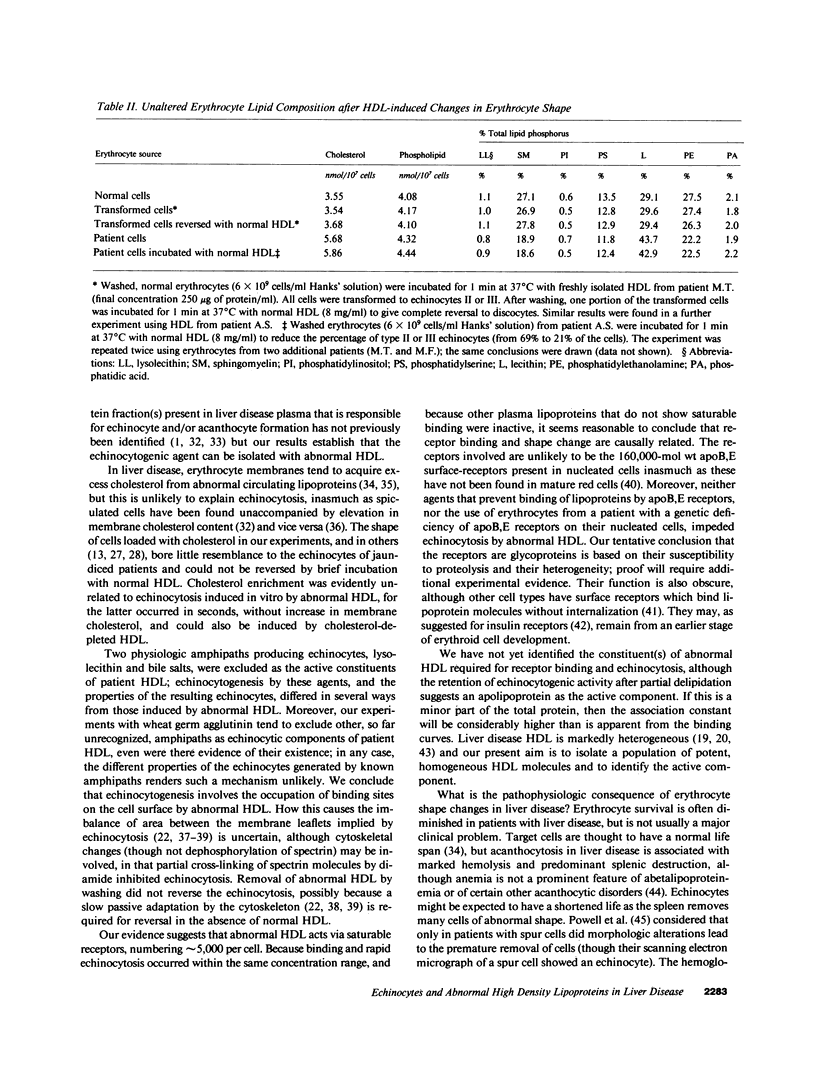
Abstract
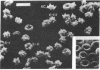
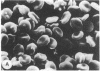
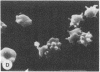
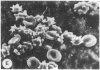
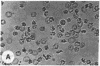
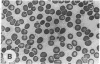
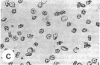
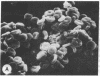
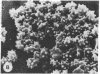
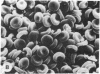
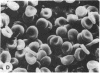
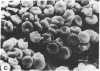
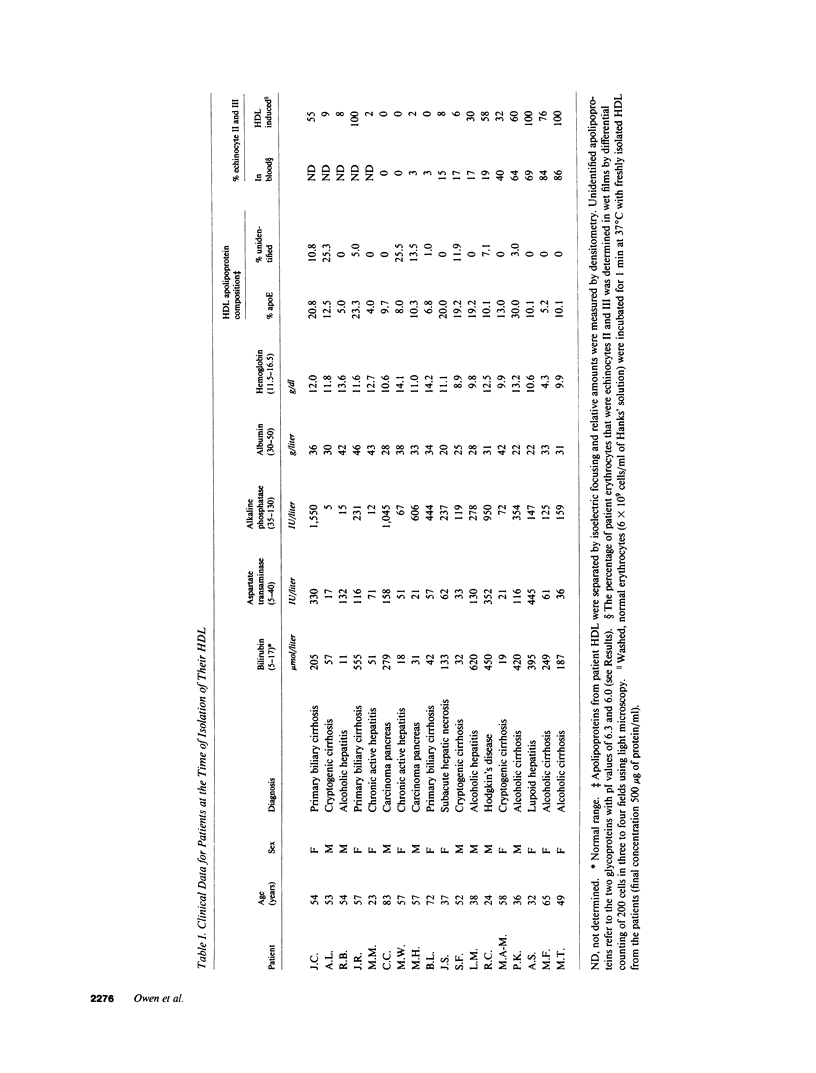
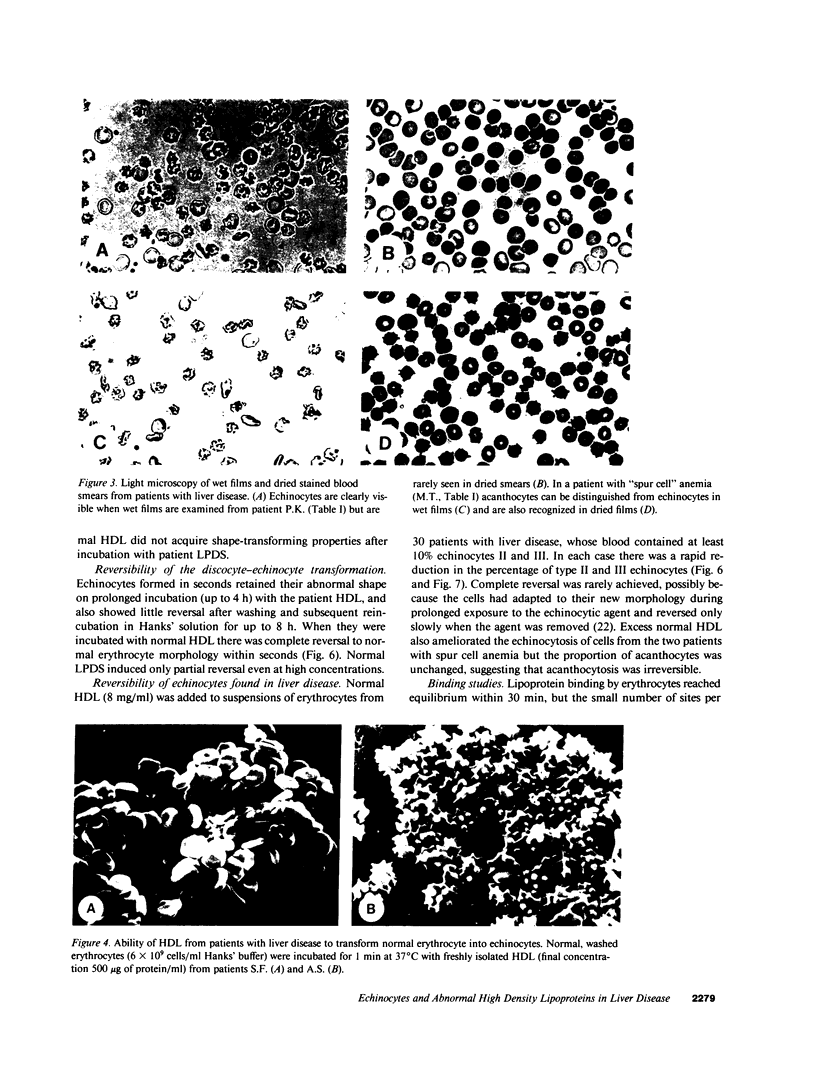
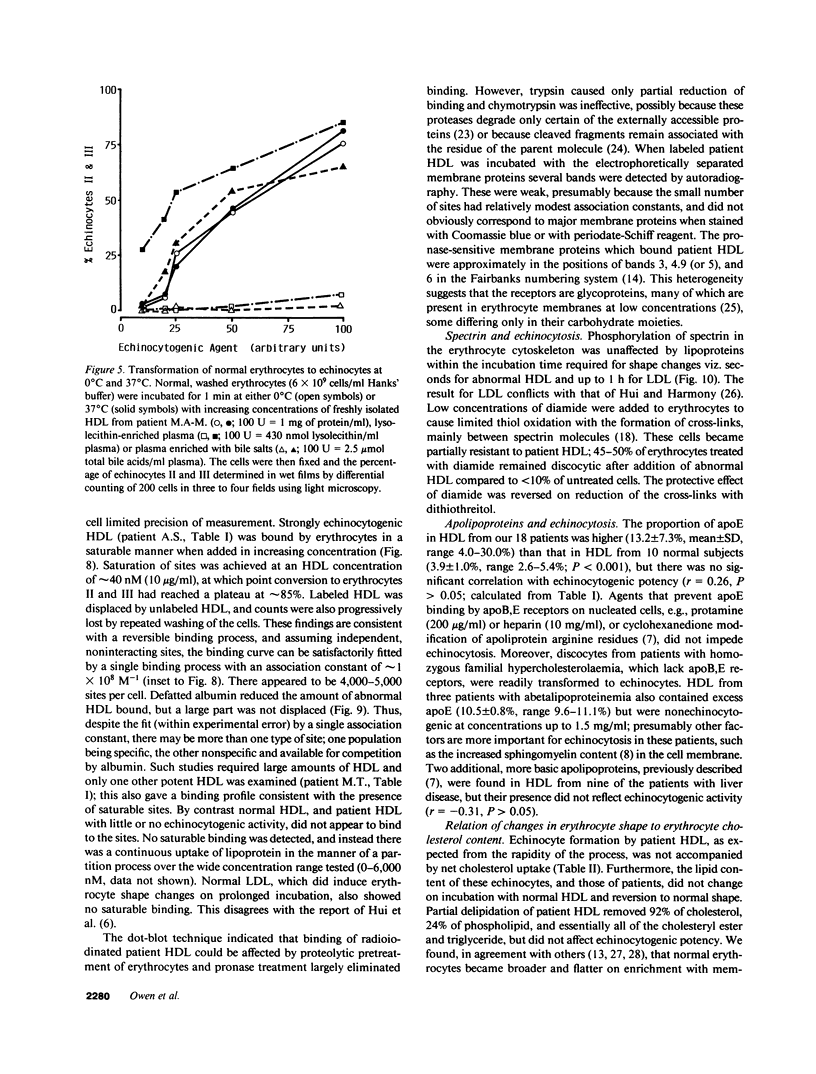
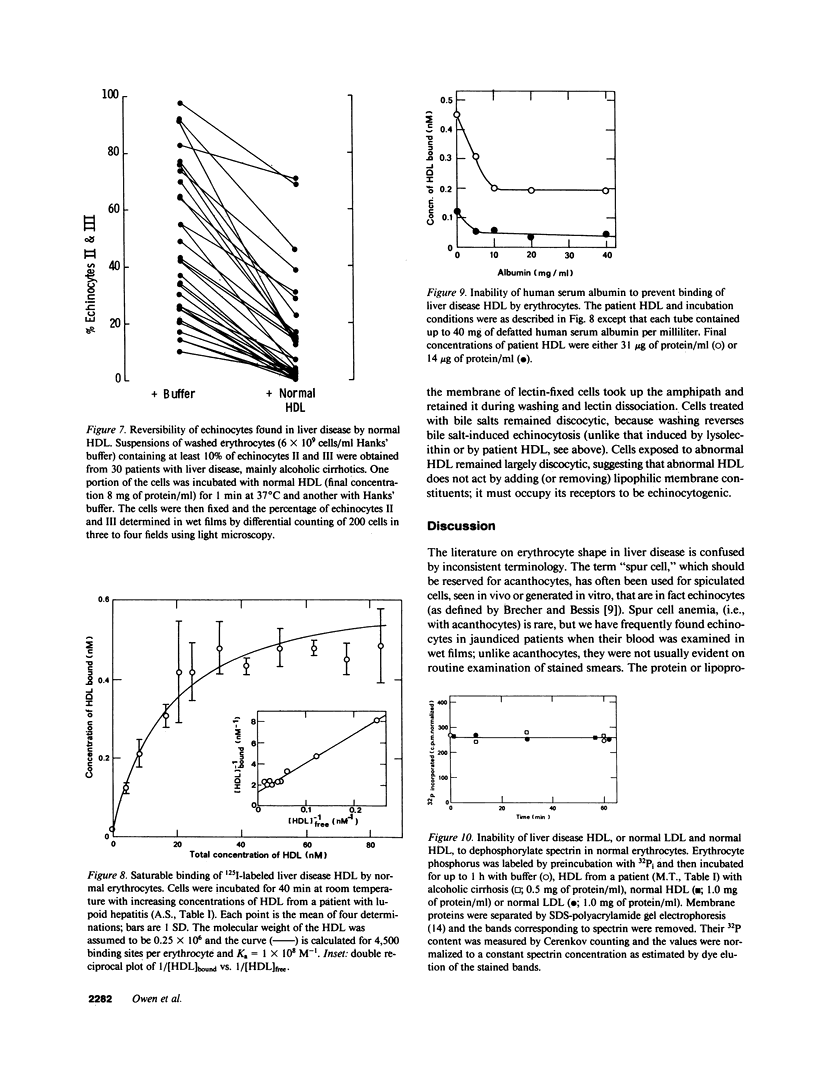
Echinocytes were frequently found in patients with liver disease when their blood was examined in wet films, but rarely detected in dried, stained smears. When normal erythrocytes (discocytes) were incubated with physiologic concentrations of the abnormal high density lipoproteins (HDL) from some jaundiced patients, echinocytosis developed within seconds. Other plasma fractions were not echinocytogenic. There was a close correlation between the number of echinocytes found in vivo and the ability of the corresponding HDL to induce discocyte-echinocyte transformation. On incubation with normal HDL, echinocytes generated in vitro rapidly reverted to a normal shape, and echinocytes from patients showed a similar trend. Echinocytosis occurred without change in membrane cholesterol content, as did its reversal, and was not caused by membrane uptake of lysolecithin or bile acids. Abnormal, echinocytogenic HDL showed saturable binding to approximately 5,000 sites per normal erythrocyte with an association constant of 10(8) M-1. Nonechinocytogenic patient HDL and normal HDL showed only nonsaturable binding. Several minor components of electrophoretically separated erythrocyte membrane proteins bound the abnormal HDL; pretreatment of the cells with trypsin or pronase reduced or eliminated binding. Echinocytosis by abnormal HDL required receptor occupancy, rather than transfer of constituents to or from the membrane, because cells reversibly prefixed in the discoid shape by wheat germ agglutinin, and then exposed to abnormal HDL, did not become echinocytes when the HDL and lectin were successively removed. Binding did not cause dephosphorylation of spectrin. We conclude that the echinocytes of liver disease are generated from discocytes by abnormal HDL, and we infer that the shape change is mediated by cell-surface receptors for abnormal HDL molecules.