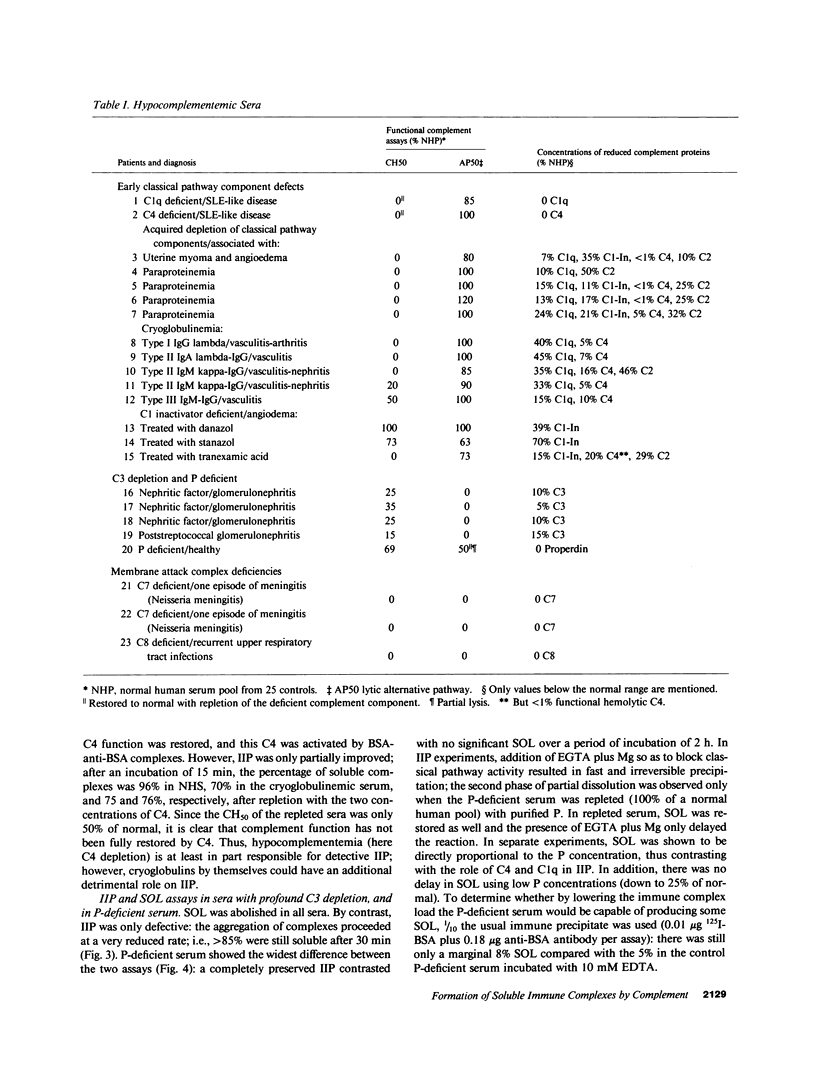
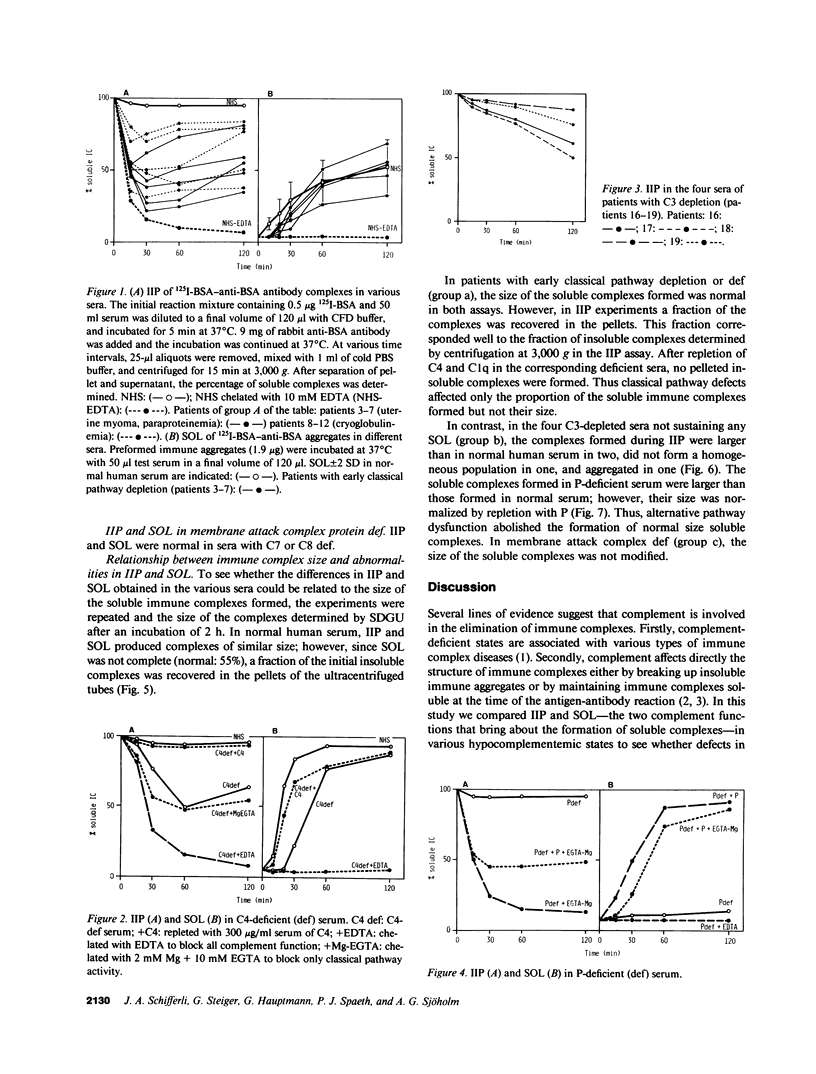
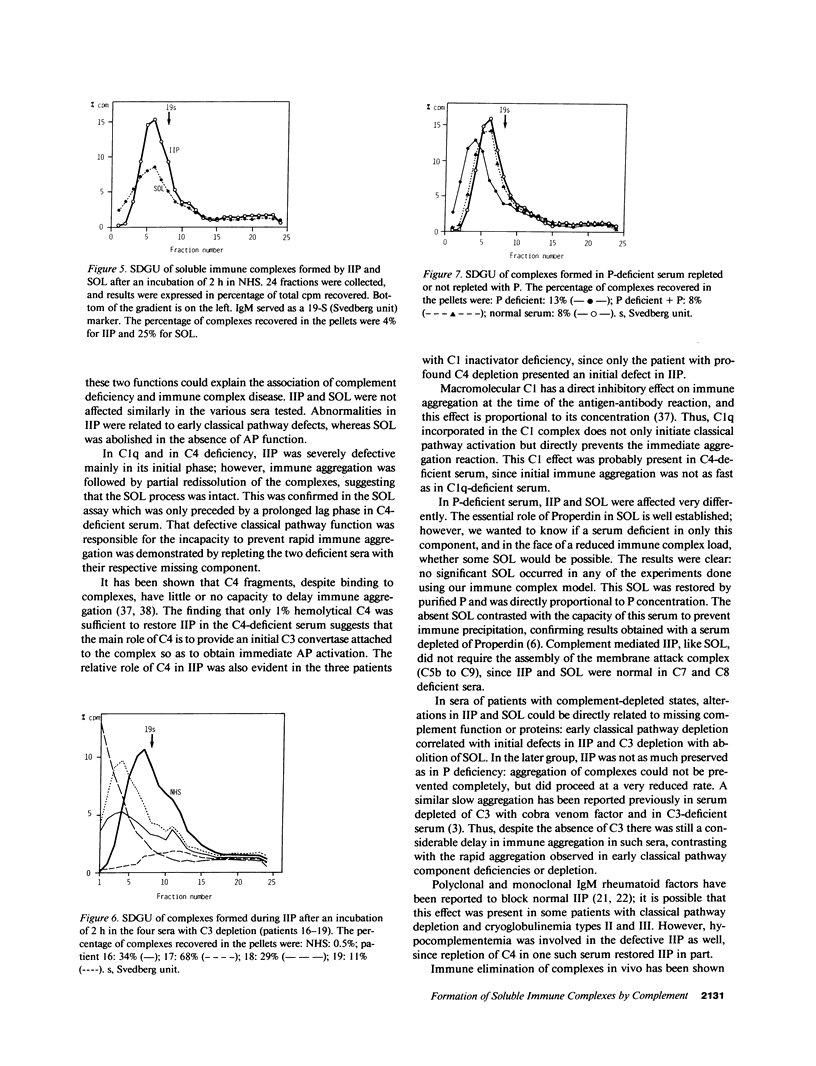
Abstract
To examine whether the ability of complement to form soluble immune complexes plays a role in preventing immune complex-mediated diseases, we analyzed the capacity of complement to inhibit immune precipitation (IIP) and to solubilize preformed immune aggregates (SOL) in 23 sera of patients with various hypocomplementemic states, and we correlated the results of these studies with the clinical syndromes found in the various patients. In sera with deficiency or depletion of early classical pathway components, IIP was profoundly altered, whereas SOL was delayed but in the normal range. In contrast, in sera with C3 depletion but intact classical pathway and in properdin-deficient serum, IIP was initially preserved, whereas SOL was abolished. Since the incidence of immune complex diseases in various hypocomplementemic states correlates with the severity of IIP defects, but not with reduced SOL, it is suggested that IIP is an essential biological function of complement that prevents the rapid formation of insoluble immune complexes in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguado M. T., Perrin L. H., Miescher P. A., Lambert P. H. Decreased capacity to solubilize immune complexes in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Oct;24(10):1225–1229. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baatrup G., Petersen I., Kappelgaard E., Jepsen H. H., Svehag S. E. Complement-mediated solubilization of immune complexes. Solubilization inhibition and complement factor levels in SLE patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):313–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baatrup G., Peterson I., Svehag S. E., Brandslund I. A standardized method for quantitating the complement-mediated immune complex solubilizing capacity of human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1983 May 13;59(3):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balestrieri G., Tincani A., Migliorini P., Ferri C., Cattaneo R., Bombardieri S. Inhibitory effect of IgM rheumatoid factor on immune complex solubilization capacity and inhibition of immune precipitation. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Oct;27(10):1130–1136. doi: 10.1002/art.1780271008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouet J. C., Clauvel J. P., Danon F., Klein M., Seligmann M. Biologic and clinical significance of cryoglobulins. A report of 86 cases. Am J Med. 1974 Nov;57(5):775–788. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90852-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. S., Turner D. R., Heaton J., Williams D. G., Ogg C. S., Chantler C., Haycock G. B., Hicks J. Idiopathic mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Comparison of types I and II in children and adults and long-term prognosis. Am J Med. 1983 Feb;74(2):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90606-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvetta A., Spaeth P. J., Ghirelli P. A., Orecchioni F., Buetler R., Montroni M., Nydegger U. E. Complement activation and impaired capacity to solubilize immune complexes or to prevent their formation in essential mixed cryoglobulinemia. Diagn Immunol. 