Abstract
Up to 93% of patients with hereditary angioedema (HAE) experience recurrent abdominal pain. Many of these patients, who often present to emergency departments, primary care physicians, general surgeons, or gastroenterologists, are misdiagnosed for years and undergo unnecessary testing and surgical procedures. Making the diagnosis of HAE can be challenging because symptoms and attack locations are often inconsistent from one episode to the next. Abdominal attacks are common and can occur without other attack locations. An early, accurate diagnosis is central to managing HAE. Unexplained abdominal pain, particularly when accompanied by swelling of the face and extremities, suggests the diagnosis of HAE. A family history and radiologic imaging demonstrating edematous bowel also support an HAE diagnosis. Once HAE is suspected, C4 and C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) laboratory studies are usually diagnostic. Patients with HAE may benefit from recently approved specific treatments, including plasma-derived C1-INH or recombinant C1-INH, a bradykinin B2-receptor antagonist, or a kallikrein inhibitor as first-line therapy and solvent/detergent-treated or fresh frozen plasma as second-line therapy for acute episodes. Short-term or long-term prophylaxis with nanofiltered C1-INH or attenuated androgens will prevent or reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. Gastroenterologists can play a critical role in identifying and treating patients with HAE, and should have a high index of suspicion when encountering patients with recurrent, unexplained bouts of abdominal pain. Given the high rate of abdominal attacks in HAE, it is important for gastroenterologists to appropriately diagnose and promptly recognize and treat HAE, or refer patients with HAE to an allergist.
Keywords: hereditary angioedema, abdominal pain, diagnosis
Introduction
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a potentially life-threatening disease that may go unrecognized or be misdiagnosed for an average of 8 years before the correct diagnosis is established.1 Abdominal symptoms are extremely common, occurring in the majority (93%) of patients with HAE,2 and may be the only manifestation of the disease. Patients with HAE may initially present with recurrent episodes of abdominal pain and distension, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.3,4
Because abdominal symptoms may precede by several years the episodes of subcutaneous tissue swelling that are characteristic of HAE, patients may undergo inappropriate surgical and medical treatment for any of a wide range of presumptive, incorrect diagnoses, including acute abdomen, biliary colic, hepatitis, regional enteritis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, choledocholithiasis, nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis, ruptured ovarian cyst, intestinal obstruction, duodenal ulcer, and ulcerative colitis.3,4 Patients who develop abdominal symptoms related to HAE are usually seen by gastroenterologists, emergency department physicians, primary care physicians, and general surgeons.5 Given that the majority of patients with HAE experience abdominal attacks, it is important for gastroenterologists to appropriately diagnose and promptly recognize and treat HAE or refer patients with HAE to an allergist.2 This review highlights HAE, its clinical presentation, and the role of the gastroenterologist in its diagnosis and management.
Disease burden
Patients with HAE who are seen in the emergency department often require hospitalization, considerably increasing the cost of care for each attack.6 Review of a national database has shown that between 2006 and 2007 there were 5,040 emergency department visits by patients with HAE at a mean cost of $1,479 per visit, and with 41% of these visits requiring hospitalization.6 Similarly, in a 4-year analysis of the epidemiology of HAE, there were 10,125 hospitalizations, with a mean length of stay of 5 days and mean charges of $22,728.7 HAE is also associated with a high rate of morbidity, with many patients experiencing depression and poor health-related quality of life. HAE also negatively affects educational and career opportunities and reduces work productivity, compounding the substantial economic burden of HAE.8
Types and pathophysiology
Estimates of the incidence of HAE worldwide vary from one in 10,000 to one in 150,000 persons.9,10 In a retrospective review of patients with HAE, the median age at disease onset was 11.2 years, 93.3% of patients had recurrent abdominal pain, and women experienced a higher number of episodes per year than men.2 HAE is caused by mutations in the C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) gene, also known as the SERPING1 gene, which has been mapped to chromosome 11.11 A known family history is present in 75% of cases, with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern; in the remaining 25% of cases, the disease results from spontaneous mutations.12–14 Two types of HAE due to C1-INH deficiency have been characterized. Type I HAE accounts for 85% of cases and is due to mutations that result in decreased antigenic levels of functionally normal C1-INH. Type II HAE accounts for 15% of cases and is due to mutations that lead to levels of C1-INH that are normal but that have dysfunctional C1-INH proteins.15 So far, more than 200 different mutations that cause HAE have been identified.16,17
A third type of HAE (HAE with normal C1-INH) has been identified, in which the level and activity of C1-INH are normal and there is no characteristic laboratory profile. The clinical presentation of this type of HAE is indistinguishable from types I and II; however, this third type tends to develop later in life. In some patients, this subtype is associated with a mutation in the coagulation factor XII gene, with subsequent increased levels of bradykinin. Estrogen exacerbates the severity of disease in patients with HAE who have normal C1-INH, and edema appears to be estrogen-dependent in a subset of patients.18,19
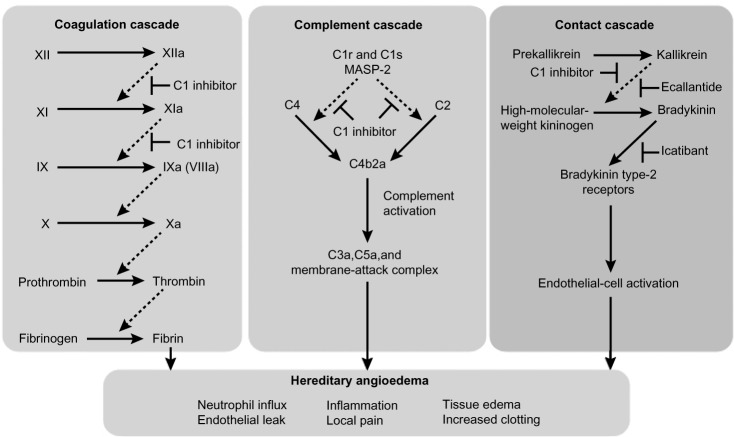
The underlying mechanism for HAE types I and II is functional impairment of C1-INH, a protease inhibitor that regulates complement activation (C1r, C1s, and mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease [MASP]-1 and MASP-2), contact system activation (factor XII and kallikrein), and inactivation of several fibrinolytic (tissue plasminogen activator and plasmin) and coagulation (factor XI and thrombin) proteases.16,20,21 Of the four systems regulated by C1-INH, regulation of plasma kallikrein, the enzyme that releases bradykinin from kininogen, is responsible for the development of angioedema. A deficiency in C1-INH leads to unregulated plasma kallikrein activity, with subsequent overproduction of bradykinin that enhances vasodilation and vascular permeability, causing extravasation of plasma into interstitial tissue, leading to angioedema.18,22 The kallikrein-kinin system has a central role in several other systems, including the clotting cascade, vasodilation, vascular permeability, and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.21,23,24 Figure 1 shows the dysregulation of the coagulation, complement, and contact cascades in HAE.25
Figure 1.