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agorastos J., Fox C., Harry D. S., McIntyre N. Lecithin--cholesterol acyltransferase and the lipoprotein abnormalities of obstructive jaundice. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1978 Apr;54(4):369–379. doi: 10.1042/cs0540369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alhanaty E., Sheetz M. P. Control of the erythrocyte membrane shape: recovery from the effect of crenating agents. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):884–888. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes S., Chitranukroh A. A simplified procedure for the isolation of bile acids from serum based on a batch extraction with the non-ionic resin--Amberlite XAD-7. Ann Clin Biochem. 1977 Jul;14(4):235–239. doi: 10.1177/000456327701400163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecher G., Bessis M. Present status of spiculed red cells and their relationship to the discocyte-echinocyte transformation: a critical review. Blood. 1972 Sep;40(3):333–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. J., Singer S. J. The solubility of amphipathic molecules in biological membranes and lipid bilayers and its implications for membrane structure. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):808–818. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A. Anemia with spur cells: a red cell defect acquired in serum and modified in the circulation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Oct;48(10):1820–1831. doi: 10.1172/JCI106148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Diloy Puray M., Lando P., Greenverg M. S. An analysis of lipoproteins, bile acids, and red cell membranes associated with target cells and spur cells in patients with liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3182–3192. doi: 10.1172/JCI107145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A. Hemolytic syndromes and red cell membrane abnormalities in liver disease. Semin Hematol. 