Abstract
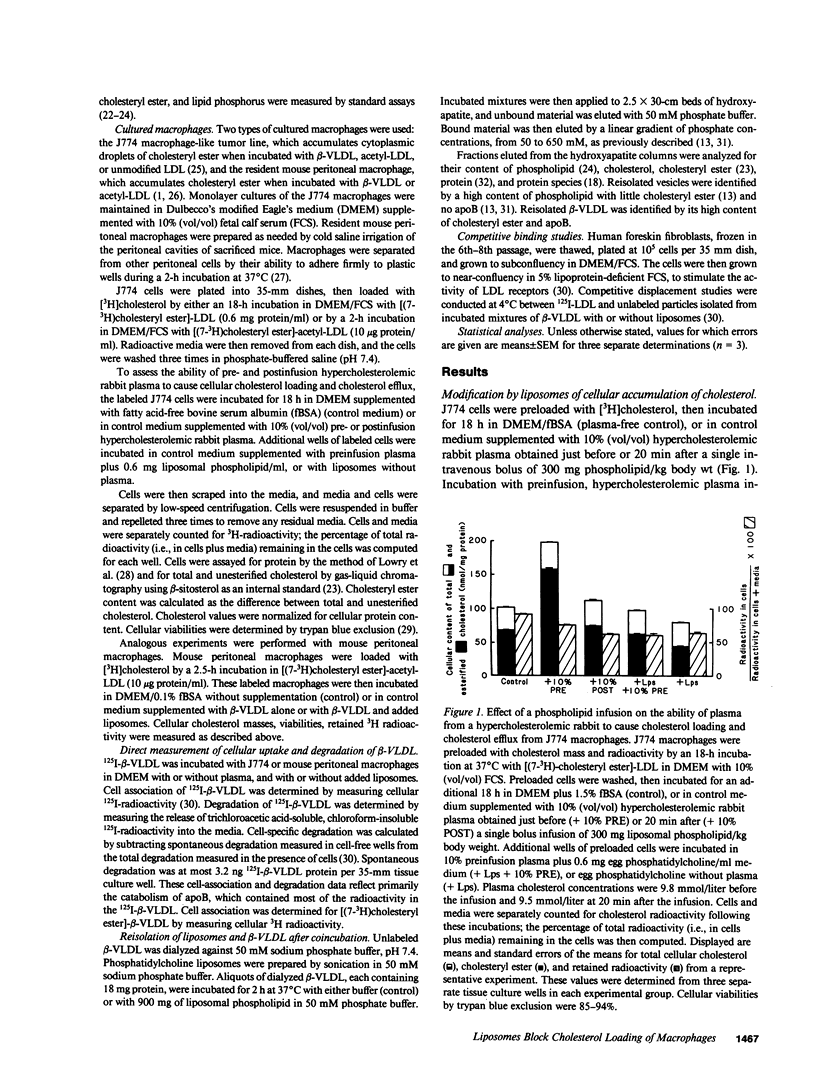
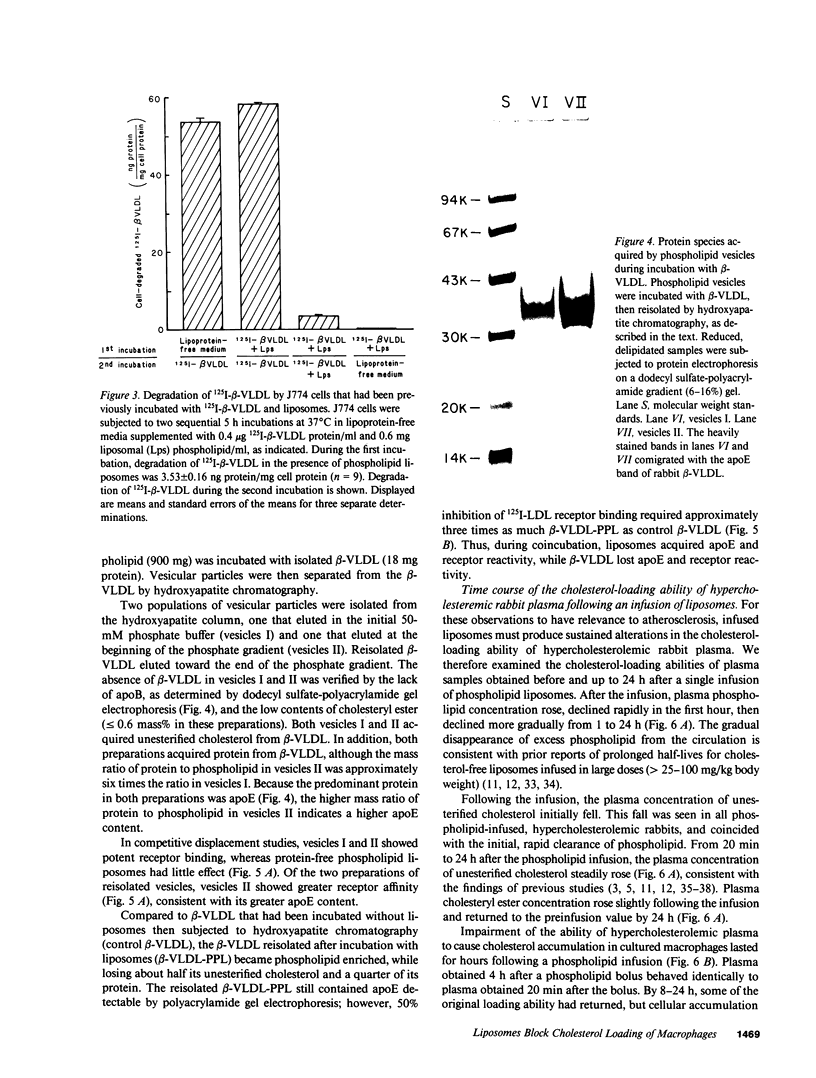
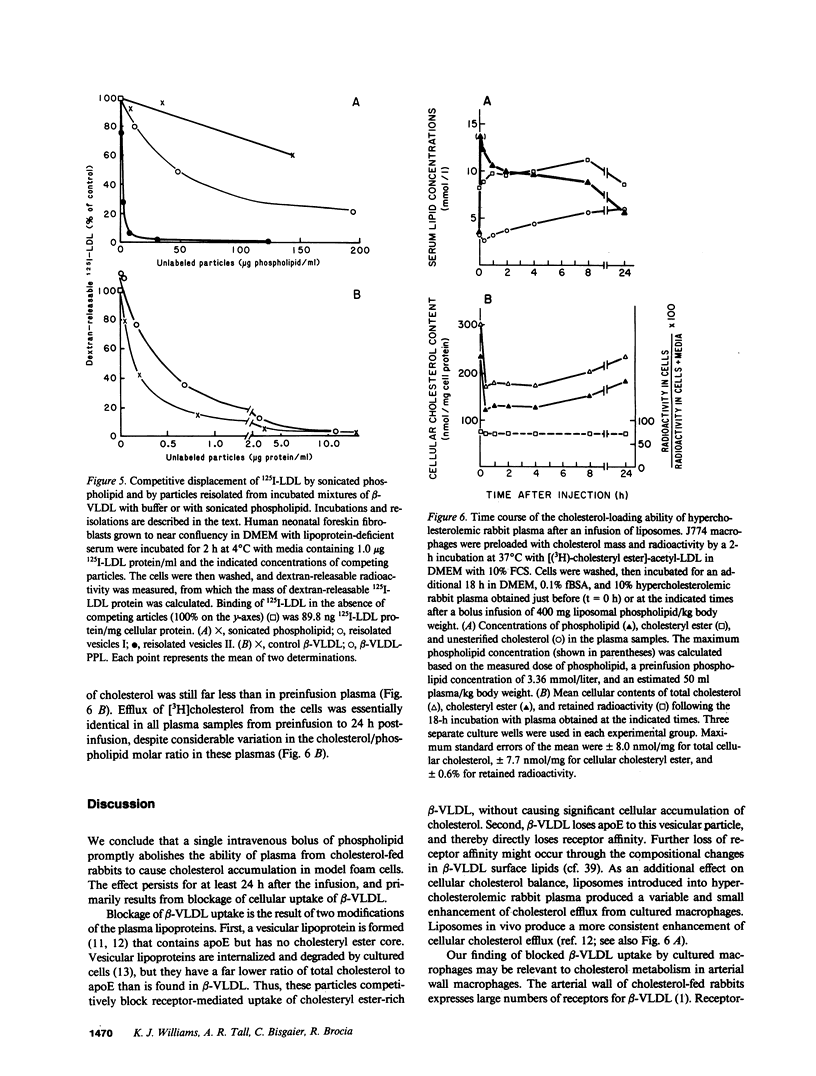
A single infusion of phospholipid liposomes promptly and persistently abolished the ability of hypercholesterolemic rabbit plasma to cause cholesteryl ester loading in cultured macrophages. This phospholipid enrichment of plasma caused moderate stimulation of cellular cholesterol efflux and, unexpectedly, almost complete inhibition of cellular uptake of beta-very low density lipoprotein (beta-VLDL), the major cholesteryl ester-rich particle in hypercholesterolemic rabbit plasma. Cell viability and LDL receptor activity were unaffected. Incubation of liposomes with beta-VLDL resulted in transfer of apolipoprotein-E (apoE) to the liposomes; reisolated apoE-phospholipid liposomes then competed efficiently for cellular apoprotein receptors. Thus, a major mechanism by which phospholipid infusions result in diminished accumulation of cholesteryl ester in cultured macrophages is by blocking cellular uptake of beta-VLDL. The liposomes deplete beta-VLDL of apoE, then compete for receptor-mediated uptake. These results suggest a novel mechanism contributing to the known antiatherogenic effect of phospholipid infusions: infused liposomes acquire apoE, then block uptake of atherogenic lipoproteins by arterial wall macrophages.