Dysregulation of coagulation, complement, and contact cascades in hereditary angioedema.
Notes: C1 inhibitor controls activation in the complement, coagulation, and contact cascades, and all three cascades are dysregulated in hereditary angioedema. Replacement of C1 inhibitor restores homeostasis. Ecallantide and icatibant specifically inhibit the contact cascade but have no direct effect on the complement or coagulation cascades.25 Dashed arrows indicate enzyme cleavage steps; T bars indicate points of inhibition. Reprinted from The New England Journal of Medicine, Morgan BP. Hereditary angioedema: therapies new and old. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(6):581–583. Copyright © 2010 Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.25
Abbreviations: HAE, hereditary angioedema; MASP-2, mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2.
Clinical presentation of type I and type II HAE
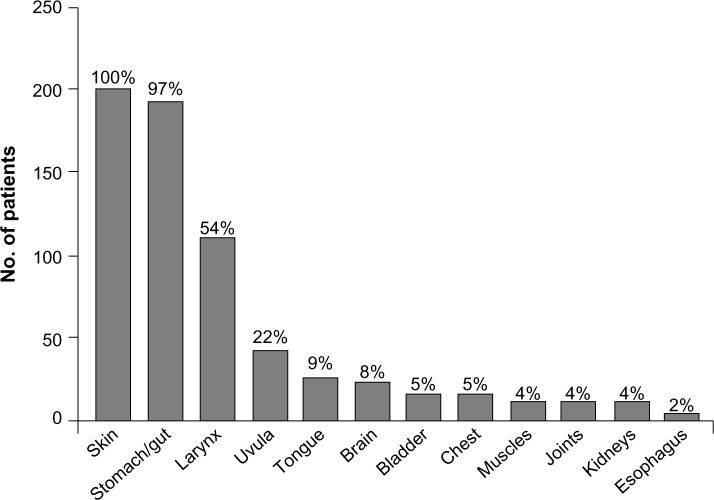
Precipitating factors for HAE episodes may include medications such as oral contraceptives or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, infection, trauma, hormonal changes, and surgical, endoscopic, or dental procedures.18,26,27 Depending on the underlying cause of angioedema, an untreated attack will typically resolve within 1–5 days; however, episodes involving the abdomen or upper airways may require acute treatment to alleviate pain, nausea, and vomiting, in the case of abdominal angioedema, and to prevent death, in the case of respiratory symptoms.5 The site of an HAE attack varies between patients and may also vary within the same patient.28 The most common symptoms of HAE are recurrent abdominal symptoms, occurring in about 93% of patients, and diffuse skin edema, particularly in the extremities, occurring in 97.5% of patients.2 The lips, eyelids, tongue, or genitalia may also be affected.2,28 The frequency and distribution of symptoms experienced by patients during an HAE attack are shown in Figure 2.2
Figure 2.
Sites affected by angioedema in patients with clinical symptoms of hereditary angioedema.
Notes: Reprinted from The American Journal of Medicine. Volume 119(3), Bork K, Meng G, Staubach P, Hardt J. Hereditary angioedema: new findings concerning symptoms, affected organs, and course pages 267–274; Copyright © 2006, with permission from Elsevier.2
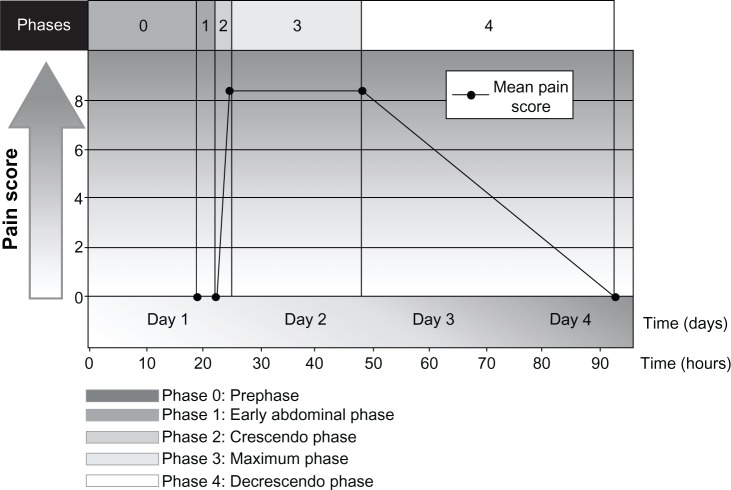
HAE may also present with episodic, recurrent, unexplained abdominal attacks that involve symptoms of tender, crampy pain and nausea or vomiting.5,29,30 The abdominal pain experienced by patients with HAE may be severe and acute in onset, or may be recurrent and chronic and of moderate severity.5,29 The diarrhea is caused by edema of the gut that may result in extravascular fluid loss, leading to hypotension and shock in some patients.29 In a prospective and retrospective analysis of 153 patients with HAE, pain caused by abdominal attacks was characterized by its intensity, quality, and time course, and was described as having four phases, as well as a prephase (phase 0) in which patients had extra-abdominal symptoms but not abdominal pain (Figure 3).30 Phase 1 was the time from the first abdominal complaint to the onset of crampy pain; phase 2 was the time between the initial crampy pain and its peak; phase 3 was the time of maximum symptoms; and phase 4 was the time from the beginning of symptom relief to complete resolution of symptoms.30 The mean duration of phase 1 was 3.3 hours, during which patients had a wide range of symptoms, which included a feeling of satiety, abdominal distension, and nausea. All patients developed worsening crampy pain during phase 2, with the mean time to maximal pain being 2.4 hours. The median duration of the maximal pain phase was 23.5 hours, with crampy pain occurring in all patients, scored as severe to excruciating in 87% of patients and associated with vomiting and diarrhea in 78% and 65% of patients, respectively. The mean time to complete resolution of symptoms was 45.0 hours. Review of the character of the pain symptoms in these patients showed the presence of two different types of abdominal pain attack, ie, an upper gastrointestinal type and a lower gastrointestinal type. Patients with the upper gastrointestinal type of abdominal pain from HAE had extreme pain, nausea, vomiting, and hypotension in the absence of diarrhea; patients with the lower gastrointestinal type of abdominal attack had crampy pain and diarrhea, but no vomiting or hypotension. Other less frequent but potentially serious symptoms or complications in patients with HAE experiencing an abdominal attack have included circulatory collapse and shock due to hypovolemia, persistent noncrampy abdominal pain, dysuria, bloody diarrhea, intussusceptions, and tetany.30
Figure 3.
