Abstract
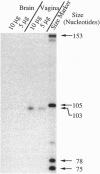
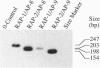
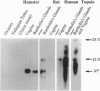
The cDNA sequence for aphrodisin, a lipocalin from hamster vaginal discharge which is involved in pheromonal activity, has been determined. Corresponding genomic clones were isolated and the promoter region was identified. Primer extension analysis revealed an adenosine residue as the main transcription initiation site, located 50 bp upstream of the translation start codon ATG, which is surrounded by a typical Kozak sequence. However, data from polymerase chain reaction analysis suggest the existence of at least one alternative transcription initiation site. The aphrodisin cDNA is 732 bp long and codes for the mature 151-aa aphrodisin and an additional N-terminal 16-aa secretory signal peptide. The 3' nontranslated region is 228 bp long. Among the known sequences, the aphrodisin cDNA shares the highest homology with the rat odorant-binding protein cDNA (45%), which verifies the protein data. Vaginal tissue and Bartholin's glands are the main aphrodisin gene-expressing tissues of the female hamster genital tract, as demonstrated by Northern blot analysis. Under less stringent hybridization conditions, RNA isolated from rat Bartholin's glands also showed a signal, indicating the occurrence of aphrodisin-related mRNA in this species.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerström B., Lögdberg L. An intriguing member of the lipocalin protein family: alpha 1-microglobulin. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jun;15(6):240–243. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90037-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böcskei Z., Groom C. R., Flower D. R., Wright C. E., Phillips S. E., Cavaggioni A., Findlay J. B., North A. C. Pheromone binding to two rodent urinary proteins revealed by X-ray crystallography. Nature. 1992 Nov 12;360(6400):186–188. doi: 10.1038/360186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy A. N., Macrides F., Singer A. G., Agosta W. C. Male hamster copulatory responses to a high molecular weight fraction of vaginal discharge: effects of vomeronasal organ removal. Physiol Behav. 1984 Oct;33(4):653–660. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(84)90386-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Velasco J., Mondragon M. The incidence of the vomeronasal organ in 1000 human subjects and its possible clinical significance. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;39(4B):561–563. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godovac-Zimmermann J. The structural motif of beta-lactoglobulin and retinol-binding protein: a basic framework for binding and transport of small hydrophobic molecules? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henzel W. J., Rodriguez H., Singer A. G., Stults J. T., Macrides F., Agosta W. C., Niall H. The primary structure of aphrodisin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16682–16687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi M., Nagata A., Toh H., Urade Y., Hayaishi O. Structural organization of the gene for prostaglandin D synthase in the rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5376–5380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini M. A., Majumdar D., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Alpha 2u-globulin in modified sebaceous glands with pheromonal functions: localization of the protein and its mRNA in preputial, meibomian, and perianal glands. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Feb;37(2):149–157. doi: 10.1177/37.2.2463299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael R. P., Keverne E. B. Primate sex pheromones of vaginal origin. Nature. 1970 Jan 3;225(5227):84–85. doi: 10.1038/225084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monti-Bloch L., Grosser B. I. Effect of putative pheromones on the electrical activity of the human vomeronasal organ and olfactory epithelium. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;39(4B):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90255-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran D. T., Jafek B. W., Rowley J. C., 3rd The vomeronasal (Jacobson's) organ in man: ultrastructure and frequency of occurrence. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;39(4B):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90251-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura A., Morita M., Nishimura Y., Sugino Y. A rapid and highly efficient method for preparation of competent Escherichia coli cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6169–6169. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papiz M. Z., Sawyer L., Eliopoulos E. E., North A. C., Findlay J. B., Sivaprasadarao R., Jones T. A., Newcomer M. E., Kraulis P. J. The structure of beta-lactoglobulin and its similarity to plasma retinol-binding protein. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):383–385. doi: 10.1038/324383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul M., Burt D. W., Krieger J. E., Nakamura N., Dzau V. J. Tissue specificity of renin promoter activity and regulation in mice. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):E644–E650. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.5.E644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitsch M. C., Boguski M. S. The first lipocalin with enzymatic activity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):363–363. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90149-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz S., Brew K. Homology and structure-function correlations between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and serum retinol-binding protein and its relatives. FASEB J. 1987 Sep;1(3):209–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.3.3622999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Reed R. R., Feinstein P. G., Snyder S. H. Molecular cloning of odorant-binding protein: member of a ligand carrier family. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):336–339. doi: 10.1126/science.3388043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Trifiletti R. R., Strittmatter S. M., Snyder S. H. Isolation and characterization of an olfactory receptor protein for odorant pyrazines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. The end of the message and beyond. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):412–413. doi: 10.1038/307412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer A. G. A chemistry of mammalian pheromones. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;39(4B):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer A. G., Macrides F., Clancy A. N., Agosta W. C. Purification and analysis of a proteinaceous aphrodisiac pheromone from hamster vaginal discharge. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13323–13326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivaprasadarao A., Boudjelal M., Findlay J. B. Lipocalin structure and function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Aug;21(3):619–622. doi: 10.1042/bst0210619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. M., Sanders J. Z., Kaiser R. J., Hughes P., Dodd C., Connell C. R., Heiner C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):674–679. doi: 10.1038/321674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Sklar P. B., Pevsner J. Molecular mechanisms of olfaction. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):13971–13974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E. Compilation of transcription regulating proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):1879–1902. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]