1983;1(4):315–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Takata Y., Tamura N. Solubilization of immune precipitates by six isolated alternative pathway proteins. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1743–1751. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaither T. A., Alling D. W., Frank M. M. A new one-step method for the functional assay of the fourth component (C4) of human and guinea pig complement. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):574–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Takata Y., Sayama K., Kozono H., Takeda J., Nakano Y., Kinoshita T., Inoue K. Inhibition of immune precipitation by complement. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1464–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Esser A. F., Fernandez H. N., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Native and activated properdin: interconvertibility and identity of amino- and carboxy-terminal sequences. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):602–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. W., Nussenzweig V. A new complement function: solubilization of antigen-antibody aggregates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):418–422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell W. S., Naama J. K., Veitch J., Whaley K. IgM-RF prevents complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation. Immunology. 1984 Jul;52(3):445–448. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naama J. K., Hamilton A. O., Yeung-Laiwah A. C., Whaley K. Prevention of immune precipitation by purified classical pathway complement components. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Nov;58(2):486–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naama J. K., Mitchell W. S., Whaley K. Inhibition of complement-mediated solubilization of antigen-antibody complexes by sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Nov;54(2):429–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naama J. K., Mitchell W. S., Zoma A., Veitch J., Whaley K. Complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation in patients with immune complex diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Feb;51(2):292–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praz F., Roque Antunes Barreira M. C., Lesavre P. A one-step procedure for preparation of classical pathway (C1q) and alternative pathway (factor D) depleted human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(2):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. C., Densen P. Complement deficiency states and infection: epidemiology, pathogenesis and consequences of neisserial and other infections in an immune deficiency. Medicine (Baltimore) 1984 Sep;63(5):243–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Fujita T., Kono I., Kabashima T., Yamane K., Tamura N., Kashiwagi H. Complement-mediated solubilization of immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):37–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Bartolotti S. R., Peters D. K. Inhibition of immune precipitation by complement. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):387–394. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Morris S. M., Dash A., Peters D. K. Complement-mediated solubilization in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, nephritis or vasculitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):557–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Peters D. K. Complement-mediated inhibition of immune precipitation. II. Analysis by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Mar;47(3):563–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli J. A., Steiger G., Schapira M. The role of C1, C1-inactivator and C4 in modulating immune precipitation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jun;60(3):605–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm A. G., Braconier J. H., Söderström C. Properdin deficiency in a family with fulminant meningococcal infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):291–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takahashi S., Brade V., Nussenzweig V. Requirements for the solubilization of immune aggregates by complement. The role of the classical pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):349–358. doi: 10.1172/JCI109135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata Y., Tamura N., Fujita T. Interaction of C3 with antigen-antibody complexes in the process of solubilization of immune precipitates. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2531–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Lesavre P. H., Cooper N. R. Purification and radiolabeling of human C1q. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman F. J., Hebert L. A., Cornacoff J. B., VanAman M. E., Smead W. L., Kraut E. H., Birmingham D. J., Taguiam J. M. Complement depletion accelerates the clearance of immune complexes from the circulation of primates. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1329–1340. doi: 10.1172/JCI111543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitz H. J., Miller G. W., Lint T. F., Ali M. A., Gewurz H. Deficiency of C7 with systemic lupus erythematosus: solubilization of immune complexes in complement-deficient sera. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Jan;24(1):87–93. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. The subunit composition and sedimentation properties of human C1. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2047–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubler R. H., Lange G., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Detection of immune complexes in unheated sera by modified 125I-Clq binding test. Effect of heating on the binding of Clq by immune complexes and application of the test to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



