Abstract
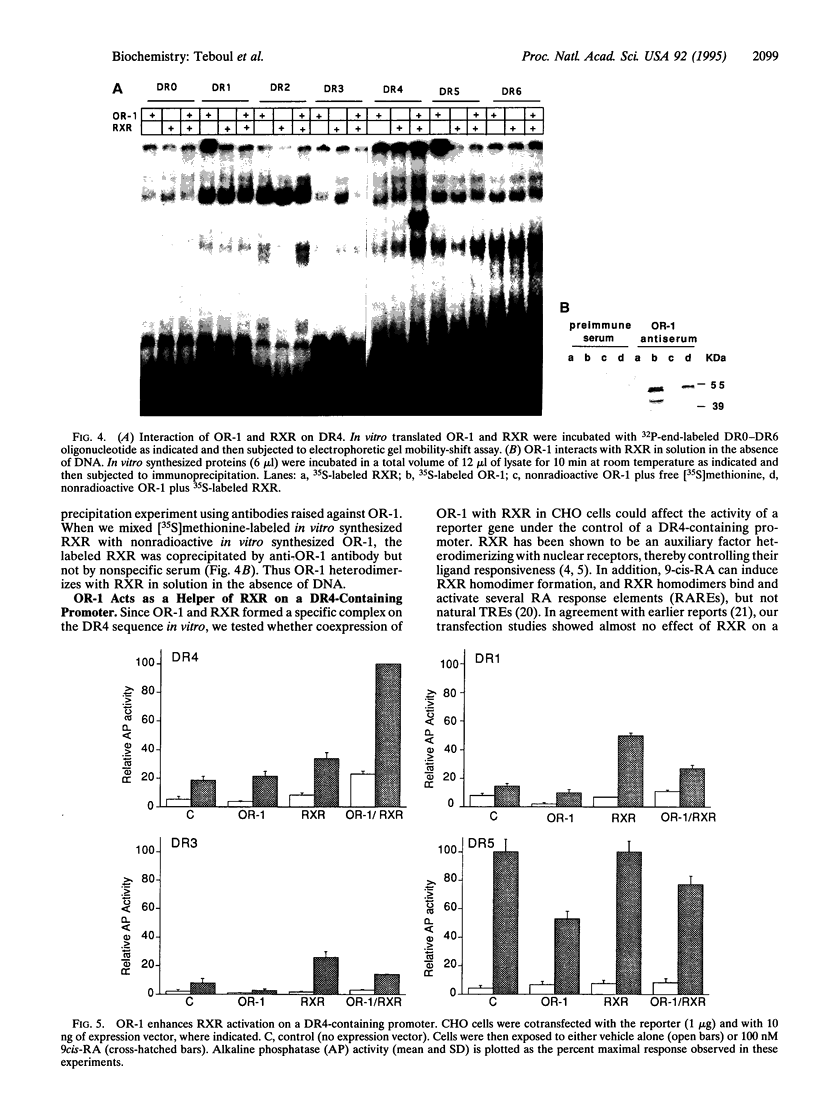
We have cloned a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily. The cDNA was isolated from a rat liver library and encodes a protein of 446 aa with a predicted mass of 50 kDa. This clone (OR-1) shows no striking homology to any known member of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. The most related receptor is the ecdysone receptor and the highest homologies represent < 10% in the amino-terminal domain, between 15-37% in the carboxyl-terminal domain and 50-62% in the DNA binding domain. The expression of OR-1 appears to be widespread in both fetal and adult rat tissues. Potential DNA response elements composed of a direct repeat of the hexameric motif AGGTCA spaced by 0-6 nt were tested in gel shift experiments. OR-1 was shown to interact with the 9-cis-retinoic acid receptor (retinoid X receptor, RXR) and the OR-1/RXR complex to bind to a direct repeat spaced by 4 nt (DR4). In transfection experiments, OR-1 appears to activate RXR-mediated function through the DR4. Therefore OR-1 might modulate 9-cis-retinoic acid signaling by interacting with RXR.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apfel R., Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Ortiz M. A., Salbert G., Pfahl M. A novel orphan receptor specific for a subset of thyroid hormone-responsive elements and its interaction with the retinoid/thyroid hormone receptor subfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):7025–7035. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.7025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barettino D., Bugge T. H., Bartunek P., Vivanco Ruiz M. D., Sonntag-Buck V., Beug H., Zenke M., Stunnenberg H. G. Unliganded T3R, but not its oncogenic variant, v-erbA, suppresses RAR-dependent transactivation by titrating out RXR. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1343–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hauber J., Hauber R., Geiger R., Cullen B. R. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Pohl J., Lonnoy O., Stunnenberg H. G. RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1409–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kokontis J. Identification of a new member of the steroid receptor super-family by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):971–977. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney A. J., Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF) dimers bind to different GGTCA response elements, allowing COUP-TF to repress hormonal induction of the vitamin D3, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4153–4163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagerlind A., Friberg K., Bean A. J., Hökfelt T. Sensitive mRNA detection using unfixed tissue: combined radioactive and non-radioactive in situ hybridization histochemistry. Histochemistry. 1992 Aug;98(1):39–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00716936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis I. J., Hazel T. G., Lau L. F. Transcriptional activation by Nur77, a growth factor-inducible member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;5(6):854–859. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-6-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denner L. A., Weigel N. L., Maxwell B. L., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Regulation of progesterone receptor-mediated transcription by phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1740–1743. doi: 10.1126/science.2176746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1293–1301. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing K. L., Göttlicher M., Teboul M., Widmark E., Gustafsson J. A. Interaction of the peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor and retinoid X receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1440–1444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg Y., Glineur C., Gesquière J. C., Ricouart A., Sap J., Vennström B., Ghysdael J. Activation of protein kinase C or cAMP-dependent protein kinase increases phosphorylation of the c-erbA-encoded thyroid hormone receptor and of the v-erbA-encoded protein. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2425–2433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlicher M., Widmark E., Li Q., Gustafsson J. A. Fatty acids activate a chimera of the clofibric acid-activated receptor and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4653–4657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck P. L., Phyillaier M., Nikodem V. M. Divergent effects of 9-cis-retinoic acid receptor on positive and negative thyroid hormone receptor-dependent gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3825–3828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazel T. G., Nathans D., Lau L. F. A gene inducible by serum growth factors encodes a member of the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8444–8448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman R. A., Mangelsdorf D. J., Dyck J. A., Stein R. B., Eichele G., Evans R. M., Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90479-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh J. C., Jurutka P. W., Galligan M. A., Terpening C. M., Haussler C. A., Samuels D. S., Shimizu Y., Shimizu N., Haussler M. R. Human vitamin D receptor is selectively phosphorylated by protein kinase C on serine 51, a residue crucial to its trans-activation function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9315–9319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin A. A., Sturzenbecker L. J., Kazmer S., Bosakowski T., Huselton C., Allenby G., Speck J., Kratzeisen C., Rosenberger M., Lovey A. 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):359–361. doi: 10.1038/355359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin K. H., Ashizawa K., Cheng S. Y. Phosphorylation stimulates the transcriptional activity of the human beta 1 thyroid hormone nuclear receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7737–7741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydon J. P., Power R. F., Conneely O. M. Differential modes of activation define orphan subclasses within the steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily. Gene Expr. 1992;2(3):273–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Leroy P., Chen J. Y., Chambon P. Multiple parameters control the selectivity of nuclear receptors for their response elements. Selectivity and promiscuity in response element recognition by retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):591–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai A., Kartha S., Sakurai A., Toback F. G., DeGroot L. J. A human early response gene homologous to murine nur77 and rat NGFI-B, and related to the nuclear receptor superfamily. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1438–1443. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-10-1438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. The steroid receptor superfamily: more excitement predicted for the future. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):363–369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power R. F., Lydon J. P., Conneely O. M., O'Malley B. W. Dopamine activation of an orphan of the steroid receptor superfamily. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1546–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.2047861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power R. F., Mani S. K., Codina J., Conneely O. M., O'Malley B. W. Dopaminergic and ligand-independent activation of steroid hormone receptors. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1636–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.1749936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinar D. M., Endo N., Rutledge S. J., Vogel R., Rodan G. A., Schmidt A. NER, a new member of the gene family encoding the human steroid hormone nuclear receptor. Gene. 1994 Sep 30;147(2):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh V. B., Moudgil V. K. Phosphorylation of rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3684–3690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C., Kokontis J. M., Hiipakka R. A., Liao S. Ubiquitous receptor: a receptor that modulates gene activation by retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10809–10813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Vacchio M. S., Ashwell J. D. 9-cis-retinoic acid inhibits activation-driven T-cell apoptosis: implications for retinoid X receptor involvement in thymocyte development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6170–6174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Lehmann J., Hoffmann B., Dawson M. I., Cameron J., Graupner G., Hermann T., Tran P., Pfahl M. Homodimer formation of retinoid X receptor induced by 9-cis retinoic acid. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):587–591. doi: 10.1038/358587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]