Phases and time course for typical abdominal pain attacks in patients with hereditary angioedema.
Notes: Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd on behalf of American Journal of Gastroenterology. Copyright © 2006. Bork K, Staubach P, Eckardt AJ, Hardt J. Symptoms, course, and complications of abdominal attacks in HAE to C1 inhibitor deficiency. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101(3):619–627.30
The abdominal symptoms of HAE are often similar to those of an acute abdomen, sometimes prompting exploratory abdominal surgery; as a result, approximately one third of patients with undiagnosed HAE undergo unnecessary surgery at the time of an abdominal attack.31 Even after HAE has been diagnosed, distinguishing between an abdominal attack and a surgical emergency can be difficult.31 In one case, a 46-year-old woman presented with recurrent abdominal pain and edema several years before developing intermittent, localized episodes of limb, trunk, neck, and facial swelling. She had undergone numerous surgical procedures for a variety of diagnoses, including pancreatitis, cholecystitis, common bile duct stone, ruptured ovarian cyst, renal stone, intestinal obstruction, pyelonephritis, duodenal ulcer, and ulcerative colitis before HAE was ultimately diagnosed.3 In another case study, a 34-year-old woman who presented to the emergency department with severe abdominal cramping on several occasions was treated for presumed gastroenteritis; this patient, too, was later found to have HAE.32 In a recent retrospective study, significant leukocytosis with neutrophilia and high hematocrit levels and no elevations in C-reactive protein levels were present in all patients with HAE during an acute gastrointestinal attack,33 suggesting that such a laboratory profile may be a consideration in the differential diagnosis of HAE.
Upper airway edema with asphyxiation is a potentially fatal clinical presentation of HAE.34 Although often referred to as “laryngeal edema,” upper airway edema often involves the mucosa of the mesopharynx and hypopharynx.35 Interestingly, however, the formation of edema spares the mucosa of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. In many cases, the exact anatomic location of swelling remains uncharted, because during attacks patients are only rarely seen by ear, nose, and throat specialists.35 Upper airway edema may occur in approximately half of all patients with HAE at least once in their lives.2 Upper airway edema has been associated with a high mortality rate, which has improved with appropriate diagnosis and treatment.29
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of HAE is often delayed due to low awareness of the disease; however, unacceptable delays in diagnosis have been reported even when a family history of HAE is known.36 Gastroenterologists should consider a diagnosis of angioedema in all patients presenting with episodic, recurrent, unexplained abdominal attacks that involve symptoms of tender, crampy pain, and nausea or vomiting (Table 1).26,30,32 Between abdominal attacks, the patient with HAE is completely asymptomatic, unlike patients with functional bowel disorders. Analysis of the history should attempt to identify triggers for the symptoms, such as medications, allergens, trauma, or infection, and to identify either a personal or family history of HAE. Although the presence of a family history is helpful in making the diagnosis, the absence of a family history does not rule out the condition, because 25% of cases are the result of spontaneous mutations.13 During an acute episode, the physical examination may show marked abdominal distension; possible cutaneous swelling; diffuse or localized tenderness, sometimes with rebound; and shifting dullness with possible ascites.5 Urticaria and pruritus are not present and are seen only in allergic forms of angioedema,5 although in some patients, erythema marginatum precedes acute events and may be misdiagnosed as urticaria.37,38
Table 1.
Differential diagnosis of intestinal angioedema
| Initial presentation | Colicky abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting |
| Possible gastrointestinal disorders | • Appendicitis |
| • Hepatitis | |
| • Pancreatitis | |
| • Biliary obstruction | |
| • Diverticulitis | |
| Test results | |
| Biochemical | Suggestive of HAE |
| • C1-INH level of <21 mg/dL | |
| • Decreased C2 and C4 levels | |
| Rules out biliary obstruction and hepatitis | |
| • Normal serum bilirubin, ALP, and ALT levels | |
| Ultrasonography | Suggestive of HAE |
| • Bowel mucosal thickening | |
| • Ascites | |
| Computed tomography | Suggestive of HAE |
| • Massive small bowel or colonic edema | |
| • Prominent mesenteric vessels | |
| • Thickened omentum | |
| • Moderate ascites | |
| Rules out appendicitis and diverticulitis | |
| • Normal pericolic fat | |
| Rules out pancreatitis | |
| • Normally shaped pancreas | |
Notes: Data from Bork, Fischer, and Dewald;26 and Bork, Staubach, and Eckardt.30 Reproduced from Locascio EJ, Mahler SA, Arnold TC. Intestinal angioedema misdiagnosed as recurrent episodes of gastroenteritis. West J Emerg Med. 2010;11(4): 391–394.32
Abbreviations: ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; C1-INH, C1 esterase inhibitor; HAE, hereditary angioedema.
Imaging studies for the diagnosis of HAE involving the abdomen include plain radiographs, ultrasonography, contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen.39 An abdominal CT scan in a patient with HAE may show thickening of the bowel wall and mucosa and an increase in enhancement when a contrast agent is used (Figure 4).39 An abdominal CT scan may also show more layers of the small bowel than are normally visible and more prominent mesenteric vessels and ascites. Abdominal ultrasonography is useful for confirming the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity during an attack and for early detection of adverse effects of therapy,40,41 and may be less expensive and more readily available than CT. A CT scan or ultrasonography is usually sufficient to diagnose angioedema of the abdomen,27,42 and magnetic resonance imaging may be necessary with manifestations of potential cerebral edema.43
Figure 4.