1980 Apr;17(2):103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Kimball D. B., Durocher J. R. Role of the spleen in membrane conditioning and hemolysis of spur cells in liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 6;290(23):1279–1284. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406062902303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. C., Harry D. S., Owen J. S., Foo A. Y., McIntyre N. Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase and the lipoprotein abnormalities of parenchymal liver disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Jan;56(6):575–583. doi: 10.1042/cs0560575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dons R. F., Corash L. M., Gorden P. The insulin receptor is an age-dependent integral component of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2982–2987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass C. C., McCall M. S., Frenel E. P. The acanthocyte in cirrhosis with hemolytic anemia. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Feb;68(2):390–397. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-2-390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H. Glycophorins A, B, and C: a family of sialoglycoproteins. Isolation and preliminary characterization of trypsin derived peptides. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(1):79–95. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin D. V., Gray G. R., Frohlich J. Erythrocyte membrane alterations in lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1978;150:162–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahn E. P., Dietz A. A., Stefani S. S., Donnelly W. J. Burr cells, hemolytic anemia and cirrhosis. Am J Med. 1968 Jul;45(1):78–87. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W., Kamp D., Plasa G., Deuticke B. Intra- and intermolecular cross-linking of membrane proteins in intact erythrocytes and ghosts by SH-oxidizing agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 5;469(2):226–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Harmony J. A. Interaction of plasma lipoproteins with erythrocytes. I. Alteration of erythrocyte morphology. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 2;550(3):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Harmony J. A. Interaction of plasma lipoproteins with erythrocytes. II. Modulation of membrane-associated enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 2;550(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Noel J. G., Harmony J. A. Binding of plasma low density lipoproteins to erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 23;664(3):513–526. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Stewart C. M., Carpenter M. P., Stewart T. P. Effects of cholesterol on lipid organization in human erythrocyte membrane. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):283–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick-Jones J., Szentkiralyi E. M., Szent-Györgyi A. G. Regulatory light chains in myosins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 15;104(4):747–775. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers F. A., Roelofsen B., Berendsen W., Op den Kamp J. A., van Deenen L. L. Shape changes in human erythrocytes induced by replacement of the native phosphatidylcholine with species containing various fatty acids. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2260–2267. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Cutler H. B., Steck T. L. The effect of cholesterol and other intercalated amphipaths on the contour and stability of the isolated red cell membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9331–9337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Gough A., Steck T. L. Role of the bilayer in the shape of the isolated erythrocyte membrane. J Membr Biol. 1982;69(2):113–123. doi: 10.1007/BF01872271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Hadesman R. A., Steck T. L. Role of the reticulum in the stability and shape of the isolated human erythrocyte membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):714–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Slayton J. M. Interaction of cholesterol and lysophosphatidylcholine in determining red cell shape. J Lipid Res. 1982 Nov;23(8):1121–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovrien R. E., Anderson R. A. Stoichiometry of wheat germ agglutinin as a morphology controlling agent and as a morphology controlling agent and as a morphology protective agent for the human erythrocyte. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):534–548. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Maldonado M. Role of lipoproteins in the formation of spur cell anaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Sep;21(5):620–625. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.5.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Greenquist A. C., Shohet S. B. Bilayer balance and regulation of red cell shape changes. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(3):453–458. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Albers J. J., Bierman E. L. Rapid regulation of the activity of the low density lipoprotein receptor of cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):475–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. S., Bruckdorfer K. R., Day R. C., McIntyre N. Decreased erythrocyte membrane fluidity and altered lipid composition in human liver disease. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):124–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. S., Goodall H., Mistry P., Harry D. S., Day R. C., McIntyre N. Abnormal high density lipoproteins from patients with liver disease regulate cholesterol metabolism in cultured human skin fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1984 Sep;25(9):919–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. S., Hutton R. A., Day R. C., Bruckdorfer K. R., McIntyre N. Platelet lipid composition and platelet aggregation in human liver disease. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):423–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. S., Ramalho V., Costa J. C., Gillett M. P. Determination of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransfer in mouse plasma and the influence of mercaptoethanol and sulphydryl blocking agents on its activity. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1979;63(2):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(79)90038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. W., Halliday J. W., Knowles B. R. The relationship of red cell membrane lipid content to red cell morphology and survival in patients with liver disease. Aust N Z J Med. 1975 Apr;5(2):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1975.