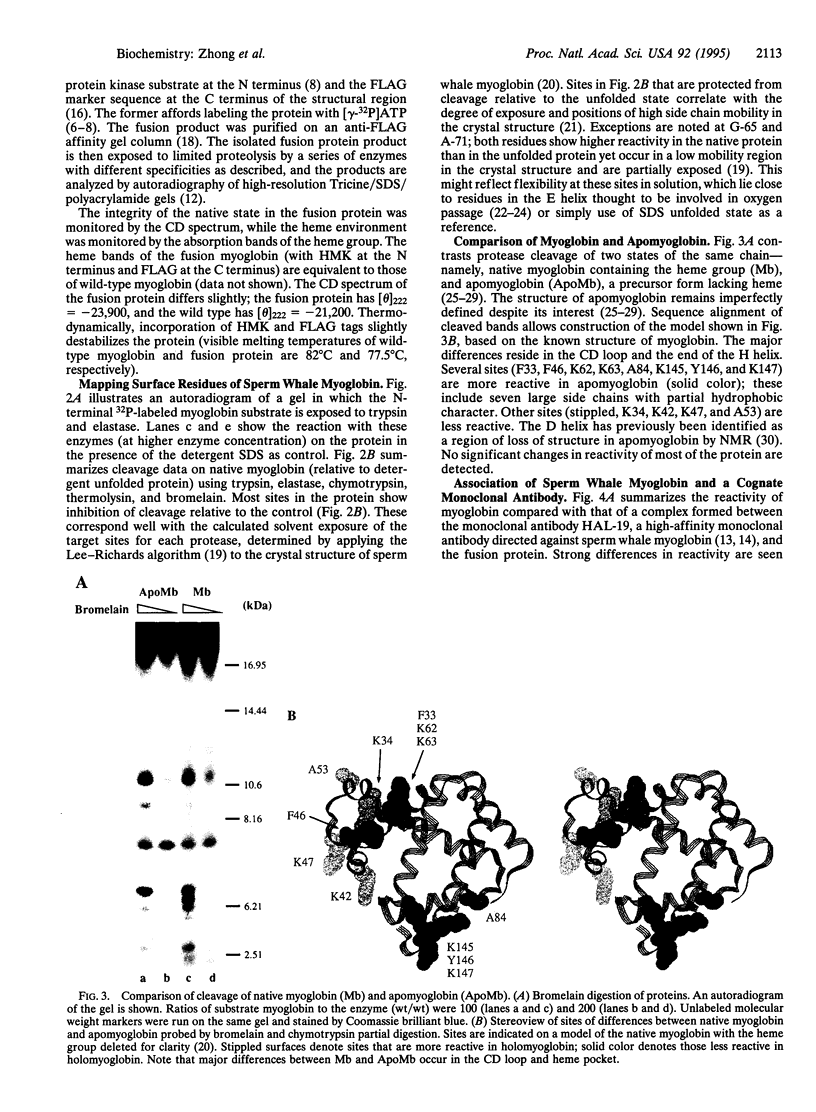
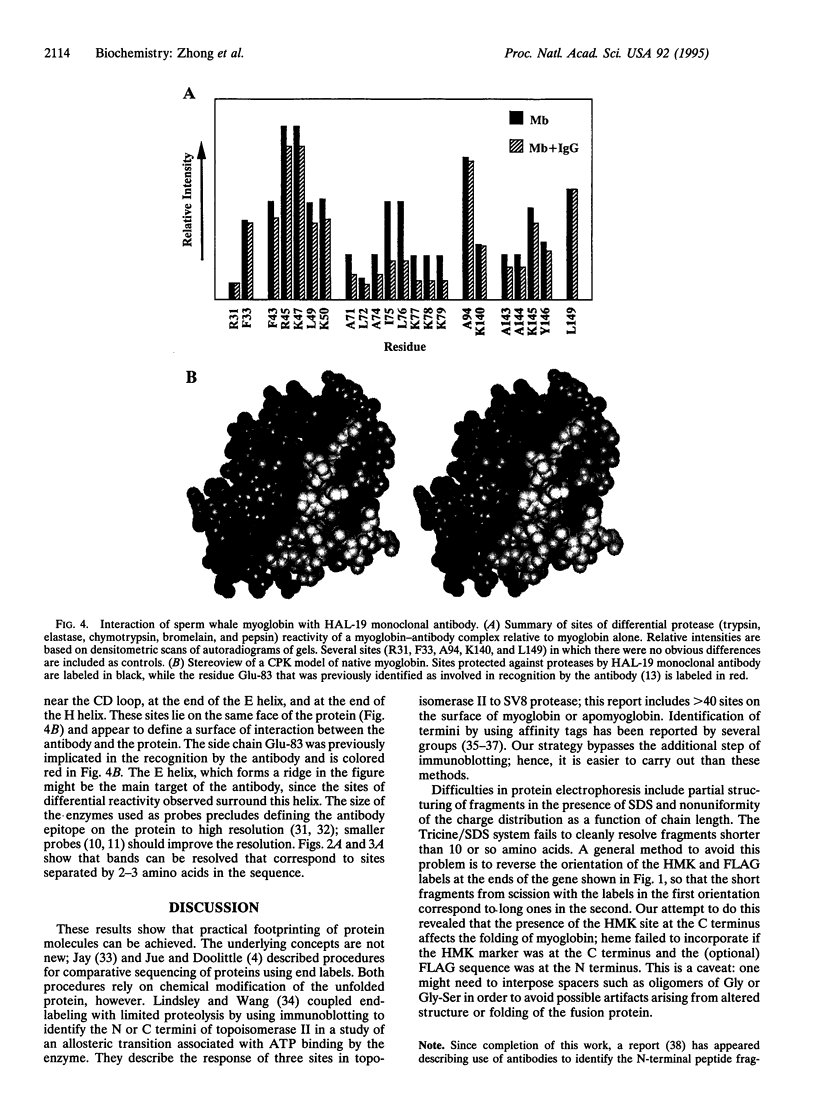
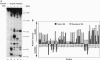Abstract
We describe a procedure for mapping residues on the surface of a protein molecule to its sequence, using a scheme that is analogous to nucleic acid footprinting. The protein is end labeled radioactively and subjected to limited proteolysis, and the products are analyzed by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. The method is tested with the heme protein myoglobin and applied to mapping the (unknown) surface of the molecule lacking the heme group: apomyoglobin. Sites of protein-protein interaction can be identified, as illustrated by footprinting the association between myoglobin and an anti-myoglobin monoclonal antibody.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRESLOW E., BEYCHOK S., HARDMAN K. D., GURD F. R. RELATIVE CONFORMATIONS OF SPERM WHALE METMYOGLOBIN AND APOMYOGLOBIN IN SOLUTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrick D., Hughson F. M., Baldwin R. L. Molecular mechanisms of acid denaturation. The role of histidine residues in the partial unfolding of apomyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 15;237(5):588–601. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A., Buckenmeyer G. K., Hicks G., Gurd F. R., Feldmann R. J., Minna J. Topographic antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies to sperm whale myoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3189–3198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berzofsky J. A. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in protein antigenic structure. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):932–940. doi: 10.1126/science.2410982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Rutter W. J. Interaction cloning: identification of a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that interacts with c-Fos. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1014–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.1589769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocco M. J., Lecomte J. T. Characterization of hydrophobic cores in apomyoglobin: a proton NMR spectroscopy study. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11067–11072. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocco M. J., Lecomte J. T. The native state of apomyoglobin described by proton NMR spectroscopy: interaction with the paramagnetic probe HyTEMPO and the fluorescent dye ANS. Protein Sci. 1994 Feb;3(2):267–281. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Sheriff S., Padlan E. A. Antibody-antigen complexes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10541–10544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchet-Beuzit J., Spotheim-Maurizot M., Sabattier R., Blazy-Baudras B., Charlier M. Radiolytic footprinting. Beta rays, gamma photons, and fast neutrons probe DNA-protein interactions. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 2;32(8):2104–2110. doi: 10.1021/bi00059a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frauenfelder H., Parak F., Young R. D. Conformational substates in proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:451–479. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griko Y. V., Privalov P. L., Venyaminov S. Y., Kutyshenko V. P. Thermodynamic study of the apomyoglobin structure. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90525-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyduk E., Heyduk T. Mapping protein domains involved in macromolecular interactions: a novel protein footprinting approach. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 16;33(32):9643–9650. doi: 10.1021/bi00198a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughson F. M., Baldwin R. L. Use of site-directed mutagenesis to destabilize native apomyoglobin relative to folding intermediates. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4415–4422. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay D. G. A general procedure for the end labeling of proteins and positioning of amino acids in the sequence. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15572–15578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. A., Olson J. S., Phillips G. N., Jr Structure of myoglobin-ethyl isocyanide. Histidine as a swinging door for ligand entry. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jue R. A., Doolittle R. F. Determination of the relative positions of amino acids by partial specific cleavages of end-labeled proteins. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):162–170. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King P. A., Jamison E., Strahs D., Anderson V. E., Brenowitz M. 'Footprinting' proteins on DNA with peroxonitrous acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2473–2478. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F., Bekesi E. Phosphorylation of human immune interferon (IFN-gamma). Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:296–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley J. E., Wang J. C. Proteolysis patterns of epitopically labeled yeast DNA topoisomerase II suggest an allosteric transition in the enzyme induced by ATP binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10485–10489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manak J. R., Prywes R. Mutation of serum response factor phosphorylation sites and the mechanism by which its DNA-binding activity is increased by casein kinase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3652–3659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P., Jakes R., Cameron L., Atherton E. Mapping the cysteine residues and actin-binding regions of villin by using antisera to the amino and carboxyl termini of the molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6788–6792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson Y., Englander S. W., Roder H. An antibody binding site on cytochrome c defined by hydrogen exchange and two-dimensional NMR. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.1697101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Arduini R. M., Springer B. A., Sligar S. G. Crystal structure of myoglobin from a synthetic gene. Proteins. 1990;7(4):358–365. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quillin M. L., Arduini R. M., Olson J. S., Phillips G. N., Jr High-resolution crystal structures of distal histidine mutants of sperm whale myoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 5;234(1):140–155. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A., Galas D. J. The interaction of RNA polymerase and lac repressor with the lac control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):111–137. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman J. D., Vinson C. R., McKnight S. L. Evidence of changes in protease sensitivity and subunit exchange rate on DNA binding by C/EBP. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):771–774. doi: 10.1126/science.2202050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer B. A., Sligar S. G. High-level expression of sperm whale myoglobin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8961–8965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D. Physical studies of protein-DNA complexes by footprinting. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:213–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]