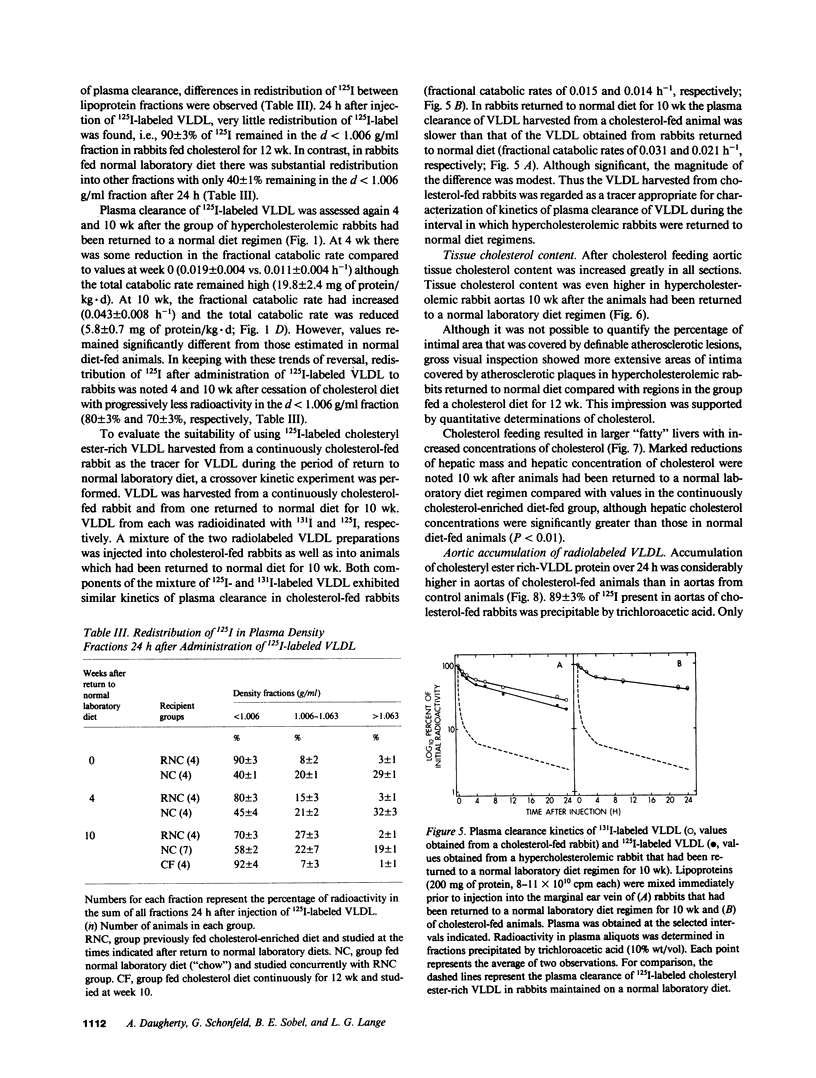
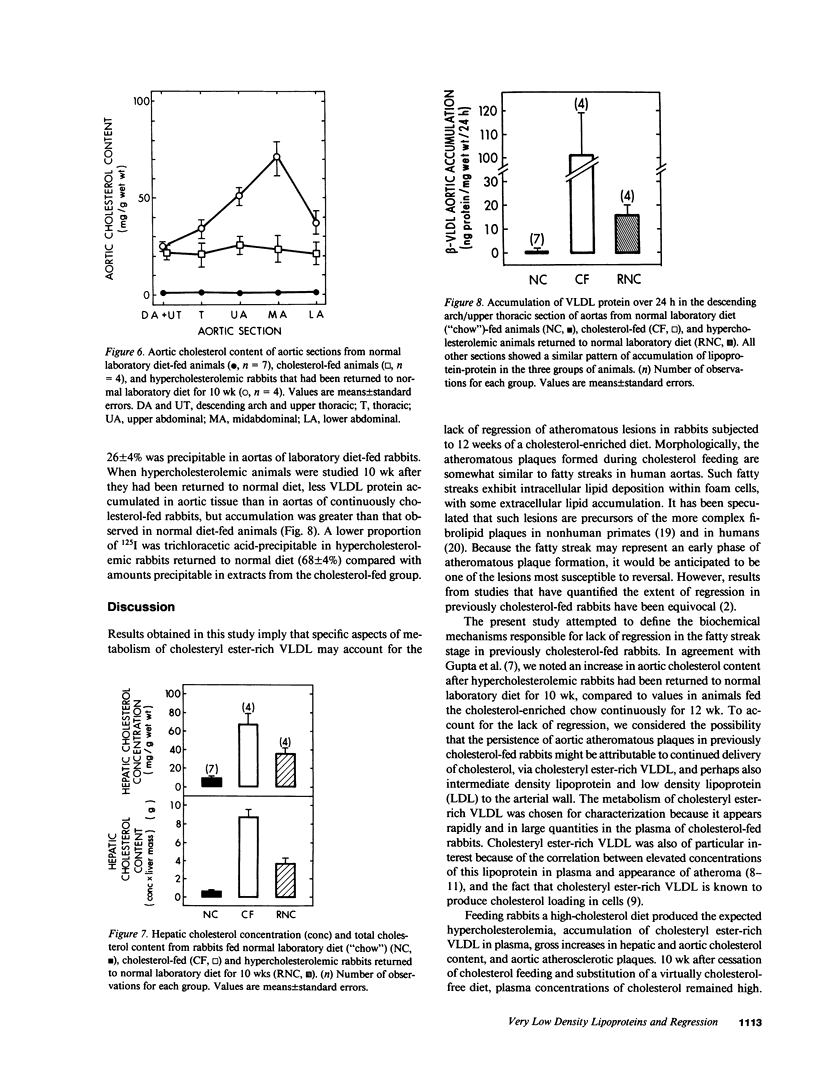
Abstract
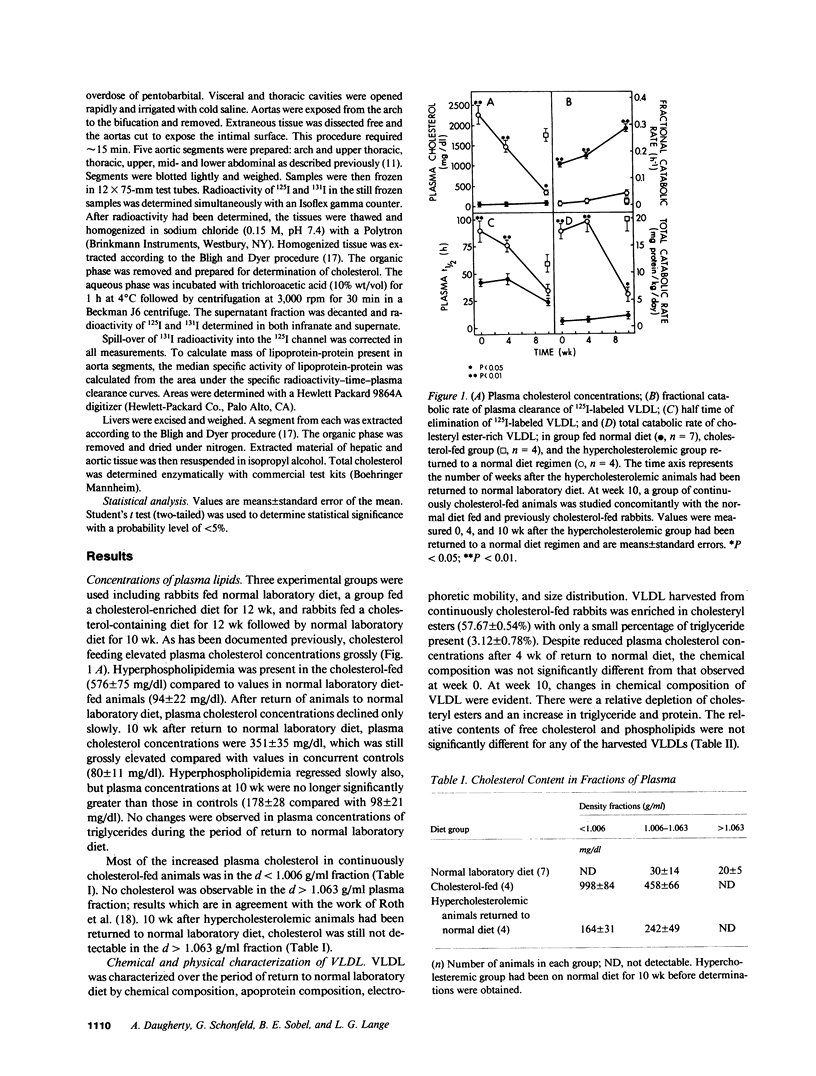
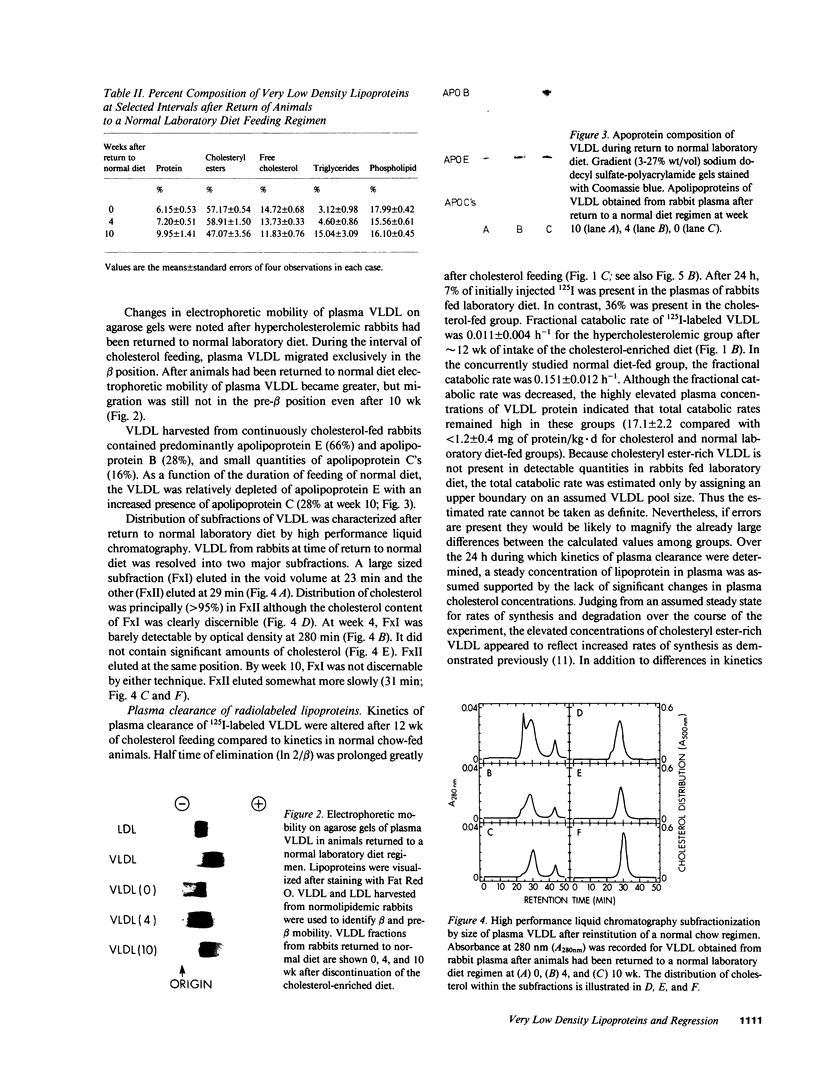
Aortic atheromatous plaques regress slowly in cholesterol-fed rabbits that have been returned to normal laboratory diet. To delineate metabolic factors potentially responsible for persistence of atherosclerosis under these conditions, the physical, chemical, and metabolic characteristics were determined for lipoproteins of d less than 1.006 g/ml; such lipoproteins are thought to be the major determinant of progression of atherosclerotic lesions in