Abstract
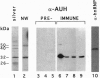
AU-rich elements within the 3' untranslated region of transcripts of lymphokines and some protooncogenes serve as signal for rapid mRNA degradation. By using an AUUUA matrix, we have affinity-purified a 32-kDa protein, microsequenced it, and cloned the corresponding cDNA. In vitro, the recombinant protein bound specifically to AU-rich transcripts, including those for interleukin 3, granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, c-fos, and c-myc. Sequence analysis revealed an unexpected homology to enoyl-CoA hydratase (EC 4.2.1.17), and the recombinant protein showed a low degree of the enzymatic activity. Thus, this gene, designated AUH, encodes an RNA binding protein with intrinsic enzymatic activity. Protein immobilized on an AUUUA matrix was enzymatically active, suggesting that hydratase and AU-binding functions are located on distinct domains within a single polypeptide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biamonti G., Buvoli M., Bassi M. T., Morandi C., Cobianchi F., Riva S. Isolation of an active gene encoding human hnRNP protein A1. Evidence for alternative splicing. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 5;207(3):491–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickel M., Iwai Y., Pluznik D. H., Cohen R. B. Binding of sequence-specific proteins to the adenosine- plus uridine-rich sequences of the murine granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10001–10005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T. AU RNA-binding factors differ in their binding specificities and affinities. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6302–6309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. An A + U-rich element RNA-binding factor regulates c-myc mRNA stability in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2460–2466. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Kenan D., Martin B. J., Keene J. D. Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18043–18051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Chen T. M., Shyu A. B. Interplay of two functionally and structurally distinct domains of the c-fos AU-rich element specifies its mRNA-destabilizing function. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):416–426. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton B. J., Nagy E., Malter J. S., Arrick B. A., Rigby W. F. Association of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 and C proteins with reiterated AUUUA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8881–8887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W. Enzymes as RNA-binding proteins: a role for (di)nucleotide-binding domains? Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Mar;19(3):101–103. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch H. H., Nair A. P., Moroni C. Suppressible and nonsuppressible autocrine mast cell tumors are distinguished by insertion of an endogenous retroviral element (IAP) into the interleukin 3 gene. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):403–411. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsteenge J., Kieffer B., Matthies R., Hemmings B. A., Stone S. R. Amino acid sequence of the ribonuclease inhibitor from porcine liver reveals the presence of leucine-rich repeats. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8537–8544. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamijo T., Aoyama T., Komiyama A., Hashimoto T. Structural analysis of cDNAs for subunits of human mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation trifunctional protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):818–825. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine T. D., Gao F., King P. H., Andrews L. G., Keene J. D. Hel-N1: an autoimmune RNA-binding protein with specificity for 3' uridylate-rich untranslated regions of growth factor mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3494–3504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S. Identification of an AUUUA-specific messenger RNA binding protein. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2814487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. RNA recognition: a family matter? Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):837–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90265-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer P., Mayer U., Bruch M., Jenö P., Mann K., Landwehr R., Engel J., Timpl R. High-affinity and low-affinity calcium binding and stability of the multidomain extracellular 40-kDa basement membrane glycoprotein (BM-40/SPARC/osteonectin). Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 1;205(1):233–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer R. E., Hendrix P., Cron P., Matthies R., Stone S. R., Goris J., Merlevede W., Hofsteenge J., Hemmings B. A. Structure of the 55-kDa regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A: evidence for a neuronal-specific isoform. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 16;30(15):3589–3597. doi: 10.1021/bi00229a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami-Ishii N., Taketani S., Osumi T., Hashimoto T. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA for rat mitochondrial enoyl-CoA hydratase. Structural and evolutionary relationships linked to the bifunctional enzyme of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation system. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 20;185(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):316–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myer V. E., Lee S. I., Steitz J. A. Viral small nuclear ribonucleoproteins bind a protein implicated in messenger RNA destabilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1296–1300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Neupert B., Kühn L. C. A specific mRNA binding factor regulates the iron-dependent stability of cytoplasmic transferrin receptor mRNA. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90851-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair A. P., Hahn S., Banholzer R., Hirsch H. H., Moroni C. Cyclosporin A inhibits growth of autocrine tumour cell lines by destabilizing interleukin-3 mRNA. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):239–242. doi: 10.1038/369239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neupert B., Thompson N. A., Meyer C., Kühn L. C. A high yield affinity purification method for specific RNA-binding proteins: isolation of the iron regulatory factor from human placenta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):51–55. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raineri I., Moroni C., Senn H. P. Improved efficiency for single-sided PCR by creating a reusable pool of first-strand cDNA coupled to a solid phase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):4010–4010. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.4010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouault T. A., Stout C. D., Kaptain S., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Structural relationship between an iron-regulated RNA-binding protein (IRE-BP) and aconitase: functional implications. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):881–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90312-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Cole M. D. GM-CSF and oncogene mRNA stabilities are independently regulated in trans in a mouse monocytic tumor. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1115–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90256-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakalopoulou E., Schaack J., Shenk T. A 32-kilodalton protein binds to AU-rich domains in the 3' untranslated regions of rapidly degraded mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3355–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanders R. J., IJlst L., Poggi F., Bonnefont J. P., Munnich A., Brivet M., Rabier D., Saudubray J. M. Human trifunctional protein deficiency: a new disorder of mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 16;188(3):1139–1145. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91350-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T. A uridylate tract mediates efficient heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C protein-RNA cross-linking and functionally substitutes for the downstream element of the polyadenylation signal. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6397–6407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Heusser C. H., Moroni C. Production of the haemopoietic growth factors GM-CSF and interleukin-3 by mast cells in response to IgE receptor-mediated activation. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):150–152. doi: 10.1038/339150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Moroni C. Regulation of interleukin 3 mRNA expression in mast cells occurs at the posttranscriptional level and is mediated by calcium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):777–781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Wagner B. J., Ehrenman K., Schaefer A. W., DeMaria C. T., Crater D., DeHaven K., Long L., Brewer G. Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of an AU-rich element RNA-binding protein, AUF1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7652–7665. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]