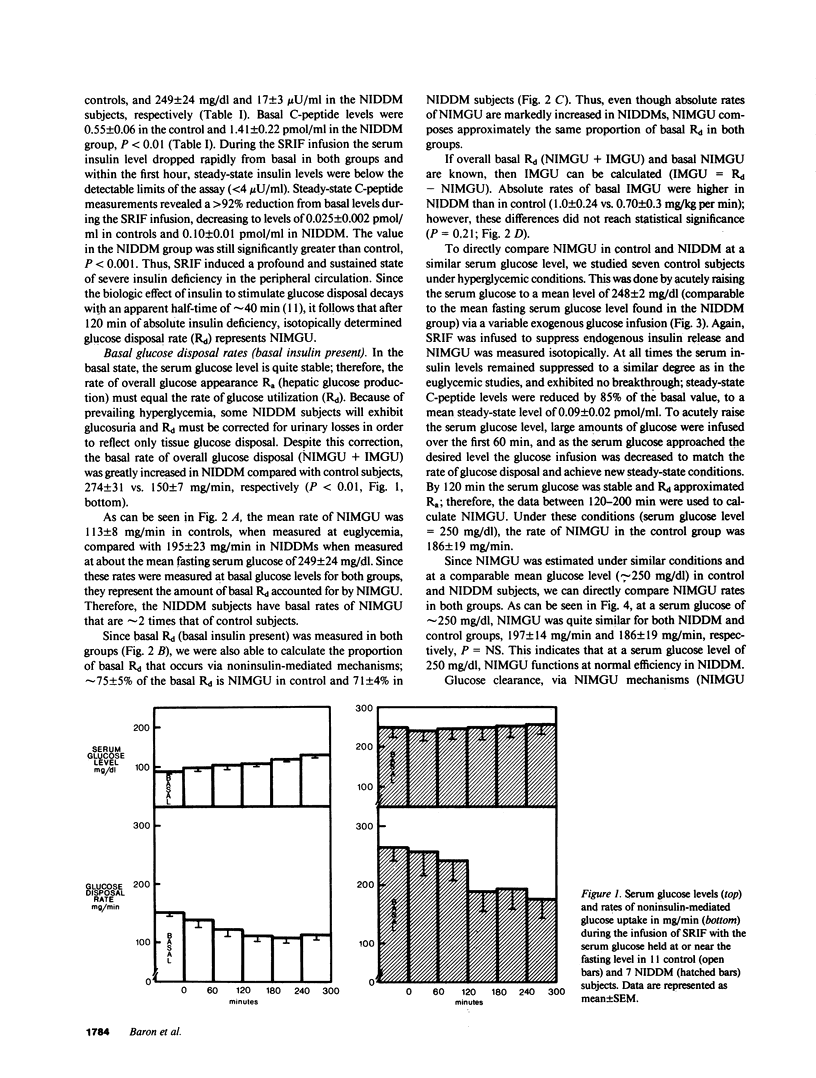
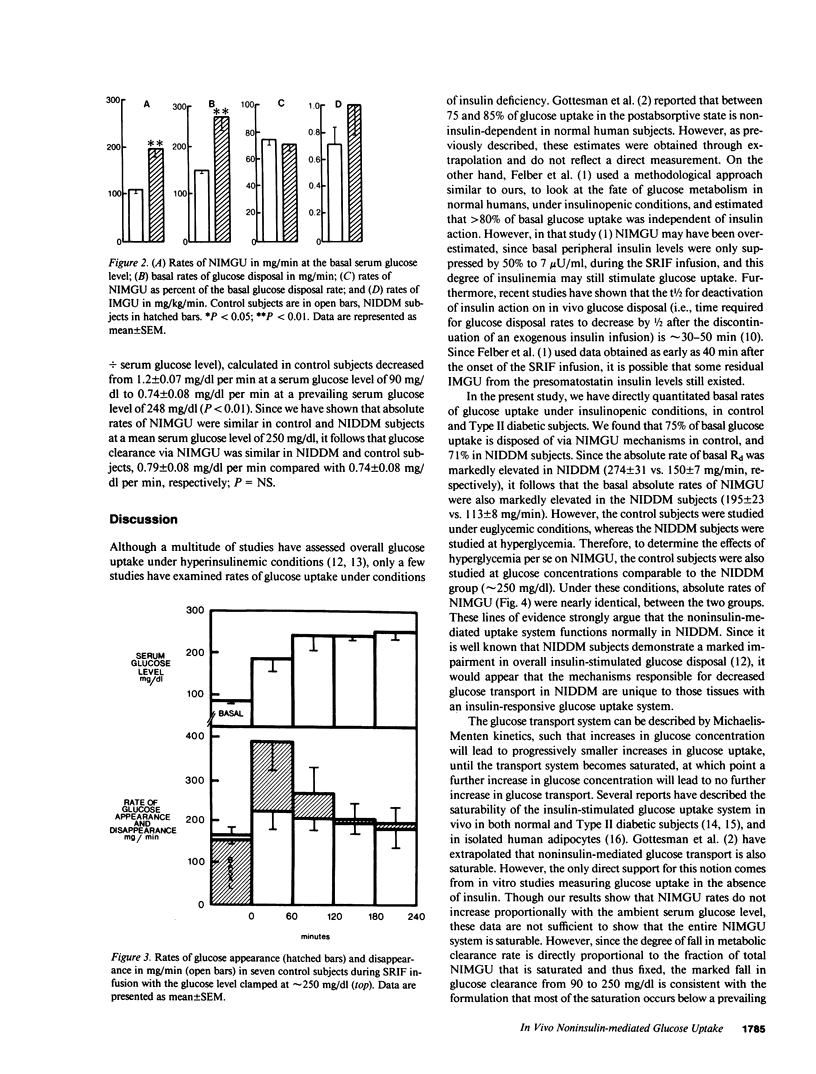
Although insulin is extremely potent in regulating glucose transport in insulin-sensitive tissues, all tissues are capable of taking up glucose by facilitated diffusion by means of a noninsulin-mediated glucose uptake (NIMGU) system. Several reports have estimated that in the postabsorptive state the majority of glucose disposal occurs via a NIMGU mechanism. However, these estimates have been either derived or extrapolated in normal humans. In the present study we have directly measured NIMGU rates in 11 normal (C) and 7 Type II noninsulin-dependent diabetic subjects (NIDDM; mean +/- SE fasting serum glucose, 249 +/- 24 mg/dl). To accomplish this, the serum glucose was clamped at a desired level during a period of insulin deficiency induced by a somatostatin infusion (SRIF, 550 micrograms/h). With a concomitant [3-3H]glucose infusion, we could isotopically quantitate glucose disposal rates (Rd) during basal (basal insulin present) and insulin-deficient (SRIF) conditions. With this approach we found that (a) basal Rd was greater in NIDDM than in C, 274 +/- 31 vs. 150 +/- 7 mg/min, due to elevated hepatic glucose output, (b) NIMGU composes 75 +/- 5% of basal Rd in C and 71 +/- 4% in NIDDM, (c) NIDDMS have absolute basal NIMGU rates that are twice that of C (195 +/- 23 vs. 113 +/- 8 mg/min, P less than 0.05), (d) when C were studied under conditions of insulin deficiency (SRIF infusion) and at a serum glucose level comparable to that of the NIDDM group (250 mg/dl), their rates of NIMGU were the same as that of the NIDDM group (186 +/- 19 vs. 195 +/- 23 mg/min; NS). We conclude that (a) in the postabsorptive state, NIMGU is the major pathway for glucose disposal for both C and NIDDM; (b) for a given glucose level the efficiency of NIMGU (NIMGU divided by serum glucose level) is equal in C and NIDDM, but since basal Rd is elevated in NIDDMs their absolute basal rates of NIMGU are higher; and (c) elevated basal rates of NIMGU in NIDDM may play a role in the pathogenesis of the late complications of diabetes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergman R. N., Ader M., Finegood D. T., Pacini G. Extrapancreatic effect of somatostatin infusion to increase glucose clearance. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 1):E370–E379. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.3.E370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berhanu P., Olefsky J. M. Effects of insulin and insulin-like agents on the glucose transport system of cultured human fibroblasts. Diabetes. 1981 Jun;30(6):523–529. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.6.