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Bull F. G., Anderton B. H., Roitt I. M. Direct autoradiographic visualisation in SDS-gels of lectin-binding components of the human erythrocyte membrane. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):330–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80291-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. A., LONERGAN E. T., STERLING K. SPUR-CELL ANEMIA: HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA WITH RED CELLS RESEMBLING ACANTHOCYTES IN ALCOHOLIC CIRRHOSIS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Aug 20;271:396–398. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196408202710804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shohet S. E. Editorial: "Acanthocytogenesis"--or how the red cell won its spurs. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 6;290(23):1316–1317. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406062902311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber R., Amorosi E., Lhowe J., Kayden H. J. Spur-shaped erythrocytes in Laennec's cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1966 Sep 22;275(12):639–643. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196609222751204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Koziarz J. J., Singh M. K., Reddy G., Köhler H. Preparation and analysis of seven major, topographically defined fragments of band 3, the predominant transmembrane polypeptide of human erythrocyte membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1216–1222. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidman S. W., Ragland J. B., Sabesin S. M. Plasma lipoprotein composition in alcoholic hepatitis: accumulation of apolipoprotein E-rich high density lipoprotein and preferential reappearance of "light'-HDL during partial recovery. J Lipid Res. 1982 May;23(4):556–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe L. C., Lux S. E. Membrane protein phosphorylation of intact normal and hereditary spherocytic erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3336–3342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]