cholesterol-fed rabbits. At the time of return to a normal laboratory diet regimen after 3 mo of feeding with cholesterol-enriched laboratory diet, plasma cholesterol concentrations were 2,275 +/- 252 mg/dl, mostly attributable to cholesteryl ester-rich very low density lipoproteins (VLDL). On the hypercholesterolemic diet, fractional catabolic rates of plasma clearance of 125I-labeled VLDL were reduced (0.011 +/- 0.002 vs. 0.151 +/- 0.015 h-1), but the total VLDL catabolic rate was increased considerably (17.1 +/- 2.2 vs. less than 1.2 +/- 0.4 mg of protein/kg X d), because of the expansion of the endogenous pool of cholesteryl ester-rich VLDL. The total catabolic rate of VLDL was maintained above estimated control values (5.8 +/- 0.7 mg protein/kg X d) even 10 wk after return of the rabbits to a normal chow regimen, an effect attributable to continued high rates of cholesteryl ester-rich VLDL synthesis in liver. Accumulation of cholesteryl ester-rich VLDL into aortic tissue persisted at a high rate. Thus the persistence of aortic atheromatous lesions after cessation of cholesterol feeding was attributable in part to continued high rates of hepatic production of cholesteryl ester-rich VLDL and its persistent delivery into the aortic wall.