Full text
PDF



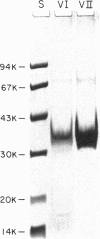
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. W., Abdulla Y. H., Bayliss O. B., Morgan R. S. Modification of aortic atheroma and fatty liver in cholesterol-fed rabbits by intravenous injection of saturated and polyunsaturated lecithins. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):77–87. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R. F., de Mendonça J. M., Schaeffer G. M., de Souza J. R., Bandoli J. G., da Silva D. J., Lopes C. R. Phospholipids in experimental atherosclerosis. Arzneimittelforschung. 1974 Jan;24(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS S. O., FRIEDMAN M. Effect of infusions of phosphatides upon the atherosclerotic aorta in situ and as an ocular aortic implant. J Lipid Res. 1960 Jul;1:343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS S. O., FRIEDMAN M. Independence of phosphatide induced hypercholesteremia and hepatic function. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jul;92(3):459–462. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS S. O., FRIEDMAN M. Role of hyperphospholipidemia and neutral fat increase in plasma in the pathogenesis of hypercholesteremia. Am J Physiol. 1956 Jul;186(1):13–18. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.186.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:223–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI LUZIO N. R., ZILVERSMIT D. B. Effect of intravenous phospholipid and Triton on lipids of normal and ethanol-treated rats. Am J Physiol. 1960 Dec;199:991–994. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.6.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson B., Johansson B. G., Petersson B. G. Separation of lipoprotein X and beta-lipoprotein by zonal centrifugation or hydroxyapatite chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Sep 14;47(3):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty A., Schonfeld G., Sobel B. E., Lange L. G. Metabolism of very low density lipoproteins after cessation of cholesterol feeding in rabbits. A factor potentially contributing to the slow regression of atheromatous plaques. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1108–1115. doi: 10.1172/JCI112409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O. Enhancement of phosphatide-induced hypercholesteremia by prior ingestion of cholesterol and triglyceride. Am J Physiol. 1958 Mar;192(3):546–548. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.3.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O., ROSENMAN R. H. Resolution of aortic atherosclerotic infiltration in the rabbit by phosphatide infusion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jul;95(3):586–588. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoprotein in cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:241–260. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. N., Patelski J., Bowyer D. E., Gresham G. A. Atherosclerosis induced in hypercholesterolaemic baboons by immunological injury; and the effects of intravenous polyunsaturated phosphatidyl choline. Atherosclerosis. 1971 Jul-Aug;14(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(71)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Thompson T. E. Preparation of homogeneous, single-walled phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:485–489. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang K. J., Luk K. F., Beaumier P. L. Hepatic uptake and degradation of unilamellar sphingomyelin/cholesterol liposomes: a kinetic study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4030–4034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihm J., Harmony J. A., Ellsworth J., Jackson R. L. Simultaneous transfer of cholesteryl ester and phospholipid by protein(s) isolated from human lipoprotein-free plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1114–1120. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90604-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T. T., MacGee J., Morrison J. A., Glueck C. J. Quantitative analysis of cholesterol in 5 to 20 microliter of plasma. J Lipid Res. 1974 May;15(3):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Wernette-Hammond M. E., Innerarity T. L. Uptake of canine beta-very low density lipoproteins by mouse peritoneal macrophages is mediated by a low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11194–11201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Saturation and suppression of hepatic lipoprotein receptors: a mechanism for the hypercholesterolemia of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patelski J., Bowyer D. E., Howard A. N., Jennings I. W., Thorne C. J. Modification of enzyme activities in experimental atherosclerosis in the rabbit. Atherosclerosis. 1970 Jul-Aug;12(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(70)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Foam cells in explants of atherosclerotic rabbit aortas have receptors for beta-very low density lipoproteins and modified low density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):2–12. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabas I., Weiland D. A., Tall A. R. Unmodified low density lipoprotein causes cholesteryl ester accumulation in J774 macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):416–420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Untracht S. H. Intravascular metabolism of an artificial transporter of triacylglycerols. Alterations of serum lipoproteins resulting from total parenteral nutrition with Intralipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 15;711(1):176–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Scanu A. M. Uptake of endogenous cholesterol by a synthetic lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 12;875(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Tall A. R., Tabas I., Blum C. Recognition of vesicular lipoproteins by the apolipoprotein B,E receptor of cultured fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1986 Aug;27(8):892–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Werth V. P., Wolff J. A. Intravenously administered lecithin liposomes: a synthetic antiatherogenic lipid particle. Perspect Biol Med. 1984 Spring;27(3):417–431. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1984.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zechner R., Dieplinger H., Roscher A., Kostner G. M. The low-density-lipoprotein pathway of native and chemically modified low-density lipoproteins isolated from plasma incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):569–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2240569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]