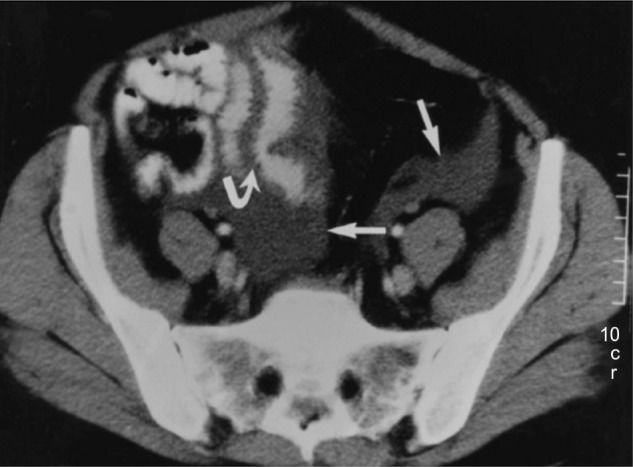
Abdominal computed tomography scan of patient with hereditary angioedema showing thickening of the small bowel (stacked-coin appearance) due to angioedema.
Notes: Curved arrow indicates prominent fold thickening; straight arrows indicate pelvic ascites. Reprinted with permission from the American Journal of Roentgenology. De Backer AI, De Schepper AM, Vandevenne JE, Schoeters P, Michielsen P, Stevens WJ. CT of angioedema of the small bowel. Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176(3):649–652.39
Capsule endoscopy can provide rapid visual confirmation of bowel occlusion due to HAE44 and may be a useful diagnostic tool. When HAE is suspected or known, proper prophylactic measures must be taken to prevent induction or exacerbation of potentially life-threatening oropharyngeal edema.5
Laboratory evaluation for HAE should include measurement of C4 complement, concentration of C1-INH, and functional measurement of C1-INH (see Table 1). C4 levels are typically less than 30% of mean normal levels, which usually range from 0.15 to 0.65 g/L in untreated HAE.45 Because C4 levels have a high sensitivity and negative predictive value for the disease, they are considered to be a good screening test for HAE.45,46 C1-INH antigen levels are low in type I HAE and are normal or high in type II HAE.15
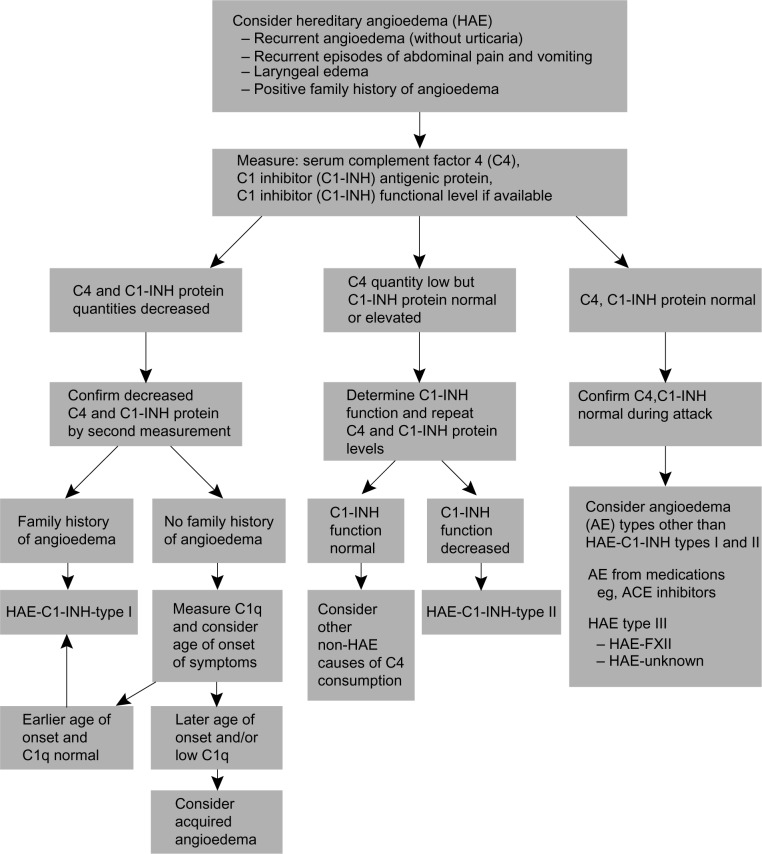
If either the C1-INH concentration or functions are low in an individual with low C4 levels, the tests should be repeated before making the diagnosis, to minimize false positive results.45 Given the high negative predictive value of C4, the diagnosis of HAE should be questioned in individuals with normal C4 and low C1-INH concentration or function.15,45,46 Normal C4 levels and normal C1-INH concentration and function in patients with a clinical presentation consistent with HAE should prompt an evaluation for HAE with normal C1-INH.47,48 A thorough patient history, along with imaging and laboratory evaluations, is critical to successfully making a differential diagnosis of acute HAE and initiating prompt and appropriate treatment (Figure 5).49,50
Figure 5.
Diagnostic algorithm for hereditary angioedema.
Notes: From Bowen T, Cicardi M, Farkas H, et al. 2010 international consensus algorithm for the diagnosis, therapy and management of hereditary angioedema. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2010;6(1):24.50
Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; C1-INH, C1 esterase inhibitor; C1q, complement component 1, q subcomponent; HAE, hereditary angioedema.
Treatment
Current awareness of treatment
Once a patient is diagnosed with HAE, the gastroenterologist should involve an allergist or immunologist to guide the long-term management of the patient.5 Patients should be well trained for self-administration of medications and should be advised to wear a medical bracelet or carry a wallet card detailing their treatment plan in the event of an acute HAE attack.51,52 Several evidence-based management guidelines and recommendations have been developed for the acute and prophylactic treatment of angioedema due to C1-INH deficiency.47,53–55 Management guidelines from the Hereditary Angioedema International Working Group are shown in Table 2.54
Table 2.
