Abstract
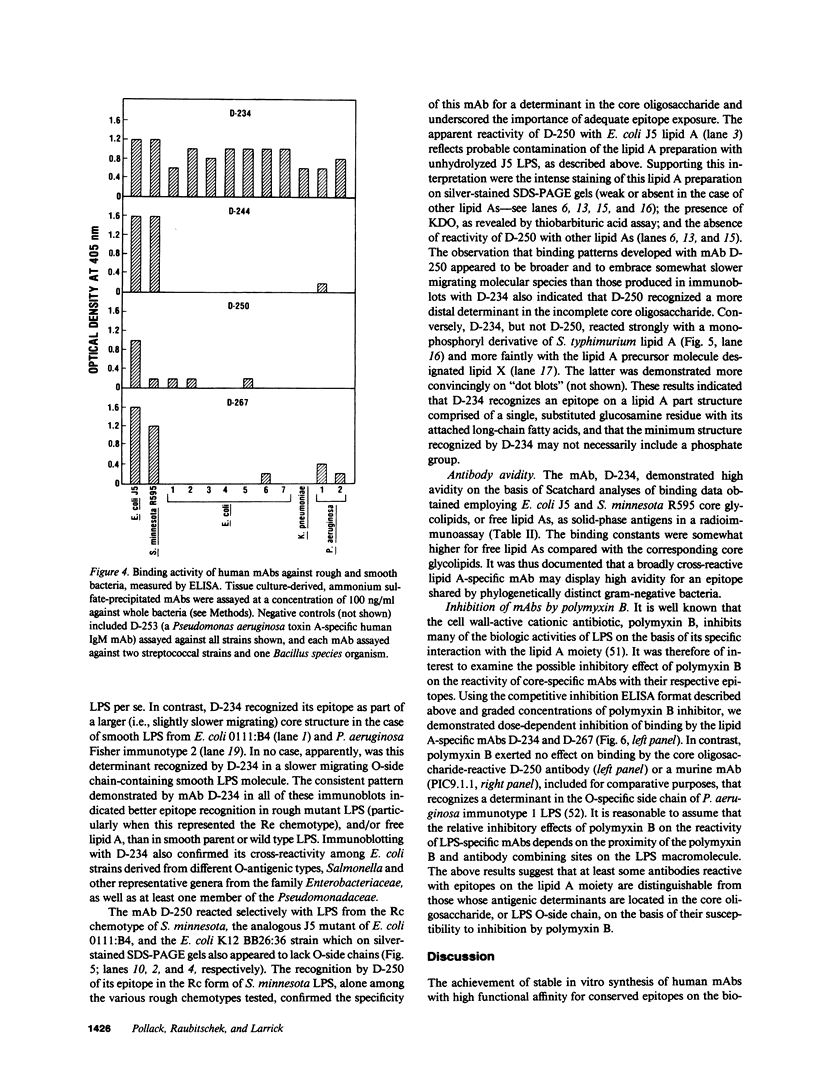
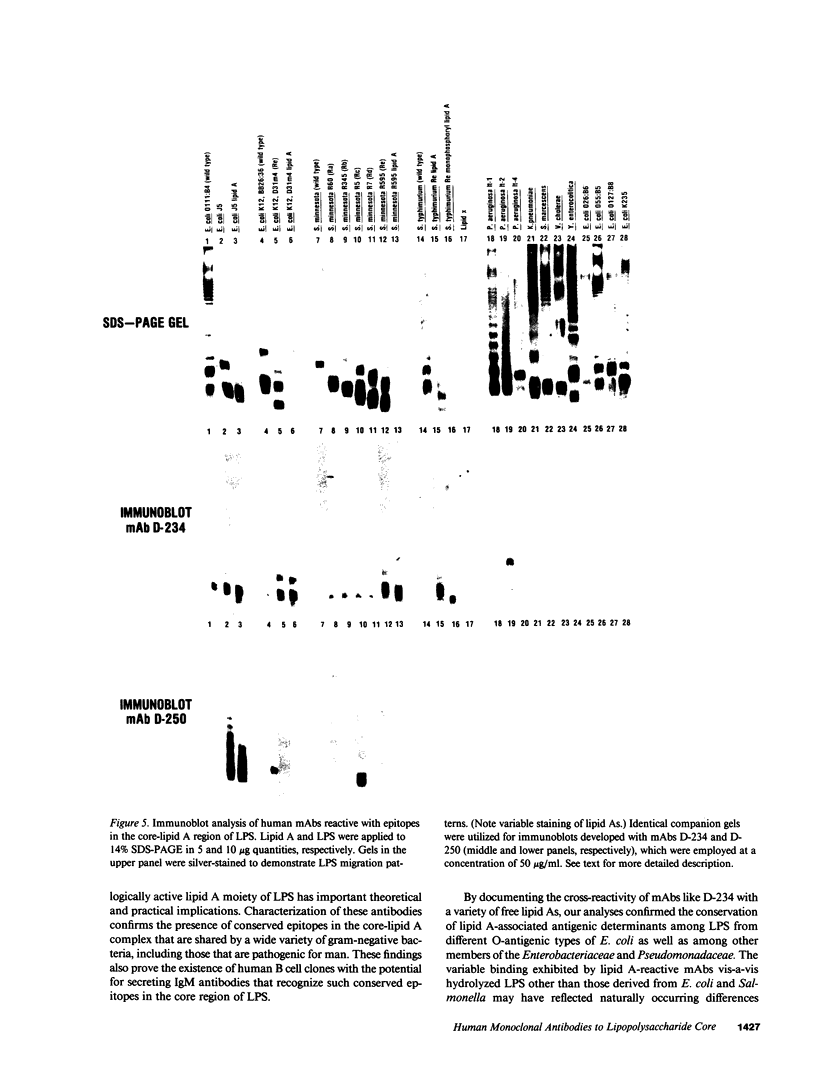
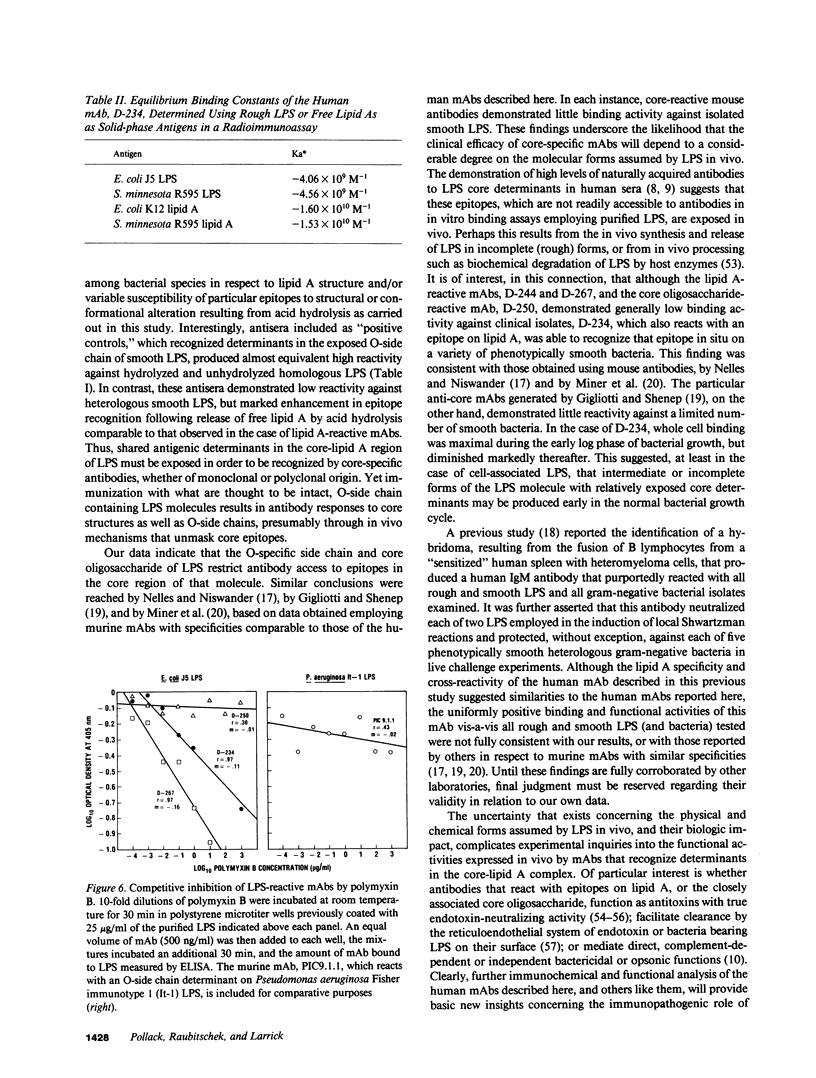
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed human B lymphocytes were fused with a murine-human heteromyeloma to produce stable hybrid cell lines that secreted human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) of the IgM class that recognized conserved epitopes in the core-lipid A region of lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Three of the mAbs reacted with epitopes on the lipid A moiety, while a fourth recognized a determinant in the core oligosaccharide. The lipid A-specific mAbs cross-reacted with heterologous rough LPS and with lipid As released by acid hydrolysis of different intact (smooth) LPS. Carbohydrate groups in the O-side chain and core oligosaccharide of isolated, smooth LPS restricted antibody access to antigenic sites on lipid A. Yet, one lipid A-reactive mAb recognized its epitope on the surfaces of a variety of intact bacteria. These findings confirm the presence of highly conserved epitopes in the core-lipid A complex and prove the existence of human B cell clones with the potential for secreting high avidity IgM antibodies that react with these widely shared determinants. Such human mAbs might provide protective activity against disease caused by diverse gram-negative bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braude A. I., Douglas H. Passive immunization against the local Shwartzman reaction. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):505–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Parant F., Boyer F. A proposed mechanism for natural immunity to enterobacterial pathogens. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):292–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Zelenetz A. D., Copper G. M. Transformation by subgenomic fragments of Rous sarcoma virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):863–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram L. S., Gomez E. R., Thoen C. O., Forslund J. C., Jett J. H. Flow microfluorometric quantitation of the blastogenic response of lymphocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Jan;24(1):383–387. doi: 10.1177/24.1.768372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. W., Braylan R. C. Flow analysis of DNA content and cell size in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):703–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBEIN A. D., HEATH E. C. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF CELL WALL LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. THE BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF A URIDINE DIPHOSPHATE GALACTOSE 4-EPIMERASELESS MUTANT. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1919–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foung S. K., Perkins S., Raubitschek A., Larrick J., Lizak G., Fishwild D., Engleman E. G., Grumet F. C. Rescue of human monoclonal antibody production from an EBV-transformed B cell line by fusion to a human-mouse hybridoma. J Immunol Methods. 1984 May 11;70(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel M. E., Gerhard W. The rapid determination of binding constants for antiviral antibodies by a radioimmunoassay. An analysis of the interaction between hybridoma proteins and influenza virus. Mol Immunol. 