Abstract
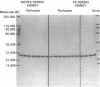
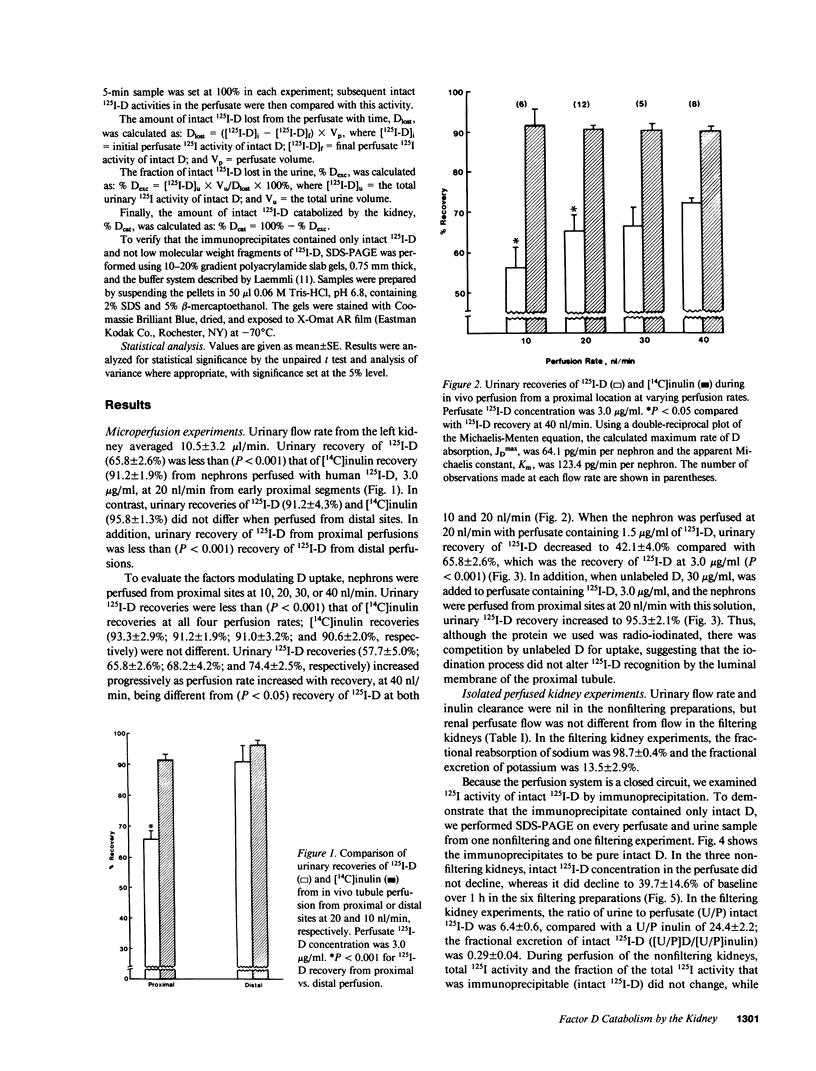
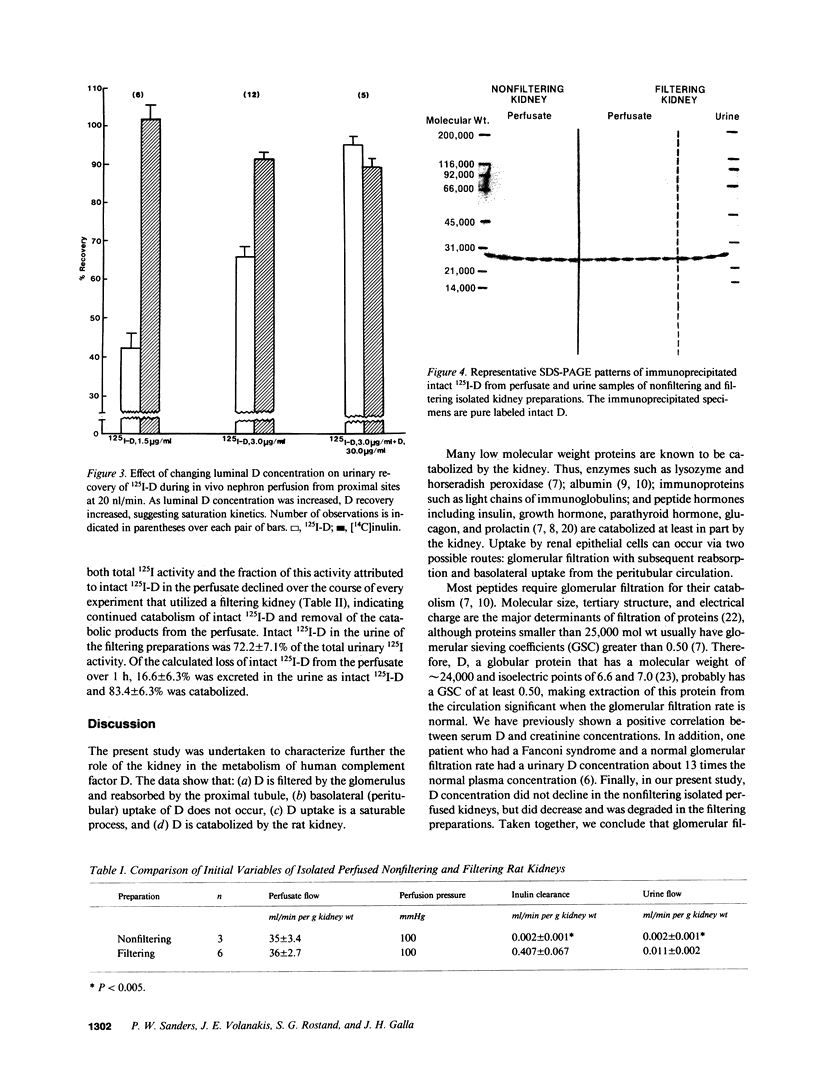
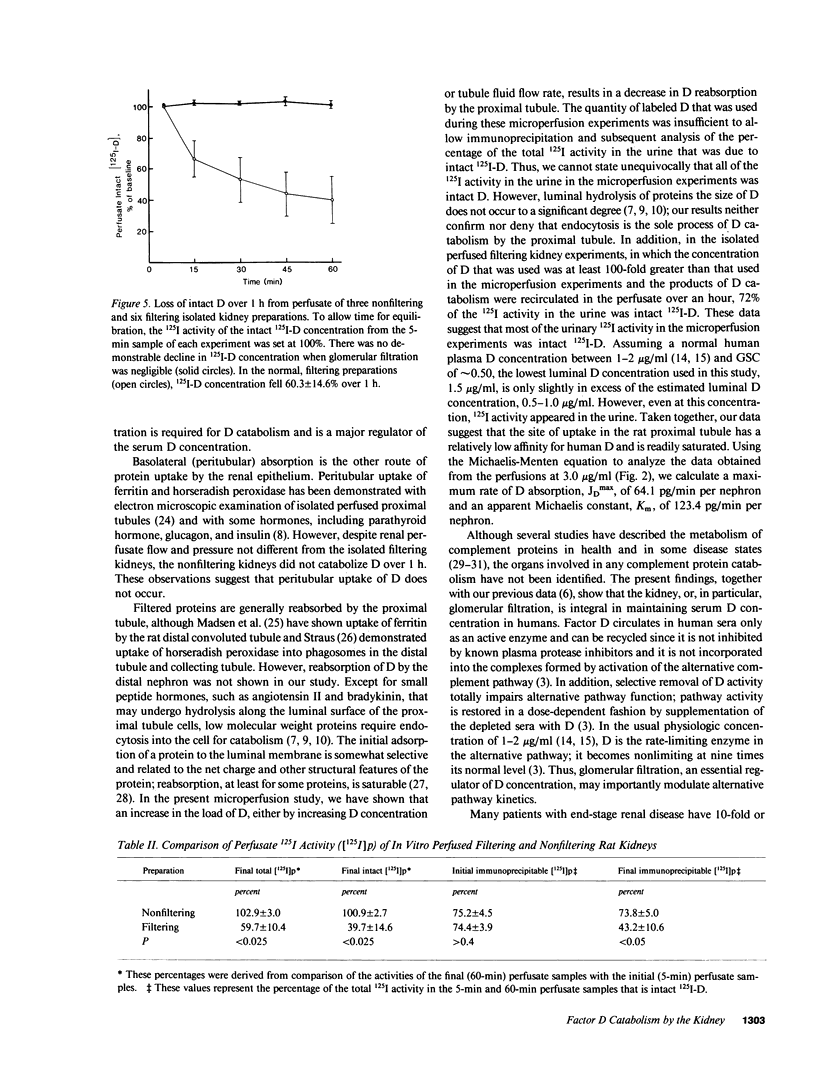
Factor D (D) is an essential component of the alternative complement pathway. To determine whether D is catabolized by the kidney and, if so, at what site, we studied the renal handling of human D by in vivo nephron microperfusion and in vitro perfusion of rat kidneys. Human D was purified and labeled with 125I. Individual nephrons were perfused in vivo at varying rates with perfusate that contained 125I-D and [14C]inulin. When nephrons were perfused from proximal sites with perfusate 125I-D in a concentration of 3.0 micrograms/ml, urinary recovery of 125I-D increased (P less than 0.05) from 57.7 +/- 5.0 to 74.4 +/- 2.5% as tubule fluid flow rate was increased from 10 to 40 nl/min; recovery of 125I-D was less than (P less than 0.001) [14C]inulin recovery at all perfusion rates. At 20 nl/min, an increase in perfusate 125I-D concentration from 1.5 to 3.0 micrograms/ml was associated with an increase (P less than 0.001) in urinary 125I-D recovery (42.1 +/- 4.0 vs. 65.8 +/- 2.6%). Similarly, the addition of unlabeled D, 30 micrograms/ml, to 125I-D, 3.0 micrograms/ml, increased urinary 125I-D recovery (95.3 +/- 2.1%) at 20 nl/min. When nephrons were perfused from early distal segments at 10 nl/min, 125I-D recovery (91.2 +/- 4.3%) did not differ from [14C]inulin recovery (95.8 +/- 1.3%). In the isolated perfused filtering kidney, the concentration of intact 125I-D in the perfusate declined 60.3 +/- 14.6% over 1 h. 83.4 +/- 6.3% of the decrement in 125I-D was catabolized by the kidney; the remainder was excreted in the urine as intact D. When glomerular filtration was prevented by increasing perfusate albumin concentration to 16 g/dl, perfusate intact (125I-D) remained unchanged over 1 h. These data show that human D is catabolized by the kidney via glomerular filtration and reabsorption by the proximal nephron. Reabsorption of D appears to be a saturable process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amadori A., Candi P., Sasdelli M., Massai G., Favilla S., Passaleva A., Ricci M. Hemodialysis leukopenia and complement function with different dialyzers. Kidney Int. 1983 Dec;24(6):775–781. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnum S. R., Niemann M. A., Kearney J. F., Volanakis J. E. Quantitation of complement factor D in human serum by a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 16;67(2):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90470-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Hostetter T. H., Humes H. D. Molecular basis of proteinuria of glomerular origin. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 13;298(15):826–833. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804132981507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carone F. A., Peterson D. R., Oparil S., Pullman T. N. Renal tubular transport and catabolism of proteins and peptides. Kidney Int. 1979 Sep;16(3):271–278. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carone F. A. Renal handling of proteins and peptides. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1978 Jul-Aug;8(4):287–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Cheung A. K., Henderson L. W. Anaphylatoxin formation during hemodialysis: effects of different dialyzer membranes. Kidney Int. 1983 Dec;24(6):764–769. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen E. I., Rennke H. G., Carone F. A. Renal tubular uptake of protein: effect of molecular charge. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):F436–F441. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.4.F436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R. Synthesis and metabolism of complement proteins. Transplant Proc. 1974 Mar;6(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Brigham K. L., Kronenberg R. S., Jacob H. S. Complement and leukocyte-mediated pulmonary dysfunction in hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 7;296(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704072961401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Zalut C., Rosen F. S., Alper C. A. Human factor D of the alternative complement pathway. Physicochemical characteristics and N-terminal amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5082–5087. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein F. H., Brosnan J. T., Tange J. D., Ross B. D. Improved function with amino acids in the isolated perfused kidney. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):F284–F292. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.3.F284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim R. M., Breillatt J., Lazarus J. M., Port F. K. Complement activation and hypersensitivity reactions to dialysis membranes. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 4;311(14):878–882. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410043111403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson V., Maack T. Renal extraction, filtration, absorption, and catabolism of growth hormone. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):F185–F196. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.3.F185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesavre P. H., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mechanism of action of factor D of the alternative complement pathway. J Exp Med. 1978 Dec 1;148(6):1498–1509. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.6.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T., Johnson V., Kau S. T., Figueiredo J., Sigulem D. Renal filtration, transport, and metabolism of low-molecular-weight proteins: a review. Kidney Int. 1979 Sep;16(3):251–270. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen K. M., Harris R. H., Tisher C. C. Uptake and intracellular distribution of ferritin in the rat distal convoluted tubule. Kidney Int. 1982 Feb;21(2):354–361. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. T., Christensen E. I. Basolateral endocytosis of protein in isolated perfused proximal tubules. Kidney Int. 1985 Jan;27(1):39–45. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann M. A., Bhown A. S., Bennett J. C., Volanakis J. E. Amino acid sequence of human D of the alternative complement pathway. Biochemistry. 1984 May 22;23(11):2482–2486. doi: 10.1021/bi00306a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann M. A., Kearney J. F., Volanakis J. E. The use of monoclonal antibodies as probes of the three-dimensional structure of human complement factor D. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostand S. G., Lewis D., Watkins J. B., Huang W. C., Navar L. G. Attenuated pressure natriuresis in hypertensive rats. Kidney Int. 1982 Feb;21(2):331–338. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostand S. G., Watkins J. B., Clements R. S., Jr The effect of insulin and of anti-insulin serum on handling of sodium by the isolated, perfused kidney of the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Diabetes. 1980 Sep;29(9):679–685. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.9.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostand S. G., Work J. Effect of 6-aminonicotinamide on renin release in isolated rat kidney: possible role for the pentose pathway. Am J Physiol. 1985 Aug;249(2 Pt 2):F213–F219. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.2.F213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUS W. OCCURRENCE OF PHAGOSOMES AND PHAGO-LYSOSOMES IN DIFFERENT SEGMENTS OF THE NEPHRON IN RELATION TO THE REABSORPTION, TRANSPORT, DIGESTION, AND EXTRUSION OF INTRAVENOUSLY INJECTED HORSERADISH PEROXIDASE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:295–308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturfelt G., Sjöholm A. G. Complement components, complement activation, and acute phase response in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1984;75(1):75–83. doi: 10.1159/000233593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturfelt G., Truedsson L., Thysell H., Björck L. Serum level of complement factor D in systemic lupus erythematosus--an indicator of glomerular filtration rate. Acta Med Scand. 1984;216(2):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1984.tb03789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpio B. E., Maack T. Kinetics, competition, and selectivity of tubular absorption of proteins. Am J Physiol. 1982 Oct;243(4):F379–F392. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.4.F379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truedsson L., Sturfelt G. Human factor D of the alternative pathway: purification and quantitation by enzyme amplified electroimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 14;63(2):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90424-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Barnum S. R., Giddens M., Galla J. H. Renal filtration and catabolism of complement protein D. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):395–399. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]