Hereditary Angioedema International Working Group consensus guidelines for the management of hereditary angioedema
| Recommendations for acute treatment |
| 1. All patients should have access to plasma-derived and recombinant C1-INH, icatibant, and ecallantide |
| 2. Patients should keep medications at home and be trained to self-administer them |
| 3. All attacks, regardless of their location on the body, should be treated as soon as recognized |
| 4. Patients should report to a hospital if laryngeal symptoms persist following initial treatment |
| Recommendations for prophylactic treatment |
| 1. Long-term prophylaxis is appropriate for patients in whom on-demand treatment is inadequate to control the disease |
| 2. Androgens can be used in patients aged >16 years, and in women who are not pregnant or lactating |
| 3. Androgens are not recommended if not tolerated by the patient or if the effective dose of danazol exceeds 200 mg/day |
| 4. All patients can be considered for plasma-derived C1-INH |
| 5. Treatment with plasma-derived C1-INH should be individualized to optimize clinical response |
Note: Data from Cicardi et al.54
Abbreviation: C1-INH, C1 esterase inhibitor.
Acute treatment
Assessment and maintenance of the airway should be the first consideration in the setting of acute episodes of HAE because angioedema involving the airway can be potentially life-threatening. Physicians should consider intubation at the first signs of airway compromise because laryngeal edema may worsen during the attack, making endotracheal intubation difficult.56 Gastrointestinal attacks can be painful and debilitating, and in extreme cases (eg, hypovolemia) can be life-threatening. Although disfiguring and painful, cutaneous attacks are not associated with serious complications.
According to several recent evidence-based recommendations, the first-line treatment option for acute episodes of HAE is a C1-INH replacement product.54,55,57 Two plasma-derived nanofiltered C1-INH products and one recombinant C1-INH product are currently available for the treatment of acute episodes of HAE58 (Table 3). Berinert® P (CSL Behring, Kankakee, IL, USA) is a plasma-derived nanofiltered C1-INH approved in Europe for self-administration to treat all acute attacks and for preprocedure prevention of attacks, and in the US for treatment of acute facial, laryngeal, and abdominal attacks of HAE.54,58,59 Cinryze® (ViroPharma Biologics, Exton, PA, USA) is another nanofiltered, plasma-derived C1-INH that is approved in Europe for treating all acute attacks of HAE and for short-term and long-term prophylaxis, and in the US for routine prophylaxis.54,60 Cetor® (Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation, Amsterdam, the Netherlands), another C1-INH, was approved in 1997 in a few European countries but has never been tested in clinical trials.54,61
Table 3.
Specific agents for hereditary angioedema (HAE)
| Drug (Trade name; manufacturer) | Approval for HAE | Age group | Dosage | Mechanism | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma-derived nanofiltered C1-INH (Berinert® P; CSL Behring, Kankakee, IL, USA)54,58,59 | In USA for acute facial, laryngeal, and abdominal attacks In Europe for all acute attacks and preprocedure prophylaxis |
Adolescents and adults | 20 U/kg IV | Inhibition of plasma kallikrein, coagulation factors XIIa, and XIa, C1s, C1r, MASP-1, MASP-2, and plasmin | Rare: risk of anaphylaxis Theoretical: transmission of infectious agent |
| Plasma-derived nanofiltered C1-INH (Cinryze®; ViroPharma Biologics, Exton, PA, USA)38,54,60 | In USA for routine prophylaxis In Europe for all acute attacks and short-term and long-term prophylaxis |
Adolescents and adults | 1000 U IV every 3–4 days | Inhibition of plasma kallikrein, coagulation factors XIIa, and XIa, C1s, C1r, MASP-1, MASP-2, and plasmin | Rare: risk of anaphylaxis Theoretical: transmission of infectious agent |
| Recombinant human C1-INH (Ruconest®; Pharming Group NV, Leiden, the Netherlands)38,62–64 | In Europe for acute attacks In USA, not yet approved, orphan drug, fast track status for acute attacks |
NR | 50–100 U/kg IV | Inhibition of plasma kallikrein, coagulation factors XIIa, and XIa, C1s, C1r, MASP-1, MASP-2, and plasmin | Uncommon: risk of anaphylaxis in rabbit-sensitized patients |
| Recombinant protein, ecallantide (Kalbitor; Dyax Corp, Burlington, MA, USA)66,67 | In USA for acute attacks | ≥16 years | 30 mg SC (3 injections of 10 mg each) | Inhibition of plasma kallikrein | Uncommon: risk of anaphylaxis; antidrug antibodies |
| Bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, icatibant (Firazyr®; Shire Orphan Therapies, Inc, Lexington, MA, USA)68–70 | In USA and Europe for acute attacks | ≥18 years | 30 mg SC | Inhibition of bradykinin | Common: injection site reactions |
Notes: Data from Cicardi et al;54 Epstein and Bernstein;58 Berinert [C1 esterase inhibitor (human)] package insert;59 Varga and Farkas;62 Ruconest (Rhucin in non-European territories). Recombinant human C1 esterase inhibitor;63 Santarus Biologics License Application;64 Kalbitor (ecallantide) package insert;66 Levy et al;67 Dubois and Cohen;68 Firazyr (icatibant) package insert,69 and Schmidt, Hirschl, Trautinger.70 From The New England Journal of Medicine, Zuraw BL, Hereditary Angioedema, Volume 359, pp 1027–1036. Copyright © 2008 Massachusetts Medical Society. Adapted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.38
Abbreviations: C1-INH, C1 esterase inhibitor; C1r, complement component 1, r subcomponent; C1s, complement component 1, s subcomponent; IV, intravenous; MASP, mannose-binding lectin serine protease; NR, not reported; SC, subcutaneous.
