Abstract
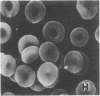
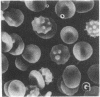
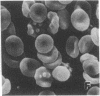
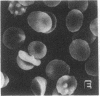
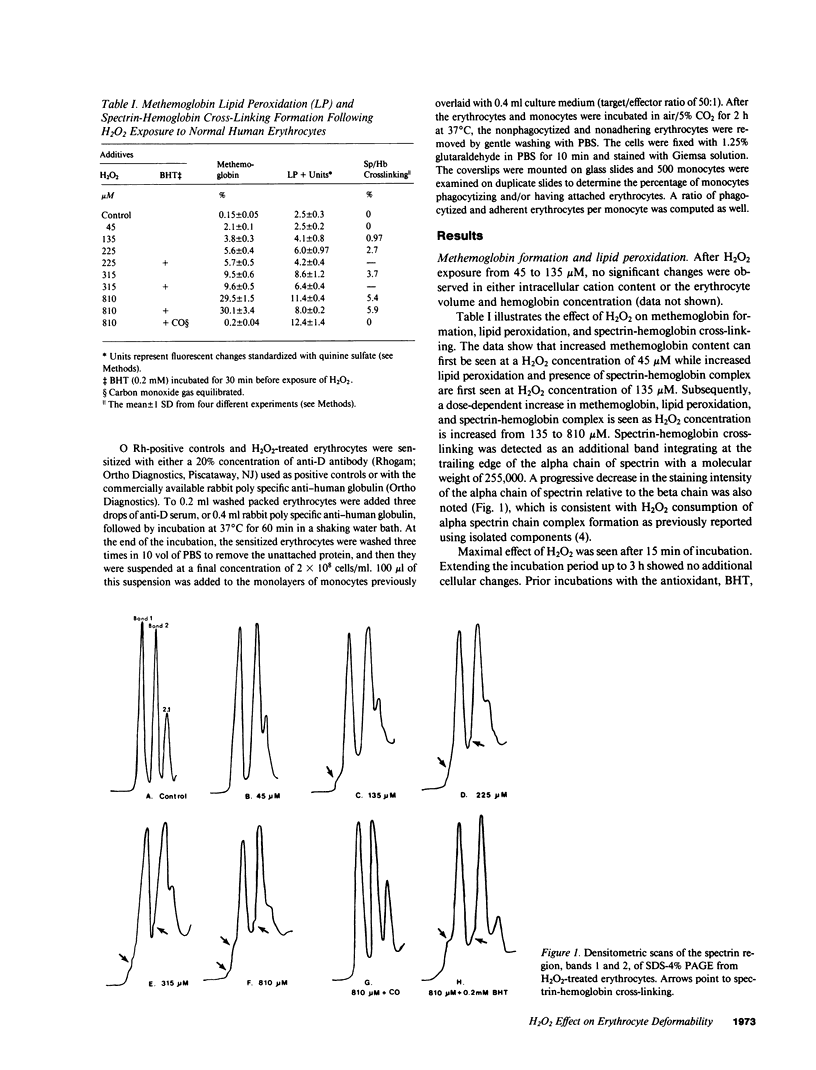
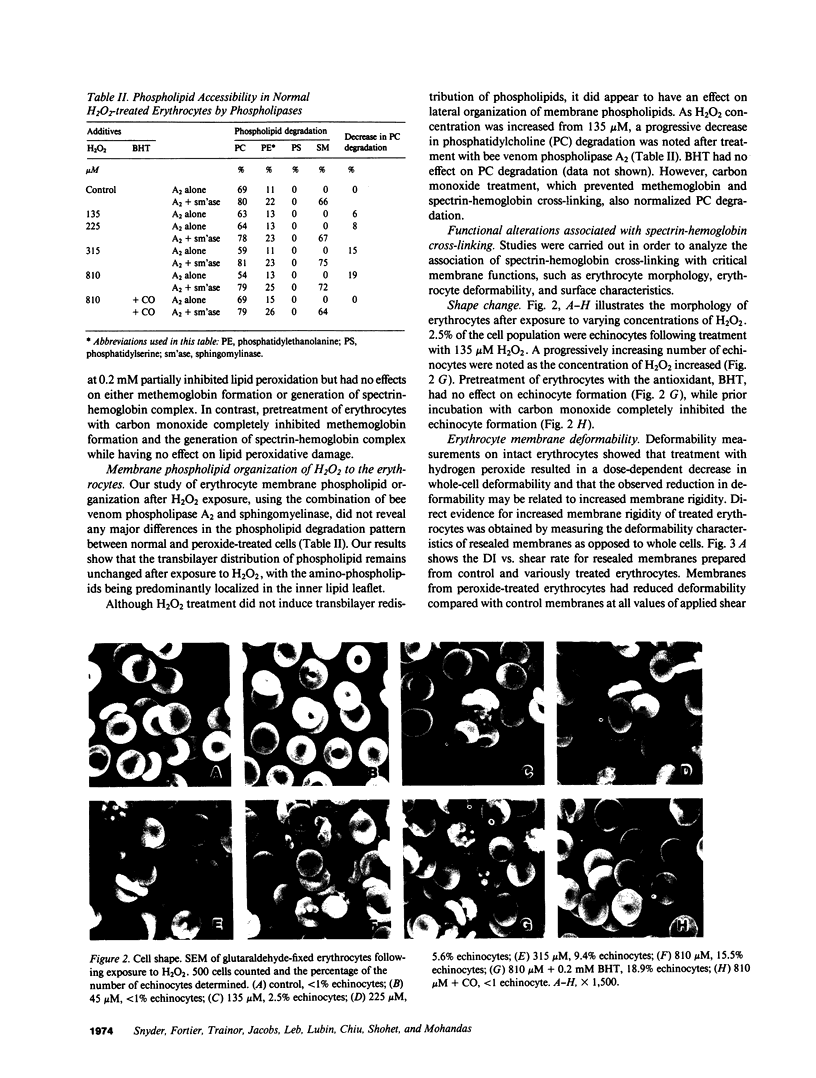
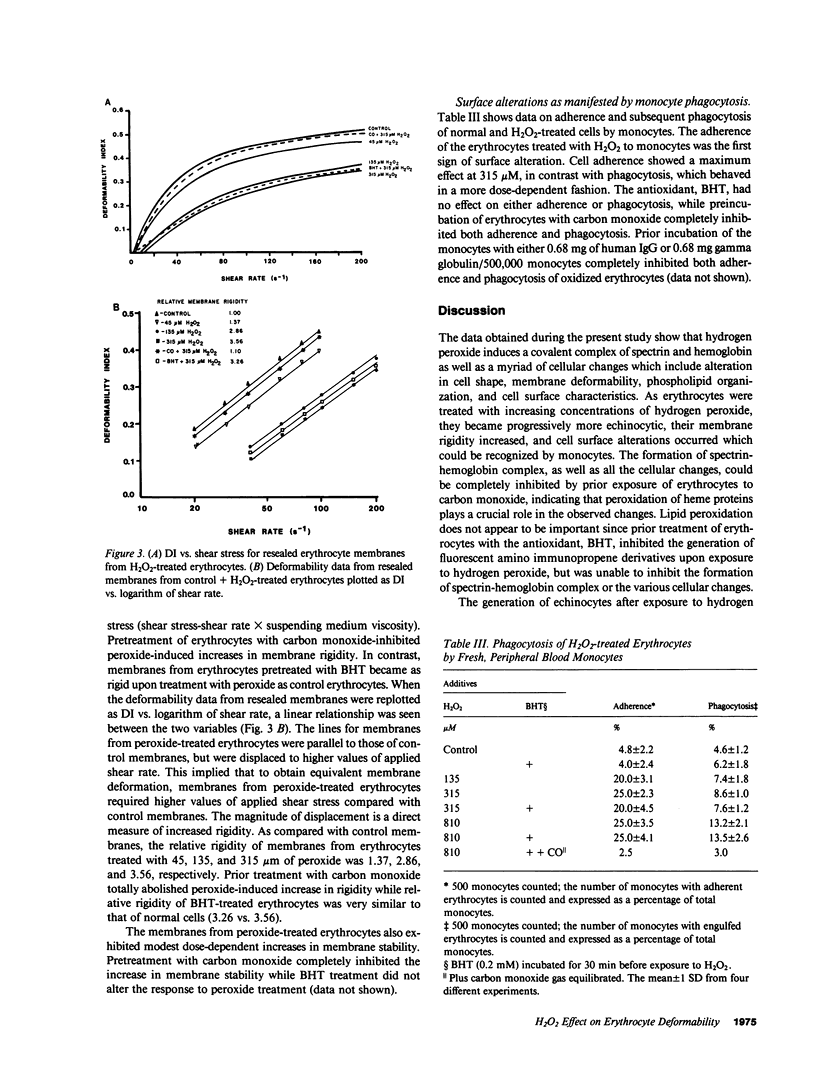
To further define the conditions for forming spectrin-hemoglobin cross-linking in human erythrocyte membranes and to examine its possible effects on membrane function, we incubated normal human erythrocytes for up to 3 h in concentrations of H2O2, varying from 45 to 180 microM, in an azide phosphate buffer, pH 7.4. The chemical changes observed indicated that methemoglobin formation occurred early and at a low concentration (45 microM). Morphologic changes characterized by increased echinocyte formation occurred in a dose-dependent fashion. In addition, decreased cell deformability commensurate with increased membrane rigidity was found. Finally, an increase in cell recognition as determined by monocyte phagocytosis and adherence in vitro, as well as decreased phosphatidylcholine accessibility to bee venom phospholipase A2, was found in H2O2-treated erythrocytes compared with controls. Both of these latter changes were closely correlated with the extent of spectrin-hemoglobin cross-linking. In addition to these protein-mediated interactions, lipid peroxidation also occurred after H2O2 exposure, as shown by generation of fluorescent amino propene derivatives. The addition of the antioxidant, butylated hydroxytoluene, decreased the fluorescent derivatives, but did not prevent the effects on membrane function. This suggests that lipid peroxidation, though present, was not necessary for the membrane changes found. In contrast, spectrin-hemoglobin aggregation and the alterations in membrane function were completely prevented by prior exposure of the erythrocytes to carbon monoxide.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Demel R. A., Geurts van Kessel W. S., Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., van Deenen L. L. Relation between various phospholipase actions on human red cell membranes and the interfacial phospholipid pressure in monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 16;406(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Bending resistance and chemically induced moments in membrane bilayers. Biophys J. 1974 Dec;14(12):923–931. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85959-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. D., Rozen M. G., Amoruso M. A. Relation of fluorescence in lipid-containing red cell membrane extracts to in vivo lipid peroxidation. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Apr;93(4):687–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath B. P., Mohandas N., Wyatt J. L., Shohet S. B. Deformability of isolated red blood cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 7;691(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. K. The accumulation of malonyldialdehyde, a product of fatty acid peroxidation, can disturb aminophospholipid organization in the membrane bilayer of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3391–3394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M. The kinetics of resealing of washed erythrocyte ghosts. J Membr Biol. 1975 Jul 24;22(3-4):231–253. doi: 10.1007/BF01868173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M. Mechanism of removal of senescent cells by human macrophages in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3521–3525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leb L., Crusberg T., Fortier N., Snyder L. M. Evaluation of methods using adherence to substrate and density gradient for the isolation of human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Mar 25;58(3):309–321. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin B., Chiu D., Bastacky J., Roelofsen B., Van Deenen L. L. Abnormalities in membrane phospholipid organization in sickled erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1643–1649. doi: 10.1172/JCI110200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin B., Chiu D. Membrane phospholipid organization in pathologic human erythrocytes. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;97:137–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti G. V., Cattieu K. Asymmetric metabolism of phosphatidylethanolamine in the human red cell membrane. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):245–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Chasis J. A., Shohet S. B. The influence of membrane skeleton on red cell deformability, membrane material properties, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):225–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Clark M. R., Jacobs M. S., Shohet S. B. Analysis of factors regulating erythrocyte deformability. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):563–573. doi: 10.1172/JCI109888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Painter R. G. Anionic sites of human erythrocyte membranes. II. Antispectrin-induced transmembrane aggregation of the binding sites for positively charged colloidal particles. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):395–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE H. G., OKLANDER M. IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR THE EXTRACTION OF LIPIDS FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimon G., Meyerstein N., Henis Y. I. Lateral mobility of phospholipids in the external and internal leaflets of normal and hereditary spherocytic human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 5;775(3):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauberman N., Fortier N. L., Joshi W., Piotrowski J., Snyder L. M. Spectrin-haemoglobin crosslinkages associated with in vitro oxidant hypersensitivity in pathologic and artificially dehydrated red cells. Br J Haematol. 1983 May;54(1):15–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier S. L., Chiu D. T., Yee M., Sizer K., Lubin B. Alteration of membrane phospholipid bilayer organization in human erythrocytes during drug-induced endocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1698–1705. doi: 10.1172/JCI111129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier S. L. Red cell membrane biology--introduction. Clin Haematol. 1985 Feb;14(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P. Membrane skeletal dynamics: role in modulation of red cell deformability, mobility of transmembrane proteins, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):175–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Singer S. J. Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D., Hanahan D. J. Identification of domains of phosphatidylcholine in human erythrocyte plasma membranes. Differential action of acidic and basic phospholipases A2 from Agkistrodon halys blomhoffii. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2908–2911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L. M., Leb L., Piotrowski J., Sauberman N., Liu S. C., Fortier N. L. Irreversible spectrin-haemoglobin crosslinking in vivo: a marker for red cell senescence. Br J Haematol. 1983 Mar;53(3):379–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L. M., Sauberman N., Condara H., Dolan J., Jacobs J., Szymanski I., Fortier N. L. Red cell membrane response to hydrogen peroxide-sensitivity in hereditary xerocytosis and in other abnormal red cells. Br J Haematol. 1981 Jul;48(3):435–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb02735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh S. M., Low P. S. Hemichrome binding to band 3: nucleation of Heinz bodies on the erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):34–39. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Comfurius P., van Deenen L. L. Organization of phospholipids in human red cell membranes as detected by the action of various purified phospholipases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 16;406(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]