1979 Feb;16(2):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Freudenberg M. A., Jay F., Nerkar D., Veleva K., Brade H., Strittmatter W. Immunogenic properties of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):546–552. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazitt Y., Deitch A. D., Marks P. A., Rifkind R. A. Cell volume changes in relation to the cell cycle of differentiating erythroleukemic cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Shenep J. L. Failure of monoclonal antibodies to core glycolipid to bind intact smooth strains of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1005–1011. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. L., Munford R. S. Enzymatic deacylation of the lipid A moiety of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharides by human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Tanamoto K., Galanos C., McKenzie G. R., Brade H., Zähringer U., Rietschel E. T., Kusumoto S., Shiba T. Lipopolysaccharides: structural principles and biologic activities. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):428–431. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen M., Johnsen H. E. A methodological study of E-rosette formation using AET-treated sheep red blood cells. J Immunol Methods. 1979 May 10;27(1):61–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90239-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrell R. E., Zollinger W. D. Measurement of antibodies to meningococcal group B polysaccharide: low avidity binding and equilibrium binding constants. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2172–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of S. Minnesota. I. Protection against challenge with heterologous gram-negative bacilli. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):601–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner K. M., Manyak C. L., Williams E., Jackson J., Jewell M., Gammon M. T., Ehrenfreund C., Hayes E., Callahan L. T., 3rd, Zweerink H. Characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies to Escherichia coli J5. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.56-62.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutharia L. M., Crockford G., Bogard W. C., Jr, Hancock R. E. Monoclonal antibodies specific for Escherichia coli J5 lipopolysaccharide: cross-reaction with other gram-negative bacterial species. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):631–636. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.631-636.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelles M. J., Niswander C. A. Mouse monoclonal antibodies reactive with J5 lipopolysaccharide exhibit extensive serological cross-reactivity with a variety of gram-negative bacteria. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):677–681. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.677-681.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Cole M. D., White A. T., Huang R. C. Sequence organization of cloned intracisternal A particle genes. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M., Huang A. I., Prescott R. K., Young L. S., Hunter K. W., Cruess D. F., Tsai C. M. Enhanced survival in Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia associated with high levels of circulating antibody to Escherichia coli endotoxin core. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):1874–1881. doi: 10.1172/JCI111150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Takayama K., Ribi E. Purification and structural determination of nontoxic lipid A obtained from the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11808–11815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Galanos C. Lipid A antiserum-mediated protection against lipopolysaccharide- and lipid A-induced fever and skin necrosis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):34–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.34-49.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Schade U., Jensen M., Wollenweber H. W., Lüderitz O., Greisman S. G. Bacterial endotoxins: chemical structure, biological activity and role in septicaemia. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;31:8–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Wollenweber H. W., Russa R., Brade H., Zähringer U. Concepts of the chemical structure of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):432–438. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll B. J., Pollack M., Young L. S., Koles N., Gascon R., Pier G. B. Functionally active monoclonal antibody that recognizes an epitope on the O side chain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunotype-1 lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):656–662. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.656-662.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., Qureshi N., Mascagni P., Nashed M. A., Anderson L., Raetz C. R. Fatty acyl derivatives of glucosamine 1-phosphate in Escherichia coli and their relation to lipid A. Complete structure of A diacyl GlcN-1-P found in a phosphatidylglycerol-deficient mutant. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7379–7385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng N. N., Kaplan H. S., Hebert J. M., Moore C., Douglas H., Wunderlich A., Braude A. I. Protection against gram-negative bacteremia and endotoxemia with human monoclonal IgM antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Armstrong D. Human immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. In-vitro interaction of bacteria, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and serum factors. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):257–276. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Stevens P., Ingram J. Functional role of antibody against "core" glycolipid of Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):850–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI108164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Douglas H., Sherman J. E., Davis C. E., Braude A. I. Treatment of E. coli and klebsiella bacteremia in agranulocytic animals with antiserum to a UDP-gal epimerase-deficient mutant. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., McCutchan J. A., Fierer J., Glauser M. P., Sadoff J. C., Douglas H., Braude A. I. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and shock with human antiserum to a mutant Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]