Abstract
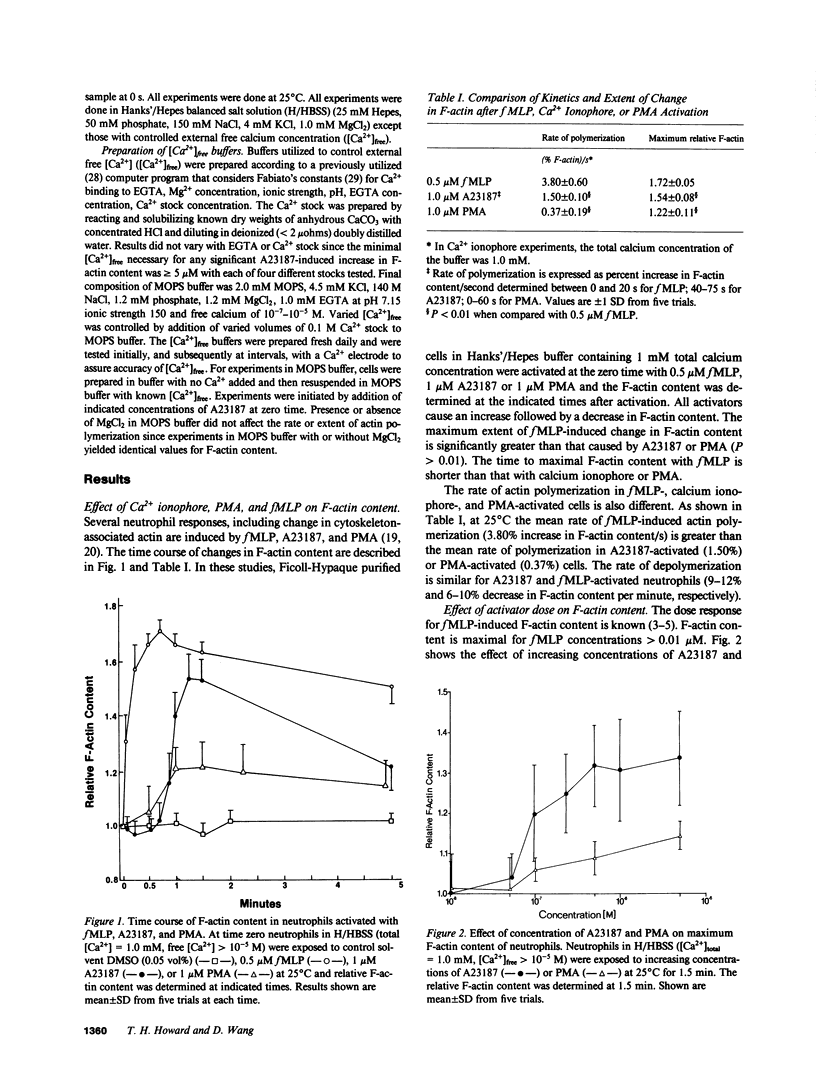
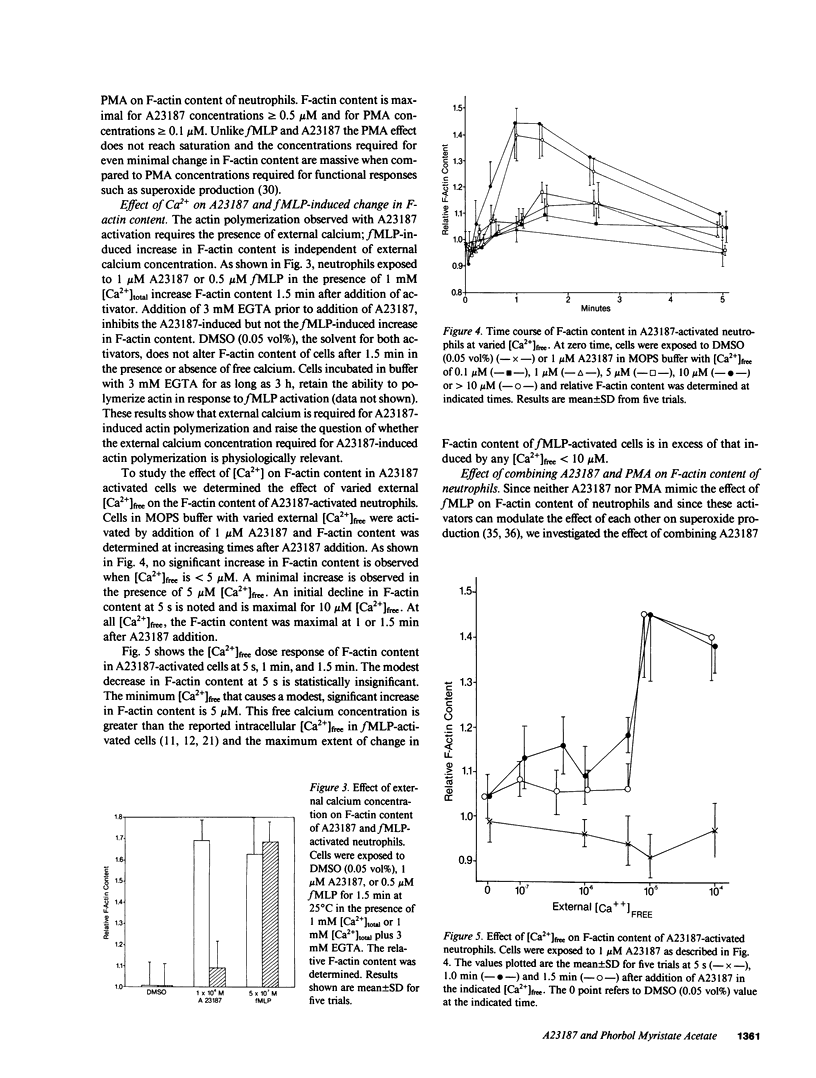
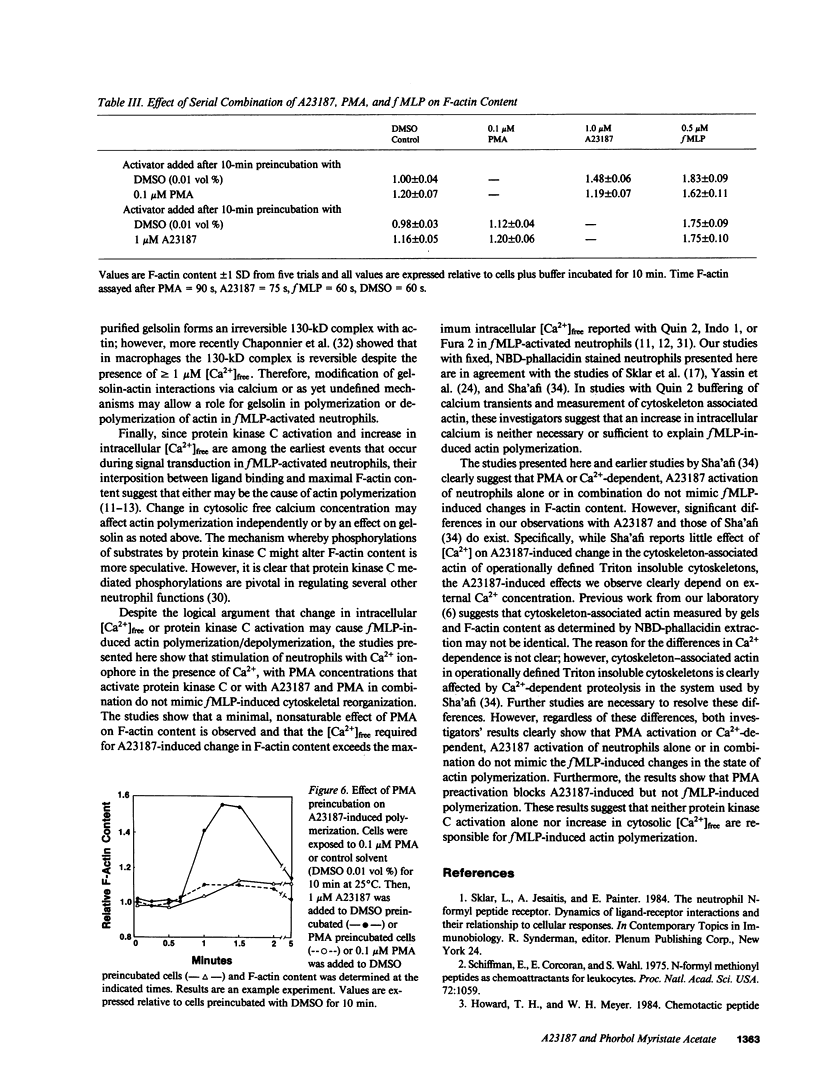
Formyl-methionylleucylphenylalanine (fMLP) activation of neutrophils causes an increase in intracellular Ca2+, activation of protein kinase C and an increase in F-actin content. To examine the role of Ca2+ and protein kinase C activation as determinants of change in F-actin content of neutrophils, we used the NBD-phallacidin extraction assay to compare the kinetics and extent of change in F-actin content of cells activated with fMLP, the calcium ionophore A23187 or phorbol myristate acetate (PMA). All stimuli increase the F-actin content in a dose-dependent manner; however, the rate of increase is slower and the maximum F-actin content is less for calcium ionophore and PMA than for fMLP-activated cells. The A23187-induced increase in F-actin content, but not that of fMLP, depends upon external free [Ca2+]. In A23187-activated cells, F-actin content increases at [Ca2+]free greater than or equal to 5 microM, is maximal at [Ca2+]free greater than or equal to 10 microM and is negligible at physiologic free [Ca2+] (10(-7)-10(-6) M). Combinations of PMA with A23187 or fMLP inhibit the A23187, but not the fMLP, activated actin polymerization. Comparison and combination of these activators shows that neither Ca2+-dependent activation with A23187 nor activation with PMA alone or in combination mimic the fMLP-induced changes in cytoskeleton organization of neutrophils.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Kurth M. C. Actin-gelsolin interactions. Evidence for two actin-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7480–7487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Bennett J. P., Gomperts B. D. Stimulus-secretion coupling in rabbit neutrophils is not mediated by phosphatidylinositol breakdown. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):275–277. doi: 10.1038/288275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale M. M., Penfield A. Synergism between phorbol ester and A23187 in superoxide production by neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):170–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancker P., Löw I. Dual effect of Ca2+ on ultrasonic ATPase activity and polymerization of muscle actin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 15;484(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Lew D. P., Pozzan T. Protein kinase C activation of physiological processes in human neutrophils at vanishingly small cytosolic Ca2+ levels. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):691–693. doi: 10.1038/310691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. W., Godfrey P. P., Hoyle P. C., Putney J. W., Jr, Freer R. J. Secretagogue-induced phosphoinositide metabolism in human leucocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2220307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Appelbaum B. D., Vogler W. R., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase and its substrates in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard T. H., Meyer W. H. Chemotactic peptide modulation of actin assembly and locomotion in neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1265–1271. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard T. H., Oresajo C. O. A method for quantifying F-actin in chemotactic peptide activated neutrophils: study of the effect of tBOC peptide. Cell Motil. 1985;5(6):545–557. doi: 10.1002/cm.970050609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard T. H., Oresajo C. O. The kinetics of chemotactic peptide-induced change in F-actin content, F-actin distribution, and the shape of neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1078–1085. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASAI M., ASAKURA S., OOSAWA F. The G-F equilibrium in actin solutions under various conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Feb 12;57:13–21. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Vienne K., Rutherford L. E., Wilkenfeld C., Finkelstein M. C., Weissmann G. Stimulus response coupling in the human neutrophil. II. Temporal analysis of changes in cytosolic calcium and calcium efflux. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4076–4082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurth M. C., Bryan J. Platelet activation induces the formation of a stable gelsolin-actin complex from monomeric gelsolin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7473–7479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. M., Badwey J. A., Karnovsky M. L., Karnovsky M. J. Superoxide release by neutrophils: synergistic effects of a phorbol ester and a calcium ionophore. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):734–739. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C. N., Broekman M. J., Korchak H. M., Marcus A. J., Weissmann G. Endogenous phospholipid metabolism in stimulated neutrophils differential activation by FMLP and PMA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):951–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'afi R. I., Shefcyk J., Yassin R., Molski T. F., Volpi M., Naccache P. H., White J. R., Feinstein M. B., Becker E. L. Is a rise in intracellular concentration of free calcium necessary or sufficient for stimulated cytoskeletal-associated actin? J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1459–1463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Omann G. M., Painter R. G. Relationship of actin polymerization and depolymerization to light scattering in human neutrophils: dependence on receptor occupancy and intracellular Ca++. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1161–1166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Yassin R., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Chemotactic factor causes rapid decreases in phosphatidylinositol,4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4-monophosphate in rabbit neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):957–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91711-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace P. J., Wersto R. P., Packman C. H., Lichtman M. A. Chemotactic peptide-induced changes in neutrophil actin conformation. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1060–1065. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yassin R., Shefcyk J., White J. R., Tao W., Volpi M., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Feinstein M. B., Sha'afi R. I. Effects of chemotactic factors and other agents on the amounts of actin and a 65,000-mol-wt protein associated with the cytoskeleton of rabbit and human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):182–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Albrecht J. H., Fattoum A. Identification of gelsolin, a Ca2+-dependent regulatory protein of actin gel-sol transformation, and its intracellular distribution in a variety of cells and tissues. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):901–906. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Hartwig J. H., Maruyama K., Stossel T. P. Ca2+ control of actin filament length. Effects of macrophage gelsolin on actin polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9693–9697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):583–586. doi: 10.1038/281583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Zaner K. S., Stossel T. P. Ca2+ control of actin gelation. Interaction of gelsolin with actin filaments and regulation of actin gelation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9494–9500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