Ruconest® (conestat alfa; Pharming Group NV, Leiden, the Netherlands) is a human recombinant C1-INH derived from the milk of transgenic rabbits with the same inhibitory profile as plasma-derived C1-INH.62,63 This recombinant C1-INH is effective in relieving symptoms of acute angioedema and is approved in Europe for the acute treatment of HAE.62 Ruconest is undergoing clinical trials in the US and at the time of this writing was under review by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of acute attacks of HAE.64
Ecallantide (Kalbitor®; Dyax Corp, Burlington, MA, USA) is a recombinant protein, synthesized in yeast, that is a potent, specific, and reversible inhibitor of plasma kallikrein.65,66 Ecallantide binds to plasma kallikrein and directly inhibits conversion of high-molecular-weight kininogen to bradykinin.65 Because elevated levels of bradykinin are essential for the development of symptoms of HAE,65 inhibition of bradykinin release is an important mechanism for treating attacks of HAE. Ecallantide is administered subcutaneously and is rapidly distributed throughout the vascular compartment.22,67 Ecallantide is approved in the US for the treatment of acute attacks of HAE.65
Icatibant (Firazyr®; Shire Orphan Therapies, Inc, Lexington, MA, USA) is a selective, competitive bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist that acts as a bradykinin inhibitor and is administered by subcutaneous injection in the abdominal area.68,69 Icatibant is approved for the acute treatment of HAE in Europe and in the US.68–70
According to Hereditary Angioedema International Working Group consensus recommendations, patients with HAE should have access to any one of these medications on demand for use during any type of HAE attack and should be trained to self-administer the medication.54 However, if laryngeal symptoms persist following treatment, patients should report to a hospital immediately.54
Second-line therapies in the absence of first-line agents or if the patient cannot tolerate them include solvent/detergent-treated plasma or fresh frozen plasma.57,71 No controlled clinical trials have been conducted on the efficacy of plasma for the treatment of HAE; however, reports of successful resolution of acute exacerbations have been published in case studies.72,73 Disease transmission with plasma products remains a concern, and fresh frozen plasma may exacerbate angioedema.57
Prophylaxis
Although acute events can be unpredictable, certain triggers for acute HAE, such as environmental allergens, medications, surgeries, or childbirth, can be managed effectively.5,53,71 Prophylactic therapy for HAE is warranted for both short-term use prior to precipitating events such as dental or surgical procedures and for long-term use in high-risk patients, ie, those with frequent or severe episodes and those whose symptoms cannot be controlled with on-demand therapy (see Table 2).
In patients with suspected HAE, endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract or oropharynx is not recommended due to the risk of inducing a potentially life-threatening laryngeal attack.5 If warranted for additional clinical reasons, prophylactic measures to protect the patient against laryngeal swelling should be initiated.5
Attenuated androgens and nanofiltered C1-INH are the only treatments for the prophylaxis of HAE approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. Attenuated androgens such as danazol, oxandrolone, and stanozolol50 work by increasing the levels of aminopeptidase P, which inactivates kinins and thereby increases production of C1-INH in the liver, and contributes to the protective effects of androgens against attacks of angioedema.74,75 Androgens can be used effectively and safely for the short-term prophylaxis of HAE.76 Long-term prophylaxis with androgens is associated with numerous adverse events, including weight gain, lipid abnormalities, liver cysts, hepatic adenomas and carcinomas, myopathies, hematuria, headaches, abnormal menses, hair loss or gain, increased or decreased libido, and anxiety.50,76 The side effects of attenuated androgens can be minimized by titrating down to the minimal effective dose.77
Owing to the risk of adverse events in patients taking attenuated androgens, currently the preferred therapy for both short-term and long-term HAE prophylaxis is nanofiltered C1-INH.78 In a randomized trial evaluating the efficacy of C1-INH for the prophylaxis of HAE attacks, patients treated with C1-INH had an average decrease of 6.47 attacks (P<0.001) compared with patients receiving placebo over the 12-week evaluation period.78 Treatment with C1-INH significantly reduced the frequency, severity, and duration of attacks, the number of rescue treatments of C1-INH needed, and the number of days of swelling.78
Antifibrinolytic agents are not commonly used in the US. Agents such as tranexamic acid and epsilon-aminocaproic acid are chemically synthesized and exert their action in HAE by inhibiting conversion of plasminogen to plasmin.50 These agents have been used for short-term and long-term prophylaxis,57,75 although they are the least effective of the available therapeutic modalities and not recommended based on recent data.57 The dosing recommendation for tranexamic acid is 25 mg 2–3 times a day, not to exceed 6 g/day for the goal. Although prophylaxis reduces the occurrence of edematous episodes, it should be emphasized that life-threatening attacks may nevertheless occur.50
Conclusion
Gastroenterologists are likely to be consulted when patients with HAE are hospitalized for acute HAE attacks involving abdominal symptoms, and may also see patients with HAE in the clinic when they are referred from the emergency department after an attack, usually during asymptomatic periods. The consequences of a missed diagnosis of HAE are considerable, with undiagnosed patients likely visiting the emergency department and undergoing hospitalization and even unnecessary surgical procedures. Furthermore, inadequately treated attacks may progress, resulting in needless significant additional morbidity and even mortality. However, because abdominal pain is often associated with HAE, a high index of suspicion should be maintained for this diagnosis, and a family history should be elicited and appropriate imaging and laboratory studies obtained. In this way, gastroenterologists can promptly diagnose and treat HAE and proceed to make the appropriate referral to an allergist, who can manage this potentially life-threatening disease with current treatment.
Footnotes
Disclosure
In developing this manuscript, writing and editorial assistance with copyediting, formatting, and the creation of tables and figures was provided by Connexion Healthcare (Newtown, PA, USA). The manuscript was financially supported by Dyax Corp (Burlington, MA, USA).