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Howard B. V., Reaven G., Mott D. Relationships between insulin secretion, insulin action, and fasting plasma glucose concentration in nondiabetic and noninsulin-dependent diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1238–1246. doi: 10.1172/JCI111533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Caldwell M. D., Dietz M. R., Exton J. H., Crofford O. B. The effect of somatostatin on glucose uptake and production by rat tissues in vitro. Diabetes. 1977 Aug;26(8):740–748. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.8.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Kolterman O. G., Siegel J. A., Olefsky J. M. Insulin-stimulated glucose transport in human adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E621–E625. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Kolterman O. G., Siegel J. A., Olefsky J. M. Insulin-stimulated glucose transport in human adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E621–E625. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Aurbach G. D. Use of polyethylene glycol to separate free and antibody-bound peptide hormones in radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):732–738. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber J. P., Thiébaud D., Maeder E., Jéquier E., Hendler R., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of somatostatin-induced insulinopenia on glucose oxidation in man. Diabetologia. 1983 Oct;25(4):325–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00253195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Barrett E. J., Bevilacqua S., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1737–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI111133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Bier D. M., Tsalikian E., Schneider V., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Effects of physiologic levels of glucagon and growth hormone on human carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Studies involving administration of exogenous hormone during suppression of endogenous hormone secretion with somatostatin. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):875–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI108364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Bier D. M., Tsalikian E., Schneider V., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Effects of physiologic levels of glucagon and growth hormone on human carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Studies involving administration of exogenous hormone during suppression of endogenous hormone secretion with somatostatin. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):875–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI108364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman I., Mandarino L., Verdonk C., Rizza R., Gerich J. Insulin increases the maximum velocity for glucose uptake without altering the Michaelis constant in man. Evidence that insulin increases glucose uptake merely by providing additional transport sites. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1310–1314. doi: 10.1172/JCI110731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. S., Scarlett J. A., Griffin J., Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G. In vivo deactivation of peripheral, hepatic, and pancreatic insulin action in man. Diabetes. 1982 Oct;31(10):929–936. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.10.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. C., Phelps M. E., Hoffman E. J., Sideris K., Selin C. J., Kuhl D. E. Noninvasive determination of local cerebral metabolic rate of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jan;238(1):E69–E82. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.1.E69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M. Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):957–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI110350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen O. E., Morgan A. P., Kemp H. G., Sullivan J. M., Herrera M. G., Cahill G. F., Jr Brain metabolism during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1589–1595. doi: 10.1172/JCI105650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky K., Jaspan J., Pugh W., Cohen D., Schneider M., Schwartz T., Moossa A. R., Tager H., Rubenstein A. H. Metabolism of C-peptide in the dog. In vivo demonstration of the absence of hepatic extraction. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1114–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI111036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revers R. R., Fink R., Griffin J., Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G. Influence of hyperglycemia on insulin's in vivo effects in type II diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):664–672. doi: 10.1172/JCI111258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Dose-response characteristics for effects of insulin on production and utilization of glucose in man. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E630–E639. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEINBERG P. OBSERVATIONS ON CEREBRAL CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM IN MAN. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Feb;62:367–371. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., DeFronzo R., Wahren J., Felic P. Glucose homeostasis during prolonged suppression of glucagon and insulin secretion by somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):348–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiébaud D., DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Golay A., Acheson K., Maeder E., Jéquier E., Felber J. P. Effect of long chain triglyceride infusion on glucose metabolism in man. Metabolism. 1982 Nov;31(11):1128–1136. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



