Abstract
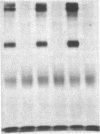
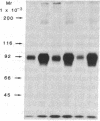
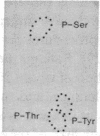
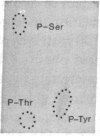
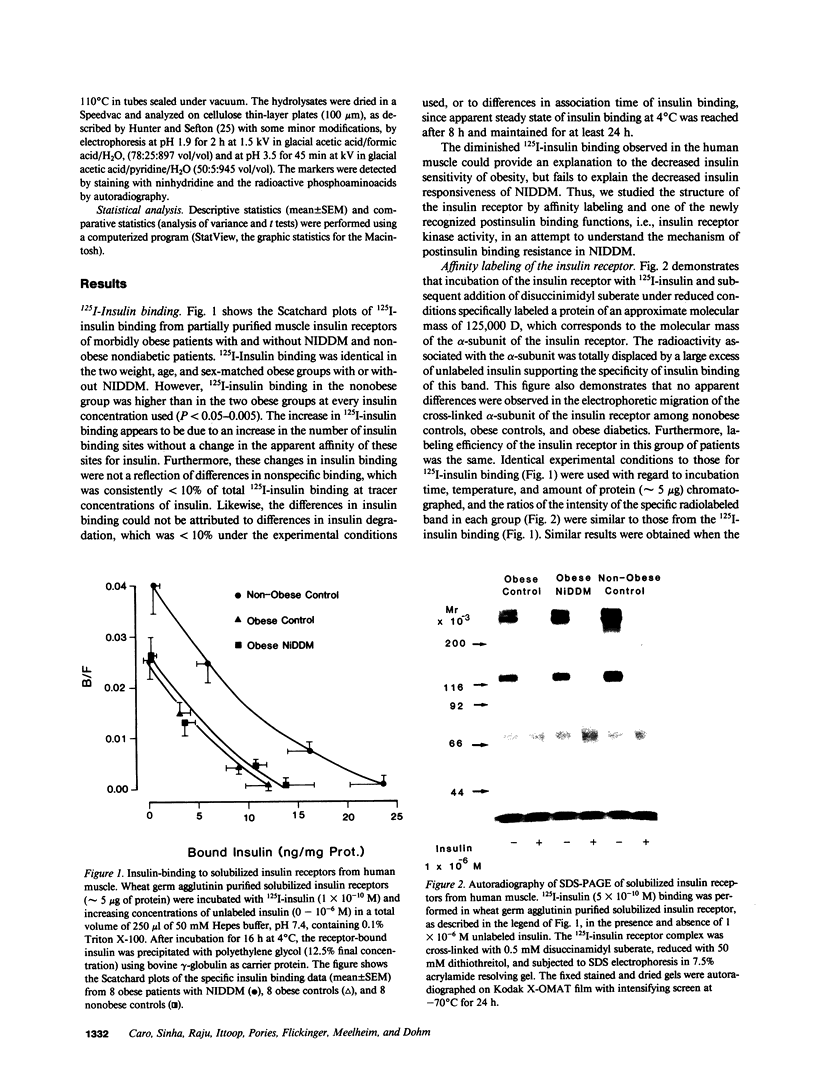
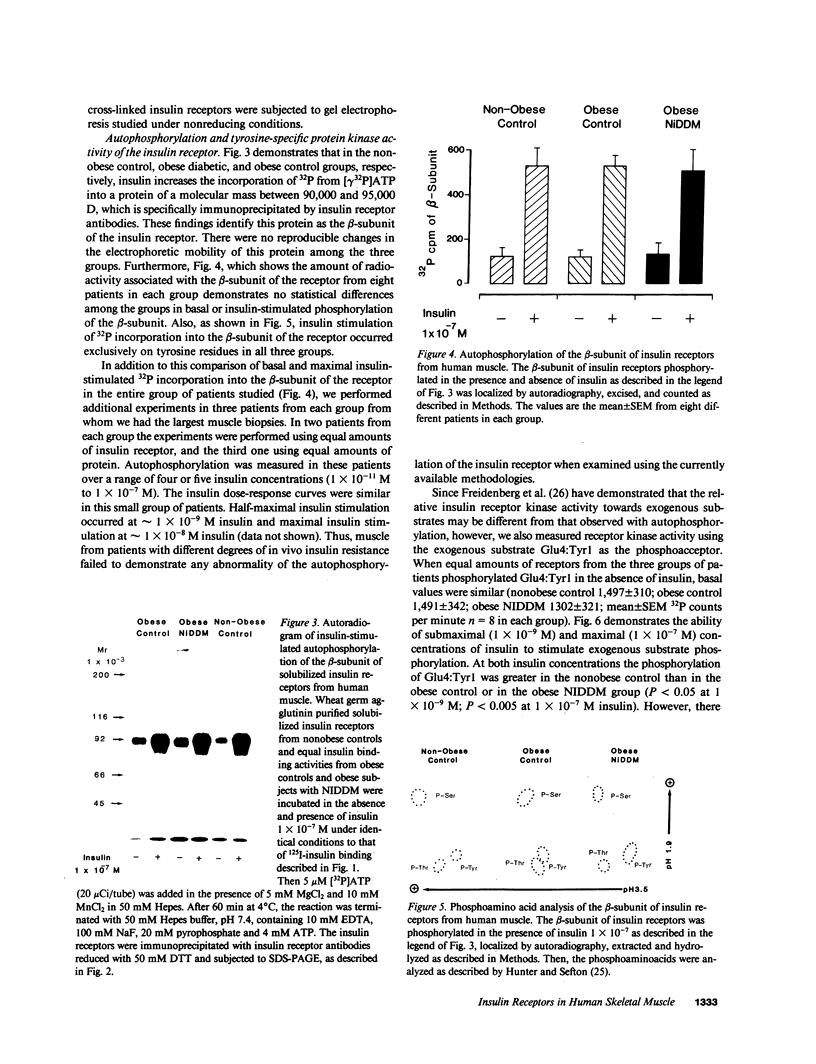
We have studied the structure and function of the insulin receptors in obese patients with and without noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) and in nonobese controls using partially purified receptors from muscle biopsies. Insulin binding was decreased in obesity due to reduced number of binding sites but no differences were observed in insulin binding between obese subjects with or without NIDDM. The structural characteristics of the receptors, as determined by affinity labeling methods and electrophoretic mobility of the beta-subunit, were not altered in obese or NIDDM compared to normal weight subjects. Furthermore, the ability of insulin to stimulate the autophosphorylation of the beta-subunit and the phosphoamino acid composition of the phosphorylated receptor were the same in all groups. However, insulin receptor kinase activity was decreased in obesity using Glu4:Tyr1 as exogenous phosphoacceptor without any appreciable additional defect when obesity was associated with NIDDM. Thus, our data are supportive of the hypothesis that in muscle of obese humans, insulin resistance is partially due to decreased insulin receptors and insulin receptor kinase activity. In NIDDM the defect(s) in muscle is probably distal to the insulin receptor kinase.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda J. M., Livingston J. N., Lockwood D. H. Insulin receptor: role in the resistance of human obesity to insulin. Science. 1975 Apr 18;188(4185):264–266. doi: 10.1126/science.164059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amatruda J. M., Roncone A. M. Normal hepatic insulin receptor autophosphorylation in nonketotic diabetes mellitus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arner P., Einarsson K., Backman L., Nilsell K., Lerea K. M., Livingston J. N. Studies of liver insulin receptors in non-obese and obese human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1729–1736. doi: 10.1172/JCI111132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Leone G. R., Martin D. B. Effects of epinephrine and insulin on phosphopeptide metabolism in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1511–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Nemenoff R. A., Blackshear P. J., Pierce M. W., Osathanondh R. Insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in detergent extracts of human placental membranes. Comparison to epidermal growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15162–15166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Nemenoff R. A., Avruch J. Characteristics of insulin and epidermal growth factor stimulation of receptor autophosphorylation in detergent extracts of rat liver and transplantable rat hepatomas. Endocrinology. 1984 Jan;114(1):141–152. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolinder J., Ostman J., Arner P. Postreceptor defects causing insulin resistance in normoinsulinemic non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1982 Oct;31(10):911–916. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.10.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burant C. F., Treutelaar M. K., Buse M. G. Diabetes-induced functional and structural changes in insulin receptors from rat skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):260–270. doi: 10.1172/JCI112285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burant C. F., Treutelaar M. K., Landreth G. E., Buse M. G. Phosphorylation of insulin receptors solubilized from rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 1984 Jul;33(7):704–708. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.7.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Cecchin F., Sinha M. K. Is glycosylation in the liver needed for insulin binding, processing, and action? Evidence for heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12810–12816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Ittoop O., Pories W. J., Meelheim D., Flickinger E. G., Thomas F., Jenquin M., Silverman J. F., Khazanie P. G., Sinha M. K. Studies on the mechanism of insulin resistance in the liver from humans with noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Insulin action and binding in isolated hepatocytes, insulin receptor structure, and kinase activity. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):249–258. doi: 10.1172/JCI112558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comi R. J., Grunberger G., Gorden P. Relationship of insulin binding and insulin-stimulated tyrosine kinase activity is altered in type II diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):453–462. doi: 10.1172/JCI112833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Koivisto V. New concepts in the pathogenesis and treatment of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1983 Jan 17;74(1A):52–81. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90654-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Gunnarsson R., Björkman O., Olsson M., Wahren J. Effects of insulin on peripheral and splanchnic glucose metabolism in noninsulin-dependent (type II) diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):149–155. doi: 10.1172/JCI111938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R., Deibert D., Hendler R., Felig P., Soman V. Insulin sensitivity and insulin binding to monocytes in maturity-onset diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):939–946. doi: 10.1172/JCI109394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Denton R. M., Brownsey R. W., Belsham G. J. A partial view of the mechanism of insulin action. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):347–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00252681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner C. C., Fraze E., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Quantitation of insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1985 Sep;34(9):831–835. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.9.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Murray R., Kissebah A. H. Relationship between skeletal muscle insulin resistance, insulin-mediated glucose disposal, and insulin binding. Effects of obesity and body fat topography. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1515–1525. doi: 10.1172/JCI111565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Smith J. D., Cobelli C., Toffolo G., Pilo A., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of insulin on the distribution and disposition of glucose in man. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):357–364. doi: 10.1172/JCI111969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flickinger E. G., Pories W. J., Meelheim H. D., Sinar D. R., Blose I. L., Thomas F. T. The Greenville gastric bypass. Progress report at 3 years. Ann Surg. 1984 May;199(5):555–562. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198405000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidenberg G. R., Klein H. H., Cordera R., Olefsky J. M. Insulin receptor kinase activity in rat liver. Regulation by fasting and high carbohydrate feeding. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12444–12453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H., Kimmerling G., Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Demonstration of insulin resistance in untreated adult onset diabetic subjects with fasting hyperglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):454–461. doi: 10.1172/JCI107951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu F., Flier J. S., Kahn C. R. Characterization of binding and phosphorylation defects of erythrocyte insulin receptors in the type A syndrome of insulin resistance. Diabetes. 1986 Feb;35(2):127–138. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu F., Flier J. S., Kahn C. R. Defect in insulin receptor phosphorylation in erythrocytes and fibroblasts associated with severe insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15003–15006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberger G., Comi R. J., Taylor S. I., Gorden P. Tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor of patients with type A extreme insulin resistance: studies with circulating mononuclear cells and cultured lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Dec;59(6):1152–1158. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-6-1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberger G., Zick Y., Gorden P. Defect in phosphorylation of insulin receptors in cells from an insulin-resistant patient with normal insulin binding. Science. 1984 Mar 2;223(4639):932–934. doi: 10.1126/science.6141638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberger G., Zick Y., Roth J., Gorden P. Protein kinase activity of the insulin receptor in human circulating and cultured mononuclear cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 15;115(2):560–566. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Martin F. I., Melick R. A. Correlation between insulin receptor binding in isolated fat cells and insulin sensitivity in obese human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1435–1441. doi: 10.1172/JCI108599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kasuga M., Akanuma Y., Ezaki O., Takaku F. Decreased autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor-kinase in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14208–14216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in cultured hepatoma cells and a solubilized system. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:609–621. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blithe D. L., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):667–669. doi: 10.1038/298667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M. Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):957–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI110350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krotkiewski M., Björntorp P., Sjöström L., Smith U. Impact of obesity on metabolism in men and women. Importance of regional adipose tissue distribution. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1150–1162. doi: 10.1172/JCI111040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Grémeaux T., Ballotti R., Van Obberghen E. Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase is defective in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):676–679. doi: 10.1038/315676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Lerea K. M., Bolinder J., Kager L., Backman L., Arner P. Binding and molecular weight properties of the insulin receptor from omental and subcutaneous adipocytes in human obesity. Diabetologia. 1984 Oct;27(4):447–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00273909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood D. H., Amatruda J. M. Cellular alterations responsible for insulin resistance in obesity and type II diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1983 Nov 30;75(5B):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth P., Digirolamo M., Krotkiewski M., Smith U. Insulin binding and responsiveness in fat cells from patients with reduced glucose tolerance and type II diabetes. Diabetes. 1983 Aug;32(8):748–754. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.8.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Ciaraldi T. P., Kolterman O. G. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent (type II) diabetes. Am J Med. 1985 Sep 20;79(3B):12–22. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(85)80003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Decreased insulin binding to adipocytes and circulating monocytes from obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1165–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI108384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer M. A., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr Insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90579-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pories W. J., Flickinger E. G., Meelheim D., Van Rij A. M., Thomas F. T. The effectiveness of gastric bypass over gastric partition in morbid obesity: consequence of distal gastric and duodenal exclusion. Ann Surg. 1982 Oct;196(4):389–399. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198210000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Chen Y. I., Coulston A. M., Greenfield M. S., Hollenbeck C., Lardinois C., Liu G., Schwartz H. Insulin secretion and action in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Is insulin resistance secondary to hypoinsulinemia? Am J Med. 1983 Nov 30;75(5B):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees-Jones R. W., Taylor S. I. An endogenous substrate for the insulin receptor-associated tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4461–4467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Mechanism and significance of insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):990–995. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Cassell D. J. Insulin receptor: evidence that it is a protein kinase. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):299–301. doi: 10.1126/science.6849137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shia M. A., Pilch P. F. The beta subunit of the insulin receptor is an insulin-activated protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):717–721. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes and cell-free extracts derived from them incorporate 32P into ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2641–2645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Maron R., Kahn C. R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):183–186. doi: 10.1038/318183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Takayama S., Kahn C. R. Differences in the sites of phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9470–9478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Whittaker J., Roth J. Insulin stimulated phosphorylation of its own receptor. Activation of a tyrosine-specific protein kinase that is tightly associated with the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3431–3434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]