References
- 1.Lunn ML, Santos CB, Craig TJ. Is there a need for clinical guidelines in the United States for the diagnosis of hereditary angioedema and the screening of family members of affected patients? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;104(3):211–214. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2009.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bork K, Meng G, Staubach P, Hardt J. Hereditary angioedema: new findings concerning symptoms, affected organs, and course. Am J Med. 2006;119(3):267–274. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.09.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Feller EJ, Spiro HM, Katz LA. Hereditary angioneurotic oedema: an unusual cause of recurring abdominal pain. Gut. 1970;11(12):983–988. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.12.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nzeako UC, Longhurst HJ. Many faces of angioedema: focus on the diagnosis and management of abdominal manifestations of hereditary angioedema. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;24(4):353–361. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283517998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nzeako UC. Diagnosis and management of angioedema with abdominal involvement: a gastroenterology perspective. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(39):4913–4921. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zilberberg MD, Nathanson BH, Jacobsen T, Tillotson G. Descriptive epidemiology of hereditary angioedema emergency department visits in the United States, 2006–2007. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2011;32(5):390–394. doi: 10.2500/aap.2011.32.3478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zilberberg MD, Nathanson BH, Jacobsen T, Tillotson G. Descriptive epidemiology of hereditary angioedema hospitalizations in the United States, 2004–2007. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2011;32(3):248–254. doi: 10.2500/aap.2011.32.3452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lumry WR, Castaldo AJ, Vernon MK, Blaustein MB, Wilson DA, Horn PT. The humanistic burden of hereditary angioedema: impact on health-related quality of life, productivity, and depression. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2010;31(5):407–414. doi: 10.2500/aap.2010.31.3394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Frank MM. Urticaria and angioedema. In: Goldman L, Bennett JC, editors. Cecil Textbook of Medicine. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA, USA: WB Saunders; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Talavera A, Larraona JL, Ramos JL, et al. Hereditary angioedema: an infrequent cause of abdominal pain with ascites. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90(3):471–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cicardi M, Johnston DT. Hereditary and acquired complement component 1 esterase inhibitor deficiency: a review for the hematologist. Acta Haematol. 2012;127(4):208–220. doi: 10.1159/000336590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Caballero T, Baeza ML, Cabanas R, et al. Consensus statement on the diagnosis, management, and treatment of angioedema mediated by bradykinin. Part II. Treatment, follow-up, and special situations. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011;21(6):422–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Agostoni A, Cicardi M. Hereditary and acquired C1-inhibitor deficiency: biological and clinical characteristics in 235 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1992;71(4):206–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199207000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gooi JHC. Hereditary angioedema: a clinical review for the general physician. Devon, UK: Priory Lodge Education Limited; [Accessed January 17, 2014]. Available from: http://www.priory.com/medicine/angioedema.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Longhurst H, Cicardi M. Hereditary angio-oedema. Lancet. 2012;379(9814):474–481. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cugno M, Zanichelli A, Foieni F, Caccia S, Cicardi M. C1-inhibitor deficiency and angioedema: molecular mechanisms and clinical progress. Trends Mol Med. 2009;15(2):69–78. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kalmar L, Hegedus T, Farkas H, Nagy M, Tordai A. HAEdb: a novel interactive, locus-specific mutation database for the C1 inhibitor gene. Hum Mutat. 2005;25(1):1–5. doi: 10.1002/humu.20112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Caballero T, Baeza ML, Cabanas R, et al. Consensus statement on the diagnosis, management, and treatment of angioedema mediated by bradykinin. Part I. Classification, epidemiology, pathophysiology, genetics, clinical symptoms, and diagnosis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011;21(5):333–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zuraw B, Bork K, Binkley KE, et al. Hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor function: consensus of an international expert panel. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012;33(Suppl 1):S145–S156. doi: 10.2500/aap.2012.33.3627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Antoniu SA. Therapeutic approaches in hereditary angioedema. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011;41(1):114–122. doi: 10.1007/s12016-011-8254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Davis AE, III, Lu F, Mejia P. C1 inhibitor, a multi-functional serine protease inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 2010;104(5):886–893. doi: 10.1160/TH10-01-0073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Levy JH, O’Donnell PS. The therapeutic potential of a kallikrein inhibitor for treating hereditary angioedema. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;15(9):1077–1090. doi: 10.1517/13543784.15.9.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bryant JW, Shariat-Madar Z. Human plasma kallikrein-kinin system: physiological and biochemical parameters. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2009;7(3):234–250. doi: 10.2174/187152509789105444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kaplan AP. Kinins, airway obstruction, and anaphylaxis. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2010;95:67–84. doi: 10.1159/000315938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Morgan BP. Hereditary angioedema: therapies new and old. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(6):581–583. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1006450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bork K, Fischer B, Dewald G. Recurrent episodes of skin angioedema and severe attacks of abdominal pain induced by oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy. Am J Med. 2003;114(4):294–298. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01526-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Agostoni A, Cicardi M, Cugno M, Zingale LC, Gioffré D, Nussberger J. Angioedema due to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Immunopharmacology. 1999;44(1–2):21–25. doi: 10.1016/s0162-3109(99)00107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kaplan AP. Enzymatic pathways in the pathogenesis of hereditary angioedema: the role of C1 inhibitor therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126(5):918–925. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Frank MM, Gelfand JA, Atkinson JP. Hereditary angioedema: the clinical syndrome and its management. Ann Intern Med. 1976;84(5):580–593. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-5-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bork K, Staubach P, Eckardt AJ, Hardt J. Symptoms, course, and complications of abdominal attacks in hereditary angioedema due to C1 inhibitor deficiency. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101(3):619–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Agostoni A, Aygoren-Pursun E, Binkley KE, et al. Hereditary and acquired angioedema: problems and progress: proceedings of the third C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency workshop and beyond. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114(Suppl 3):S51–S131. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.06.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Locascio EJ, Mahler SA, Arnold TC. Intestinal angioedema misdiagnosed as recurrent episodes of gastroenteritis. West J Emerg Med. 2010;11(4):391–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ohsawa I, Nagamachi S, Suzuki H, et al. Leukocytosis and high hematocrit levels during abdominal attacks of hereditary angioedema. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013;13:123. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-13-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bork K, Siedlecki K, Bosch S, Schopf RE, Kreuz W. Asphyxiation by laryngeal edema in patients with hereditary angioedema. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000;75(4):349–354. doi: 10.4065/75.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Farkas H. Management of upper airway edema caused by hereditary angioedema. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2010;6(1):19. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-6-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zanichelli A, Magerl M, Longhurst H, Fabien V, Maurer M. Hereditary angioedema with C1 inhibitor deficiency: delay in diagnosis in Europe. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2013;9(1):29. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-9-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Farkas H, Harmat G, Fáy A, et al. Erythema marginatum preceding an acute oedematous attack of hereditary angioneurotic oedema. Acta Derm Venereol. 2001;81(5):376–377. doi: 10.1080/000155501317140188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zuraw BL. Hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(10):1027–1036. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp0803977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.De Backer AI, De Schepper AM, Vandevenne JE, Schoeters P, Michielsen P, Stevens WJ. CT of angioedema of the small bowel. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176(3):649–652. doi: 10.2214/ajr.176.3.1760649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Farkas H, Harmat G, Kaposi PN, et al. Ultrasonography in the diagnosis and monitoring of ascites in acute abdominal attacks of hereditary angioneurotic oedema. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;13(10):1225–1230. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200110000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pedrosa M, Caballero T, Gómez-Traseira C, Olveira A, López-Serrano C. Usefulness of abdominal ultrasonography in the follow-up of patients with hereditary C1-inhibitor deficiency. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009;102(6):483–486. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dinkel HP, Maroske J, Schrod L. Sonographic appearances of the abdominal manifestations of hereditary angioedema. Pediatr Radiol. 2001;31(4):296–298. doi: 10.1007/s002470000409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hoxha M, Meta D, Kalo T. Hereditary angioedema as a potential cause of cerebral edema. Otorhinolaryngologia – Head and Neck Surgery. 2013;51:31–34. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zingale LC, Zanichelli A, Deliliers DL, Rondonotti E, De Franchis R, Cicardi M. Successful resolution of bowel obstruction in a patient with hereditary angioedema. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20(6):583–587. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3282f1c995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gompels MM, Lock RJ, Morgan JE, Osborne J, Brown A, Virgo PF. A multicentre evaluation of the diagnostic efficiency of serological investigations for C1 inhibitor deficiency. J Clin Pathol. 2002;55(2):145–147. doi: 10.1136/jcp.55.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gompels MM, Lock RJ, Abinun M, et al. C1 inhibitor deficiency: consensus document. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005;139(3):379–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bowen T. Hereditary Angioedema Consensus 2010. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2010;6(1):13. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-6-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bork K. Diagnosis and treatment of hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2010;6(1):15. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-6-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Eidelman FJ. Hereditary angioedema: New therapeutic options for a potentially deadly disorder. BMC Blood Disord. 2010;10:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2326-10-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bowen T, Cicardi M, Farkas H, et al. 2010 international consensus algorithm for the diagnosis, therapy and management of hereditary angioedema. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2010;6(1):24. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-6-24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Caballero T, Sala-Cunill A, Cancian M, et al. Current status of implementation of self-administration training in various regions of Europe, Canada and the USA in the management of hereditary angioedema. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;161(Suppl 1):10–16. doi: 10.1159/000351233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Riedl MA. Creating a comprehensive treatment plan for hereditary angioedema. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am. 2013;33(4):471–485. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2013.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Craig T, Aygören-Pürsün E, Bork K, et al. WAO guideline for the management of hereditary angioedema. World Allergy Organ J. 2012;5(12):182–199. doi: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e318279affa. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Cicardi M, Bork K, Caballero T, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for the therapeutic management of angioedema owing to hereditary C1 inhibitor deficiency: consensus report of an International Working Group. Allergy. 2012;67(2):147–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Banerji A. Current treatment of hereditary angioedema: an update on clinical studies. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2010;31(5):398–406. doi: 10.2500/aap.2010.31.3387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Temino VM, Peebles RS., Jr The spectrum and treatment of angioedema. Am J Med. 2008;121(4):282–286. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zuraw BL, Bernstein JA, Lang DM, et al. American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology A focused parameter update: hereditary angioedema, acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-associated angioedema. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131(6):1491–1493. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.03.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Epstein TG, Bernstein JA. Current and emerging management options for hereditary angioedema in the US. Drugs. 2008;68(18):2561–2573. doi: 10.2165/0003495-200868180-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Berinert [C1 esterase inhibitor (human)] package insert. Kankakee, IL, USA: CSL Behring; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Cinryze (C1 esterase inhibitor) package insert. Exton, PA, USA: ViroPharma Biologics; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Cetor (C1 esterase inhibitor) 500 U powder and solvent for solution for injection (package leaflet) Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Sanquin Blood Supply Foundation; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Varga L, Farkas H. rhC1INH: a new drug for the treatment of attacks in hereditary angioedema caused by C1-inhibitor deficiency. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2011;7(2):143–153. doi: 10.1586/eci.11.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ruconest (Rhucin in non-European territories) Recombinant human C1 esterase inhibitor. Pharming: Leiden, the Netherlands; 2013. [Accessed February 17, 2014]. Available from: http://www.pharming.com/index.php?act=prod. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Santarus Santarus and Pharming announce FDA acceptance for review of Ruconest (recombinant human C1 esterase inhibitor) Biologics License Application. Jun 18, 2013. [Accessed January 17, 2014]. [Accessed October 8, 2013]. Available from: http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20130617006581/en/Santarus-Pharming-Announce-FDA-Acceptance-Review-RUCONEST#.UtlxG50o7IU.
- 65.Lunn M, Banta E. Ecallantide for the treatment of hereditary angiodema in adults. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2011;5:49–54. doi: 10.4137/CMC.S4434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kalbitor (ecallantide) package insert. Burlington, MA, USA: Dyax Corp; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Levy RJ, Lumry WR, McNeil DL, et al. EDEMA4: a phase 3, double-blind study of subcutaneous ecallantide treatment for acute attacks of hereditary angioedema. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;104(6):523–529. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2010.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Dubois EA, Cohen AF. Icatibant. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;69(5):425–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03642.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Firazyr (icatibant) package insert. Lexington, MA: Shire Orphan Therapies, Inc; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Schmidt PW, Hirschl MM, Trautinger F. Treatment of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-related angioedema with the bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist icatibant. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63(5):913–914. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Prematta M, Gibbs JG, Pratt EL, Stoughton TR, Craig TJ. Fresh frozen plasma for the treatment of hereditary angioedema. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007;98(4):383–388. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60886-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Longhurst HJ. Emergency treatment of acute attacks in hereditary angioedema due to C1 inhibitor deficiency: what is the evidence? Int J Clin Pract. 2005;59(5):594–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2005.00352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pekdemir M, Ersel M, Aksay E, Yanturali S, Akturk A, Kiyan S. Effective treatment of hereditary angioedema with fresh frozen plasma in an emergency department. J Emerg Med. 2007;33(2):137–179. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2007.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Drouet C, Desormeaux A, Robillard J, et al. Metallopeptidase activities in hereditary angioedema: effect of androgen prophylaxis on plasma aminopeptidase P. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121(2):429–433. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.10.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bork K. Current management options for hereditary angioedema. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012;12(4):273–280. doi: 10.1007/s11882-012-0273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Frank MM. Update on preventive therapy (prophylaxis) of hereditary angioedema. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2011;32(1):17–21. doi: 10.2500/aap.2011.32.3412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sloane DE, Lee CW, Sheffer AL. Hereditary angioedema: Safety of long-term stanozolol therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(3):654–658. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.06.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Zuraw BL, Busse PJ, White M, et al. Nanofiltered C1 inhibitor concentrate for treatment of hereditary angioedema. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(6):513–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]