Sir,
A 73-year-old female presented with progressive exertional dyspnea and cough with clear sputum. She had chronic urinary tract infection and had been on nitrofurantoin, 50 mg daily for the past 2 years. She was also on omeprazole 20 mg and aspirin 75 mg daily. Physical examination revealed tachypnea and stable vital signs, and room air oxygen saturation was 90%. Lung examination showed vesicular lung sounds with fine crackles at the bases. Spirometry revealed severely restrictive lung disease with forced expiratory volume 0.88 L (53% predicted) and forced vital capacity (FVC) 0.95 L (47% predicted). High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) showed pleural based inter- and intralobular septal thickening involving both lower lobe basal segments predominantly, with traction bronchiectatic changes [Figure 1]. Nitrofurantoin was stopped and prednisone was initiated at 40 mg/d. After 2 months, her symptoms had improved dramatically, and HRCT showed complete resolution of abnormalities. The FVC normalized (>90% predicted) within 3 months and there was progressive improvement in her DLCO.
Figure 1.
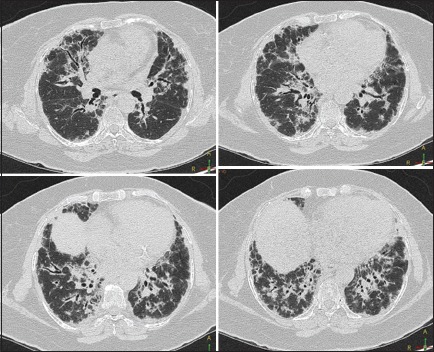
Serial axial computed tomography sections of chest showing pleural-based inter-and intralobular septal thickening involving both lower lobe basal segments with traction bronchiectatic changes
The adverse effects of nitrofurantoin include pulmonary toxicity, hepatitis, cholestasis, peripheral neuropathy and aplastic anemia.[1] Pulmonary toxicity is seen in <1%, but nitrofurantoin is one of the commonest causes of drug-induced pulmonary disease, with potentially fatal outcomes.[2]
The exact mechanism of nitrofurantoin-induced pulmonary reaction is unknown. Mendez et al. found that all 18 cases of chronic nitrofurantoin-induced lung disease in their series improved after discontinuation of nitrofurantoin. Objective evidence of improvement (pulmonary function test, chest X-ray [CXR] and computed tomography [CT]) was observed in all but two patients, although 12 had residual infiltrates on follow-up CXR or CT scans.[3] In Australia, Adverse Drug Reactions Advisory Committee reported 46 nitrofurantoin-induced pulmonary reactions from 1995 to 2004; 87% of them were related to chronic nitrofurantoin use (NIILD) with exposure between 8 months and 16 years. They all have evidence of interstitial pneumonitis or pulmonary infiltrates on radiological images. Elderly females were more commonly affected. Twelve cases had significant recovery but some patients had persistent lung damage; two patients died.[4] Although chronic NIILD is rare, it is recommended that nitrofurantoin should only be used in a proven and uncomplicated urinary infection, and the duration should not exceed 6 months when used for prophylactic purposes.[5]
References
- 1.Israel KS, Brashear RE, Sharma HM, Yum MN, Glover JL. Pulmonary fibrosis and nitrofurantoin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973;108:353–6. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Holmberg L, Boman G, Böttiger LE, Eriksson B, Spross R, Wessling A. Adverse reactions to nitrofurantoin. Analysis of 921 reports. Am J Med. 1980;69:733–8. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mendez JL, Nadrous HF, Hartman TE, Ryu JH. Chronic nitrofurantoin-induced lung disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:1298–302. doi: 10.4065/80.10.1298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pulmonary toxicity with long-term nitrofurantoin. [Last accessed on 2014 Sep 20];Aust Adverse Drug React Bull. 2004 23 Available from: http://www.tga.gov.au/adr/aadrb/aadr0408.html . [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tatley M. Pulmonary reactions with nitrofurantoin. [Last accessed on 2014 Sep 20];Prescr Update (MEDSAFE) 2002 23:24–5. Available from: http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/PUarticles/nitrofurant.html . [Google Scholar]


