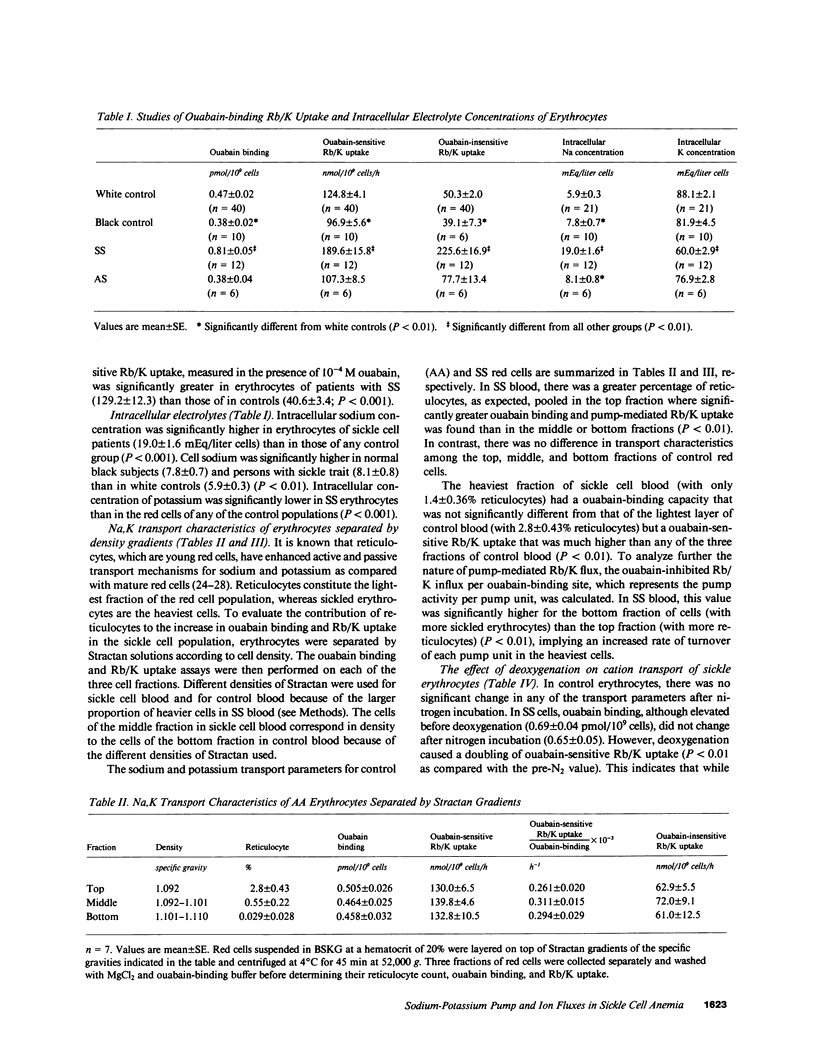
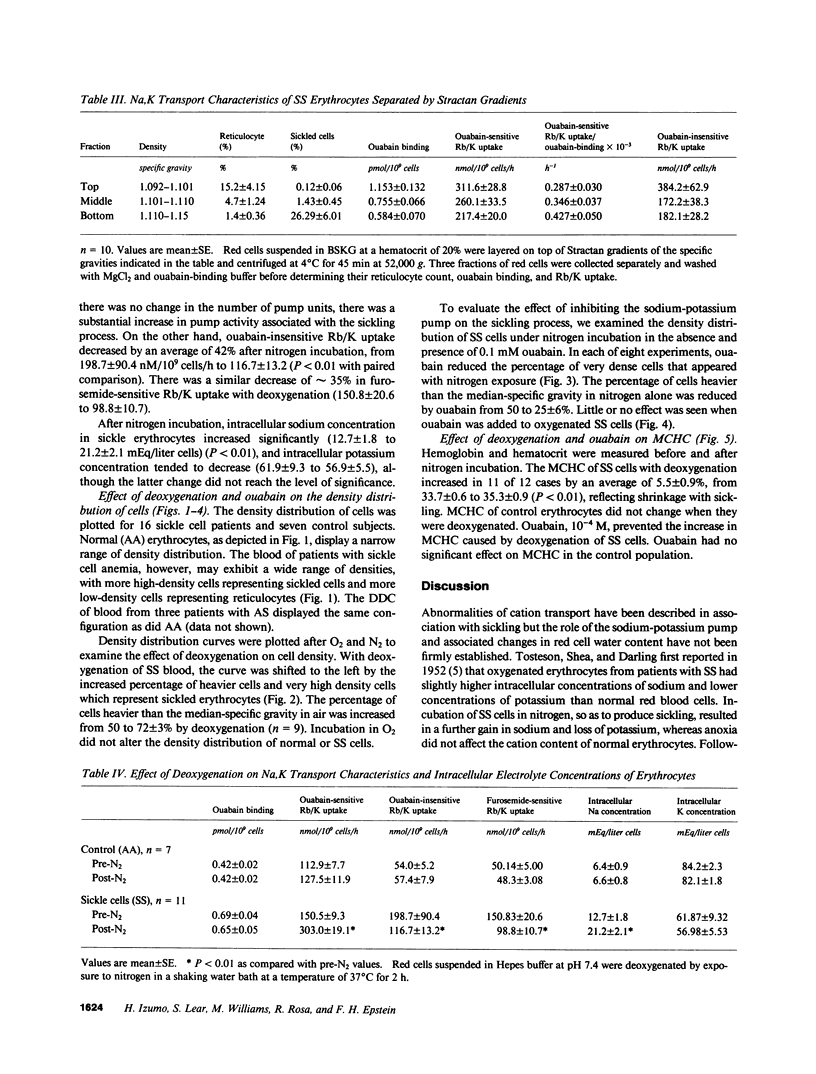
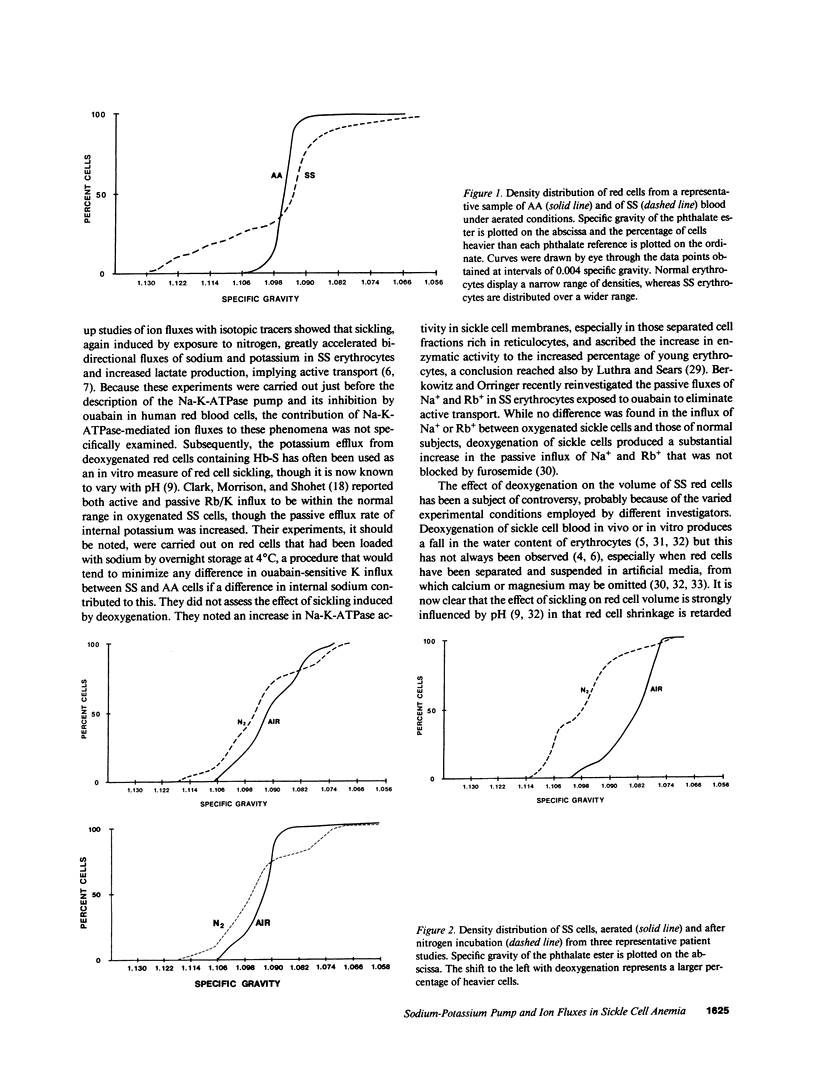
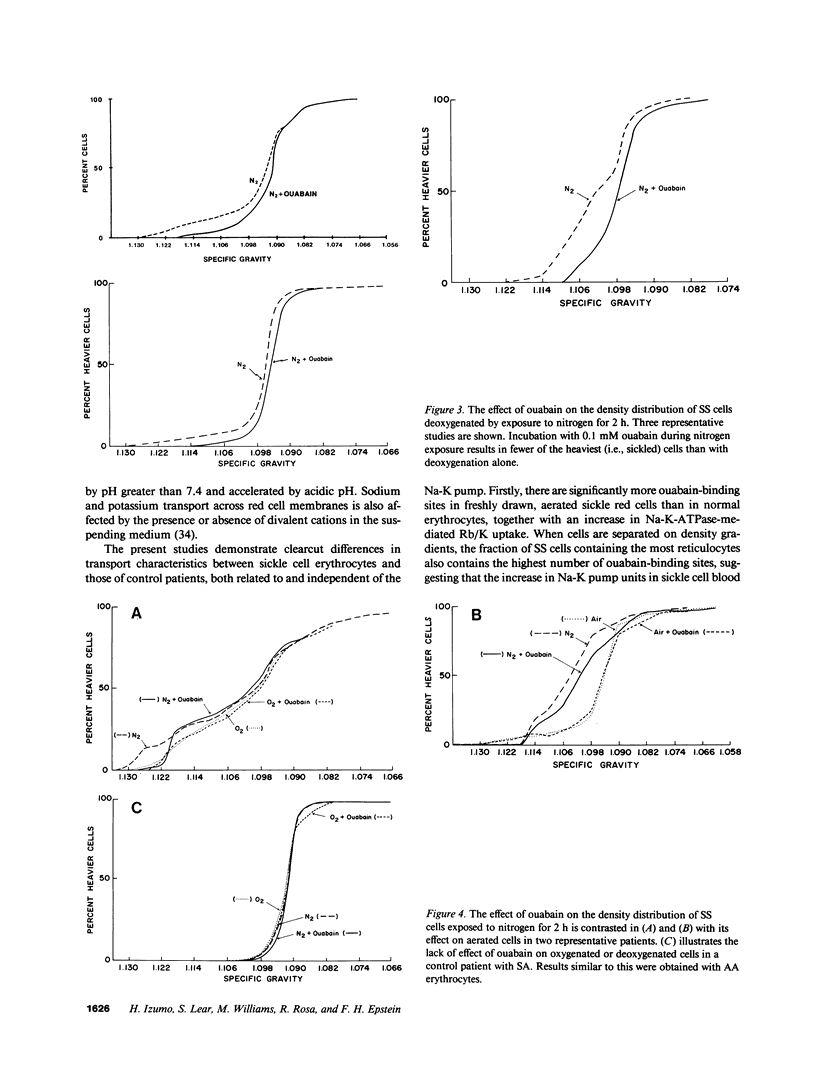
Abstract
We studied the role of the sodium-potassium pump in erythrocytes of 12 patients with sickle cell anemia (SS). Ouabain-binding sites per cell and pump-mediated Rb/K uptake were significantly higher in SS patients than in white or black controls. Ouabain-resistant Rb/K influx was also greater than in normal controls or patients with sickle cell trait. Deoxygenation of SS erythrocytes increased ouabain-sensitive Rb/K influx without altering ouabain binding, presumably as the consequence of an increase in the passive influx of sodium. Deoxygenation increased mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) by 5.5%, and studies of the density distribution of SS cells indicated an increase in highly dense fractions known to contain sickled erythrocytes. Ouabain prevented the rise in MCHC and reduced the percentage of dense cells. These findings indicate a magnified role for the sodium-potassium pump in the pathophysiology of SS erythrocytes and suggest that its inhibition might prove useful in therapy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrup J. The effect of hypokalaemia and of digoxin therapy on red cell sodium and potassium content. Some clinical aspects. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Feb;33(1):11–16. doi: 10.3109/00365517409114191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauge L. A., Adragna N. The kinetics of ouabain inhibition and the partition of rubidium influx in human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1971 May;57(5):576–592. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.5.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz L. R., Orringer E. P. Passive sodium and potassium movements in sickle erythrocytes. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C208–C214. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J. C., Israel Y. Active transport of Rb86 in human red cells and rat brain slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Aug;174(2):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blostein R., Drapeau P., Benderoff S., Weigensberg A. M. Changes in Na+-ATPase and Na,K-pump during maturation of sheep reticulocytes. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;61(1):23–28. doi: 10.1139/o83-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Lew V. L. Effect of a 'sickling pulse' on calcium and potassium transport in sickle cell trait red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:265–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Guatelli J. C., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Influence of red cell water content on the morphology of sickling. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):823–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Guatelli J. C., White A. T., Shohet S. B. Study on the dehydrating effect of the red cell Na+/K+-pump in nystatin-treated cells with varying Na+ and water contents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 7;646(3):422–432. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90311-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Hydration of sickle cells using the sodium ionophore Monensin. A model for therapy. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1074–1080. doi: 10.1172/JCI110695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Morrison C. E., Shohet S. B. Monovalent cation transport in irreversibly sickled cells. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):329–337. doi: 10.1172/JCI109133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corash L. M., Piomelli S., Chen H. C., Seaman C., Gross E. Separation of erythrocytes according to age on a simplified density gradient. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jul;84(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANON D., MARIKOVSKY V. DETERMINATION OF DENSITY DISTRIBUTION OF RED CELL POPULATION. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Oct;64:668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Stewart G. W., Ellory J. C. Chloride-activated passive potassium transport in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1711–1715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. A., Hofrichter J., Ross P. D. Editorial: Delay time of gelation: a possible determinant of clinical severity in sickle cell disease. Blood. 1976 Apr;47(4):621–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellory J. C., Flatman P. W., Stewart G. W. Inhibition of human red cell sodium and potassium transport by divalent cations. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:1–17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellory J. C., Stewart G. W. The human erythrocyte Cl-dependent Na-K cotransport system as a possible model for studying the action of loop diuretics. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry M. E., Nagel R. L. The effect of deoxygenation on red cell density: significance for the pathophysiology of sickle cell anemia. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1370–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fales F. W. Water distribution in blood during sickling of erythrocytes. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):703–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa H., Bilezikian J. P., Loeb J. N. Potassium fluxes in the rat reticulocyte. Ouabain sensitivity and changes during maturation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 21;649(3):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glader B. E., Nathan D. G. Cation permeability alterations during sickling: relationship to cation composition and cellular hydration of irreversibly sickled cells. Blood. 1978 May;51(5):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo H., Izumo S., DeLuise M., Flier J. S. Erythrocyte Na,K pump in uremia. Acute correction of a transport defect by hemodialysis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):581–588. doi: 10.1172/JCI111455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlubowski M., Agutter P. S. Changes in the activities of some membrane-associated enzymes during in vivo ageing of the normal human erythrocyte. Br J Haematol. 1977 Sep;37(1):111–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettlewell M., Nowers A., White R. Effect of digoxin on human red blood cell electrolytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Jan;44(1):165–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer H. J., Glänzer K., Freitag T., Schönfeld J., Sorger M., Schlebusch H., Düsing R., Krück F. Studies on the role of sodium- and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase inhibition in the pathogenesis of human hypertension. Changes in vascular and cardiac function following inhibition of the sodium pump in normotensive subjects and effects of calcium entry blockade. Klin Wochenschr. 