Abstract
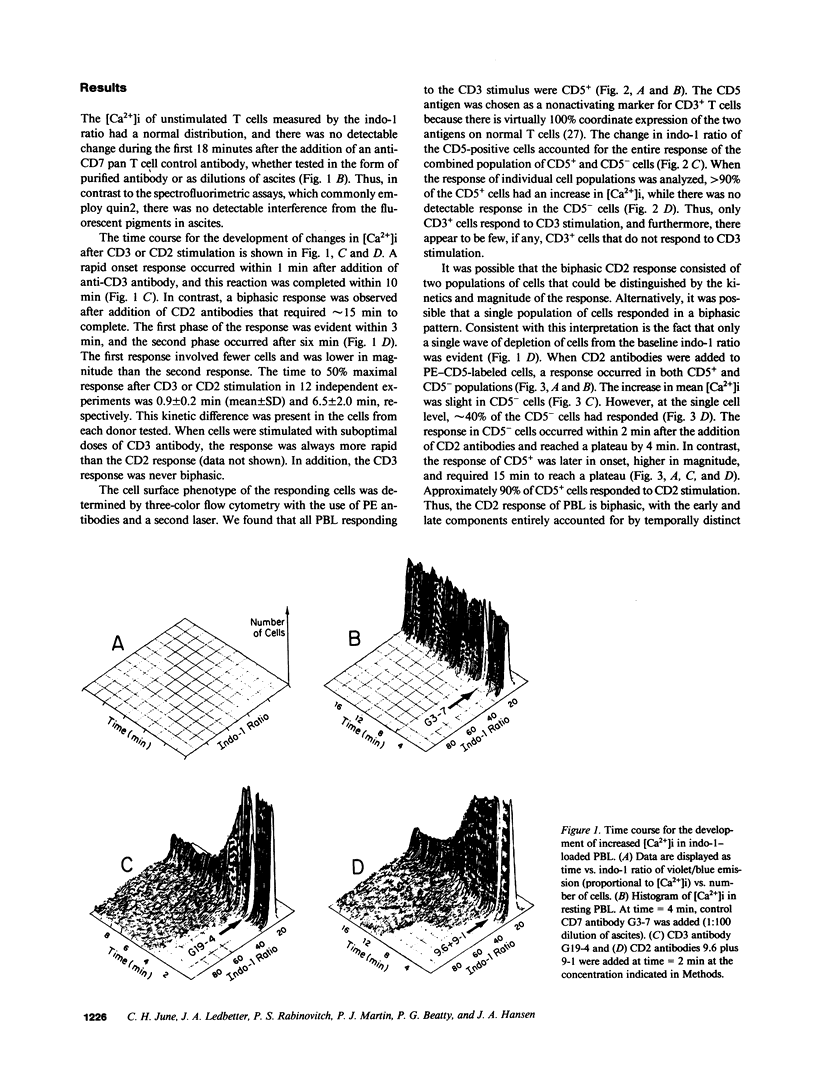
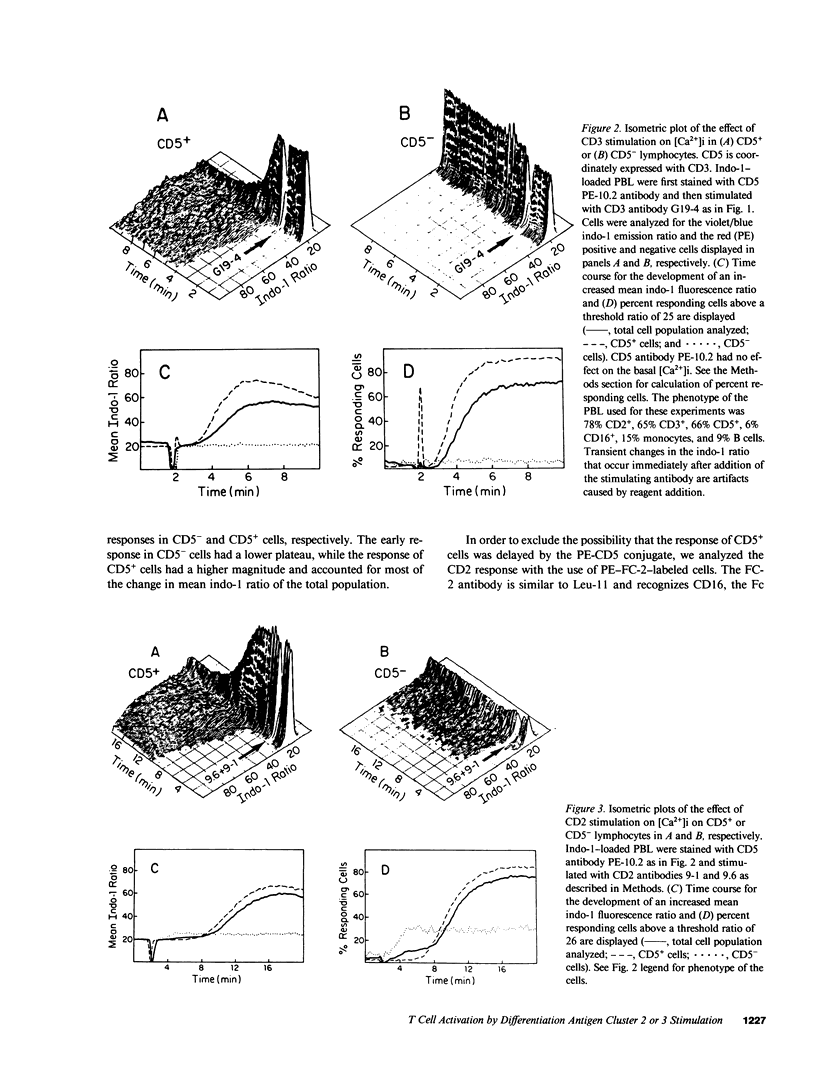
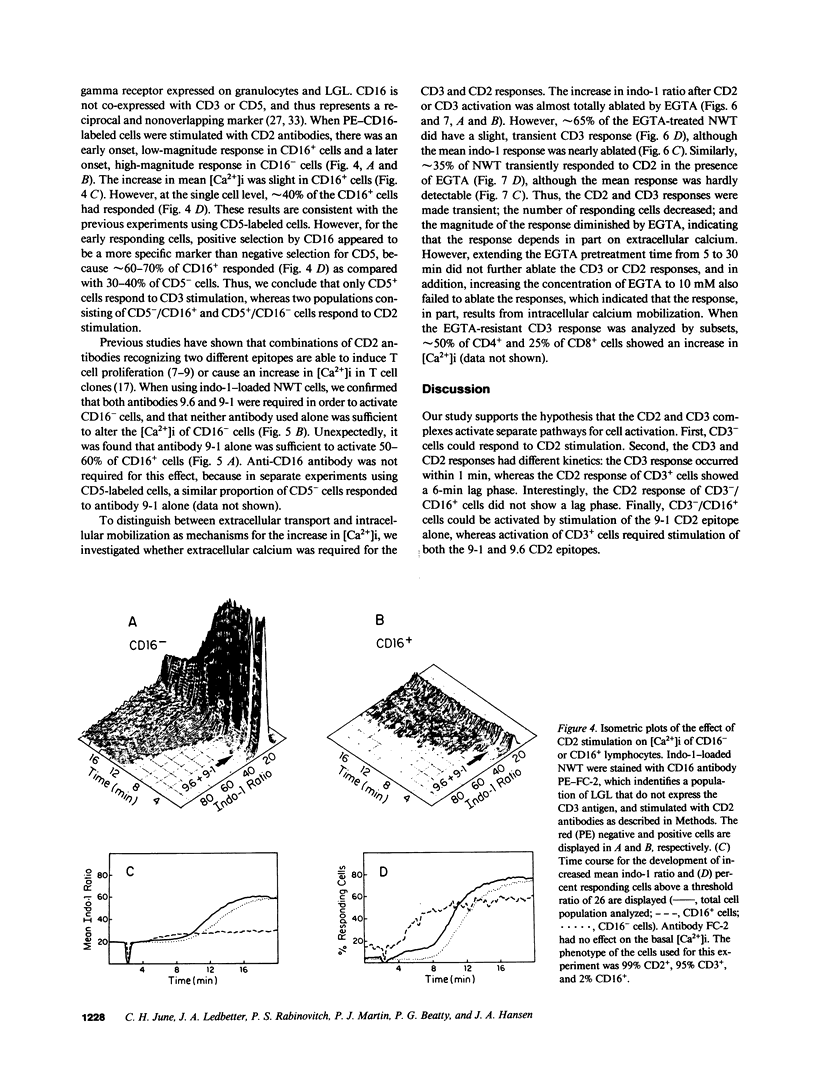
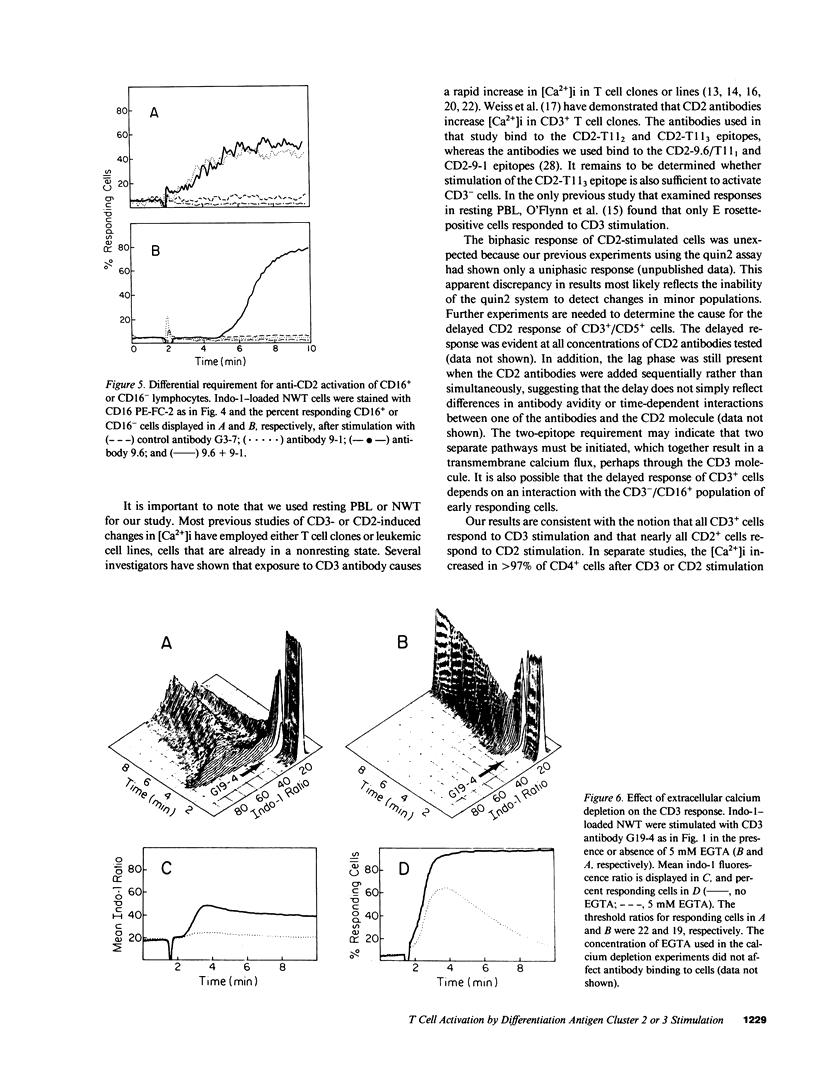
We evaluated CD2 (E rosette) and CD3 (T3)-triggered activation of resting lymphocytes by measuring the intracellular free calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) of individual cells. The [Ca2+]i of indo-1-loaded cells was measured by flow cytometry and responses were correlated with cell surface phenotype. Stimulation with anti-CD3 antibody caused an increase in [Ca2+]i in greater than 90% of CD3+ cells within 1 min, and furthermore, the response was restricted to cells bearing the CD3 marker. In contrast, stimulation of cells with anti-CD2 antibodies produced a biphasic response pattern with an early component in CD3- cells and a late component in CD3+ cells. Thus, the CD2 response does not require cell surface expression of CD3. In addition, stimulation of a single CD2 epitope was sufficient for activation of CD3- cells, whereas stimulation of two CD2 epitopes was required for activation of CD3+ cells. Both the CD2 and CD3 responses were diminished in magnitude and duration by EGTA. However, approximately 50% of T cells still had a brief response in the presence of EGTA, indicating that the increased [Ca2+]i results in part from intracellular calcium mobilization, and furthermore demonstrates that extracellular calcium is required for a full and sustained response. Our results support the concept that CD2 represents the trigger for a distinct pathway of activation both for T cells that express the CD3 molecular complex and for large granular lymphocytes that do not.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard A., Boumsell L. The clusters of differentiation (CD) defined by the First International Workshop on Human Leucocyte Differentiation Antigens. Hum Immunol. 1984 Sep;11(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst J., Coligan J. E., Oettgen H., Pessano S., Malin R., Terhorst C. The delta- and epsilon-chains of the human T3/T-cell receptor complex are distinct polypeptides. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):455–458. doi: 10.1038/312455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brottier P., Boumsell L., Gelin C., Bernard A. T cell activation via CD2 [T, gp50] molecules: accessory cells are required to trigger T cell activation via CD2-D66 plus CD2-9.6/T11(1) epitopes. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1624–1631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Shu G., Ledbetter J. A. Role of the Bp35 cell surface polypeptide in human B-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1766–1770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Krönke M., Noguchi P. D., Cunningham R. E., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Regulation of interleukin 2 receptor expression: effects of phorbol diester, phospholipase C, and reexposure to lectin or antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3054–3061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast L. D., Hansen J. A., Newman W. Evidence for T cell nature and heterogeneity within natural killer (NK) and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) effectors: a comparison with cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTL). J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):448–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Bensussan A., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Activation of human thymocytes via the 50KD T11 sheep erythrocyte binding protein induces the expression of interleukin 2 receptors on both T3+ and T3- populations. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Stobo J. D. Transmembrane signalling by the T cell antigen receptor. Perturbation of the T3-antigen receptor complex generates inositol phosphates and releases calcium ions from intracellular stores. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):446–456. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Weiss A., Stobo J. D. The antigen receptor on a human T cell line initiates activation by increasing cytoplasmic free calcium. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):663–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun M., Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Brown M. A., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Identification of a human T lymphocyte surface protein associated with the E-rosette receptor. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):207–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen D., Chu E., Terhost C., Leung D. Y., Gesner M., Miller R. A., Geha R. S. Mechanisms of human T cell response to mitogens: IL 2 induces IL 2 receptor expression and proliferation but not IL 2 synthesis in PHA-stimulated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1840–1845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Phillips J. H., Warner N. L., Babcock G. F. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1789–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman A. H., Segel G. B., Lichtman M. A. The role of calcium in lymphocyte proliferation. (An interpretive review). Blood. 1983 Mar;61(3):413–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Hansen J. A., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing normal human T lymphocytes and malignant human B lymphocytes: a comparative study. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1920–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Longton G., Ledbetter J. A., Newman W., Braun M. P., Beatty P. G., Hansen J. A. Identification and functional characterization of two distinct epitopes on the human T cell surface protein Tp50. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):180–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Acuto O., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Evidence for the T3-associated 90K heterodimer as the T-cell antigen receptor. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):808–810. doi: 10.1038/303808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Cantrell D. A., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Smith K. A., Reinherz E. L. Triggering of the T3-Ti antigen-receptor complex results in clonal T-cell proliferation through an interleukin 2-dependent autocrine pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Krensky A. M., Beverley P. C., Burakoff S. J., Linch D. C. Phytohaemagglutinin activation of T cells through the sheep red blood cell receptor. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):686–687. doi: 10.1038/313686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Linch D. C., Tatham P. E. The effect of mitogenic lectins and monoclonal antibodies on intracellular free calcium concentration in human T-lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):661–666. doi: 10.1042/bj2190661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn K., Zanders E. D., Lamb J. R., Beverley P. C., Wallace D. L., Tatham P. E., Tax W. J., Linch D. C. Investigation of early T cell activation: analysis of the effect of specific antigen, interleukin 2 and monoclonal antibodies on intracellular free calcium concentration. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jan;15(1):7–11. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. C., Terhorst C., Cantley L. C., Rosoff P. M. Stimulation of the T3-T cell receptor complex induces a membrane-potential-sensitive calcium influx. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Martinez-Maza O. Is the E receptor on human T lymphocytes a "negative signal receptor"? J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2479–2485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Trinchieri G., Jackson A., Warner N. L., Faust J., Rumpold H., Kraft D., Lanier L. L. The Fc receptor for IgG on human natural killer cells: phenotypic, functional, and comparative studies with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):180–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Hercend T., Fox D. A., Bensussan A., Bartley G., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L., Ritz J. The role of interleukin 2 and T11 E rosette antigen in activation and proliferation of human NK clones. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):672–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano R. F., Pratt J. C., Schmidt R. E., Ritz J., Reinherz E. L. Activation of cytolytic T lymphocyte and natural killer cell function through the T11 sheep erythrocyte binding protein. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):428–430. doi: 10.1038/317428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Shoback D., Stobo J. Role of T3 surface molecules in human T-cell activation: T3-dependent activation results in an increase in cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4169–4173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Wiskocil R. L., Stobo J. D. The role of T3 surface molecules in the activation of human T cells: a two-stimulus requirement for IL 2 production reflects events occurring at a pre-translational level. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Daley J. F., Hodgdon J. C., Reinherz E. L. Calcium dependency of antigen-specific (T3-Ti) and alternative (T11) pathways of human T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6836–6840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. M., Deloria D., Hansen J. A., Dinarello C. A., Loertscher R., Shapiro H. M., Strom T. B. The events of primary T cell activation can be staged by use of Sepharose-bound anti-T3 (64.1) monoclonal antibody and purified interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2249–2255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