Full text
PDF



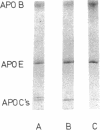
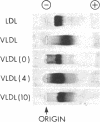
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. W., Bayliss O. B., Turner D. R. Phagocytes, lipid-removal and regression of atheroma. J Pathol. 1975 Aug;116(4):225–238. doi: 10.1002/path.1711160406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams C. W., Morgan R. S. Regression of atheroma in the rabbit. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Dec;28(4):399–404. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Davis P. A., Forte T. M. Elevated levels of apolipoprotein E in the high density lipoproteins of human cord blood plasma. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jun;26(6):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortz W. M. Reversibility of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Circ Res. 1968 Feb;22(2):135–139. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Bosch V., López A. The very low density lipoproteins of cholesterol-fed rabbits. A study of their structure and in vivo changes in plasma. Atherosclerosis. 1974 Jan-Feb;19(1):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(74)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty A., Thorpe S. R., Lange L. G., Sobel B. E., Schonfeld G. Loci of catabolism of beta-very low density lipoprotein in vivo delineated with a residualizing label, 125I-dilactitol tyramine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14564–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O. OBSERVATIONS CONCERNING THE EVOLUTION OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE RABBIT AFTER CESSATION OF CHOLESTEROL FEEDING. Am J Pathol. 1963 Sep;43:349–359. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggiotto A., Ross R. Studies of hypercholesterolemia in the nonhuman primate. II. Fatty streak conversion to fibrous plaque. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 Jul-Aug;4(4):341–356. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.4.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Mahley R. W., Hamilton R. L., Innerarity T. L. Structural and metabolic heterogeneity of beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed dogs and from humans with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):702–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P. P., Tandon H. D., Ramalingaswami V. Experimental atherosclerosis in rabbits with special reference to reversal. J Pathol. 1970 Aug;101(4):309–317. doi: 10.1002/path.1711010403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusk L., Chung J., Scanu A. M. Properties and metabolic fate of two very low density lipoprotein subfractions from rhesus monkey serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 15;710(2):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. Cholesteryl ester synthesis in macrophages: stimulation by beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed animals of several species. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):970–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. Canine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. II. Characterization of the plasma lipoproteins associated with atherogenic and nonatherogenic hyperlipidemia. Circ Res. 1974 Nov;35(5):722–733. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.5.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Foam cells in explants of atherosclerotic rabbit aortas have receptors for beta-very low density lipoproteins and modified low density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):2–12. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. I., Gaubatz J. W., Gotto A. M., Jr, Patsch J. R. Effect of cholesterol feeding on the distribution of plasma lipoproteins and on the metabolism of apolipoprotein E in the rabbit. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair R. W. Atherosclerosis regression in animal models: current concepts of cellular and biochemical mechanisms. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;26(2):109–132. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(83)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman M. P., Wiggans G., 3rd, Mao R. Anemia and hypercholesterolemia in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jun;75(6):893–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Determinants of hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5475–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Havel R. J. Inhibitory effects of C apolipoproteins from rats and humans on the uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants by the perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1985 May;26(5):556–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilversmit D. B. Atherogenesis: a postprandial phenomenon. Circulation. 1979 Sep;60(3):473–485. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.60.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]