1985 Jan 2;63(1):32–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01537484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVE W. D., BURCH G. E. A comparison of potassium 42, rubidium 86, and cesium 134 as tracers of potassium in the study of cation metabolism of human erythrocytes in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Mar;41(3):351–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVE W. D., BURCH G. E. Plasma and erythrocyte sodium and potassium concentrations in a group of southern white and Negro blood donors. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Feb;41(2):258–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasker N., Hopp L., Grossman S., Bamforth R., Aviv A. Race and sex differences in erythrocyte Na+, K+, and Na+-K+-adenosine triphosphatase. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1813–1820. doi: 10.1172/JCI111894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthra M. G., Sears D. A. Increased Ca++, Mg++, and Na+ + K+ ATPase activities in erythrocytes of sickle cell anemia. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1332–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Karnovsky M. J. Irreversible deformation of the spectrin-actin lattice in irreversibly sickled cells. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):955–963. doi: 10.1172/JCI108549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masys D. R., Bromberg P. A., Balcerzak S. P. Red cells shrink during sickling. Blood. 1974 Dec;44(6):885–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro-Faure A. D., Hill D. M., Anderson J. Ethnic differences in human blood cell sodium concentration. Nature. 1971 Jun 18;231(5303):457–458. doi: 10.1038/231457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi C. T., Schechter A. N. The intracellular polymerization of sickle hemoglobin and its relevance to sickle cell disease. Blood. 1981 Dec;58(6):1057–1068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet R., Atlan H. Inhibitory effects of two potassium ionophores on ouabain-resistant potassium fluxes in reticulocyte cell membrane. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 1;103(1):172–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. P., Schechter A. N., Noguchi C. T. Cell heterogeneity in sickle cell disease: quantitation of the erythrocyte density profile. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jul;106(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa R. M., Bierer B. E., Thomas R., Stoff J. S., Kruskall M., Robinson S., Bunn H. F., Epstein F. H. A study of induced hyponatremia in the prevention and treatment of sickle-cell crisis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Nov 13;303(20):1138–1143. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198011133032002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth E. F., Jr, Nagel R. L., Bookchin R. M. pH dependency of potassium efflux from sickled red cells. Am J Hematol. 1981;11(1):19–27. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830110104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A. K. The permeability of the human erythrocyte to sodium and potassium. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;36(1):57–110. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. F., 3rd, Asakura T., Schwartz E. Effect of cetiedil on cation and water movements in erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):589–594. doi: 10.1172/JCI110485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSTESON D. C., CARLSEN E., DUNHAM E. T. The effects of sickling on ion transport. I. Effect of sickling on potassium transport. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Sep 20;39(1):31–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSTESON D. C., SHEA E., DARLING R. C. Potassium and sodium of red blood cells in sickle cell anemia. J Clin Invest. 1952 Apr;31(4):406–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI102623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOSTESON D. C. The effects of sickling on ion transport. II. The effect of sickling on sodium and cesium transport. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Sep 20;39(1):55–67. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigensberg A. M., Blostein R. Energy depletion retards the loss of membrane transport during reticulocyte maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4978–4982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S., Cooper R. A. A furosemide-sensitive cotransport of sodium plus potassium in the human red cell. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):745–755. doi: 10.1172/JCI107613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


